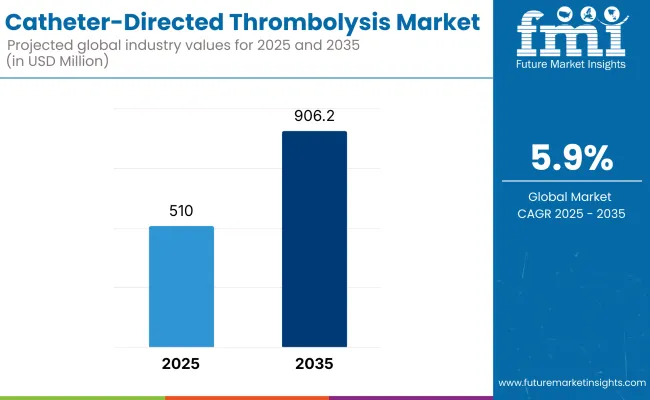
The market for Catheter-Directed Thrombolysisis expected to reach approximately USD 510.0 million in 2025 and expand to around USD 906.2 million by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% over the forecast period.
Volume of catheter directed thrombolysis is growing exponentially from the specificity seen in endovascular procedures while, patient pool is anticipated to grow owing to substitutes for open surgical procedures. The trend of healthcare providers is moving towards minimally invasive and rapid recanalization techniques; therefore, catheter-based thrombolysis has become preferred in clinical settings as compared with traditional systemic thrombolytic therapies.
Strategic changes among interventional radiology departments and increasing outpatient vascular lab procedure integration have elevated commercial opportunities. Drivers of adoption include bundled procedure reimbursements and cost-efficiency across thrombosis management pathways.
The pivotal contribution of this technology in more complex clinical scenarios such as iliofemoral DVT (deep vein thrombosis) and PE (pulmonary embolism) participation is also quickly adding to its clinical worth and heralding a new era in the interventional vascular therapeutics.
Market Metrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 510.0 million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 906.2 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.9% |
The catheter-directed thrombolysis market held a steady growth trajectory during 2020 to 2024 period due to a significant change in the physicians' preference towards catheter-guided solutions compared to other approaches, in acute thrombosis cases. Early adoption was driven by enhanced procedural outcomes for high-risk patients with deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism resulting in a greater procedural volume in vascular surgery facilities.
Ambulatory surgical centers strategically procured thrombolysis systems and payors aligned on device-assisted thrombolysis, creating a commercially viable ecosystem between manufacturers and service providers. The consolidation of vascular labs and cross-specialty training initiatives accelerated procedural throughput, driving up utilization rates.
Furthermore, innovations in infusion catheter design and integration of imaging guidance directly influenced hospital purchasing behavior. The market also saw a notable shift in device distribution strategies, with an emphasis on direct-to-facility partnerships and performance-based supply agreements, reshaping traditional procurement channels.
A major impetus for catheter-directed thrombolysis in North America is the move toward site-of-service optimization, with outpatient vascular centers replacing hospital-based interventions for cost-containment and procedural throughput. This has created a new direct-to-clinic pathway for device manufacturers to drive utilization, particularly in states that have relaxed ASC ownership laws.
Furthermore, vascular surgeons and interventional radiologists are uniting through integrated service lines to provide bundled thrombolysis care packages, thus enhancing procedural volume per site. Hospitals are also using catheter-directed thrombolysis to shorten length of stay for patients with acute DVT, making it a strategy of choice in value-based care settings.
Increased use of catheter-directed thrombolysis as a limb salvage technique in the peripheral artery disease patient population, representing procedural crossover between vascular specialties, is another regional growth lever. In addition, expedited FDA 510(k) clearances for thrombolytic catheters with integrated pressure modulation capabilities have reduced product development cycles, allowing USA Companies a first-mover advantage in the innovation adoption curve.
In Europe, clinical adoption of catheter-directed thrombolysis is being fueled by the continent’s rising preference for pharmacomechanical approaches in post-thrombotic syndrome prevention. Multi-center clinical trials sponsored by public health institutions are validating outcomes for device-assisted thrombolysis in early-stage iliofemoral DVT, accelerating technology inclusion into regional treatment guidelines.
Additionally, the presence of publicly funded thrombosis registries in countries like the Netherlands and Norway is enabling longitudinal tracking of procedural efficacy, making hospitals more confident in scaling thrombolysis programs. Procurement agencies in the EU are also prioritizing devices with low systemic dosage delivery mechanisms, aligning with patient safety mandates.
Device developers are gaining competitive advantage by offering compliance-ready kits designed around strict EU MDR classifications, streamlining the tender approval process. Lastly, cross-border purchasing agreements among hospital consortia are fostering regional price normalization, allowing hospitals in mid-tier economies like Portugal and Czechia to access premium thrombolysis devices previously limited to top-tier institutions.
Asia-Pacific’s catheter-directed thrombolysis market is being propelled by the rise of procedural localization in emergency medicine, particularly in trauma-heavy urban centers. In countries like China and Indonesia, stroke-ready hospitals are investing in thrombolysis devices not just for neuro care but also for rapid response to PE and massive DVT cases.
Japan is leading in hybrid catheterization suite installations across secondary hospitals, enabling real-time imaging-guided thrombolysis outside academic settings. Meanwhile, private hospital chains in India and Thailand are offering catheter-directed thrombolysis as a premium service for medical tourism patients, bundling it into rapid-recovery vascular packages.
Another distinctive factor is the rise of regional manufacturing hubs producing price-accessible thrombolytic catheters with CE certification, accelerating adoption in tier-2 cities. In South Korea and Singapore, national health data repositories are integrating procedural data from thrombolysis cases, allowing policymakers to evaluate ROI and support volume-based funding to facilities demonstrating high procedural success rates.
Limited Reimbursement Alignment for Outpatient Thrombolysis Procedures Slowing Market Penetration
One of the primary challenges restricting broader adoption of catheter-directed thrombolysis is the lack of aligned reimbursement structures for outpatient-based procedures. While clinical protocols have advanced to allow thrombolysis to be performed safely in ambulatory vascular labs and office-based settings, payor frameworks-particularly in markets like the USA, Germany, and South Korea-remain geared toward hospital-based delivery.
This mismatch restricts procedural migration and limits the growth of independent interventional clinics aiming to provide same-day thrombolysis care. Additionally, many reimbursement codes fail to differentiate between systemic thrombolysis and catheter-directed approaches, undercutting the value-based positioning of device-assisted interventions.
This results in financial disincentives for providers to adopt more precise, catheter-based solutions. In developing markets, inconsistent insurance coverage for thrombolysis devices and drug kits adds another barrier, leading to variable adoption across urban and rural centers. Until reimbursement models fully reflect the procedural efficiency and long-term cost savings of catheter-directed thrombolysis, the market’s potential in outpatient care environments will remain underrealized.
Growing Procedural Adoption in Post-Surgical Prophylaxis and Oncology-Linked Thrombosis Management
Recent interest in catheter-directed thrombolysis as a primary therapeutic modality may be more focused towards its expanded use for the treatment of thrombotic events related to post-surgical complications and oncology care. There is an increasing incidence of deep vein thrombosis resulting from prolonged immobility or hypercoagulable states in surgical departments with high throughput, particularly orthopedic, oncologic, and transplant surgeons.
Hospitals are increasingly seeing catheter-based thrombolysis as a direct, on-demand intervention that stops it from becoming a life-threatening “massive” pulmonary embolism. Just like cancer treatment centers are integrating catheter directed solutions in their efforts to manage chemotherapy-induced thrombosis when systemic anticoagulants are contraindicated.
With the growth of innovative surgical and oncology pathways and multidisciplinary care teams, referral of patients for catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) is increasing. The strategic operational integration of these modalities drives not only the volume of catheters used but market access to predictable recurring demand forms, emerging within care models associated with oncology that serve as high-margin, underpenetrated manufacturing expansion vectors.
From 2020 to 2024, as the intervention rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism increases, the procedural adoption rate was exceptionally rapid in the catheter-directed thrombolysis market. The drive toward less invasive means of clot management away from the operating room accelerated in the wake of clinicians being pressured to ease both the ICU burden and post-surgical recovery times. Manufacturers responded with targeted innovations dual-lumen catheters, directional infusion tips, customizable flow control systems to enhance the therapeutic precision.
Looking ahead, the market is moving toward platformization, where catheter systems will integrate with AI-based clot assessment software, enabling dynamic dosing and real-time thrombus response tracking. Another emerging trend is value-tier product segmentation, with high-performance catheters for tertiary hospitals and cost-optimized kits for emerging markets.
Additionally, expansion into outpatient vascular clinics and subscription-based device access models is set to redefine device monetization strategies. The future of this market lies in hybrid procedural ecosystems built around data-enabled thrombolytic delivery.
Market Shifts: A Comparative Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| Market Shift | 2020 to 2024 |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Approvals based on safety and efficacy in hospital settings |
| Technological Advancements | Basic mechanical infusion systems with ultrasound guidance |
| Consumer Demand | Driven by acute VTE cases requiring hospitalization |
| Market Growth Drivers | Aging population, sedentary lifestyle, post-COVID VTE cases |
| Sustainability | Single-use catheters with limited environmental focus |
| Supply Chain Dynamics | OEM-dominated supply chains with regional distributors |
| Market Shift | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Expanded regulatory pathways for outpatient CDT; value-based care alignment |
| Technological Advancements | AI-enhanced imaging, smart catheters with dose control, integrated outcome tracking |
| Consumer Demand | Increased adoption in outpatient centers ; preventive interventions in high-risk patients |
| Market Growth Drivers | Early diagnosis programs, ambulatory surgical growth, reimbursement model expansion |
| Sustainability | Biocompatible materials, reusable components, eco-compliant packaging |
| Supply Chain Dynamics | Globalized logistics, device-EHR integration, cross-platform compatibility |
Market Outlook
The United States remains the most commercially advanced market for catheter-directed thrombolysis, driven by procedural decentralization and aggressive outpatient adoption. Office-based labs (OBLs) and ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) are at the forefront, offering same-day thrombolysis for acute DVT and submassive PE.
This shift has opened direct-access sales channels for device makers targeting high-volume private vascular groups. Additionally, the USA has led early adoption of pharmacomechanical thrombolysis (PMT), combining catheter delivery with mechanical clot disruption to shorten infusion times and hospital stays. Clinical guidelines by societies like SVS and SIR continue to support early intervention, increasing referral rates.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
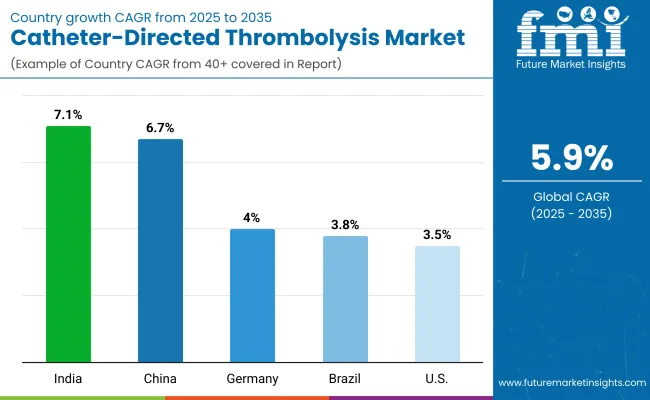
| United States | 3.5% |
Market Outlook
India’s catheter-directed thrombolysis market is expanding rapidly due to rising thrombotic case volumes in both public and private hospitals. Demand is especially strong in metro cities, where tertiary centers are introducing thrombolysis as a minimally invasive alternative to surgical thrombectomy.
Market entry by domestic manufacturers producing cost-effective catheters has made procedures more accessible in tier-2 and tier-3 cities. Medical tourism is another accelerant, with private chains offering thrombolysis in fast-track DVT/PE treatment packages. Clinical adoption is also rising in trauma and orthopediccenters, where venous thromboembolism prophylaxis is a critical post-operative focus.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| India | 7.1% |
Market Outlook
China's catheter-directed thrombolysis market is witnessing a rapid uptick, supported by the country’s massive expansion of advanced interventional capabilities in county and provincial hospitals. State-backed hospital upgrades are equipping vascular departments with the imaging and hybrid suite infrastructure needed to perform thrombolysis with precision.
Additionally, National Health Commission guidelines have recognized catheter-based interventions for DVT and PE, formalizing their place in clinical practice. The emergence of local OEMs with CE-certified products has boosted domestic supply, while public-private joint ventures are accelerating training programs to expand procedural expertise beyond top-tier cities.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 6.7% |
Market Outlook
Germany’s catheter-directed thrombolysis market is shaped by strong clinical preference for image-guided precision therapies and data-supported procedural protocols. University hospitals and vascular centers are applying thrombolysis for early-stage DVT to prevent post-thrombotic syndrome, supported by extensive clinical validation.
Devices with ultra-low dose infusion capabilities and integrated pressure feedback are in high demand, driven by regulatory scrutiny under EU MDR. Moreover, national reimbursement systems encourage adoption of evidence-based, minimally invasive interventions that reduce hospitalization days. Collaborations between German med-tech firms and clinical research institutes are also accelerating the introduction of next-gen thrombolysis platforms.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Germany | 4.0% |
Market Outlook
Brazil represents a high-growth frontier for catheter-directed thrombolysis, driven by rising awareness among vascular specialists and expanding private-sector investment in interventional capabilities. Urban hospitals in São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Brasília are adopting catheter-based DVT treatment to reduce dependency on long-stay anticoagulation therapies. Private hospital chains are investing in portable thrombolysis kits suited for emergency use, especially in trauma care.
The Brazilian Society of Angiology and Vascular Surgery has begun publishing clinical guidance favoring localized thrombus resolution over systemic methods, promoting training adoption. Meanwhile, a rise in insurance coverage for minimally invasive vascular interventions is opening new billing pathways for outpatient thrombolysis.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Brazil | 3.8% |
Direct Delivery to Blood Clot Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis Remains the Leading Delivery Mode Due to Precise Targeting and Reduced Systemic Impact
Catheter-directed thrombolysis has evolved in response to the need for a highly effective method to treat acute deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and intermediate- to high-risk pulmonary embolism (PE), and the direct delivery to blood clot approach has now become the go-to method. This procedure sends thrombolytic agents directly into the clot via a catheter, allowing for very local therapy and vastly minimizing systemic exposure to thrombolytics.
This approach reduces the associated bleeding complications risk by delivering the drug directly at the site of the clot, which is essential for patients who are at a greater risk. In addition, hospitals and outpatient facilities prefer this method because it allows for faster treatment with a better-controlled infusion rate.
Because of its effectiveness in managing DVT and PE and other thrombotic illness with less complications, it has become the gold standard in interventional therapy. With increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, direct delivery continues to be the modality of choice in both acute care and chronic therapy scheduling.
Positioning Medical Device at Clot Site Emerging as a Precision-Driven, Highly Personalized Approach to Thrombolysis Treatment
Catheter-directed thrombolysis by placing the medical device near the clot site is an emerging trend that is gaining rapid traction following advances in imaging and navigation technologies. It is especially useful in the more complicated cases where direct infusion is less effective and or may lead to complications. The catheter becomes placed at the site of the clot through advanced imaging techniques, such as 3D fluoroscopy or intravascular ultrasound, to ensure optimal drug delivery while limiting the thrombolytics' effects on the normal surrounding tissue.
This approach offers the benefit of adjusted therapy to target where the problems are occurring, for example anatomical areas that are challenging to navigate, such as the iliac veins, or patients with highly organized clots. It is perfect for patients with big or embolic clots, where precise navigation and targeted therapy are critical. While the market is still in the phase of adoption, the increasing integration of these technologies and the emphasis on patient-specific treatment protocol are anticipated to underpin the growth of the market over the next few years.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Continues to Lead the Indication Market Due to High Incidence and Complication Risk
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) remains the most common use of catheter-directed thrombolysis due to its high incidence and the well-described long-term sequela primary post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS). DVT refers to the formation of blood clots within deep veins, usually the limbs, in the absence of treatment; it can cause serious complications including chronic venous insuffeciency and pulmonarychamber embolism (PE). The rise in incidence of DVT due to the escalation in the prevalence of global risk factors, including old age, sedentary lifestyle, and obesity, is also fueling the demand for effective and minimally invasive treatment options.
However, thrombolysis is almost exclusively delivered in the acute setting, as the goal is early intervention that prevents further extension of the clot and reduces the potential for vascular ischemia, with the overarching impetus for thrombolysis remaining the prevention of irreversible ischemic damage and the necessary execution of clinical workflow responsible for its continued success.
But catheter-directed thrombolysis for proximal DVT is much more cost effective than surgical therapies if for no other reason than as our systems focus on cost containment measures and also demand high clinical outcomes.
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Gaining Ground as an Emerging Indication for Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis Due to Improved Safety and Precision
Many studies are discovering that catheter-directed thrombolysis has been able to provide a lower-risk treatment in cases of pulmonary embolism (PE), and PE has the potential to become a very desirable indication of catheter-directed thrombolysis, however for the moment PE remains less of a mainstay of this approach than DVT because of the inherent risks of intracranial hemorrhage.
PE is the infiltration of a blood clot in to the lungs causing obstruction of pulmonary blood flow and life-threatening. Conventional systemic thrombolytic therapy can be associated with significant bleeding risk in intermediate-risk PE patients. Thus, catheter-directed thrombolysis has gained increasing traction because it allows regional clot lysis with less systemic delivery.
More recent catheter-based devices, employing modern navigation capabilities such as ultrasound and mechanical thrombectomy adjuncts, have significantly enhanced the accuracy of this technique while minimizing the inherent risks of the procedure. It has been shown to improve survival and shorten recovery time in patients with PE. Given the increasing diagnostic and procedural efficiencies, catheter-directed thrombolysis for PE will soon form an integral adjunct to an acute PE management protocol.
The global market for Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis (CDT) Market is growing steadily. There is a demand for minimally invasive treatment options which is driving the innovation in catheter based technologies. Participants are focused on device efficacy, improved safety, and broadened clinical indications. North America leads the market based on advanced healthcare systems and high awareness, and the Asia-Pacific is anticipated to become a rapidly growing region on account of better access to healthcare and rising diagnosis rates.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
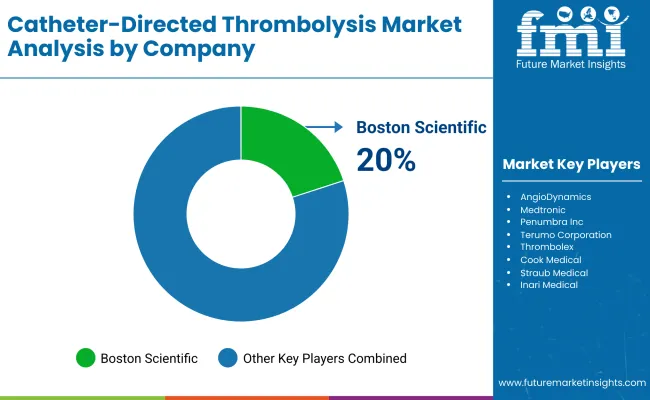
| Boston Scientific | 20-25% |
| AngioDynamics | 18-22% |
| Medtronic | 12-16% |
| Penumbra Inc. | 10-14% |
| Terumo Corporation | 6-9% |
| Thrombolex | 4-6% |
| Others | 10-15% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| Boston Scientific | Offers thrombectomy and thrombolysis catheters; strong clinical research pipeline and integrated vascular solutions. |
| AngioDynamics | Known for the Uni -Fuse™ and Pulse Spray™ infusion systems; emphasizes DVT/PE treatment and hospital partnerships. |
| Medtronic | Provides advanced peripheral vascular catheters and imaging-guided thrombolysis tools. Focused on minimally invasive therapies. |
| Penumbra Inc. | Manufactures Indigo® Aspiration System for clot removal; growing footprint in acute thrombus management. |
| Terumo Corporation | Offers peripheral vascular and interventional catheters; investing in Asia-Pacific expansion and R&D. |
| Thrombolex | Specializes in catheter-based infusion systems; focuses on rapid thrombus resolution and USA clinical trials. |
Key Company Insights
Other Key Players Beyond the leading companies, several other manufacturers contribute significantly to the market, enhancing product diversity and technological advancements. These include:
Direct Delivery to Blood Clot Catheter-directed Thrombolysis and Catheter-directed Thrombolysis by Positioning Medical Device at Clot Site
Pulmonary Embolism (PE), Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), Strokes and Other Indications
Hospitals, Surgical Centers and Radiology Clinics
North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Middle East & Africa
The overall market size for catheter-directed thrombolysis market was USD 510.0 million in 2025.
The catheter-directed thrombolysis market is expected to reach USD 906.2 million in 2035.
AI-guided catheter placement is making procedures faster and more precise by helping doctors target clots with pinpoint accuracy.
The top key players that drives the development of catheter-directed thrombolysis market are Boston Scientific, AngioDynamics, Medtronic, Penumbra Inc. and Terumo Corporation
Direct delivery to blood clot catheter-directed thrombolysis is expected to command significant share over the assessment period.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 21: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 25: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: East Asia Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Indication, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User , 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Delivery Mode, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Indication, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by End User , 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA