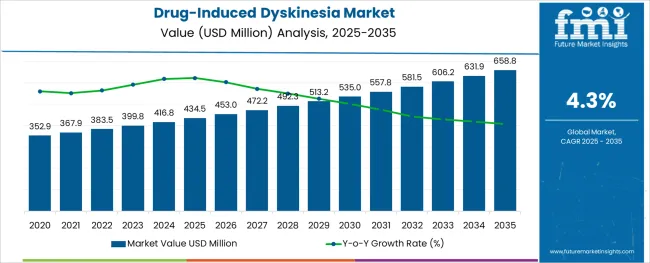
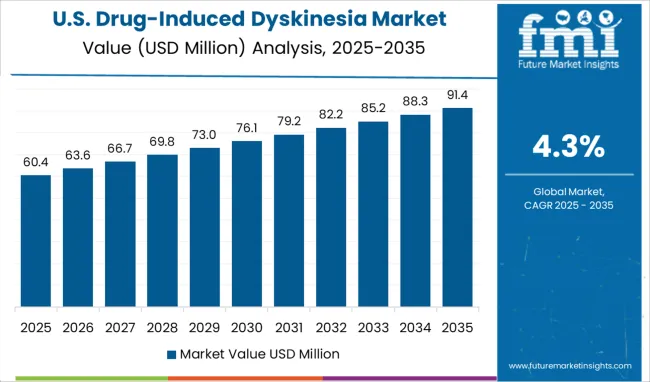
The Drug-Induced Dyskinesia Market is estimated to be valued at USD 434.5 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 658.8 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% over the forecast period.
The drug induced dyskinesia market is evolving steadily as increasing awareness of movement disorders, advancements in neuropharmacology, and growing patient access to specialty treatments converge to drive demand. Rising diagnosis rates and the availability of targeted therapies have shifted clinical management from symptomatic relief to more mechanism-based interventions.
Clinical guidelines are progressively incorporating newer therapies that aim to balance efficacy with tolerability, addressing a long-standing unmet need in this space. Future growth is expected to be influenced by the development of novel drug candidates, expanding geriatric populations susceptible to dyskinesias, and greater investments in neuroscience research.
Supportive healthcare policies, coupled with enhanced diagnostic capabilities and multidisciplinary care models, are paving the way for more personalized and effective treatment pathways in managing drug induced movement disorders.
The market is segmented by Drug Class and End User and region. By Drug Class, the market is divided into VMAT2 Inhibitors, Dopamine-Depleting Medications, GABA Receptor Agonist Medications, and Anticholinergic Medications. In terms of End User, the market is classified into Hospitals, Clinics, and Others. Regionally, the market is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
Insights into the VMAT2 Inhibitors Drug Class Segment
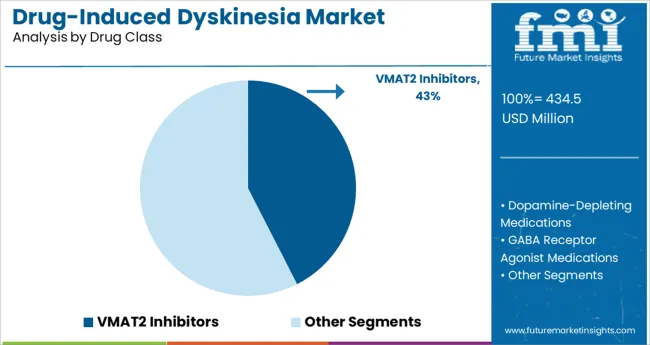
When segmented by drug class, VMAT2 inhibitors are projected to hold 42.5% of the total market revenue in 2025, making them the leading segment. This leadership has been reinforced by the demonstrated efficacy of these agents in mitigating hyperkinetic movements associated with drug induced dyskinesias while maintaining an acceptable safety profile.
Their mechanism of selectively modulating monoamine transmission has addressed key pathophysiological pathways, which has enhanced physician confidence and widened adoption in clinical practice. The ability to offer sustained symptom control, reduced off-target effects, and improved quality of life for patients has supported their dominance.
Additionally, consistent incorporation of VMAT2 inhibitors into treatment guidelines and favorable reimbursement frameworks have further solidified their position as the preferred pharmacologic option within this therapeutic category.
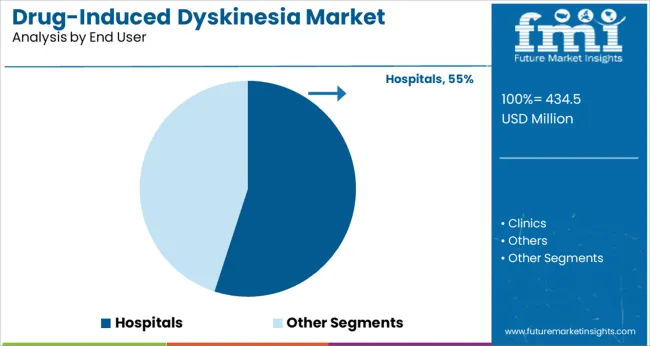
Segmented by end user, hospitals are expected to account for 55.0% of the drug induced dyskinesia market revenue in 2025, retaining their lead in the segment. This prominence has been driven by the concentration of specialized neurology services, availability of multidisciplinary care teams, and access to advanced diagnostic and therapeutic resources within hospital settings.
Hospitals have been positioned as the primary point of care for patients requiring initiation, titration, and monitoring of complex pharmacologic regimens, including those involving VMAT2 inhibitors. Their infrastructure supports comprehensive evaluation and management of comorbidities, which has been critical in optimizing patient outcomes.
Furthermore, hospitals’ ability to deliver coordinated care and adhere to standardized treatment protocols has strengthened their role as the preferred environment for managing moderate to severe cases, reinforcing their continued leadership in the market.
The global drug-induced dyskinesia market grew at a CAGR of 3.1% from 2020 to 2025, as per Future Market Insights, a provider of market research and competitive intelligence. Due to the growing frequency of drug-induced dyskinesia linked to an increased incidence of neurologic diseases such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and Alzheimer's disease, the worldwide market for drug-induced dyskinesia is anticipated to post a consistent revenue CAGR in 2024.
Additionally, rising Research and Development efforts, elevated awareness, technical advancements, a robust product pipeline, a desire for more potent therapies, and innovation in treatment are predicted to drive market expansion throughout the course of the projection period.
Such factors are expected to boost the global sales of drug-induced dyskinesia solutions. As a result, the global drug-induced dyskinesia market is expected to forecast a CAGR of over 4% from 2025 to 2035.
Increasing cases of schizophrenic as well as other neurological diseases to boost the demand
Dyskinesia has been proven to be much more prevalent among patients who suffer from diseases like schizophrenia and other neurological disorders. Patients with schizophrenia who use antipsychotic medications for a prolonged period of time have a substantial risk of developing drug-induced dyskinesia. As a result, an increasing number of antipsychotic medications come with a significant risk, which encourages the market's expansion. For instance, according to a report from the World Health Organization published in January 2025, schizophrenia affects 24 million people worldwide, or 0.32%, out of which a ratio of 1 in 222 people (0.45%) were adults.
Additionally, according to figures released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in October 2024, 1 in 6 individuals throughout the world will be 60 years of age or older by 2035, increasing the likelihood that they may acquire Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Thus, it is anticipated that the pool demographic for drug-induced dyskinesia would increase as Alzheimer's disease prevalence rises, increasing the demand for treatment and potentially stimulating the market. Such factors are sure to propel the market for drug-induced dyskinesia during the forecast period.
Various neuroleptic drugs cause dyskinesia among the patients
Long-term neuroleptic medication usage raises the likelihood of drug-induced dyskinesia and hence boosts the market for drug-induced dyskinesia medicines. When used for a few weeks or longer, specific medications that disrupt dopamine receptors within the brain can result in drug-induced dyskinesia. Antipsychotics, antiemetics, and antidepressants are some of these medications.
Schizophrenia is treated with typical antipsychotic medications, commonly referred to as first-generation antipsychotic medications. Some of these medications also address other disorders including nausea and vomiting. However, when used over an extended length of time, these medications cause dyskinesia in the patients.
Since a side effect of neuroleptic medications is drug-induced dyskinesia, the frequency of neurological conditions including Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder is rising, and so is the need for antipsychotic medications.
Such factors are expected to accelerate the demand for drug-induced dyskinesia during the forecast period.
Clonidine-induced hypotension and other relevant factors will impede the growth
The market for medications that produce drug-induced dyskinesia is anticipated to suffer from adverse effects such as clonidine-induced hypotension as well as sedation. These elements are recognized to lessen patients' dyskinesia symptoms as well as effectively treat their illnesses for an extended length of time.
The market is also anticipated to be hampered by high treatment costs, poor diagnosis rates, societal stigma, a shortage of qualified healthcare professionals, and the relatively high price of a clinical trial over the projection period.
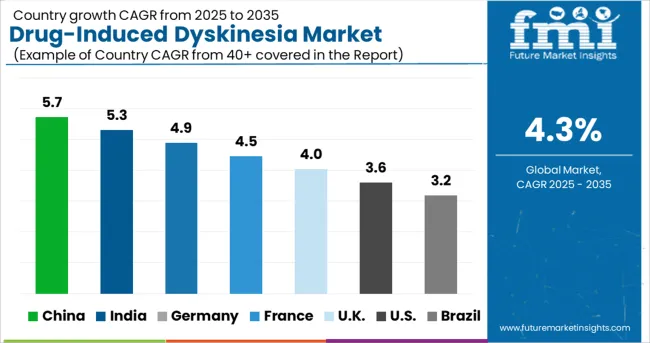
High prevalence of neuropathic diseases to boost the regional demand
North America is predicted to hold the dominant market share of 41% revenue share in 2025 and is the fastest-growing market for drug-induced dyskinesia, with a dominant 4.3% CAGR from 2025 to 2035.
A large portion of the global market for drug-induced dyskinesia treatments is anticipated to be accounted for by North America, owing to factors such as an aging population, a higher incidence of schizophrenia, rising dyskinesia awareness, rising healthcare costs, and developed healthcare infrastructure. As the world's population ages, various neurological illnesses will emerge, necessitating the use of antipsychiatric medications. As a result, these groups are more likely to get certain illnesses. In May 2024, the National Alliance on Mental Health reported that 1.5 million Americans, or 0.25% to 0.64% of the population, were living with schizophrenia.
Thus, the high prevalence of the condition among the elderly population of nations across North America is expected to increase demand for the development of therapeutic medications, resulting in the market's expansion. A further factor supporting the growth of the drug-induced dyskinesia treatment market in this area is the association of this illness with specific patient pools such as individuals treated for schizophrenia as well as bipolar disorder in this area.
Large patient pool and more research and awareness programs to propel the sales
During the forecast period, the APAC market for drug-induced dyskinesia is expected to garner a steady CAGR of 3.5%. But at the time, this market is presently acquiring a 31% market share in the global drug-induced dyskinesia market.
Due to a larger patient pool, more involvement in research and public awareness campaigns about drug-induced dyskinesia therapy, and enhanced public health awareness, the Asia Pacific area is anticipated to develop at the quickest rate throughout the projection period.
The drug-induced dyskinesia APAC market is also anticipated to develop throughout the projected period as a result of an expanding patient base for neuroleptic illnesses including bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and others as well as improved healthcare infrastructure and greater healthcare spending.
The VMAT 2 segment will gain the dominant market share
Over the course of the forecast period, the VMAT 2 segment by drug class is anticipated to occupy a significant share of the global drug-induced dyskinesia market. In 2025, this category is anticipated to dominate with a 46% revenue share.
VMAT2 inhibitors are drugs that produce dopamine depletion in nerve endings and are employed to treat chorea caused by neurodegenerative disorders (like Huntington's chorea) or dyskinesias caused by neuroleptic medicines. With more neurological disorders and more people being prescribed antipsychotic medications, VMAT is predicted to have healthy development in the next few years. According to the research article Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: Past, Present, and Future released in February 2025, there are an estimated 6.1 million people worldwide who have Parkinson's disease. The prevalence rises with age, reaching 1% to 3% in people over 65.
Additionally, according to figures released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in October 2024, 1 in 6 persons worldwide would be 60 years of age or older by the year 2035. Parkinson's therapy is linked to drug-induced dyskinesia, and it is anticipated that the prevalence of the illness would increase during the projection period, increasing demand for the possible treatment and driving segment growth. Such factors are expected to accelerate the growth prospects for drug-induced dyskinesia from 2025 to 2035.
The hospital's segment will become more significant from 2025 to 2035
On the basis of the sales channel, the most dominant segment is the hospital segment, which is expected to occupy a global market share of 32% from 2025 to 2035.
The hospital segment is expected to acquire the dominant position on the basis of channel type. This can be attributed to the increasing number of elderly patients admitted to hospitals. When it comes to the elderly, no one wants to take risks and keep the patient at home, particularly in case of any neurological disorder. In hospitals, the patients can be monitored effectively 24X7 and given the medicines at the apt time they need. Hence, with such advantages, the segment is expected to witness immense growth during the forecast period.
The new companies are aimed at developing their products with enhanced safety features and new technology to make the products stand out in the global market.
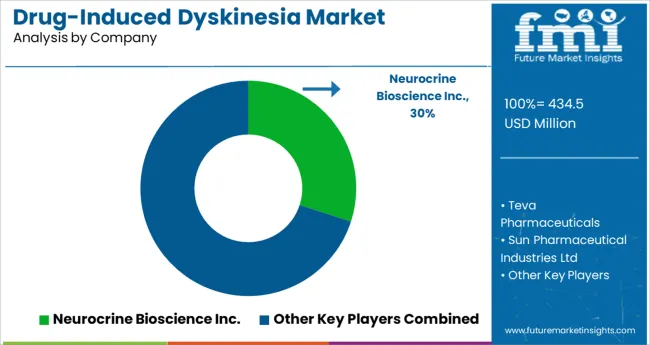
Some of the prominent players in the global market for drug-induced dyskinesia are:
Some of the prominent developments of the key players in the market are:
The global drug-induced dyskinesia market is estimated to be valued at USD 434.5 million in 2025.
It is projected to reach USD 658.8 million by 2035.
The market is expected to grow at a 4.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types are vmat2 inhibitors, dopamine-depleting medications, gaba receptor agonist medications and anticholinergic medications.
hospitals segment is expected to dominate with a 55.0% industry share in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) Treatment Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA