The ozempic market reached a valuation of USD 22.3 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow to USD 58.4 billion by 2035, with a projected CAGR of 10.1%. Growth has been steered by broader acceptance of semaglutide for type 2 diabetes and weight-related indications, including widespread off-label prescribing patterns.
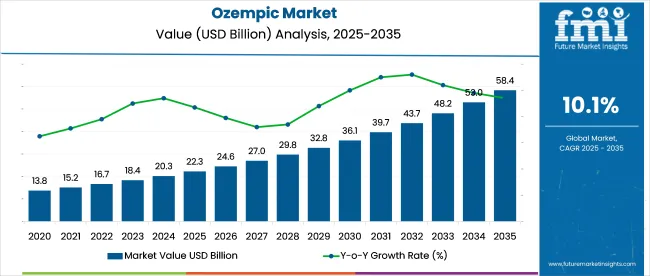
Demand has been reinforced by payer shifts, expanding telehealth-based prescriptions, and elevated interest in GLP1 receptor agonists as a non-invasive alternative to bariatric procedures. Competitive activity within the ozempic market has been shaped by aggressive pricing, patient adherence programs, and strategic partnerships aimed at scaling production and ensuring uninterrupted supply across priority channels.
"Obesity is a serious, chronic disease, and access to obesity medications should be treated with the same urgency as other chronic conditions,"said Rhonda Pacheco, Group Vice President of USACardiometabolic Health at Eli Lilly. "Lilly was the first company to offer a self-pay solution for an FDA-approved obesity medication, and we continue to work to expand coverage for Zepbound. In the meantime, the availability of the two highest-dose Zepbound vials gives providers and patients another important treatment option."(Source: Eli Lilly & Co., June 2025)
Ozempic captures close to 60% of the GLP-1 receptor agonist category, underscoring its lead among semaglutide-based therapies. Within the type 2 diabetes drug sector, valued at around USD 88 billion, its contribution is estimated at 20-25% based on treatment volumes and sales. In the weight management therapeutics domain, including obesity drugs, Ozempic and its related formulations represent about 65% of the segment’s total value.
When both anti-obesity and anti-diabetic therapies are considered together, the total is roughly USD 200 billion. Ozempic commands a 10-15% slice. Compared to the broader prescription drug industry, projected at over USD 1.5 trillion, Ozempic’s anticipated 2025 sales of USD 22 billion translate to just over 1.5%, reflecting its high revenue yield in targeted treatment classes.
The market has been segmented by indication, dosage strength, distribution channel, patient type, and region. The indication segment comprises type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dosage strength is divided into 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, and 2 mg/3 mL (0.68 mg/mL).
Distribution channels include hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online platforms. The patient type segmentation covers insured patients and uninsured patients. The regional breakdown includes North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
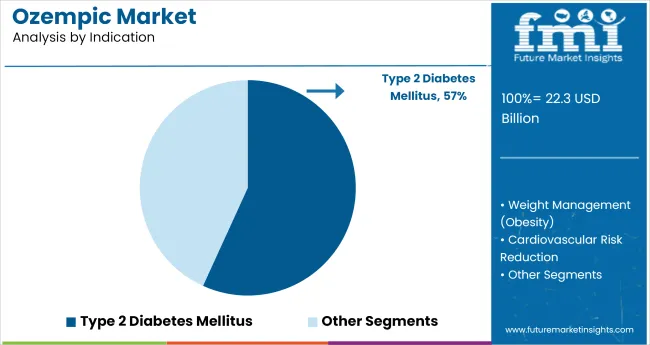
In 2025, 57% of ozempic prescriptions were written for type 2 diabetes mellitus, reflecting widespread alignment with updated global guidelines. The American Diabetes Association included GLP-1 receptor agonists as preferred therapy for patients with cardiovascular risk, increasing ozempic’s usage in USA clinics such as Cleveland Clinic and Mayo.
The NHS in the UK incorporated semaglutide for overweight diabetic adults, driving national procurement. In India, hospital chains like Max and Fortis adopted ozempic within cardiometabolic protocols. Clinical preference stemmed from consistent weight reduction, blood glucose control, and cardiovascular safety data, with endocrinologists and internists both contributing to steady prescription volume.
Retail pharmacies accounted for 50.1% of ozempic dispensation in 2025, driven by insured prescription processing and direct patient access. USA chains like Walgreens and Rite Aid handled high weekly volumes, aided by pharmacy benefit manager integrations. In Japan, Welcia and Matsumoto Kiyoshi pharmacies maintained semaglutide availability under national health insurance systems.
Brazilian chains such as Drogasil expanded stock across São Paulo and Rio to serve urban diabetic populations. These pharmacies played a key role in refill adherence, with pharmacists offering injection guidance. High-frequency demand created strong inventory turnover across global retail channels equipped with cold storage facilities.
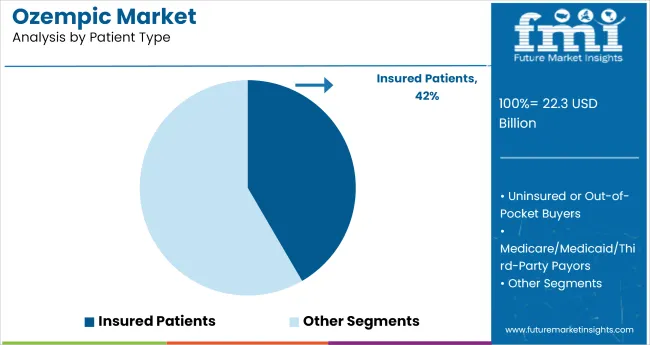
Insured patients represented 42% of ozempic volume in 2025, driven by broad access under national and private reimbursement schemes. USA coverage through Medicare and insurers like Aetna and Blue Cross supported higher uptake, especially for patients with comorbid cardiovascular risks. Germany’s public insurance bodies fully reimbursed semaglutide in cases meeting metabolic syndrome criteria.
In Japan, prescriptions were facilitated by favorable co-payment structures under the universal health plan. Hospitals such as Charité in Berlin and St. Luke’s in Tokyo reported increased ozempic initiations for eligible insured patients. Refill compliance remained higher among this segment due to minimal out-of-pocket expenses.
The market is being shaped by increasing off-label use in obesity and cardiometabolic care, alongside persistent supply challenges. While once-weekly GLP-1 therapies gain clinical favor, manufacturing and regulatory bottlenecks continue to restrict rollout, especially in cost-sensitive and emerging regions.
Broadening Use in Obesity and Cardio-Metabolic Treatment
Ozempic is no longer confined to type 2 diabetes care, as physicians increasingly prescribe it for obesity and cardiovascular risk reduction. Clinical guidelines now support early GLP-1 initiation in at-risk patients, expanding access through insurance plans and digital prescribing channels.
The drug’s once-weekly dosing schedule has improved adherence in both chronic and preventive care settings. As telehealth usage rises and weight-loss protocols integrate GLP-1s, off-label adoption has grown rapidly, reshaping demand across the USA, UK, and select European regions.
Production Strains and Global Access Challenges
Persistent manufacturing constraints have challenged ozempic’s global scale-up. Semaglutide API shortages, coupled with limited injector fill-finish capacity, have led to delayed approvals and fragmented regional supply. Dependency on a few contract manufacturing sites has heightened risk exposure, particularly in emerging markets.
Retail shortages in Europe have been worsened by parallel export channels, while regulatory hurdles continue to delay rollout in Latin America and Southeast Asia. These issues have limited inventory flexibility and weakened market responsiveness during demand surges.
| Countries | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United States | 7.6% |
| United Kingdom | 8.2% |
| India | 14.8% |
| China | 11.6% |
| Japan | 9.1% |
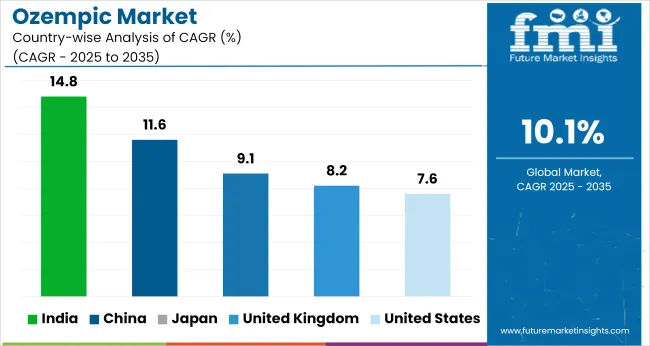
The ozempic market is projected to grow at a 10.1% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. Growth varies across BRICS, OECD, and ASEAN economies, with BRICS countries showing the strongest momentum. India leads at 14.8%, outpacing the global average by 47%, followed by China at 11.6%.
Both nations benefit from fast-expanding diabetic and obesity-related pharmaceutical demand, paired with improved insurance inclusion and local production incentives. Japan (9.1%) and the United Kingdom (8.2%) reflect moderate growth among OECD peers. The United States, also in the OECD group, lags at 7.6% due to coverage limits and supply challenges.
The report covers detailed analysis of 40+ countries and the top five countries have been shared as a reference.
The ozempic market in the United States is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% between 2025 and 2035. Adoption has broadened beyond diabetes care following ADA endorsements for GLP-1 use in cardiometabolic management.
Telehealth-driven access has surged, particularly across mid-sized cities, while payer resistance has emerged through step therapy and audit protocols. Mail-order services have expanded prescription volumes due to refill incentives. Payer heterogeneity continues to shape co-pay variability and coverage exclusions, limiting nationwide uniformity in therapy access.
A projected CAGR of 8.2% is estimated for ozempic sales in the United Kingdom from 2025 to 2035. Demand has grown under NICE’s 2023 obesity guidance, with regional disparities emerging due to NHS capacity limits. Scotland and Northern Ireland have outpaced England in per capita dispensing.
Reliance on private clinics and online D2C services has intensified, especially where public-sector availability is capped. Nurse prescribers in virtual clinics have increased initiation of GLP-1 therapy, signaling a shift in prescribing responsibility within weight management frameworks.
Demand ozempic market in India is expanding at a CAGR of 14.8% from 2025 to 2035. Cardiometabolic clinic growth and CME-backed GLP-1 promotion have accelerated prescriber interest. Beyond metros, tier-2 cities have seen uptake through diagnostic networks tied to multispecialty hospitals.
High out-of-pocket costs have led to modified usage, including alternate-week dosing in semi-urban belts. Draft proposals under NPPA may soon impose pricing ceilings. Pre-diabetes screening programs in corporate health camps have also increased new-user conversion rates across private health networks.
Ozempic usage in China is expected to grow at 11.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. National metabolic programs have integrated semaglutide into dual-management pathways for obesity and hypertension. City-level e-prescription platforms now support refill and post-discharge continuation through pharmacy chains.
Regional pilot schemes have used semaglutide for CV-metabolic overlap, covering tens of thousands of patients. Conditional hospital access has been granted to several domestic biosimilars, with formulary reviews underway in key provinces for broader inclusion.
Sale of ozempic in Japan is growing at a 9.1% CAGR through 2035. Prescriptions remain concentrated in institutional settings following 2023 MHLW inclusion of GLP-1s for cardiovascular secondary prevention. Adoption by outpatient clinics has lagged, hindered by limited staffing for injectable patient training.
Consumer education has shifted toward digital platforms, with health forums and influencers driving awareness in the absence of commercial promoting. Uptake has been strongest among working males aged 40-60 in metropolitan regions.
Leading Company - Novo Nordisk Industry Share - 58%
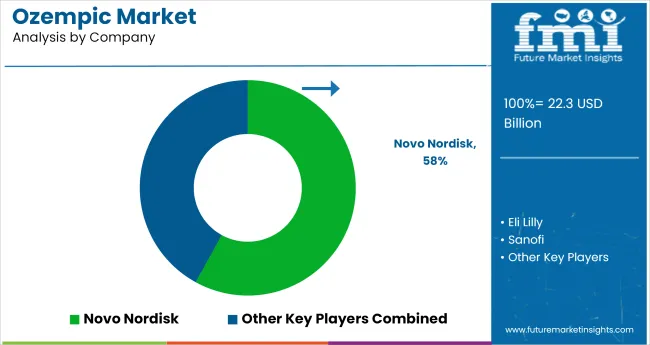
The ozempic market is anchored by Novo Nordisk, which developed and commercialized Ozempic and Wegovy. The company has scaled both formulation and delivery innovations, enabling global access while reinforcing physician loyalty through clinical trial data and patient adherence programs.
Eli Lilly, though a late entrant, has aggressively gained share via tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound), which demonstrated superior weight-loss outcomes in head-to-head trials. Its weekly injectables are reshaping prescribing behavior, especially in the USA
Sanofi, previously dormant in GLP1s, is investing in new analogues and platform licensing, seeking reentry through differentiated delivery formats. AstraZeneca is building an early-stage pipeline, banking on GLP1 combination therapies. In China, Jiangsu Hansoh is enabling localized semaglutide supply, securing regulatory clearance faster than foreign entrants.
Biocon, Dr. Reddy’s, and Cipla are progressing toward biosimilar filings, focusing on price-sensitive markets where reimbursement limits access to branded semaglutide. This evolving landscape combines originator dominance with strategic biosimilar disruption.
Recent Industry News
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 22.3 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 58.4 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 10.1% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for value and million doses for volume |
| Indications Analyzed (Segment 1) | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Weight Management (Obesity), Cardiovascular Risk Reduction, Others (Prediabetes, Insulin Resistance Syndromes) |
| Dosage Strengths Analyzed (Segment 2) | 0.25 mg Solution for Injection, 0.5 mg Solution for Injection, 1 mg Solution for Injection, 2 mg/3 mL (0.68 mg/mL), Other Custom Dosages |
| Distribution Channels Analyzed (Segment 3) | Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies |
| Patient Types Analyzed (Segment 4) | Insured Patients, Uninsured or Out-of-Pocket Buyers, Medicare/Medicaid/Third-Party Payors |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa |
| Key Players | Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Jiangsu Hansoh, Biocon, Dr. Reddy’s, Cipla |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by indication and dosage strength, demand trends in GLP-1 therapies, rising obesity-linked prescriptions, payer segmentation and coverage shifts, growth in online and out-of-pocket access points |
The segment includes Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Weight Management (Obesity), Cardiovascular Risk Reduction, and Others such as Prediabetes and Insulin Resistance Syndromes.
This includes 0.25 mg Solution for Injection, 0.5 mg Solution for Injection, 1 mg Solution for Injection, 2 mg/3 mL (0.68 mg/mL), and Other Custom Dosages.
The industry is segmented into Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies.
This segment is divided into Insured Patients, Uninsured or Out-of-Pocket Buyers, and Medicare/Medicaid/Third-Party Payors.
Regional analysis includes North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa.
The industry is projected to reach USD 22.3 billion in 2025.
The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2025 to 2035.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is expected to capture 57% in 2025.
The Asia Pacific region, particularly India, is projected to register a CAGR of 14.8% from 2025 to 2035.
The industry is projected to reach USD 58.4 billion by 2035.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA