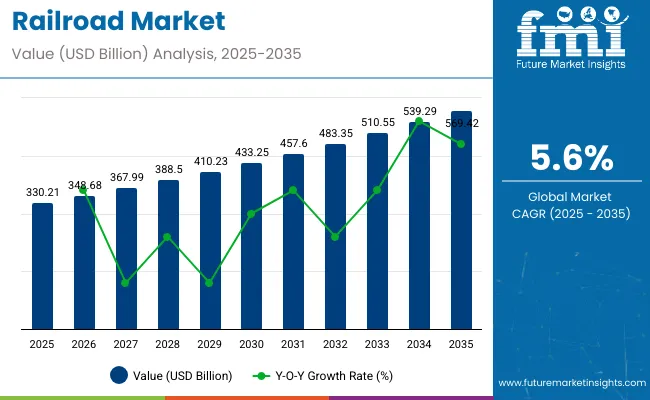
The railroad market is valued at USD 330.21 billion in 2025 and is likely to reach approximately USD 569.42 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 5.6%. The multiplying factor over the decade is around 1.73x, indicating that the 2035 market will be 1.73 times its 2025 base. The acceleration and deceleration pattern illustrates periods of strong expansion followed by moderated growth, influenced by infrastructure investments, technological upgrades, and regional demand variations.
Between 2025 and 2028, the market accelerates due to modernization of rail networks, development of high-speed rail corridors, and increased cargo and passenger demand. From 2029 to 2032, growth slightly decelerates as major infrastructure projects reach completion and investment cycles stabilize. Between 2033 and 2035, expansion resumes, supported by adoption of advanced signaling systems, electrification projects, and smart rail technologies.
This acceleration and deceleration pattern, combined with a multiplying factor of 1.73x, highlights the market’s steady long-term trajectory, providing rail operators, equipment manufacturers, and technology providers predictable opportunities to optimize investments and scale operations across the decade.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 330.21 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 569.42 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.6% |
The market is influenced by multiple parent markets with different contributions. Transportation infrastructure accounts for approximately 30%, covering track networks, signaling systems, and station development. Global logistics and freight transport contribute around 28%, driven by rail-based cargo movement and intermodal transport solutions. Rail equipment and rolling stock represent roughly 22%, supplying locomotives, passenger coaches, and freight wagons.
Industrial manufacturing contributes close to 12%, supporting production of steel, machinery, and track components. Information and communication technology (ICT) makes up about 8%, enabling digital signaling, train control systems, and operational monitoring. Collectively, these sectors underpin railroad market expansion and modernization.
The industry is seeing innovation in electrification, digitalization, and eco-friendly solutions. Key players such as CRRC, Siemens Mobility, Alstom, and Bombardier are deploying electric locomotives, automated control systems, and predictive maintenance platforms. Integration of IoT sensors and AI-based monitoring improves safety, efficiency, and operational transparency.
Expansion of high-speed rail, urban transit systems, and dedicated freight corridors is driving global growth, particularly in Asia and Europe. Energy-efficient traction systems, lightweight rolling stock, and low-emission locomotives are reshaping rail operations. Strategic partnerships between technology providers and operators are enhancing connectivity, capacity, and service reliability.
The railroad industry is expanding due to growing investments in freight and passenger rail infrastructure. Global rail networks exceed 1.3 million kilometers, with Asia Pacific leading in expansion projects. Modernization focuses on high-speed rail, electrification, and automation to improve operational efficiency and reduce travel times. Freight rail supports rising demand for bulk commodities, containerized goods, and intermodal transport, while passenger rail ridership exceeds 8 billion trips annually. Digital signaling, GPS tracking, and predictive maintenance enhance safety and reliability.
Infrastructure investment and rising freight demand are key market drivers. Freight rail offers cost-effective, energy-efficient transport for bulk commodities and industrial goods. Electrification projects cover over 45% of global track length, reducing emissions while increasing train speeds. High-speed passenger rail networks in Asia and Europe shorten travel times between urban centers by 30-40%.
Governments are funding modernization, while digital signaling and automated train control improve safety and reliability. Increased rail adoption reduces congestion on highways and enhances supply chain efficiency, making rail a preferred option for long-distance logistics and sustainable urban mobility.
High-speed rail and urban transit projects present major growth opportunities. Asia, particularly China and India, is adding over 40,000 kilometers of high-speed rail combined. Metro and commuter rail expansions in North America and Europe address urban congestion and support millions of daily passengers. Freight corridors are being upgraded with heavier tracks and automated terminals to enhance cargo throughput.
Integration of rail with ports and highways strengthens intermodal transport efficiency. Advanced ticketing, scheduling, and real-time passenger information systems improve convenience and utilization rates, while continuous investments in rolling stock ensure better service reliability.
Railway electrification and smart technology adoption are reshaping operations. Europe has electrified more than 60% of its rail network, while Asia and South America are rapidly following. IoT-enabled monitoring, predictive maintenance, and smart signaling reduce delays and improve uptime. Regenerative braking and energy storage systems optimize electricity consumption and lower operational costs.
Passenger-facing technologies, including automated ticketing and AI-based scheduling, enhance convenience and service reliability. Smart rail systems support capacity management, safer operations, and lower maintenance costs, making both freight and passenger services more efficient while aligning with environmental targets.
High capital investment and regulatory complexity restrict market expansion. Constructing new rail lines or upgrading tracks can cost billions, with long payback periods. Environmental clearances, land acquisition, and safety regulations slow project implementation. Freight rail faces competition from road and air transport, while passenger services must maintain affordability.
Skilled labor shortages in maintenance, signaling, and automation present operational challenges. Cost pressures and modernization needs require careful planning, technological adoption, and public-private collaboration to sustain growth. Despite high entry barriers, long-term investments in efficient, electrified, and digitally monitored rail networks promise steady returns and improved connectivity.
The railroad industry is shaped by type and end-user demand, with freight rails capturing 50% share due to high-volume goods transport requirements. Passenger rails hold 40%, addressing urban transit and intercity travel needs. Mining leads end-user demand at 30%, supporting bulk mineral and coal transport, while construction follows at 25% for infrastructure materials. Subways account for 20%, agriculture 15%, and other industries 10%. Investment in durable tracks, high-capacity wagons, and modern rail cars is increasing globally.
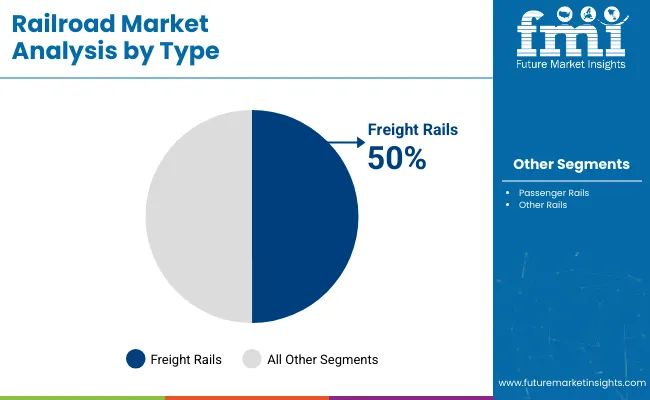
Freight rails dominate the railroad market with 50% share, reflecting the need to transport bulk commodities such as coal, minerals, and steel efficiently. Operators prioritize higher load capacities, reduced transit times, and cost-effective logistics, driving investments in high-strength rails and advanced railcars.
Passenger rails follow at 40%, serving urban and intercity travel, while other rails, including industrial and heritage lines, make up 10%. Freight rail growth is supported by industrial expansion in Asia-Pacific and North America, modernized track infrastructure, and increased automation in loading and unloading operations, helping companies meet rising demand for timely delivery and operational efficiency.
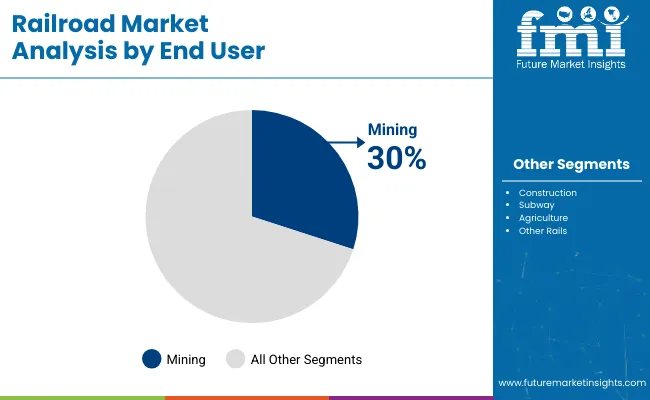
Mining represents the largest end-user segment at 30%, driven by the need to transport raw materials such as coal, iron ore, and bauxite. Rail infrastructure provides reliable, high-volume transport that supports mining operations globally. Construction accounts for 25%, moving cement, aggregates, and equipment to support infrastructure projects. Subways and urban transit systems make up 20%, reflecting ongoing metropolitan expansion. Agriculture represents 15% due to grain and fertilizer transportation, while other industries contribute 10%. Mining operations drive the adoption of robust tracks, larger freight wagons, and automated scheduling systems, improving logistics efficiency, reducing operational costs, and supporting the global supply chain.
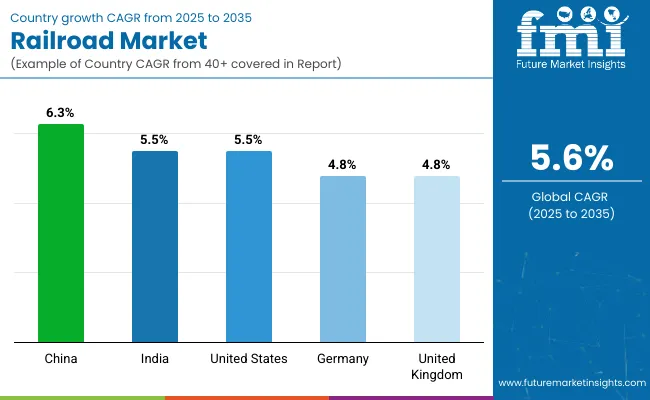
The global railroad market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2035. China leads at 6.3%, +12% above the global benchmark, supported by BRICS-driven infrastructure investment and high-speed rail expansion. India records 5.5%, roughly in line with the global rate, fueled by ASEAN-linked modernization programs and increasing freight and passenger rail demand.
The United States also stands at 5.5%, +0% relative to the global average, reflecting steady upgrades in OECD transport networks and rail technology. Germany and the United Kingdom both register 4.8%, -14% below the global benchmark, influenced by structured OECD infrastructure projects and incremental system modernization. TheBRICS countries like China are advancing faster than OECD peers, while India and the United States maintain steady growth, balancing modernization with strategic investment in rail systems.
China is expanding at a CAGR of 6.3%, above the global rate of 5.6%. The country is investing heavily in high-speed rail networks, connecting urban and regional centers efficiently. Rail freight services are growing to support e-commerce, manufacturing, and logistics sectors. Advanced signaling and track maintenance technologies are implemented across new and existing lines.
China is also integrating automated operations and smart ticketing systems to enhance passenger experience. Regional clusters in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong are leading infrastructure development, attracting international partnerships for equipment supply and rail technology innovation.
India is registering a CAGR of 5.5%, slightly below the global CAGR of 5.6%. Growth is driven by expansion of freight corridors and modernization of passenger rail infrastructure. Investments include electrification of lines, track upgrades, and improved signaling systems. Indian Railways is introducing semi-high-speed trains to improve connectivity between major cities.
Regional projects in Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh focus on integrating advanced track monitoring and automated control systems. Public-private partnerships support development of logistics hubs and rolling stock manufacturing.
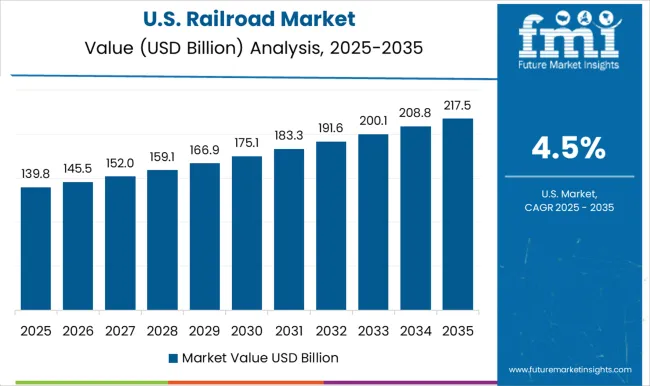
The United States is showing a CAGR of 5.5%, just below the global rate of 5.6%. Rail freight dominates market growth, particularly for intermodal and bulk commodity transport. Investments in track upgrades, signaling systems, and energy-efficient locomotives are increasing operational efficiency. Modernization programs include automated monitoring, predictive maintenance, and positive train control systems.
Regional hubs in Texas, California, and Illinois drive both freight and passenger improvements. Collaboration with technology providers supports implementation of smart rail systems to enhance safety, reduce delays, and lower operational costs.
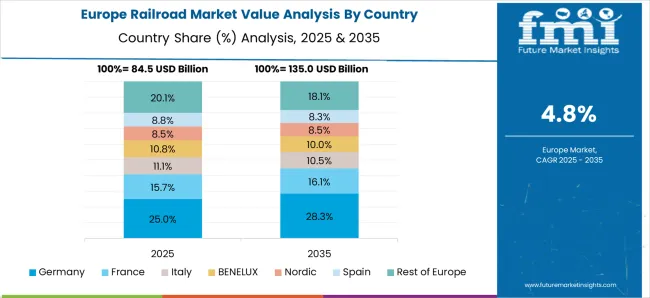
Germany is progressing at a CAGR of 4.8%, below the global 5.6%. The market benefits from investments in high-speed rail, freight corridors, and modernized regional networks. Electric locomotives and energy-efficient rolling stock are being adopted to improve sustainability and reduce operating costs. Advanced signaling and automated control systems support safety and operational efficiency. Key development projects in Berlin, Hamburg, and Munich focus on both passenger comfort and cargo logistics. Germany is also exporting rail technology and components to international markets.
The United Kingdom is expanding at a CAGR of 4.8%, below the global benchmark of 5.6%. Growth is focused on passenger rail modernization, electrification, and track upgrades. Investments include advanced signaling systems, predictive maintenance, and improved station facilities. The government supports high-speed rail and urban commuter network enhancements. Regional projects in London, Manchester, and Birmingham aim to increase capacity, reduce delays, and improve safety. Freight rail improvements are also ongoing, targeting better logistics and intermodal connectivity.
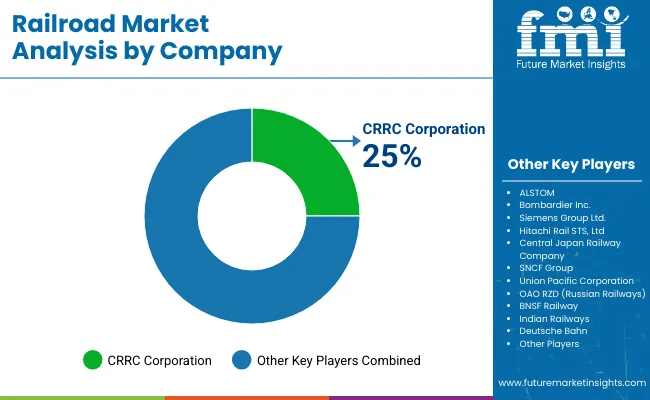
The market is shaped by established operators and emerging manufacturers, each focusing on strategies to enhance operational efficiency and expand market presence. Central Japan Railway Company invests in high-speed rail development and regularly upgrades rolling stock to maintain reliability and safety standards. SNCF Group emphasizes modernization of locomotives and freight wagons, along with R&D initiatives for signaling and control systems.
Union Pacific Corporation and BNSF Railway focus on network expansion and improving freight handling capacity, while Indian Railways continues to introduce new routes and upgrade infrastructure to accommodate growing traffic. Deutsche Bahn emphasizes digital monitoring and predictive maintenance to optimize train operations, and CSX Corporation enhances its logistics solutions to improve freight turnaround times.
Manufacturers and suppliers also play a key role in market growth through product launches and partnerships. Siemens Group Ltd. and Hitachi Rail STS develop advanced train control systems and electric locomotives for global clients. Wabtec Corporation and The Greenbrier Companies focus on freight cars and rail components, offering modular designs and custom solutions.
ALSTOM and Bombardier Inc. continue to expand production of high-speed trains and commuter rail solutions, while CRRC Corporation leads in large-scale rolling stock production for both domestic and international markets. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation provides signaling and automation solutions, supporting safe and efficient railway operations. These strategies help companies remain competitive while meeting the evolving demands of the railroad industry.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 330.21 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 569.42 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.6% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for value |
| Rail Types Analyzed (Segment 1) | Freight Rails, Passenger Rails, Other Rails |
| End-User Segments Analyzed (Segment 2) | Mining, Construction, Agriculture, Subway, Others |
| Regions Covered | North America; Latin America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, China, Japan, India, UAE, South Africa, Russia, others |
| Key Players Influencing the Market | Central Japan Railway Company, SNCF Group, Union Pacific Corporation, OAO RZD (Russian Railways), BNSF Railway, Indian Railways, Deutsche Bahn, CSX Corporation, Siemens Group Ltd., Wabtec Corporation, The Greenbrier Companies, Progressive Rail Locomotive, Trinity Industries, ALSTOM, Bombardier Inc., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Hitachi Rail STS, Ltd, CCRC |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by rail type and service segment, demand dynamics across freight, passenger, and urban transit, regional adoption trends across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, innovation in high-speed trains, signaling systems, and smart rail infrastructure, environmental impact of energy efficiency, emerging use cases in automated operations and intermodal logistics |
By Type
By End User
By Region
The global railroad market is estimated to be valued at USD 330.2 billion in 2025.
The market size for the railroad market is projected to reach USD 556.1 billion by 2035.
The railroad market is expected to grow at a 5.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in railroad market are freight rails, passenger rails and other rails.
In terms of end user, mining segment to command 41.7% share in the railroad market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Railroad Ties Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA