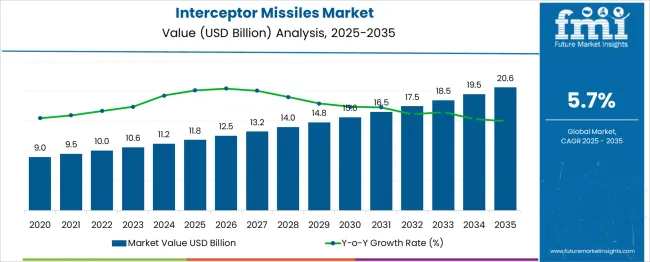
The Interceptor Missiles Market is estimated to be valued at USD 11.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 20.6 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% over the forecast period. This steady climb reflects incremental adoption and modernization initiatives across national defense establishments. Saturation Point Analysis highlights how close the market approaches its growth ceiling within the forecast window by assessing annual incremental gains and relative deceleration patterns.
Between 2025 to 2028, the market expands by USD 2.2 billion, moving from USD 11.8 billion to USD 14.0 billion. This early period accounts for approximately 25.6 % of the total decade-long growth, indicating initial capacity enhancements and procurement ramp-ups. The middle phase, 2028 to 2031, shows moderate expansion of USD 2.5 billion, slightly higher than the early years but spread over three years, pointing toward a more gradual pace.
From 2031 to 2035, the increase is USD 3.1 billion, yet the annual deltas shrink progressively, from USD 1.0 billion in 2031–2032 to only USD 1.1 billion in the final three years combined. This tapering rate reveals signs of growth plateauing, suggesting that most high-priority acquisition goals may be met by 2033. The narrowing annual increases underscore an approaching saturation point, where new demand begins to match or trail fleet renewal rates.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Interceptor Missiles Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 11.8 billion |
| Interceptor Missiles Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 20.6 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.7% |
The interceptor missiles market is experiencing significant advancement, driven by growing geopolitical tensions, rapid modernization of defense capabilities, and the global prioritization of multi-layered air defense systems. With increasing investments in both homeland and strategic defense, nations are shifting toward integrated missile defense networks that can intercept various airborne threats at different altitudes and speeds.
Technological convergence involving radar tracking, propulsion systems, and precision guidance has enabled greater interception accuracy and reaction times. Government-backed initiatives, defense pacts, and multilateral cooperation in missile development have further encouraged cross-border R&D partnerships and system upgrades.
The market outlook remains robust, supported by new threat profiles, such as hypersonic and maneuverable reentry vehicles, prompting expansion of interceptor capabilities across multiple defense tiers.
The interceptor missiles market is segmented by type, range, threat type, component, and geographic regions. The interceptor missiles market is divided into Surface-to-air and Water-to-air. In terms of range, the interceptor missiles market is classified into medium-range, short-range, and long-range. Based on threat type, the interceptor missiles market is segmented into Supersonic missiles, Hypersonic missiles, and subsonic missiles.
The interceptor missiles market is segmented into Guidance systems, Propulsion systems, Sensors, and Inertial navigation systems (INS). Regionally, the interceptor missiles industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
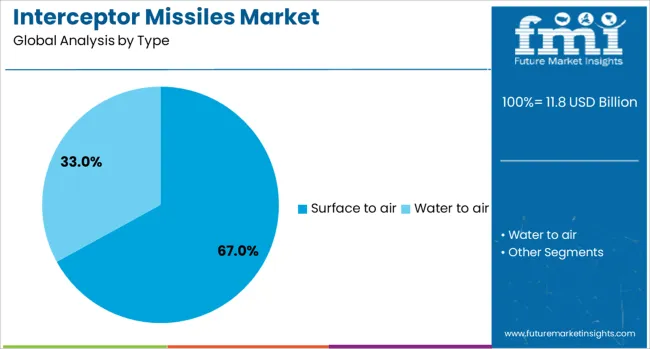
Surface to air interceptor systems are projected to hold 67.0% of the total revenue in 2025, making them the leading type in the market. Their dominance is being driven by their essential role in national air defense grids, capable of neutralizing incoming threats such as ballistic missiles, UAVs, and hostile aircraft.
These systems are preferred due to their mobility, deployment versatility, and compatibility with land-based radar and command units. Their ability to integrate into both static and mobile defense environments makes them ideal for a variety of operational scenarios.
Government defense ministries and allied forces are increasingly favoring surface to air solutions due to cost-effectiveness, deployment speed, and layered defense coordination, solidifying their market leadership across both emerging and established defense economies.
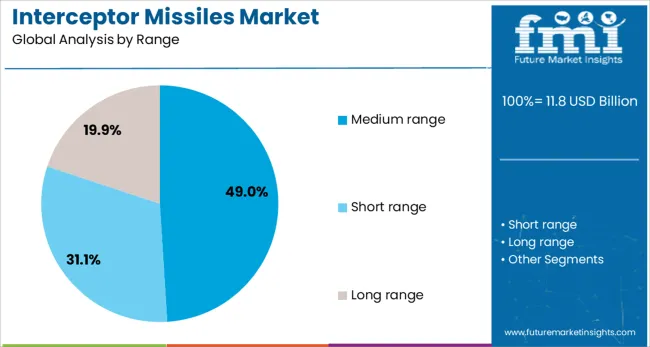
Medium range interceptor missiles are expected to contribute 49.0% of total market revenue by 2025, positioning them as the leading range segment. This prominence is being supported by the operational need to counter threats during their mid-course phase, particularly within the atmosphere but beyond short-range thresholds.
Medium range interceptors offer an optimal balance of engagement altitude, interception timing, and cost, making them integral to defense doctrines that prioritize flexible, multi-tier missile defense systems. Their deployment enables rapid response across strategic installations, border zones, and critical infrastructure.
Increasing procurement of scalable defense platforms and mobile missile systems is enhancing the adoption of medium range interceptors, especially in response to evolving air and missile strike capabilities from near-peer adversaries.
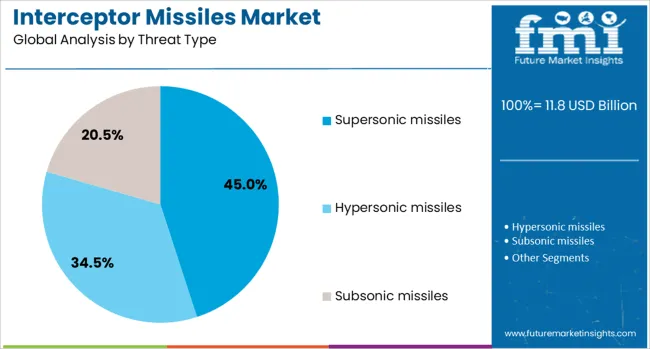
Supersonic missiles are forecast to drive 45.0% of the total market revenue in 2025, making them the most targeted threat type in the interceptor missile landscape. Their speed, combined with low-altitude penetration tactics, has made them one of the most challenging threats for national defense agencies.
The increasing development and deployment of cruise and anti-ship missiles traveling at supersonic velocities have necessitated the upgrade and adaptation of interceptor systems that offer rapid detection, high-G maneuverability, and quick launch capabilities. Nations are intensifying research into propulsion and sensor fusion to neutralize such fast-moving threats.
As strategic deterrence strategies expand to address next-generation offensive capabilities, the focus on intercepting supersonic threats is expected to accelerate innovation and funding in this critical segment.
The interceptor missiles market has evolved in response to rising threats from ballistic, cruise, and hypersonic weapons systems. Nations have prioritized layered missile defense architectures where interceptor missiles function as core kinetic kill components. These systems have been integrated into both land-based and naval-based platforms, providing responsive, scalable, and autonomous defensive capabilities. Increasing missile proliferation and modernization of offensive arsenals have intensified investment in precision-guided interceptors with extended range and improved hit-to-kill accuracy. Development efforts have concentrated on dual-use platforms that can counter diverse threats across high altitudes, short-range theater, and terminal phases.
Interceptor missile systems have undergone major upgrades as threat complexity has increased, particularly from maneuverable reentry vehicles and multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) warheads. Missile defense planners have emphasized faster interceptors, capable seekers, and real-time guidance systems to neutralize advanced threats before impact. Radars with high-resolution tracking and integrated fire-control systems have been coupled with missiles possessing dual-pulse solid propulsion for enhanced agility and terminal maneuvering. Technologies supporting midcourse and boost-phase intercepts have been explored for broader coverage. Defense agencies have also developed kill-vehicle payloads with enhanced discrimination and in-flight correction capabilities. This trend has resulted in interceptor families with modular designs suitable for integration into national missile defense networks or regional security alliances.
Interceptor missiles have formed key elements of multi-layered missile defense systems combining early warning sensors, command and control architecture, and integrated launcher arrays. Deployment has been favored in strategic zones near conflict-prone borders, airbases, and critical infrastructure. Land-based systems such as mobile air defense batteries and fixed launch platforms have enabled scalable interception capabilities at tactical and strategic levels. Naval destroyers and cruisers have deployed interceptors to provide regional missile defense coverage and protect carrier strike groups. High-altitude interceptors have been configured for exo-atmospheric engagement, while lower-tier interceptors have protected populated and industrial areas. The modular and networked nature of these systems has allowed rapid upgrades and cross-domain operability across joint forces.
Global military modernization efforts have led to increased interceptor missile procurement through direct government programs and joint development partnerships. Many countries have engaged in co-development projects to reduce development cycles, share technology risks, and promote defense self-reliance. Procurement strategies have included both off-the-shelf acquisitions and licensed manufacturing arrangements. Interceptor missile systems have been included in broader integrated air and missile defense (IAMD) frameworks funded through long-term defense budgets. International collaborations have improved system interoperability and facilitated regional security alliances. Several nations have invested in indigenous interceptor variants suited to national threat profiles, leading to diversification in interceptor configurations and increasing export potential for established system developers.
Despite strong demand, the interceptor missile market has faced challenges related to rising development costs, technology integration hurdles, and operational testing requirements. Developing interceptors capable of neutralizing hypersonic and maneuverable threats has required extensive R&D investments and prolonged testing cycles. Sensor fusion, propulsion control, and mid-course tracking algorithms have posed technical difficulties. Operational costs have been heightened by system upgrades, simulator training, and logistics support. Budgetary constraints have delayed full-scale deployments in certain regions. Moreover, evolving countermeasures such as decoys and electronic jamming have necessitated continuous improvements. Defense forces have had to balance the urgency of deployment with cost-effectiveness, making system modularity and upgradeability essential for sustained viability.
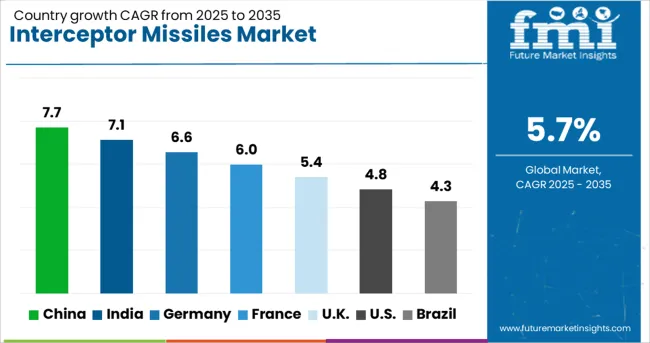
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.7% |
| India | 7.1% |
| Germany | 6.6% |
| France | 6.0% |
| UK | 5.4% |
| USA | 4.8% |
| Brazil | 4.3% |
The interceptor missiles market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2025 to 2035, driven by heightened geopolitical tensions and strategic air defense initiatives. China is anticipated to lead with a projected CAGR of 7.7%, reflecting its aggressive missile defense modernization programs and substantial indigenous manufacturing. India, following at 7.1%, is scaling investments in both ballistic and cruise missile interception capabilities. Germany, with a forecast CAGR of 6.6%, is enhancing its integrated defense frameworks under multilateral European agreements. The UK, expected to grow at 5.4%, focuses on upgrades of naval and land-based interceptor platforms. The USA, while growing at 4.8%, remains a key exporter and innovator in multi-layered defense systems. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China is projected to record a CAGR of 7.7 % between 2025 and 2035 in the interceptor missiles market, backed by consistent defense modernization efforts and vertical integration across domestic aerospace complexes. The expansion of national ballistic missile defense systems has accelerated indigenous development of midcourse and terminal interceptors. Entities such as CASIC and Norinco have focused on dual-role interceptor systems for layered deterrence. Increased investments in mobile launch platforms and phased-array radar integration are strengthening short to medium-range response capabilities. Cooperative trials with hypersonic tracking platforms have further reinforced precision targeting in the lower atmosphere.
India is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.1 %, with a focus on dual-layer air defense networks and upgraded interceptor capabilities. DRDO-led programs such as the PAD and AAD systems have entered iterative phases to enhance interception reliability. Indigenous production has ramped up for long-range precision missiles capable of neutralizing threats in both exo and endo-atmospheric environments. Cross-service testing involving land-based and naval interceptor systems has highlighted the push for operational flexibility. Collaboration between defense PSUs and private suppliers is enhancing system digitization and response coordination.
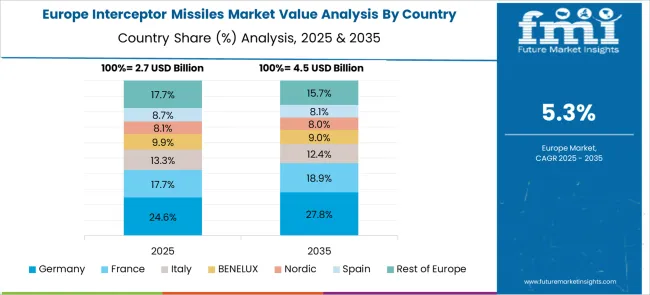
Germany is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.6 %, driven by enhanced NATO alignment and efforts to expand integrated aerial defense infrastructure. German defense authorities have reinforced procurement of next-generation interceptor platforms, particularly for theatre-level protection. The TLVS program remains a focal point for medium-range interception in coordination with MEADS development. Investment into radar coordination systems and multi-sensor fusion has enabled early target acquisition in simulated scenarios. Industrial partnerships have supported design upgrades in kinetic kill vehicles to improve probability of hit across varied altitudes.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to witness a CAGR of 5.4 %, with investments focusing on agile interception of missile threats within high-risk corridors. The development of kinetic and directed energy-based interceptors has gained institutional backing. Defense initiatives under the Land Ceptor and Sky Sabre programs are evolving to include faster response times and higher seeker accuracy. Procurement of naval-based missile interceptors has increased under maritime threat mitigation mandates. Private sector collaboration with MOD has accelerated system testing under simulated swarm threat conditions.
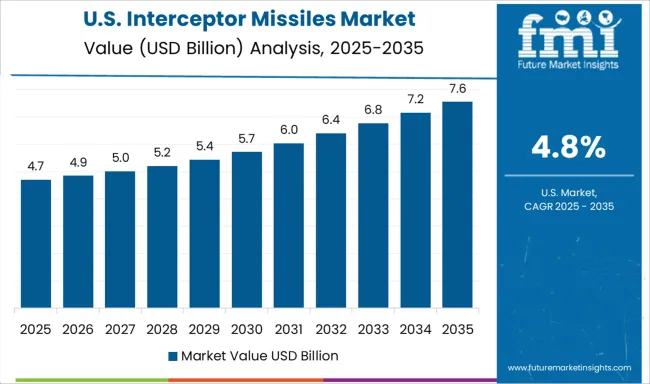
The United States is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8 %, supported by layered defense strategies and emphasis on next-generation kill vehicle development. The USA Missile Defense Agency continues to expand the Ground-based Midcourse Defense and Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense programs. Interceptor upgrades have centered on expanded maneuverability and enhanced kill vehicle agility. Private contractors including Raytheon and Lockheed Martin have invested in AI-enhanced guidance systems to improve threat discrimination. Testing has increasingly involved multiple incoming threat scenarios to validate system resilience.
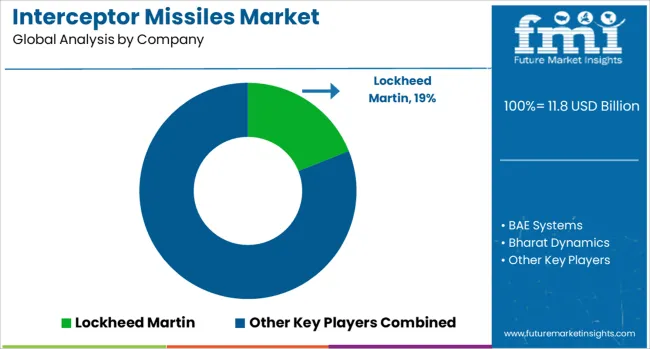
The market comprises global defense contractors and specialized state-backed manufacturers serving national missile defense programs and multi-layered air defense architectures. Lockheed Martin and Raytheon Technologies dominate the landscape with extensive interceptor portfolios such as PAC-3 and SM-series systems deployed in strategic defense across NATO-aligned countries. Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Israel Aerospace Industries provide battle-tested systems like Iron Dome and Arrow, integrated with multi-tier defense networks in high-threat regions.
Northrop Grumman and General Dynamics support interceptor production through propulsion and guidance subsystems, while MBDA offers joint European missile defense solutions tailored for interoperability. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries leads Japan’s missile shield contributions with co-developed platforms, and Hanwha spearheads South Korea’s indigenous advancements.
China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation supplies interceptor platforms to the PLA with a focus on strategic deterrence, while Bharat Dynamics delivers systems for India’s domestic missile defense strategy. BAE Systems, L3Harris, Denel Dynamics, and Roketsan address varied tactical and medium-range threats with modular, scalable interceptors suitable for both naval and ground-based deployments.
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace supports Nordic and NATO interoperability via advanced sensor-fused missile integration. Rising threats from hypersonic glide vehicles and evolving aerial attack capabilities are driving interceptor innovation in kill vehicle precision, sensor fusion, and multi-domain response integration. The market’s direction increasingly favors networked architectures that couple radar tracking with real-time fire control, creating new demand for agile, software-driven interceptor designs.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 11.8 Billion |
| Type | Surface to air and Water to air |
| Range | Medium range, Short range, and Long range |
| Threat Type | Supersonic missiles, Hypersonic missiles, and Subsonic missiles |
| Component | Guidance systems, Propulsion systems, Sensors, and Inertial navigation systems (INS) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Lockheed Martin, BAE Systems, Bharat Dynamics, China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation, Denel Dynamics, General Dynamics, Hanwha, Israel Aerospace Industries, Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace, L3Harris, MBDA, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Northrop Grumman, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems, Raytheon Technologies, and Roketsan |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by missile type and threat range, demand dynamics across homeland defense, naval warfare, and battlefield protection, regional trends in deployment across North America, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East, innovation in hypersonic interception, kinetic kill vehicles, and dual-mode guidance systems, environmental impact of missile testing, material waste, and propulsion emissions, and emerging use cases in satellite defense, mobile air defense platforms, and multi-layered missile shield architectures. |
The global interceptor missiles market is estimated to be valued at USD 11.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the interceptor missiles market is projected to reach USD 20.6 billion by 2035.
The interceptor missiles market is expected to grow at a 5.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in interceptor missiles market are surface to air and water to air.
In terms of range, medium range segment to command 49.0% share in the interceptor missiles market in 2025.
Explore Similar Insights

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA