About The Report
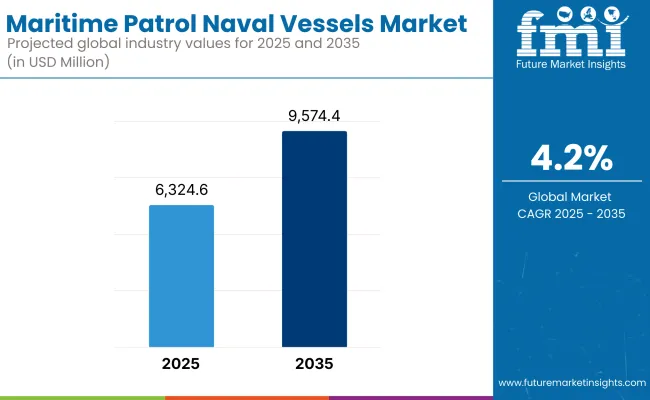
Estimated at USD 6,324.6 million in 2025, the maritime patrol naval vessels market is set to grow impressively with a value projection of USD 9,574.4 million by 2035, at an increase of a 4.25% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period. The increased global focus on maritime security, anti-piracy operations, coastal surveillance, and the complexity of naval missions in contested and strategic waters contributes to significant development.
At the macro level, the various catalysts drive demand for maritime patrolling naval vessels. The first and foremost of these catalysts is increased maritime territorial disputes, such as in the South China Sea, the Arctic region, and even the Eastern Mediterranean. These governments pursue strengthening their naval capabilities. Second, increasing defense budgets, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region and the Middle East, trigger new investments from governments for the acquisition of next-generation patrol vessels capable of multi-mission operations.
Another growth driver is technology. Typical characteristics of today's patrol vessels include modular mission systems, stealth designs, longer endurance, and integrated unmanned vehicle capabilities (UAVs, USVs, and UUVs). Those investments will allow navies to better respond to the ever-evolving types of threats, both from coastal perspectives and open seas. Vessel operation automation and digitization also decrease crew requirements while improving operational efficiency and intelligence sharing.
Another major development is increasing local manufacturing and self-reliance in defense, as countries have started promoting indigenous naval shipbuilding programs to reduce dependency on foreign suppliers. Hence, impetus is being created for the local shipbuilding industry, but the interest of the global defense contractor in co-development or technology transfer with regional partners is also being elevated.
North America and Europe are reportedly continuing to dominate, given mature naval industries and continuous fleet modernization programs. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a high-growth industry powered by the rapid naval expansion efforts of countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan. Africa and Latin America are growing smaller markets, but they are now also investing in patrol vessels for maritime law enforcement and the protection of vital offshore assets.
The industry has great potential for healthy growth within the next decade. The intermingling of geopolitical pressures, advancements in technology, and enlarged defense budgets will continue to govern the procurement strategies and development priorities of navies across the globe. Industry stakeholders that position themselves with an investment strategy toward multi-role capabilities, surveillance systems, and low-cost solutions will ensure themselves with a greater strategic advantage in this evolving maritime defense landscape.
Market Matrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 6,324.6 million |
| Market Value (2035F) | USD 9,574.4 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.25% |
There have been increasing threats to maritime security, and hence, the need for the protection of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and naval modernization projects has increased. Such vessels play an important role in performing anti-piracy, coastal defense, search and rescue, and intelligence missions.
Shipbuilders are prioritizing a red/amber-green process wherein combat endurance, modularity, and affordability become priority metrics, with the aim being to produce vessels that maintain an acceptable balance between performance criteria, construction timelines, and cost parameters. The defense contractors responsible for integrating sophisticated weapons, sensors, and communication systems are paying attention to sensor technology, cybersecurity, and fleet alignment so that new vessels will be designed to align with future needs and network-centric warfare protocols.
Government agencies and other defense authorities, being the end buyers and regulators, tend to weigh their decisions on strategic readiness, interoperability, and affordability. The procurement complaints have appeased peculiarities like international tensions, regional balance of power, and national defense modernization roadmaps. The technology providers for sonar, radar, satellite systems, etc., work toward Red customization (mission-tailored), surveillance enhancement, and cyber-secure integrations with requirements across coastal and deep-sea operations.

The industry is being stimulated by increased investments from NATO countries, defense expansion into the Indo-Pacific, and the requirement for multi-role vessels with better offensive and humanitarian capabilities. As global maritime security becomes increasingly complicated and data-driven, ships need to be incorporated as floating command centers, bringing in advanced technology while being able to operate in disparate environments.
Between 2020 and 2024, the industry was driven by growing international tensions, heightened interest in maritime border protection, and fleet renewal programs. The United States, China, and India emphasized the acquisition of multi-role warships with sensors, onboard radar, and anti-submarine warfare capabilities to maintain maritime dominance and meet the new threats.
The operation of human-crewed vessels incorporating advanced communication and monitoring devices became the norm during this period. However, the COVID-19 pandemic interfered with the supply chain, as well as defense outlays, leading to temporary production and delivery interference.
Between 2025 and 2035, the sector will see a revolutionary technological transformation. AI-driven autonomous naval patrol boats, unmanned system integration, and modularity-based design architectures will dominate the future.
Defense agencies are focusing on cost-effective, remotely operated systems with lower personnel risk and improved patrol range and mission flexibility. Increased investments in AI, radar imagery, and submersible drones will further enable real-time threat alerts. As ever more contested strategic sea lanes are emerging, particularly in the Indo-Pacific and Arctic, next-generation ships with stealth, long endurance, and autonomous surveillance will be a sine qua non-asset for modern naval fleets.
A Comparative Market Shift Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Naval forces invested in multi-role, human-crewed patrol vessels with radar, sonar, and surveillance equipment. | Future fleets will consist of hybrid arrangements with autonomous and optionally crewed ships for long mission duration. |
| Ships that were integrated with GPS, thermal imaging, and communications for maritime security operations. | Next-generation AI, edge computing, and real-time data analysis will be integrated for autonomous operation and threat detection. |
| Patrol operations were performed with the complete onboard crew, augmented by satellite communication and air cover. | Autonomous patrol missions will be the order of the day, with a minimal crew operated remotely and with real-time data transmission. |
| Upgrade of legacy fleets with modular weapon systems and better detection systems received priority. | R&D spending in unmanned surface craft and AI-assisted decision-making systems will find increased allocations in budgets. |
| Traditional manual threat detection and slow response times were universal constraints. | Artificial intelligence vessels will provide predictive threat response and automated interception of unauthorized intrusions. |
| The USA , China, and European nations directed sea-based procurement to keep vital sea lanes under their command. | Indo-Pacific countries and Arctic-fringing nations will increase naval expansion to handle rising territorial conflicts. |
The industry faces numerous and complex risks interlinked by considerations of geopolitical instability, technological evolution, and stringent procurement standards. One of the primary risks includes budget uncertainties and shifts in political winds-the acquisition of naval vessels calls for a long-term capital commitment. Still, new political administrations or changed defense policies or economic considerations may postpone or cancel procurement projects, especially in developing or financially constrained nations.
Next, the obsolescence of technology poses another major risk. As naval warfare becomes more dependent on digital advances, vessels ought to be outfitted with high-tech sensor arrays, communication systems, and cyber-protection protocols. Rapid technological developments may, however, supersede production cycles, resulting in systems that are obsolete by the time of their intended deployment. Such scenarios present an associated strategic and financial risk to shipbuilders and defense contractors.
A growing threat in this area is cybersecurity: modern patrol vessels are heavily networked and operate in joint forces environments. Manipulation of vulnerabilities in communication or navigation systems can threaten the country's national security. Therefore, constant updates, a specialist workforce, and defense-grade layers of security all coalesce to add to the complexity and higher cost of a given project.
There are possible supply chain disruptions of critical components such as propulsion systems, advanced radar, and weapon modules. Global conflicts, trade limitations, or shortages in rare materials can all combine to delay construction and increase costs. Interoperability issues, especially in multinational environments, also pose risks to joint operations requiring seamless interaction between platforms from different nations.
From the operational point of view, there are risks relating to the underestimation of lifecycle costs encompassing maintenance, crew training, and system upgrades. Failure to account for such considerations at the tender stage may lead to cost escalations and low fleet readiness in the long run. Lastly, regulatory and export restrictions on international collaborative efforts will aggravate the limitation of access to vital technology, especially regarding dual-use or high-tech systems.
The government demand, maritime tensions, and modernization programs make the industry robust. Stakeholders who focus on adaptable designs, robust cybersecurity, and agile supply strategies are better able to reduce the risks and provide long-term returns.
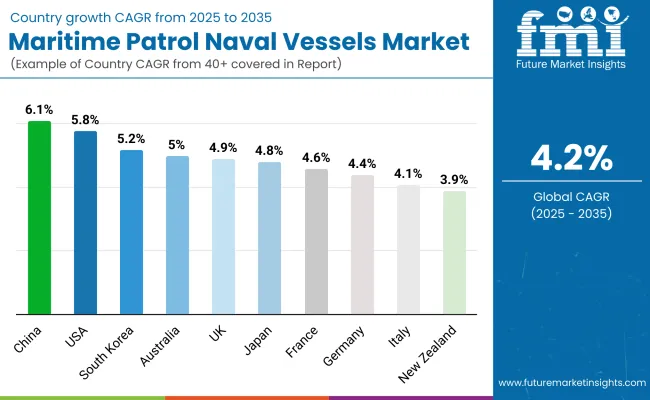
| Countries | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
| The USA | 5.8% |
| UK | 4.9% |
| France | 4.6% |
| Germany | 4.4% |
| Italy | 4.1% |
| South Korea | 5.2% |
| Japan | 4.8% |
| China | 6.1% |
| Australia | 5.0% |
| New Zealand | 3.9% |
The USA is anticipated to witness a robust CAGR of 5.8% from 2025 to 2035. Growth is primarily driven by ongoing investment to equip naval fleets with future-proof surveillance and reconnaissance features. The primary investment programs for the USA Navy are multi-role maritime patrol vessels equipped with advanced sensors, combat systems, and UAV interoperability. Strategic objectives also support this modernization urge to maintain naval supremacy in every theater of the globe, particularly the Indo-Pacific.
Principal manufacturers such as Huntington Ingalls Industries and Lockheed Martin are central to industry momentum, with a significant contribution through technological innovation and advanced vessel construction. Increasing demand for additional coastal surveillance, counter-piracy, and anti-submarine warfare capabilities is boosting acquisition budgets. Emphasis on sustainable propulsion technology and artificial intelligence-based situational awareness systems is also shaping next-generation naval patrol platforms across USA maritime forces.
The UK is anticipated to post a CAGR of 4.9% from 2025 to 2035. Growth is being stimulated by the Royal Navy's strategic initiatives to enhance maritime domain awareness and strengthen homeland defense capabilities. Growing defense budgets for advanced patrol craft and supporting systems are being fueled by an increased focus on deterring regional threats and protecting critical maritime infrastructure.
Companies such as BAE Systems and Rolls-Royce Marine are also important in supplying technologically advanced patrol ships with increased endurance, mission payloads that are modular, and enhanced radar systems. Interoperability with NATO's collective security operations also enhances procurement plans. Ships that have hybrid drive and stealth qualities are in the highest demand and suitable for diverse missions, ranging from trafficking to exclusive economic zone (EEZ) administration.
France is anticipated to develop at a CAGR of 4.6% during the period from 2025 to 2035. Growth is being influenced by French Navy-led modernization programs to support blue-water operational capabilities and maritime surveillance missions. The increasing need to secure sea approaches and overseas territories is fueling investment in manned and unmanned patrol solutions.
Naval Group and Thales Group remain at the center of French market activity, equipping next-generation ships with onboard electronic warfare systems and advanced sonars. The focus is shifting towards multi-mission boats, allowing for easy deployment in anti-smuggling, humanitarian, and reconnaissance operations. A significant portion of the industry is fueled by strategic alliances with European Union naval programs and shared platform development programs.
Germany will record a CAGR of 4.4% during the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. Growth in demand is fueled by the Bundeswehr's modernization strategy to develop coastal defense and intelligence surveillance capacities within the North and Baltic Seas. National priority on defense readiness and alliance obligations within NATO underpins the strategic importance of maritime patrol assets.
ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems and Atlas Elektronik are leading drivers in the development of high-end patrol platforms with low acoustic signatures and high communications interoperability. Ships of the future are presently being designed with a much stronger focus on environmental monitoring, coastal patrol, and maritime interdiction missions. Germany is supported by research on AI-based command systems and high maritime situational awareness technology.
Italy will register a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2035. It grows due to the Italian Navy's plans to procure new assets for fleet replenishment and operating flexibility within the Mediterranean Sea. Demand stems from the necessity to enhance border control, enforce anti-smuggling measures, and respond to disaster readiness.
Fincantieri and Leonardo dominate the industry and offer platforms that are characterized by modularity, extended range, and multi-role combat systems. The trend in purchasing is towards highly maneuverable ships with advanced surveillance integration for the purpose of supporting national defense as well as international peacekeeping operations. Enhanced interoperability with EU sea operations and the funding of dual-use technologies are the critical drivers of the expansion of the Italian industry.
South Korea shall witness a growth rate of CAGR 5.2% for the 2025 to 2035 forecast period. Regional maritime security in the nation, particularly competition on the East Sea, is generating demand for efficient and technically superior patrol capability. Strategic importance is placed on defending maritime sovereignty and sustaining capacities for quick reaction.
Hyundai Heavy Industries and Hanwha Ocean are key leaders in the export of high-speed radar-equipped ships, which are equipped for littoral warfare and the detection of submarines. Focus on integrating AI-powered navigation, autonomous platforms, and electronic warfare defense is increasing levels of domestic development. South Korea has a drive for defense exports and is expanding cooperation with ASEAN nations.
Japan is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% over the forecast period. Rising security tensions in the East China Sea and the broader Indo-Pacific region are compelling the strategic need to invest in long-range patrol vessels and multi-domain surveillance systems. The Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force is prioritizing readiness and maritime situational awareness enhancement.
Key players such as Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries are leaders in the advancement and engineering of light, stealth-optimized patrol boats. Priority is on improved sensor integration, autonomous function, and inter-agency interoperability. Japan's shifting defense strategies and commitments to regional stability in the framework of international maritime security coalitions also influence the market.
China will be the leading player, with a projected CAGR of 6.1% for 2025 to 2035. Market growth is driven by enormous investment in the maritime projection of power, especially in the South China Sea disputed waters. Building the highly armed, long-endurance patrol vessels is central to the People's Liberation Army Navy's modernization.
Leadership contenders such as China State Shipbuilding Corporation and China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation are taking the lead, providing ships with integrated electronic warfare systems, vertical launching capability, and unmanned maritime systems. Coastal defense, anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) capabilities, and surveillance infrastructure take center stage in strategic procurement. Export programs to Africa and Southeast Asia remain supportive of the robust market direction.
Australia will expand with a CAGR of 5.0% from 2025 to 2035. Reorienting towards Indo-Pacific security and sovereign capability development spur demand for wider maritime patrol systems. Sea lane protection, anti-pirate fishing, and the reinforcement of northern maritime defenses are themes of national campaigns.
Austal and ASC Shipbuilding are central to the delivery of next-generation ships that are oriented to endurance, low radar detectability, and multi-role mission adaptability. Government initiatives such as the current naval ship construction plan and coastal maritime security treaties are facilitating regular investment. The integration of AI-generated threat detection and digital situational awareness technology is shaping the upcoming vessel design and operations strategy to a greater degree.
New Zealand is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.9% through the forecast period. Demand is driven by commitments to defend exclusive economic zones, promote regional stability, and participate in humanitarian missions in the South Pacific. Investment is in multipurpose ships for long-range patrolling, surveillance, and disaster relief. Key leaders are Babcock, New Zealand, and shipbuilding alliances with Australia.
Procurement focus is placed on high-endurance vessels, multi-mission bays, and increased environmental monitoring. Hybrid propulsion technology take-up and increased investment in maritime security infrastructure are the top national industry trends. Interoperability with allies and emphasis on sustainable operations are the pillars of New Zealand's naval defense policy.
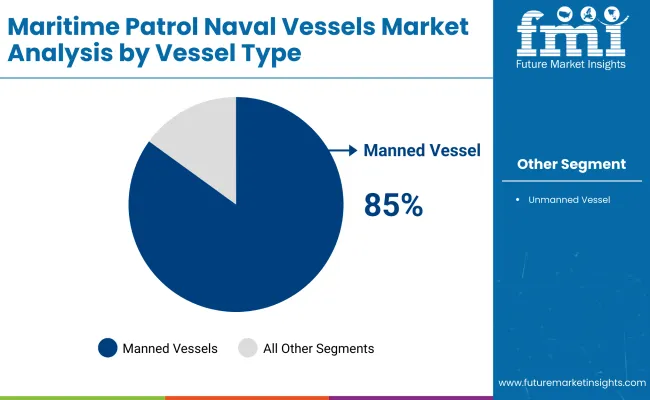
By vessel type, manned vessels are expected to account for nearly 85% of the estimated total revenue share, and uncrewed vessels, only 15%. This illustrates the relevance of an established manned asset in conducting complicated naval operations despite the steady advancement of autonomous technology progressing unmanned platforms.
Manned maritime patrol vessels remain the backbone of naval surveillance, anti-submarine warfare (ASW), and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) enforcement operations. These vessels, ranging from offshore patrol vessels (OPVs) and corvettes to frigates, are favored for operational flexibility, onboard crew intelligence, and integrated sensor systems.
The modernization of the USA Navy, Indian Navy, and Royal Navy has occurred to a great extent. The fleets are equipped with hybrid propulsion systems, complex radar arrays, and modular mission packages. Among the major navies, BAE Systems (River-class OPVs), Damen Shipyards (Stan Patrol series), and Naval Group (Gowind-class) are contesting for proven designs that provide a balance between endurance, speed, and surveillance capabilities.
On the other hand, uncrewed vessels-also referred to as Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs)-are gaining a share, projected at 15% in 2025. These vessels are increasingly used for mine countermeasures, persistent ISR (intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance), and coastal monitoring missions where risks to human life must be minimized.
There are many naval programs, such as the USA Navy's Mid and Large USV initiatives and the Royal Navy's Project VIGILUS, that are focused on developing and actively deploying unmanned platforms within the maritime domain. Key providers in this category are L3Harris Technologies, Teledyne FLIR, and Elbit Systems, which offer the required autonomous vessel systems with AI-enabling navigation, satellite communications, and remote command functionalities.
While manned vessels will continue to occupy maritime patrols in the near term, the increasing need for persistent surveillance and cost-effective patrolling is expected within a short while to boost its acceptance around the globe.
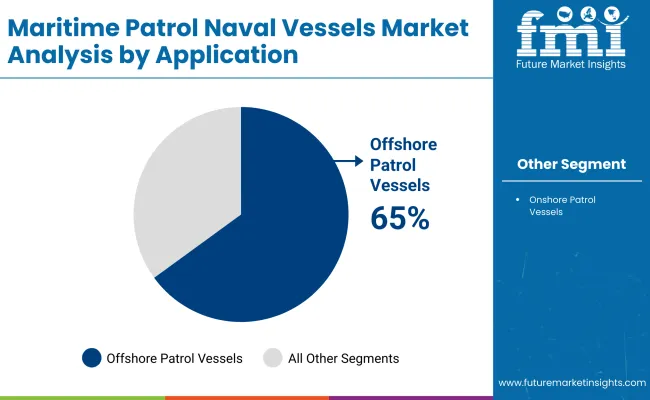
By application, the offshore patrol vessels (OPVs) were the leading segment in 2025, and held approximately 65% of the total share, while onshore patrol vessels claimed the remaining 35%.
Offshore Patrol Vessel is most valued for its long-range endurance, seakeeping, and versatility against piracy and smuggling, search and rescue, and environmental monitoring. Countries like the United States, India, Brazil, and Australia are prioritizing OPVs in their naval inventory due mainly to their lower operational costs compared to destroyers and frigates.
Some OPVs are the USA Coast Guard's Sentinel-class, India's ICGS Vikram-class, and Australia's Arafura-class. BAE Systems, Damen Shipyards, and Navantia are manufacturers offering modular OPV platforms with advanced radar, unmanned aerial systems (UAS) launch capabilities, and mission flexibility.
Onshore Patrol Vessels account for 35% of the share and undertake coastal surveillance, law enforcement, port security, and littoral operations Companies. Vessels of this class are generally smaller and more maneuverable, designed primarily for fast operations in shallow or constricted waters.
Countries with long coastlines, such as Japan, Indonesia, and some EU coastal states, prefer these vessels for their national maritime safety jobs. Companies such as Fassmer, Lürssen, and Austal design lightweight, high-speed offshore patrol vessels equipped with integrated command systems and day/night surveillance optics.
A strong performance by both segments indicates that the maritime defense strategy integrates deep-sea presence with agile coastal response to, among other things, illegal fishing, smuggling, and asymmetric naval conflict.
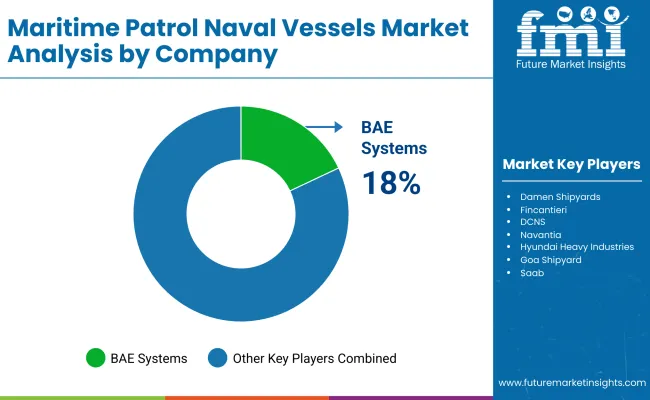
The maritime patrol naval vessels market is constantly changing with advances in technology, perhaps because of naval modernization programs on the geopolitical security aspects. Indeed, prominent shipbuilders like Damen Shipyards, BAE Systems, and Fincantieri have all geared up toward the manufacture of multi-role, stealth-capable and AI-enabled patrol vessels to meet the dynamic demand for coastal defense, surveillance, and law enforcement operations. Furthermore, the key players are incorporating advanced sensor suites, unmanned capabilities, and next-generation communication systems to increase operational efficiency in modular designs and hybrid propulsion systems.
Expansion and establishment of state-of-the-art fleets, strategic alliances, and localization are the components that drive competition. BAE Systems tops the list for multi-mission patrol vessels with integrated command-and-control solutions. Damen Shipyards emphasizes modularity for rapid customization.
Fincantieri features stealth and hybrid propulsion technologies that further increase vessel performance and sustainability. Meanwhile, high-endurance designs are available from Navantia, and DCNS is focused on extended patrol missions, especially coastal surveillance and anti-piracy missions.
Technology innovation is the main game change with autonomous navigation systems in development by Lürssen Werft; AI-driven threat detection for Mitsubishi and Hyundai Heavy Industries advances in composite materials for survivability of ships. Uncrewed surface vehicles and remotely operated defense systems are gaining use among the naval forces for reconnaissance and patrolling missions, thereby enabling more effective and risk-free missions.
However, confluence in the overall setting yields a competitive environment for an enterprise. Again, under long-term contracts, companies serve the navies and coast guards. Goa Shipyard strengthens its presence in emerging industries by providing cost-efficient patrol vessel solutions.
The naval division of Saab combines expertise in radar and electronic warfare systems, thus delivering highly adaptable patrol vessels. These vessels will provide high situational awareness. Multi-domain integration, sustainability initiatives, and innovations in maritime cybersecurity will thematize future growth.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| BAE Systems | 18-22% |
| Damen Shipyards | 15-19% |
| Fincantieri | 12-16% |
| DCNS | 10-14% |
| Navantia | 8-12% |
| Combined Others | 25-35% |
| Company Name | Offerings & Activities |
|---|---|
| BAE Systems | Multi-role patrol vessels with integrated combat management and cybersecurity solutions. |
| Damen Shipyards | Modular patrol vessel designs with flexible mission configurations and rapid deployment capabilities. |
| Fincantieri | Hybrid propulsion patrol vessels with stealth technology and extended mission endurance. |
| DCNS | Advanced surveillance vessels equipped with electronic warfare and anti-submarine capabilities. |
| Navantia | High-endurance patrol ships with autonomous navigation and unmanned systems integration. |
Key Company Insights
BAE Systems (18-22%)
BAE Systems dominates with next-generation naval patrol vessels featuring AI-driven surveillance, integrated cybersecurity, and advanced radar systems for global maritime defense forces.
Damen Shipyards (15-19%)
Damen Shipyards excels in modular vessel construction, enabling rapid customization for coastal defense, anti-piracy, and exclusive economic zone (EEZ) protection.
Fincantieri (12-16%)
Fincantieri leads in hybrid propulsion and stealth-enhanced naval patrol vessels, offering low radar signature and high fuel efficiency for long-range missions.
DCNS (10-14%)
DCNS specializes in integrated naval warfare systems, equipping patrol vessels with electronic warfare, anti-submarine, and long-range detection capabilities.
Navantia (8-12%)
Navantia is at the forefront of autonomous naval solutions, integrating AI-enhanced navigation, unmanned surveillance, and multi-domain connectivity for next-gen patrol fleets.
Other Key Players
The segmentation is into Unmanned Vessel and Manned Vessel.
The segmentation is into Onshore Patrol Vessels and Offshore Patrol Vessels.
The segmentation is into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Russia and Belarus, and Balkan and Baltic Countries.
The industry is expected to be valued at USD 6,324.6 million in 2025.
By 2035, global sales are projected to reach USD 9,574.4 million, driven by increasing investments in naval surveillance and maritime security.
China leads the industry, showing a growth rate of 6.1% amid rising focus on coastal defense and strategic maritime initiatives.
Human-crewed vessels continue to dominate, offering robust capabilities for patrol, reconnaissance, and response operations.
Notable players include BAE Systems, Damen Shipyards, Fincantieri, DCNS, Navantia, Lürssen Werft, Mitsubishi, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Goa Shipyard, and Saab.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Maritime Patrol Aircraft Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Coastal Patrol Military Vessels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Maritime Satellite Communication Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Maritime Cybersecurity Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Naval Destroyers and Submarines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Naval Based Remote Weapons Station Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Naval Artillery System Market
Marine Vessels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Crew boats (Standby Crew Vessels) Market
Emergency Response and Rescue Vessels Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.