The vehicle-to-grid (V2G) market is undergoing rapid evolution, fueled by rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing demand for grid flexibility and energy decentralization. Utility providers and grid operators are integrating V2G technology into their load balancing strategies to manage renewable energy intermittency and enhance grid resilience. Automakers and energy companies have formed strategic alliances to develop bidirectional charging infrastructure, enabling EVs to act as distributed energy resources.
Regulatory developments supporting energy storage integration and grid modernization have further accelerated deployment in key markets. Investor presentations and utility sector press briefings have emphasized the potential of V2G to deliver revenue streams through frequency regulation, demand response, and peak shaving services.
With advancements in bidirectional charging protocols, power electronics, and real-time energy communication systems, the market is expected to grow substantially. Segmental growth is led by battery electric vehicles due to their storage capacity, EVSE as the key interface component, and power management technology for controlling energy flow between vehicles and the grid.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
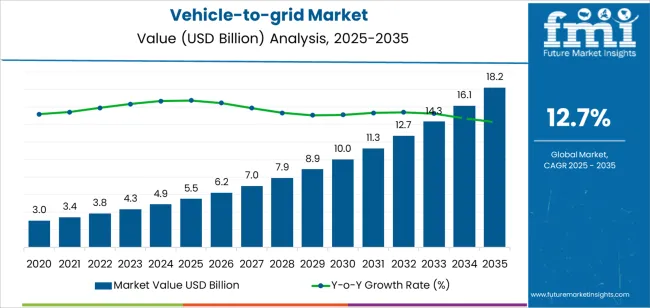
| Vehicle-to-grid Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 5.5 billion |
| Vehicle-to-grid Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 18.2 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 12.7% |
The market is segmented by Vehicle Type, Components, Technology, and Charging Type and region. By Vehicle Type, the market is divided into Battery Electric Vehicles, Plug In Hybrid Electric Vehicles, and Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs). In terms of Components, the market is classified into Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), Smart Meters, Home Energy Management (HEM), and Others. Based on Technology, the market is segmented into Power Management and Software. By Charging Type, the market is divided into Bidirectional Charging and Unidirectional Charging. Regionally, the market is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
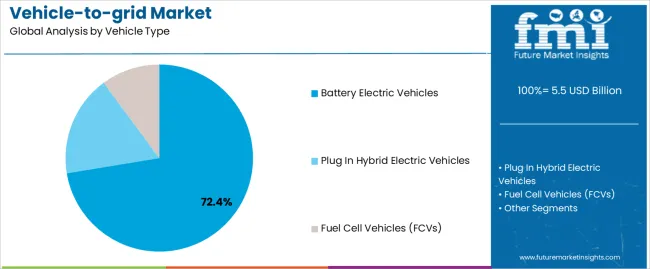
The Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) segment is projected to account for 72.4% of the vehicle-to-grid market revenue in 2025, emerging as the dominant vehicle type. This growth has been propelled by the increasing penetration of BEVs in global automotive markets, supported by strong policy incentives, improved charging infrastructure, and declining battery costs.
BEVs have been preferred for V2G applications due to their larger onboard battery capacities and compatibility with bidirectional charging systems. Automakers have been integrating V2G capabilities directly into BEV models, allowing them to feed energy back into the grid during peak demand periods.
Moreover, energy storage policies and utility-led pilot programs have prioritized BEVs in grid-interactive mobility solutions. The lack of internal combustion components enables BEVs to maximize energy availability and reduce mechanical complexity, further reinforcing their suitability for V2G functionality. As governments and energy providers seek to scale up decentralized energy systems, the BEV segment is expected to remain the backbone of V2G integration.
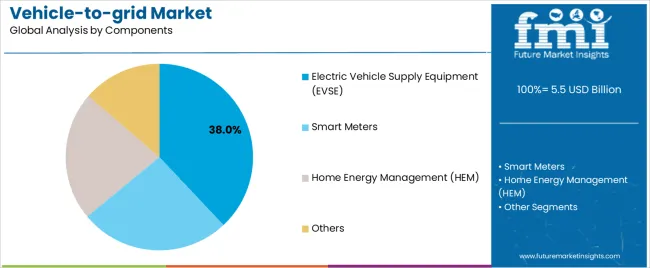
The Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) segment is anticipated to capture 38.0% of the vehicle-to-grid market revenue in 2025, establishing itself as the most critical component. Growth in this segment has been driven by the need for bidirectional charging infrastructure that can facilitate both energy intake and discharge between EVs and the grid.
EVSE systems have been engineered to incorporate grid communication protocols, energy metering capabilities, and safety features to manage bidirectional power flow. Equipment manufacturers have advanced the development of V2G-compatible EVSE units to meet interoperability standards and local utility regulations.
Investment announcements from energy companies and smart grid developers have consistently highlighted the deployment of next-generation EVSE to support residential, commercial, and fleet-based V2G applications. With increasing deployment of public and private charging stations across urban networks, the EVSE segment is expected to remain pivotal in scaling the vehicle-to-grid ecosystem globally.
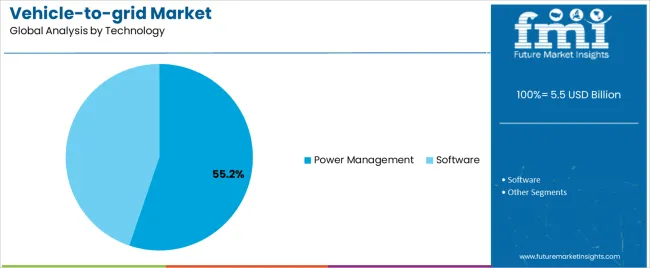
The Power Management segment is expected to contribute 55.2% of the vehicle-to-grid market revenue in 2025, maintaining its lead among technology categories. Growth in this segment has been influenced by the central role of power management systems in optimizing energy distribution between electric vehicles and the grid.
These systems have been deployed to control voltage, monitor frequency, and coordinate real-time communication with grid operators to ensure stable energy transactions. Energy companies and software developers have focused on enhancing the intelligence of power management platforms, integrating AI-driven algorithms for predictive load balancing and peak demand forecasting.
The effectiveness of V2G systems in providing grid support services such as demand response, frequency regulation, and energy arbitrage has been largely dependent on robust power management capabilities. As more EVs are connected to the grid, dynamic power allocation and load synchronization will become essential, ensuring the continued dominance of this segment in the evolving V2G landscape.
Integration of Vehicle-to-grid Systems with Home Energy Management Solutions
V2G systems are increasingly being integrated with smart grid infrastructure, enabling bidirectional energy flow between electric vehicles (EVs) and the grid. This trend allows EVs to serve as distributed energy resources, providing grid support services such as load balancing, peak shaving, and frequency regulation.
Adoption of Vehicle-to-grid Technology in Electric Vehicle (EV) Fleets
The growing adoption of electric vehicles worldwide is driving the expansion of V2G deployments. As EV fleets continue to grow, there is an increasing opportunity to aggregate their battery capacity for grid services, helping utilities manage energy demand and optimize grid operations.
Renewable Energy Integration to Fuel Sales
As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources, V2G systems offer an opportunity to integrate intermittent renewables like solar and wind power into the grid more effectively. EV batteries are set to store excess renewable energy during periods of low demand and discharge it when needed, helping to mitigate variability and ensure grid reliability.
Technical and Operational Challenges tom Hinder Growth
Technical and operational challenges, such as system complexity, reliability, and performance variability, are set to affect the operational effectiveness of V2G systems. Issues such as grid stability, bidirectional power flow management, and real-time control require robust technical solutions and operational protocols to ensure the safe and efficient operation of V2G deployments.
With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) across the country, there is a growing opportunity to leverage EV batteries for grid services and energy storage. The United States government's support for clean energy initiatives, coupled with regulatory incentives and funding programs, further accelerates the development and deployment of V2G infrastructure.
Key players in the automotive, energy, and technology sectors are investing in V2G research, development, and pilot projects to demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of bidirectional power flow between EVs and the grid. Additionally, advancements in smart grid technologies, renewable energy integration, and energy management systems create favorable conditions for the expansion of the V2G market in the United States.
Challenges such as interoperability, regulatory barriers, and consumer acceptance remain significant considerations for widespread V2G adoption. V2G technology is set to revolutionize the United States energy landscape by enhancing grid resilience and accelerating the transition towards a sustainable, decentralized energy future.
The vehicle-to-grid market in China is experiencing rapid growth and development, driven by various factors. With the country being the world's leading market for electric vehicles (EVs), there is immense potential to utilize EV batteries for grid services and energy storage.
The government's strong support for electric mobility and renewable energy initiatives, including subsidies, incentives, and policy directives, creates a conducive environment for V2G deployment. Key automotive, energy, and technology sectors are investing in V2G research and pilot projects to showcase the feasibility and benefits of bidirectional power flow between EVs and the grid.
Additionally, advancements in smart grid infrastructure, energy management systems, and renewable energy integration technologies further propel the growth of the V2G market in China. However, challenges such as grid stability, interoperability, and regulatory frameworks need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of V2G technology in China.
The United Kingdom's is experiencing significant growth and innovation. With the country's ambitious goals to decarbonize its transportation sector and transition to renewable energy, V2G technology plays a crucial role in balancing grid demand and integrating intermittent renewable energy sources.
Leading automakers, energy companies, and technology providers are participating in pilot projects and trials to showcase the feasibility and benefits of bidirectional energy flow between electric vehicles and the grid. The United Kingdom’s energy landscape is set for transformation with V2G technology playing a vital role in achieving a sustainable and resilient future.
Battery electric vehicles (EVs) are playing a pivotal role in the vehicle-to-grid market, offering a two-way energy exchange between vehicles and the grid. In V2G systems, EV batteries can store excess electricity from the grid during periods of low demand and feed it back into the grid when demand is high or during peak hours.
The bidirectional flow of electricity enables EVs to serve as distributed energy resources, providing grid support services such as demand response, frequency regulation, and energy storage. By participating in V2G programs, EV owners can earn revenue or receive incentives for allowing their vehicles to be used as grid assets.
V2G technology not only helps to balance grid demand and supply but also enhances grid stability, reliability, and resilience. Growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the expansion of V2G infrastructure are expected to significantly impact energy management and grid optimization in the future.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) plays a crucial role in promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), which are essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. Several governments offer subsidies, tax credits, and other incentives for both EV buyers and infrastructure developers, making EVSE investments more attractive.
Advances in battery technology have increased the range and efficiency of EVs, making these more appealing to consumers. Developments in EVSE, such as fast and ultra-fast chargers, reduce charging times significantly, addressing one of the main concerns of potential EV buyers. The development and installation of EVSE create jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors, thereby boosting demand.
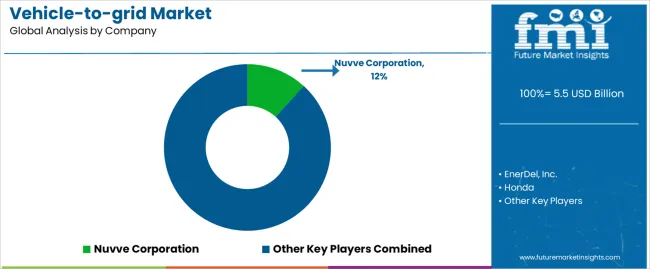
Leading companies are focusing on life cycle assessment and investing in research and development to innovate cost-effective applications for rare earth metals.
Strategic partnerships and collaborations help leading companies to capitalize on collective expertise and resources. AC Propulsion, Inc., Edison International, DENSO CORPORATION, Boulder Electric Vehicle, and Nissan are key players in the vehicle-to-grid industry.
Companies are expanding their presence in regions with high demand for vehicle-to-grid and adopting product diversification to provide europium-based items tailored to specific applications. Key companies are also focusing on environmentally friendly manufacturing and processing practices to meet regulatory requirements. Several leading manufacturers and companies are taking proactive measures to drive growth, foster innovation, and uphold sustainable practices.
Industry Updates
The industry is segmented into battery electric vehicles and plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs), and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs).
Based on components, the industry is segregated into electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), smart meters, and home energy management (HEM).
The industry is segmented into power management and software.
Unidirectional charging and bidirectional charging are two key charging types.
Industry analysis has been carried out in key countries of North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia and Pacific, East Asia, and the Middle East and Africa.
The global vehicle-to-grid market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.5 billion in 2025.
The market size for the vehicle-to-grid market is projected to reach USD 18.2 billion by 2035.
The vehicle-to-grid market is expected to grow at a 12.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in vehicle-to-grid market are battery electric vehicles, plug in hybrid electric vehicles and fuel cell vehicles (fcvs).
In terms of components, electric vehicle supply equipment (evse) segment to command 38.0% share in the vehicle-to-grid market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA