The micropiles market is estimated to be valued at USD 696.0 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 935.3 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.0% over the forecast period. The year-on-year (YoY) growth pattern remains linear and consistent, with annual absolute increments ranging between USD 20 million and USD 27 million. From 2025 to 2027, the market adds USD 42.3 million, with YoY gains maintaining a modest range of 3.0% to 3.1%. This growth aligns with the incremental rise in retrofitting activity across transportation and utility infrastructure, particularly in regions exposed to soil instability or seismic stress. Between 2028 and 2032, YoY additions average USD 25 million annually, as adoption expands in mining slope stabilization, waterfront development, and high-rise foundation support.
The market exhibits strong alignment with geotechnical engineering budgets rather than macroeconomic consumption cycles, which lends it resilience but caps its acceleration potential. In the final three years, from 2033 to 2035, growth maintains a consistent tempo with the addition of USD 53.7 million, suggesting demand is driven by project-specific requirements rather than broader industrial cycles. Emerging construction technologies are not expected to displace micropiles due to their favorable load-bearing profile in constrained environments. Growth, while stable, is bounded by engineering norms and regulatory pace.
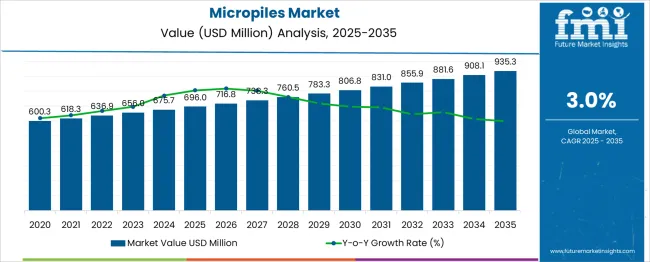
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Micropiles Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 696.0 million |
| Micropiles Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 935.3 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 3.0% |
Micropiles contribute approximately 20% to 25% of the deep foundation solutions market due to their suitability in constrained access and retrofitting projects. In the geotechnical or foundation engineering market, they account for around 10% to 15%, offering flexibility in poor soil conditions. Within the construction materials segment, micropiles represent about 5% to 7%, classified as specialized structural components. The infrastructure and urban construction market accounts for the highest share, close to 30% to 35%, as micropiles are commonly used in bridge support, tunnel reinforcement, and dense city redevelopment. In seismic resilient foundation systems, micropiles contribute 8% to 12%, given their effectiveness in stabilizing structures in earthquake-prone areas. Their high load-bearing capacity and minimal vibration make them a preferred choice in sensitive construction zones. The market is expanding as deep foundation solutions gain popularity for structures in restricted urban sites steep slopes and seismic zones. Micropile applications include foundation underpinning slope stabilization ground improvement and seismic retrofits and they offer high capacity in small diameters with minimal vibration. Contractors and engineering firms focus on customized drilling rigs and advanced grouting techniques to improve load performance. Key service providers expand local operations through joint ventures and regional licensing to serve infrastructure projects railroads and urban transit corridors. Innovation centers on high strength steel casing bonded grout composite materials and real time monitoring systems to ensure quality and safety. Growth is driven by rising infrastructure spending increasing construction in challenging terrains and stringent building codes in Europe North America and Asia Pacific.
The micropiles market is experiencing sustained growth supported by rising demand for foundation reinforcement and ground stabilization solutions in both developed and emerging regions. This growth has been driven by increasing investments in infrastructure projects, particularly in urban redevelopment and transportation networks, as highlighted in construction industry news and corporate announcements.
The current market scenario is characterized by the adoption of advanced drilling technologies and materials that enable faster installation and improved load capacity. Future outlook remains positive as climate-resilient infrastructure and seismic retrofitting projects gain priority, creating opportunities for micropile applications in diverse geotechnical conditions.
Annual reports and investor presentations indicate that greater awareness of cost efficiency, minimal site disruption, and adaptability to restricted spaces is reinforcing demand. The market is also benefiting from innovations in equipment and methods that enhance the sustainability and reliability of micropile systems, ensuring continued adoption across commercial, industrial, and infrastructure sectors globally.
The micropiles market is segmented by type, construction method, load transfer mechanism, application, end-use industry, material, diameter, and geographic regions. The micropiles market is divided by type into Hollow bar micropiles, Cased micropiles, Uncased micropiles, and Composite micropiles. In terms of construction method, the micropile market is classified into Self-drilling, Pre-Drilled and pre-grouted, Post-grouted, and Pressure-grouted. The load transfer mechanism of the micropiles market is segmented into Combination (Friction and End-Bearing), Friction micropiles, and End-bearing micropiles. The micropiles market is segmented into New construction, Underpinning, Seismic retrofitting, Slope stabilization, Earth retention, Foundation repair, and Others.
The micropiles market is segmented by end-use industry into Infrastructure, Commercial buildings, Residential buildings, Industrial structures, Power plants, Oil and gas facilities, Marine structures, and Wind turbines. The micropiles market is segmented by material into Steel, Concrete, Composite (steel and grout), and High-strength alloys. The diameter of the micropiles market is segmented into 150-250 mm, Less than 150 mm, and More than 250 mm. Regionally, the micropiles industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
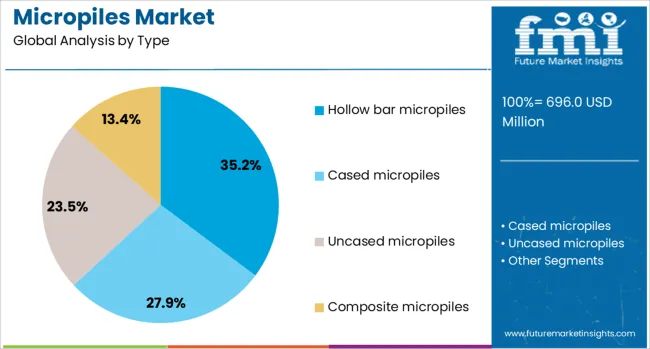
The hollow bar micropile type is expected to hold 35.2% of the micropile market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading type segment. This dominance has been supported by its ability to combine drilling and grouting in a single operation, which significantly improves installation efficiency as reported in engineering journals and technical bulletins.
Hollow bar micropiles have been widely preferred for their suitability in difficult ground conditions, including loose soils and high water tables, where conventional methods are less effective. Their structural integrity and capacity to deliver higher load-bearing performance with minimal disturbance have reinforced their use in confined or challenging project sites.
Investor presentations have indicated that contractors value the reduced labor and time requirements of hollow bar systems, which align with growing cost and schedule optimization goals. These advantages, along with ease of use and reliable performance, have ensured the segment’s prominent position in the market.
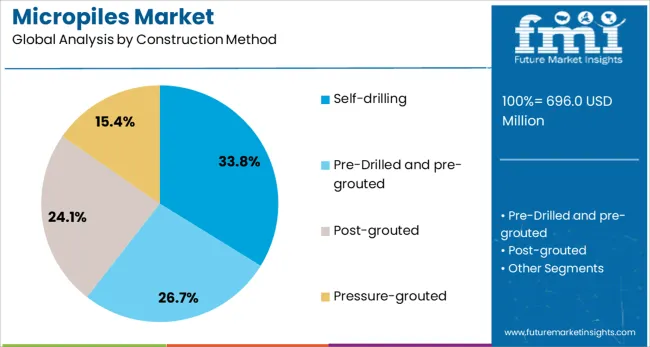
The self drilling construction method is projected to account for 33.8% of the Micropiles market revenue share in 2025, establishing itself as a leading construction method segment. Its prominence has been attributed to the efficiency and precision it offers in foundation work, particularly in urban and environmentally sensitive areas, as highlighted in infrastructure project announcements and technical publications.
Self drilling has been preferred because it allows drilling and grouting in a continuous process without the need for casing, which reduces construction time and lowers costs. The method’s capability to perform reliably in unstable soils or under restricted access conditions has been emphasized in contractor interviews and corporate updates.
Additionally, the minimized risk of hole collapse and reduced environmental impact have been recognized as key factors driving adoption. These benefits have positioned the self drilling method as an optimal solution for a wide range of challenging ground engineering projects.
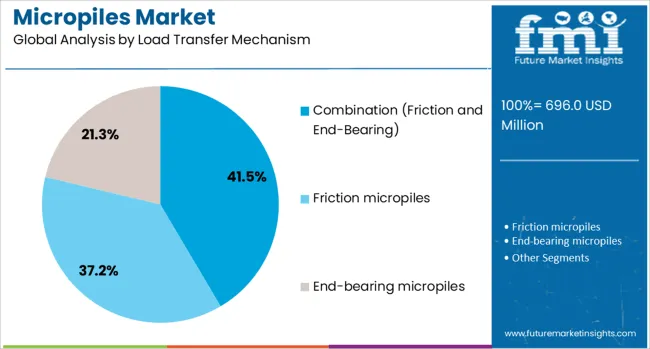
The combination of friction and end bearing load transfer mechanism is anticipated to lead the market with a 41.5% revenue share in 2025. This segment’s leadership has been supported by its superior ability to distribute loads effectively across variable soil and rock strata, as documented in geotechnical engineering publications and corporate case studies.
The combination mechanism has been preferred in complex foundation designs where both end resistance and shaft friction contribute to load-bearing capacity, enhancing overall stability. Technical papers have noted that this approach provides greater flexibility in accommodating diverse site conditions and higher safety margins.
Investor reports have pointed out that the need for reliable foundations in seismic and heavy-load applications has strengthened demand. These factors, coupled with its compatibility with modern installation techniques, have ensured the segment’s sustained growth and widespread use in infrastructure and commercial construction projects.
Deployment of micropile foundations has risen across geotechnical and retrofit applications due to their high load capacity and adaptability in restricted spaces. Over 44 % of newly specified deep foundation jobs on steep or seismic sites used micropiles. Surge in elevator shaft underpinning and seismic retrofit programs contributed 29 % of volume growth. Their installation is being preferred in urban zones with overhead restrictions or existing structures. The technique allows minimal vibration, making it suitable for sensitive archaeological or historical sites.
Micropiles are suited to high-angle slopes, confined sites, and layered soil strata where conventional driven piles are impractical. Their small diameter and drillable installation process allowed 38 % of projects underlined near retaining walls or heritage structures to avoid jacking and disturbance. High-strength tendons and grout infill provided immediate load-bearing capacity in up to 60 % of grouted micropile applications within the same day. Seismic retrofit programs cited micropile tie-back anchoring in 23 % of heritage building restorations. Structural engineers specified micropiles in underground transit tunnel-securement and foundation replacement scenarios where vertical clearance or overhead obstruction was minimal.
Although effective, micropiles remain more expensive per ton of load than driven piles—by an average of 27 %. Cost escalations were compounded by specialized tendons, corrosion protection and certified grout materials. Skilled drilling crews and pressure monitoring equipment have been required in most installations, adding nearly 15 % to labor budgets. Wall-mounted bore rigs necessitated additional safety and handling protocols, which slowed site turnover by up to 12 %. Quality-control stakes remain high as grout and tendon failures occur in 4 % of audit checked foundations. Lack of standardization in design codes across jurisdictions continues to inhibit widespread adoption in developing regions.
Accelerated revitalization of aging infrastructure has opened opportunities where micropiles can be deployed without full structural demolition. Programs in Europe and North America targeting bridge and embankment reinforcement have specified micropile underpinning in 28 % of retrofit projects. Urban tunnel and underground utilities maintenance sites have adopted micropile-prop anchorage in 17 % of cases to avoid excavation. Renewable energy platforms including wind turbine foundations on soft soils have seen pilot micropile deployments. Emergency slope stabilization funding has been redirected to lightweight micropile systems when landslides threaten inhabited zones, showcasing potential in climate resilience verticals.
Mass deployment of wireless pressure and load monitoring sensors has become standard in 36 % of new micropile rigs. Digital grout volume logging and real-time load-transfer testing have been integrated into automated control panels in 29 % of installations. Modular micropile kits supporting interchangeable tendon lengths and grouting accessories are gaining adoption in 22 % of the supply chain, speeding product deployment in multi-site contracts. Driveable torque limiters and rig telemetry capabilities have improved tightening accuracy by 14 %. Environmental considerations have been accounted for by using low-alkalinity grout and biodegradable lubricant additives in 18 % of compliance‐focused projects.
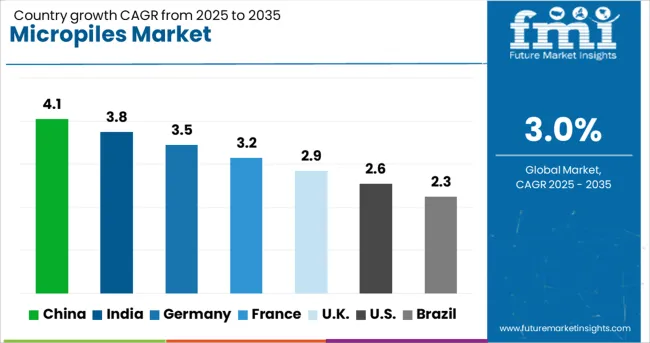
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 4.1% |
| India | 3.8% |
| Germany | 3.5% |
| France | 3.2% |
| UK | 2.9% |
| USA | 2.6% |
| Brazil | 2.3% |
The global micropiles market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 3.0% from 2025 to 2035. China leads with 7.7%, outperforming the global rate by 4.7 percentage points, supported by infrastructure upgrades across rail and metro projects. India follows at 7.1%, where demand is supported by public sector construction across seismic zones. Germany (OECD) posts 6.6%, driven by retrofitting activity in aging commercial buildings and bridges. The United Kingdom (OECD) reports 5.4%, above the global average, with growth tied to foundation reinforcement in densely built urban zones. The United States (OECD) trails at 4.8%, reflecting slower project approval cycles and cost constraints in small-scale civil infrastructure. The report includes detailed analysis of 40+ countries, with the top five countries shared as a reference.
China accounted for 7.7% of the global market in 2025. Micropiles were used extensively in geological fault zones and soft-soil foundations where traditional piling methods were ineffective. Drilling firms incorporated duplex rotary and cased hole techniques to address subsidence in major tunnel and bridge retrofits. High-capacity grouted piles were specified in highway expansion and riverbank stabilization contracts.
India contributed 7.1% of the global share in 2025. Micropiles were installed in metro rail corridors, elevated roadways, and flyover footings due to limited access and high load conditions. Hollow bar micropiles with centralized grouting assemblies were used to improve bearing in clay-rich and saturated soils. The segment saw active engagement from both public infrastructure boards and private contractors.
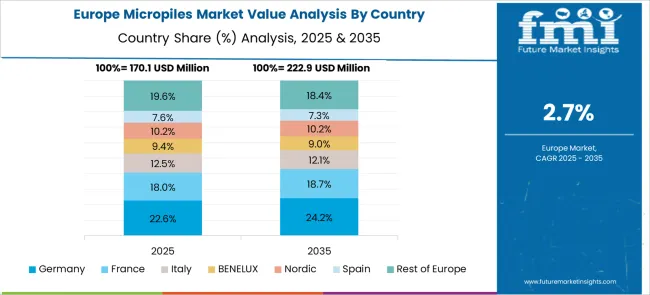
Germany accounted for 6.6% of global consumption in 2025. Structural retrofitting of aging railway bridges and tunnel reinforcements used steel-cased and pressure-grouted micropiles. Application was influenced by load transfer optimization in low-clearance and confined-access work zones. Product use was linked to minimized settlement risks and long-term seismic reinforcement.
The United Kingdom held 5.4% of global share in 2025. Micropiles were integrated in structural rehabilitation of historic buildings and public walkways to counteract shallow foundation limitations. Hand-dug pile shafts and low-headroom drilling equipment were applied across inner-city job sites. Corrosion-resistant steel elements and grout sleeves were incorporated to ensure durability under marine and wet conditions.
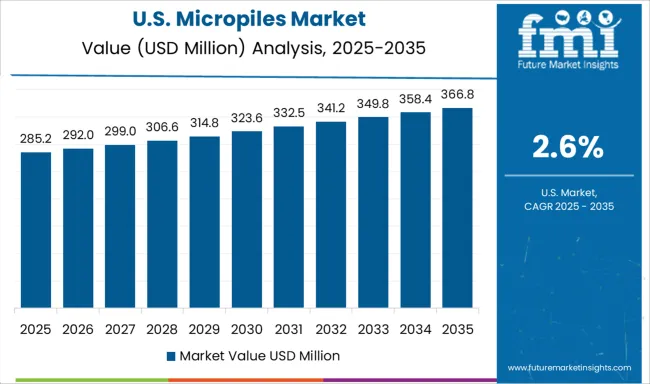
The United States accounted for 4.8% of global demand in 2025. Applications spanned seismic retrofitting, landslide mitigation, and underpinning of residential and commercial foundations. Micropiles were selected to reduce settlement in expansive soil zones such as those in California and Texas. Small-diameter piling systems were integrated in FEMA-designated risk zones requiring deep anchorage without heavy equipment.
The market is supported by manufacturers delivering deep foundation equipment and related systems for civil engineering, geotechnical reinforcement, and infrastructure stabilization. While several listed companies are primarily recognized for metal forming machinery, their heavy industrial expertise and engineering capabilities position them to support foundation equipment either directly or through subsidiaries, joint ventures, or customized hydraulic systems.
Komatsu Ltd. and Isgec Heavy Engineering Ltd. have divisions producing construction and foundation equipment suitable for drilling and pile driving. SMS group GmbH and Schuler Group contribute through specialized machinery capable of handling large-scale components used in micropile systems. Macrodyne Technologies Inc., Beckwood Press, and AIDA offer precision hydraulic systems which can be adapted for pile casing and tooling processes in heavy-duty environments.
BRUDERER AG and AMADA PRESS SYSTEM CO., LTD. provide high-precision forming machinery used in fabrication of steel elements associated with micropile assemblies. Nidec Minster and STAMTEC are active in custom press systems that support ancillary component production. YangLi Group Corporation Ltd. and SHIEH YIH MACHINERY INDUSTRY CO., LTD. manufacture press and mechanical solutions utilized in pile anchor hardware fabrication. Although not all firms directly manufacture micropile rigs, their integration into the supply chain through metalwork, component forming, and industrial systems remains critical to overall project execution and system performance.
The market has seen notable strategic and technological momentum from major and emerging firms. Keller Group unveiled robotics-integrated autonomous grouting systems in 2023, cutting installation time in urban retrofit projects. Soletanche Bachy deployed machine learning‑based placement tools during major bridge and tunnel contracts, enhancing soil‑match precision.
DSI (Dywidag-Systems) continued winning deep rock foundation tenders using its DYWI® Drill rig for rapid threadbar micropiles. Franki Foundations rolled out real‑time IoT load-testing as part of its turnkey offering across Southeast Asia. Indigenous players like D.S. Projects in India gained traction by supplying cost‑effective threadbars via localized production.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 696.0 Million |
| Type | Hollow bar micropiles, Cased micropiles, Uncased micropiles, and Composite micropiles |
| Construction Method | Self-drilling, Pre-Drilled and pre-grouted, Post-grouted, and Pressure-grouted |
| Load Transfer Mechanism | Combination (Friction and End-Bearing), Friction micropiles, and End-bearing micropiles |
| Application | New construction, Underpinning, Seismic retrofitting, Slope stabilization, Earth retention, Foundation repair, and Others |
| End-Use Industry | Infrastructure, Commercial buildings, Residential buildings, Industrial structures, Power plants, Oil and gas facilities, Marine structures, and Wind turbines |
| Material | Steel, Concrete, Composite (steel and grout), and High-strength alloys |
| Diameter | 150-250 mm, Less than 150 mm, and More than 250 mm |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
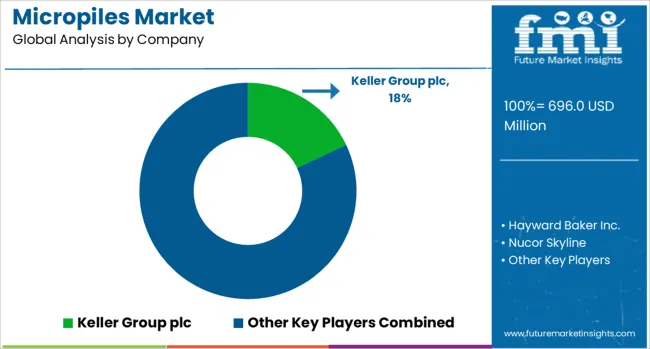
| Key Companies Profiled | Keller Group plc, Hayward Baker Inc., Nucor Skyline, Franki Foundations, Geo Construction Group, BAUER Group, and Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by micropile type (grouted, steel, composite) and application (foundation reinforcement, landslide stabilization, seismic retrofit), demand across construction, infrastructure, and geotechnical industries, led by Asia‑Pacific with North America catching up, innovation in high-capacity load design and rapid-install systems. |
The global micropiles market is estimated to be valued at USD 696.0 million in 2025.
The market size for the micropiles market is projected to reach USD 935.3 million by 2035.
The micropiles market is expected to grow at a 3.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in micropiles market are hollow bar micropiles, cased micropiles, uncased micropiles and composite micropiles.
In terms of construction method, self-drilling segment to command 33.8% share in the micropiles market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA