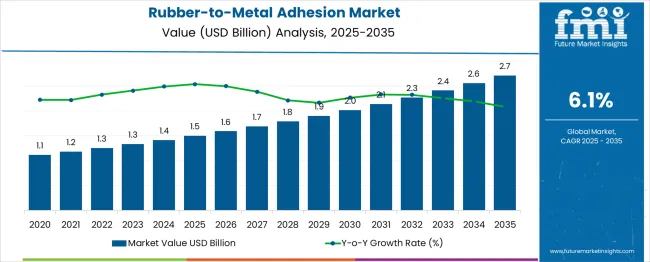
The rubber-to-metal adhesion market is projected to grow from USD 1.5 billion in 2025 to USD 2.7 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.1%. Annual gains steadily increase from USD 0.09 billion in 2026 to USD 0.17 billion by 2035.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 1.5 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 2.7 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.1% |
This consistent rise highlights strong demand in the automotive, construction, and machinery sectors, where bonding strength and vibration damping are critical. Early-stage growth is driven by tire and bushing applications, while later years see broader industrial usage in anti-vibration mounts and sealing systems.
Technological improvements in adhesives, such as waterborne chemistries and dual-cure systems, support adoption. Regional momentum builds in Asia and Eastern Europe due to OEM expansions and cost-effective contract manufacturing.
The rubber-to-metal adhesion market holds distinct yet niche shares within its parent markets. In the rubber-to-metal bonded articles market, it constitutes nearly 100% since adhesives are essential for manufacturing vibration-damping mounts and bushings. Within the global adhesives and sealants market, rubber-to-metal adhesion accounts for about 1-2%, serving a specialized industrial need.
In the rubber-based adhesives market, it captures an estimated 5-8% share, driven by automotive and machinery applications. Across the automotive components market, rubber-to-metal adhesion contributes approximately 3-5%, mainly in engine mounts, suspension, and NVH systems. In the industrial machinery and aerospace markets, it comprises 2-4%, enabling critical sealing and isolation functions.
The industry has been segmented by product type, bonding technology, substrate type, end-use industry, and region. Product offerings include adhesives and primers. Bonding technologies cover direct and indirect bonding methods. Substrate types include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, and others.
Key end-use industries comprise automotive, industrial machinery, construction, and aerospace. Regionally, the industry spans North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa, with demand shaped by vehicle production rates, polymer innovation, and regulatory shifts toward material safety and performance standards.
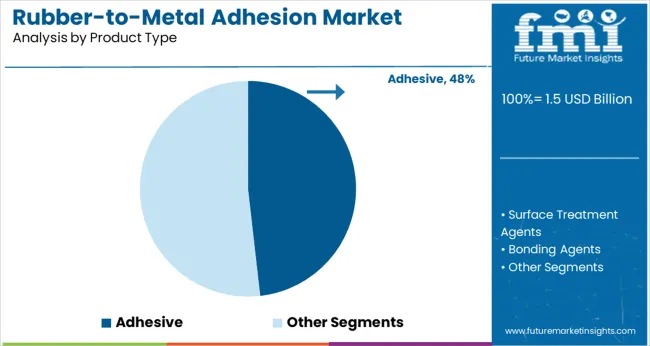
Adhesives led the product type segment with a 48% share in 2025, supported by their versatility in bonding rubber to various metal substrates. Between 2025 and 2027, adoption expanded across USA tire manufacturing plants and European anti-vibration component suppliers.
From 2028 to 2031, solvent-based and waterborne adhesive innovations improved compatibility with high-performance elastomers in electric vehicle parts. Asia Pacific witnessed rapid uptake in India and China as localized manufacturing grew. Adhesives remained critical in molding applications involving bushings, engine mounts, and seals across the automotive and rail sectors.
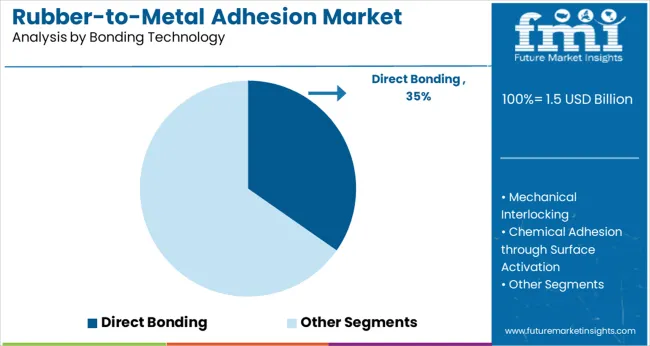
Direct bonding accounted for 35% of the bonding technology segment in 2025, driven by improved durability, chemical resistance, and faster production workflows. From 2025 to 2027, North American OEMs integrated direct bonding in brake systems and chassis dampers. Between 2028 and 2030, Japanese electronics firms adopted this method in compact rubber-metal isolators.
Growth was further supported by automated bonding systems used in German automotive Tier-1 suppliers. Despite rising complexity in rubber-metal combinations, direct bonding continued to dominate due to low surface preparation requirements and consistent bond integrity.
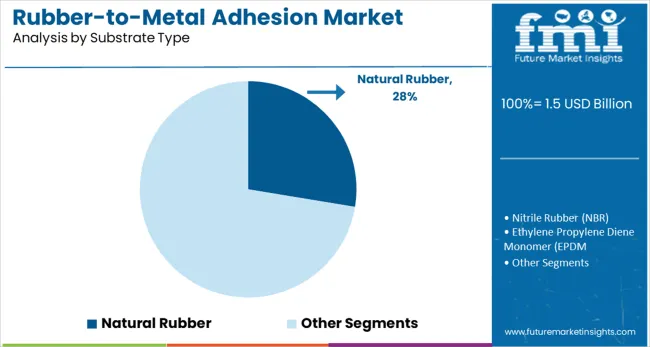
Natural rubber held a 28% share in 2025 as the primary substrate due to its elasticity and vibration absorption properties. Southeast Asian countries, particularly Thailand and Indonesia, served as major sourcing hubs.
From 2025 to 2028, usage in commercial vehicle bushings and engine mounts drove volume in the APAC region. By 2030, demand rose in Europe for agricultural and heavy equipment tires using natural rubber compounds. Its compatibility with common adhesives and mold-release cycles reinforced its position in bonded automotive and industrial parts.
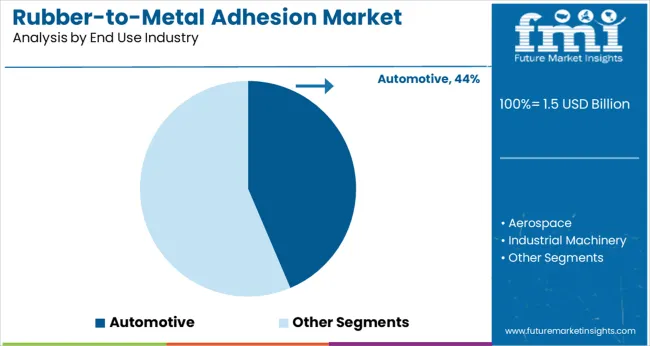
The automotive industry led the end-use segment with a 44% share in 2025, driven by demand for bonded parts like suspension systems, engine mounts, and vibration isolators. Between 2025 and 2027, EV growth boosted adhesive demand in battery casings and e-axle assemblies.
From 2028 onward, global vehicle electrification targets and lightweighting strategies increased the need for flexible rubber-metal interfaces. OEMs across Germany, South Korea, and the USA specified multi-substrate adhesion in their component procurement cycles. High-performance bonding technologies remained integral to thermal insulation, sealing, and NVH (noise, vibration, and harshness) management.
The industry is evolving as industries seek durable, flexible bonding solutions for vibration damping, corrosion resistance, and high-stress environments. While demand is rising in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery, challenges persist due to raw material cost fluctuations and complex approval pathways.
Adhesive Integration Expands Across Mobility and Machinery
Rubber-to-metal adhesives are being increasingly adopted in sectors like automotive and aerospace for bonding components such as engine mounts, vibration isolators, and suspension systems. These adhesives enhance structural performance by minimizing vibration, noise, and fatigue.
Their ability to reduce part count and support lightweighting goals has made them a preferred choice in high-performance assemblies. Advanced formulations also offer rapid curing, better heat resistance, and compatibility with a range of metal and rubber substrates.
Material Cost Pressure and Regulatory Complexity
The industry faces persistent challenges from volatile raw material prices, especially in rubber compounds, solvents, and synthetic resins. These fluctuations complicate budgeting and supply chain planning. Environmental and safety regulations vary by region, creating delays in formulation approvals and increasing R&D costs.
Furthermore, traditional sectors that rely on mechanical fasteners and molded bonding alternatives remain hesitant to adopt adhesives, especially where production is highly standardized.
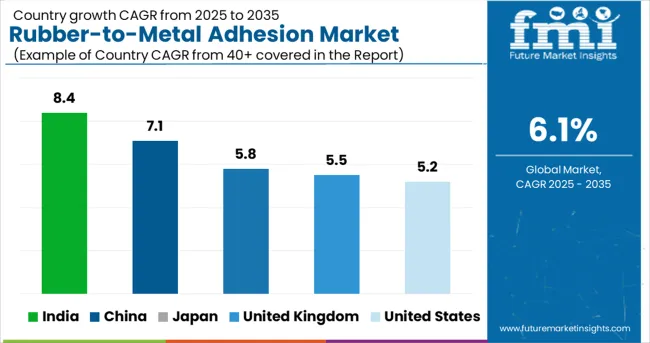
The global CAGR for the rubber-to-metal adhesion market is projected at 6.1% from 2025 to 2035. India leads among the profiled countries with 8.4%, exceeding the global pace by over 35%, followed by China at 7.1%.
These BRICS economies are scaling adhesive technologies in response to surging demand for engine mounts, bushings, and suspension components in domestic automotive and rail sectors. Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States post 5.8%, 5.5%, and 5.2% respectively, reflecting below-average growth.
India’s performance is underpinned by backward integration across adhesive manufacturing and component molding in tiered auto clusters. China’s trajectory is fueled by the rapid adoption of industrial vibration dampening and growing exports in bonded assemblies. Slower gains in OECD markets are linked to high regulatory thresholds, slower equipment modernization, and reshoring-induced volatility in Tier 1 supplier contracts. These five nations were selected as strategic references from over 40 markets evaluated.
| Countries | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United States | 5.2% |
| United Kingdom | 5.5% |
| India | 8.4% |
| China | 7.1% |
| Japan | 5.8% |
Sale of rubber-to-metal adhesion in the United States is growing at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2025 to 2035. Growth is expected to be driven by advancements in automotive suspension systems, vibration isolators, and electric vehicle mounts. Applications in aerospace and heavy machinery are also expanding as OEMs seek higher performance and longer durability.
Between 2020 and 2024, demand remained steady, supported by automotive OEMs in the Midwest and renewed interest in reindustrialization initiatives across the South.
The United Kingdom market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.5% from 2025 to 2035. Demand is anticipated to rise due to material substitution in automotive NVH components, railway couplings, and wind energy damping systems. Lightweighting strategies in transport and marine segments are creating new adhesive bonding opportunities.
Between 2020 and 2024, industry activity was largely driven by post-Brexit investment in localized supply chains and limited import substitution in industrial manufacturing zones.
Demand for rubber-to-metal adhesive in India is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 8.4% between 2025 and 2035, the fastest among all major economies. Demand is expected to rise from automotive parts manufacturing, railway modernization, and two-wheeler engine systems.
Domestic suppliers are investing in local formulation plants to serve Tier 1 and Tier 2 automotive vendors. From 2020 to 2024, adoption was primarily limited to OEM-specified use cases, with wider adoption emerging only post-PLI scheme rollout in the auto sector.
The China market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2035. Rising investments in EV platforms, high-speed rail, and construction equipment manufacturing will shape long-term demand. Increased focus on vertical integration by domestic adhesive companies is expected to strengthen supply security.
From 2020 to 2024, applications were concentrated in shock absorber components and bushings for commercial vehicles, with joint ventures and licensing agreements enabling technology localization.
Japan market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2025 to 2035. Growth is expected to be supported by integration in electric powertrain mounts, high-durability vibration dampers, and industrial automation components. Adhesive bonding is also replacing mechanical joining in niche aerospace and robotics applications.
Between 2020 and 2024, adoption was stable, with moderate innovation driven by OEMs in Kansai and Chubu regions focusing on heat- and oil-resistant bonding agents.
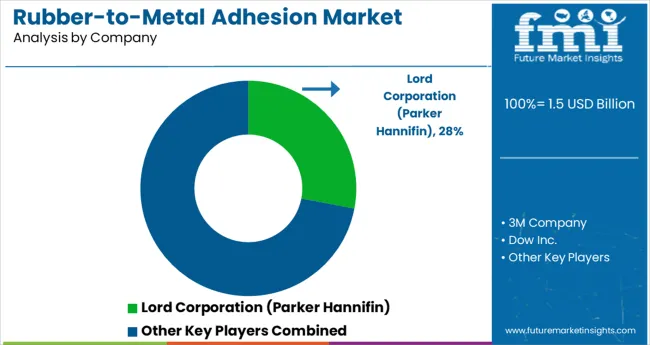
The rubber-to-metal adhesion market is characterized by specialized adhesive manufacturers supporting critical bonding needs across automotive, construction, and industrial machinery sectors. Lord Corporation (a Parker Hannifin brand) remains a benchmark in NVH (noise, vibration, and harshness) bonding systems, with robust adoption across OEM platforms.
3M Company provides a broad range of bonding tapes, sealants, and adhesives for diverse metal-rubber applications. Dow Inc. focuses on silicone and hybrid chemistries engineered for durability under extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. H.B. Fuller tailors industrial-grade bonding solutions for heavy equipment and rail infrastructure.
Sika AG holds a strong footprint in elastomeric adhesives for structural and mobility systems. Henkel’s LOCTITE line is widely applied in damping and dynamic joints. Chemence Performance Materials is emerging with custom bonding agents for engineered rubber-metal interfaces. These players advance formulation science, substrate compatibility, and application-specific performance.
Leading Company - Lord Corporation (Parker Hannifin)Industry Share - ~28%
Recent Industry News
Research Coverage and Scope Summary
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025) | USD 1.5 billion |
| Projected Industry Size (2035) | USD 2.7 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.1% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for value and thousand metric tons for volume |
| Product Types Analyzed (Segment 1) | Surface Treatment Agents, Adhesives, and Bonding Agents |
| Bonding Technologies Analyzed (Segment 2) | Direct Bonding, Mechanical Interlocking, Chemical Adhesion through Surface Activation, Hybrid Systems |
| Substrate Types Analyzed (Segment 3) | Natural Rubber, Nitrile Rubber (NBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer ( EPDM), Silicone Rubber, Others. |
| End Use Industries Analyzed (Segment 4) | Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Machinery, Railway, Construction Equipment |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa |
| Key Players | Lord Corporation (Parker Hannifin), 3M Company, Dow Inc., H.B. Fuller, Sika AG, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Chemence Performance Materials |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share by bonding type and substrate, demand from vibration-damping components in automotive, growth in chemical surface activation, regional diversification of OEM suppliers |
This includes Surface Treatment Agents, Adhesives, and Bonding Agents
The segment is categorized into Direct Bonding, Mechanical Interlocking, Chemical Adhesion through Surface Activation, and Hybrid Systems.
The industry is segmented into Natural Rubber, Nitrile Rubber (NBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), Silicone Rubber, and Others.
This segment covers Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Machinery, Railway, and Construction Equipment applications.
Regional analysis includes North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
The industry is projected to reach USD 1.5 billion in 2025.
The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2025 to 2035.
Adhesives are expected to capture 48% of the industry in 2025.
The Asia Pacific region, particularly India, is projected to register a CAGR of 8.4% from 2025 to 2035.
The industry is projected to reach USD 2.7 billion by 2035.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Anti-Adhesion Barrier Gels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Management Market - Innovations & Treatment Trends 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA