The demand for inorganic fungicides globally is also likely to continue a moderate level growth from 2025 to 2035, based on growing farm disease pressures, orbiting need for food security and cost-effectiveness of mineral based formulations.
In general, the biocide is several inorganic fungicides (primarily containing the metals coppers, sulphur, and mercury (recently discontinued)) that because of the protective and contact action and their compatibility with integrated pest management (IPM) systems, are the most utilized fungicides in cereal, fruit, vegetable, and ornamental crop host production .
In developing regions with a long history of robust adoption of modern agriculture, inorganic fungicides remained a critical aspect of grower's toolkit, despite growing use of organic farming methods and biofungicides. Their long life, lower cost than alternatives, and ability to manage resistance means that it seems unlikely that these will be dropped.
According to, The global Inorganic Fungicide market was valued at USD 4,264.1 Million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 7,781.6 Million by the year 2035, at a CAGR of 6.2%.
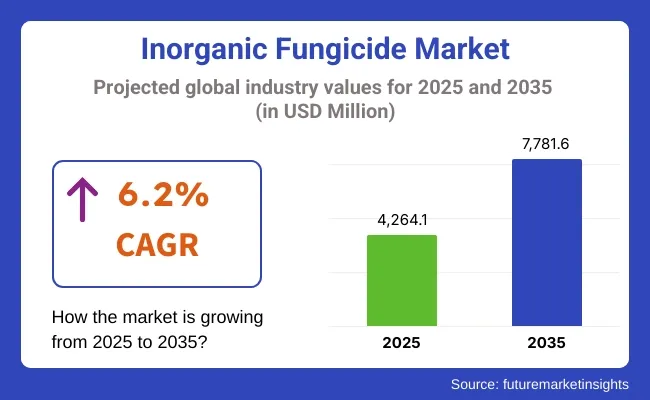
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 4,264.1 Million |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 7,781.6 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.2% |
The inorganic fungicide market shows steady growth, trending upward on the rise of its demand for disease control for cereals, fruit and vegetable crops. Inorganic fungicides, especially based on elemental sulfur, copper, and lime-sulfur compounds, are preferred due to their multi-site mode of action, their low resistance risk and their efficacy in integrated pest management (IPM) programs.
Globally, there is a much higher market share of copper compound-based fungicides and wettable powder formulation types than other available raw materials and formulation types, because they are effective against a variety of fungal pathogens, inexpensive to use, and can be employed in large field applications.
They are important in managing leaf spotting, mildews, blights and cankers for both traditional and organic agriculture. References underlining the essentiality of copper-based fungicides in water-dispersible forms in crop protection programs even as regulatory frameworks promote lower-residue fungicides and restrict synthetic organics, especially in humid regions or where fungal outbreaks persist.
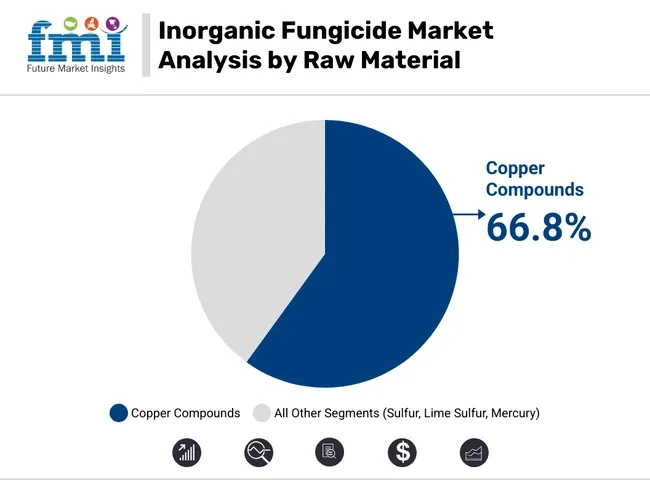
| Raw Material | Market Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Copper Compounds | 66.8% |
The largest segment within inorganic fungicides is copper compounds, which are well-established and highly efficient against pathogenic fungi and bacteria on major crops of fruit, vegetables, and cereal crops. Oxychloride, hydroxide and Bordeaux mixture are common forms that are also commonly applied in agricultural systems around the globe.
Due to their ability to provide a degree of protective action against fungal pathogens on plant surfaces, and best fit with both synthetic and organic pest control strategies, copper based fungicides are preferable to farmers. With residual activity and a multi-site mechanism, these compounds minimize the development of pathogen resistance.
Global organic farming standards, such as those from the USDA and European Commission, allow the use of copper compounds in controlled conditions, and therefore they remain a staple in organic vineyards and orchards.
Copper compounds continue to be the mainstay of the global chemical control toolbox, including in crops subject to more stringent residue regulatory systems and across climatic zones, being the mainstay of the chemical control toolbox for vine crops and tree fruits in regions where sulfur and lime sulfur are also used in other crops and climates.
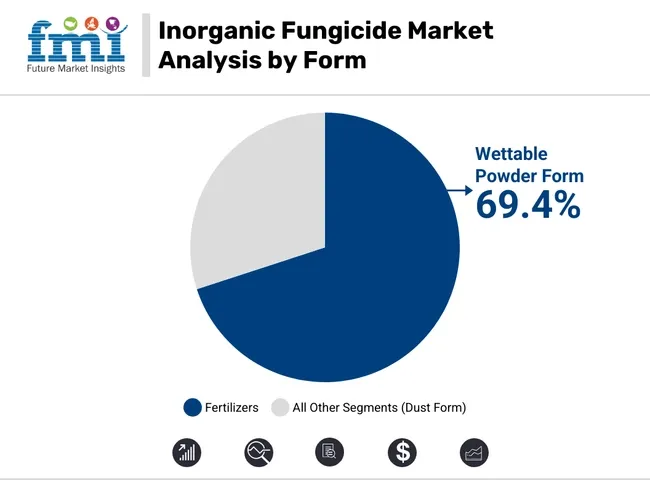
| Form | Market Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Wettable Powder Form | 69.4% |
Among WP (wettable powder) formulations dominate the inorganic fungicide market as they are easy to store, stable, and can be easily prepared as tank mix used in different fields. Then, the resultant powders are mixed with water to create a fine suspension that is suitable for foliar spraying on both broadacre and horticultural crops.
For example, WP formulations cover evenly and uniformly over waxy, hairy plant surfaces and may I be re-applied several times over the course of the growing season. For extensive use, farmers depend on wettable powders for consistent performance and minimum application cost.
The compatibility of useful wettable powders with existing spray equipment and their ability to be tank-mixed with other agrochemicals also makes them attractive on smallholder and commercial farms. Moreover, WP forms have a longer shelf life than emulsifiable concentrates or ready-to-use liquids, and they are more readily available in regions with little cold storage or distribution infrastructure.
Though dust forms are still utilized in certain dryland farming regions, or for post-harvest applications, wettable powders tend to be widely used as they provide the best field performance along with the most flexibility for users and compatibility with broad crops.
Environmental toxicity, regulatory restrictions, and resistance management pose hurdles.
Environmental persistence is one of the main problems with inorganic fungicides. Excessive use of copper and sulfur contributes to soil degradation and microbial imbalance with residues in runoff contributing to water pollution. These environmental impacts are driving regulators to implement maximum residue limits (MRLs) and ban multiple applications.
Another difficulty concerning fungal resistance management arises where mismanagement of ECM practices with systemic fungicides, or misuse, can result in lowered efficacy against fungal diseases. In addition, the limited curative ability of inorganic fungicides, which mostly serve as protectants, necessitates timely application (onset of infection) and reapplication, which in turn hikes labor cost and complicates the adherence of farmers.
Hybrid formulations, micronutrient integration, and smart application methods fuel innovation.
There are opportunities for the development of hybrid fungicide formulations, combining inorganic species with bio controls and low-toxicity organics for better spectrum control. Plant health benefits are also being delivered with disease prevention as manufacturers incorporate micronutrients (e.g., zinc, manganese) with copper or sulfur carriers.
Drone spraying, variable rate technology, and electrostatic sprayers enable increased efficiency and targeting in the application of inorganic fungicides, with implications for overall volumes and environmental protection. With countries adopting residue monitoring systems and supporting incentives for precision agriculture, demand for inorganic fungicide solutions that are environmentally optimized is expected to increase.
The USA inorganic fungicide industry is evolving due to the extensive usage of inorganic fungicides in fruit & vegetable & ornamental crop protection. For example, copper-based and sulfur-based fungicides can be used in vineyards, citrus groves and greenhouse farming where the regulatory framework is standalone and low toxicity and residue compliant.
Under its Re-Evaluation Program, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues the review of active ingredients, facilitating the development of safer formulas. There is also growing demand in organic-certified operations, especially in California and Florida. Some domestic producers are working on micronized particle technologies to improve efficacy and reduce runoff.
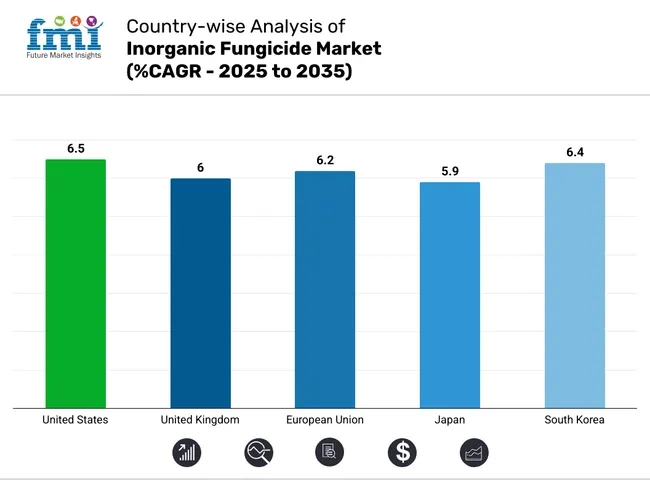
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United States | 6.5% |
Apple orchards, barley cultivation, and horticulture in the UK are some extensive applications of inorganic fungicides. Harmonized pesticide approval pathways have transitioned to a more local basis in the post-Brexit period, in conjunction with sustainable use directives. Many organic and low-input farms, where the copper and sulfur are the primary tools for fungal disease control, are seeing demand increase.
Research institutions are looking at the environmental impact of multiple applications of copper, which is leading growers to consider rotation strategies. The government is providing funding to develop precision application techniques to mitigate residue and protect biodiversity.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 6.0% |
Strict residue limits and the Sustainable Use of Pesticides Directive, which encourages integrated pest management (IPM), regulate the EU inorganic fungicides market. Copper and sulfur compounds are extensively used in the vineyards and olive groves of southern European countries like Spain, Italy and Greece.
Technological innovations in formulation, such as nano-dispersed and slow-release, have emerged for the reduction of cumulative copper soil levels. Demand for non-synthetic fungicidal agents is robust, driven by EU support for organic farming and agroecological practices.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| European Union | 6.2% |
Countrywise Japan’s inorganic fungicide market will be propelled by the Japan’s focus on food safety and integrated crop protection in rice, citrus and vegetable cultivation. The Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) impose stringent maximum residue levels (MRLs) and prefer the use of low-risk fungicides such as sulfur and copper.
The formulations are in the order of ultra-fine particle which increases coverage and minimize environmental run-off. Usage is being promoted via agricultural cooperatives in greenhouse settings and smallholder farms. Moreover, key pathogens are commonly managed by alternating schedules of inorganic fungicides to minimize resistance development.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 5.9% |
Inorganic fungicides market in South Korea is supported by its high intensity of cultivation of vegetables and fruits, mainly apples, pears and chili peppers. Australia's “Green Food Strategy 2030” calls for eco-friendly pest control options, pushing demand for copper and sulfur.
Regional agricultural research and development (R&D) centers are fine-tuning dosage prescriptions and incorporating remote sensing tools for timely application. Demand is also being driven in the country’s booming organic sector as part of efforts to reduce the use of synthetic pesticides
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 6.4% |
The inorganic fungicides market is witnessing steady growth on account of cost-effectiveness, multi-site mode of action, and sustained demand from conventional agriculture. Mineral-based fungicides like copper compounds, sulfur, and lime-sulfur solutions provide broad-spectrum disease control and are less prone to inducing resistance development compared to synthetic organic fungicides.
The consistent market demand is driven by their common usage in fruits, vegetables, cereals, and horticulture, particularly in organic and integrated pest management (IPM) systems. Supportive regulatory consideration for sustainable crop protection and low-residue agrochemicals is further bolstering adoption in developing economies.
UPL Ltd. (13-16%)
UPL is a leading supplier of copper- and sulfur-based inorganic fungicides, particularly in Asia and Latin America. In 2024, it introduced finely milled copper oxychloride formulations for enhanced adhesion on citrus and apple trees. In 2025, it launched advanced sulfur dispersions tailored for humid climates, reducing residue accumulation and improving compatibility with organic farming protocols. UPL supports integrated disease management strategies aligned with FAO-backed IPM initiatives.
Bayer AG (11-14%)
Bayer continues to innovate in traditional crop protection with a modern twist. In 2024, it improved the rainfastness and field stability of its copper hydroxide-based products to enhance efficacy during wet seasons. In 2025, Bayer launched tank-mix-ready inorganic fungicides designed to delay resistance development in rotation with single-site fungicides. The company’s sustainability agenda promotes judicious copper use in line with EU agricultural standards and Codex MRL frameworks.
Nufarm Ltd. (9-12%)
Nufarm emphasizes accessibility and field adaptability in its inorganic fungicide offerings. In 2024, it introduced flowable sulfur approved for use in certified organic farming systems under the OMRI standard. By 2025, Nufarm collaborated with cooperatives in Eastern Europe and Australia to promote responsible copper usage in wheat, barley, and oats especially for rust and leaf spot prevention. Its educational outreach aligns with FAO crop protection principles for sustainable farming.
Albaugh LLC (7-10%)
Albaugh is known for its cost-effective generic formulations and robust presence in Latin American agriculture. In 2024, it launched improved Bordeaux mixture alternatives for large-acreage crops including bananas and coffee. In 2025, Albaugh introduced dust-controlled wettable powders to enhance worker safety during manual mixing and application. Its continued investment in post-patent technologies helps increase access to essential crop protection tools in price-sensitive regions.
Certis Biologicals (6-9%)
Certis specializes in bio-rational and compatible crop inputs, including a growing line of inorganic fungicides. In 2024, it expanded the distribution of lime-sulfur concentrates for dormant spray programs in grapes and stone fruits. In 2025, it launched a line of OMRI-listed sulfur fungicides suitable for strawberries, cucurbits, and tree nuts, reinforcing its position in the high-value organic crop market. Certis advocates for residue-free exports and supports agroecological transition models.
Other Key Players (38-45% Combined)
Numerous regional manufacturers and specialty suppliers contribute to the growth and innovation of the inorganic fungicide market. These include:
The overall market size for the inorganic fungicide market was USD 4,264.1 Million in 2025.
The inorganic fungicide market is expected to reach USD 7,781.6 Million in 2035.
The demand for inorganic fungicides is rising due to increasing global food demand, the need to protect crops from fungal infections, and the growing popularity of broad-spectrum solutions. Copper compound formulations and wettable powder forms are particularly favored for their efficacy and compatibility with sustainable agricultural practices.
The top 5 countries driving the development of the inorganic fungicide market are China, the USA, India, Brazil, and France.
Copper compound formulations and wettable powder forms are expected to command a significant share over the assessment period.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Inorganic Cobalt Blue Pigments Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inorganic Scintillators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inorganic filler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inorganic Oxides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inorganic Salts Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Inorganic Zinc Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fungicide Active Ingredients Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industry Share Analysis for Inorganic Scintillators Companies
Inorganic Flame Retardants Market
Inorganic Ion Exchange Materials Market
White Inorganic Pigment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Copper Fungicides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Amphimobile Fungicides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Bio-rational Fungicides Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Bacillus-based Biofungicides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Bio-rational Fungicides in USA Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA