The Japan electric sub-meter market is anticipated to be valued at USD 13.68 million in 2025. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period and reach a value of USD 24.96 million in 2035. The Japan electric sub-meter market exhibited steady growth in 2024, with industry earnings reaching USD 12.9 million, up from USD 12.2 million in 2023.
This expansion was primarily driven by the increasing demand for energy monitoring in the residential and commercial building sectors, particularly in metropolitan areas. As companies demanded increased energy efficiencies and real-time monitoring, the adoption of advanced sub-meters with Wi-Fi capabilities and IoT connectivity was expanded.
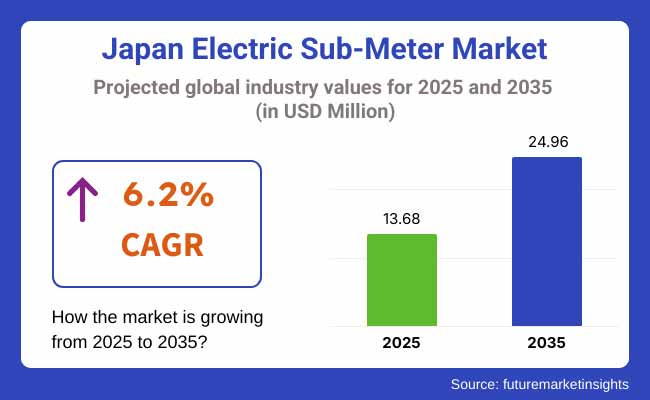
Governments at all levels continued to ramp up interest in state-of-the-art smart grid infrastructures and conservation programs, producing further increases in adoption. It is expected that from 2025 and beyond, 6.2% CAGR will continue because of the increase in the use of electric power and strict regulations mandating energy monitoring systems. Emerging technologies, such as AI-enabled analytics and cloud-based monitoring, will foster this growth.
The rise in net-zero energy buildings and renewed integration with renewable energy sources further exacerbate the demand for next-generation sub-meters. By 2035, the industry is likely to garner USD 24.96 million, sustaining its growth.
FMI Survey on Japan Electric Sub-Meter Market: Key Stakeholder Insights and Market Dynamics
(The survey was conducted in Q4 2024, with n=500 stakeholder participants evenly distributed across utilities, commercial developers, residential consumers, and manufacturers in Japan.)
Nearly three-quarters of respondents prioritize real-time energy monitoring and enhanced energy efficiency, resulting in a significant move toward IoT penetration for smart sub-meters. More than two-thirds of commercial property developers say that embedding advanced sub-metering systems into new projects is now a matter of course. This trend aligns with the increasing demand for smart energy management and the decarbonization policies emphasized in Japan.
Regional Variance
Energy efficiency regulations and compliance mandates play a crucial role in purchase decisions. 68% of utilities claim energy efficiency policies are speeding up the take-up of smart sub-meters. Policy-led initiatives are also prompting industrial as well as residential customers to improve their metering solutions.
Key Regulatory Drivers
Despite the attractive growth potential, cost and compatibility are still significant barriers to adoption. 45% of small companies hesitated to adopt smart sub-meters due to initial costs and integration challenges with legacy systems.
Cost and ROI are seen differently
The survey revealed a swift shift toward AI-based analytics and cloud energy monitoring. More than 50% of respondents anticipate that predictive analytics and remote monitoring will become standard offerings within the next five years.
Adoption Rates for Advanced Technologies
Japanese consumers are becoming increasingly concerned about sustainability. 38% of residential customers expressed interest in connecting sub-meters to renewable energy sources like solar panels and home energy storage systems.
Key Drivers of Residential Demand
Manufacturers are concentrating on innovation & differentiation of product to maintain competition. Three critical priorities emerged from the survey:
Unlock detailed industry insights and stay ahead of industry trends-request your copy of the full report today!
| Country | Regulatory Impact & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| Japan |
|
| 2020 to 2024 (Historical Analysis) | 2025 to 2035 (Future Outlook) |
|---|---|
| Industry expansion was moderate but consistent, paced by urbanization and infrastructure growth. | The industry will pick up speed, driven by the adoption of smart grids, renewable energy integration, and regulatory requirements. |
| Smart sub-meters picked up steam, but electromechanical meters persisted, especially in older structures. | Smart sub-meters will reign supreme, as demand rises for IoT-based, AI-powered energy management solutions. |
| Single-phase sub-meters dominated the industry, mainly because of residential demand. | Three-phase sub-meters will gather steam, particularly in commercial and industrial segments due to energy efficiency regulations. |
| The residential industry was the biggest end-use sector, paced by apartment buildings and energy cost-sharing requirements. | The commercial segment, data centers, and retail chains will grow at a fast pace, which will call for sophisticated energy monitoring solutions. |
| Government policies centered on simple energy efficiency practices, with limited utilization of smart grid infrastructure. | Stricter enforcement of regulations and incentives will prompt the implementation of smart sub-metering and real-time energy monitoring systems. |
| Industry expansion was affected by supply chain disruptions and economic deceleration caused by COVID-19. | There will be steady growth in terms of a predicted 6.2% CAGR reaching USD 25.0 million in 2035. |
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Top Product | Smart Sub-Meters |
| Market Share in 2025 | 61.5% |
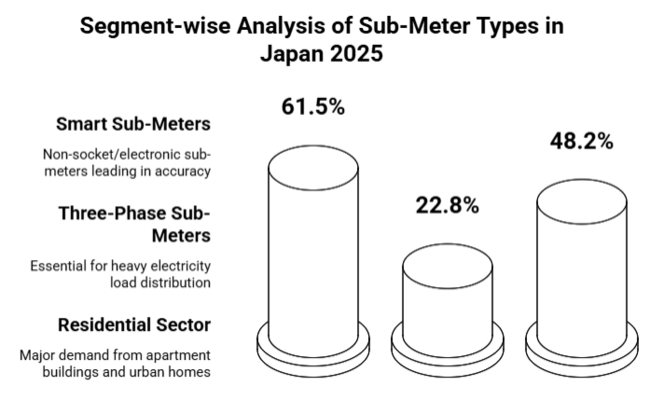
Smart sub-meters are expected to dominate Japan, holding 61.5% of the industry share in 2025. Among them, non-socket/electronic sub-meters lead due to their higher accuracy, digital monitoring, and IoT compatibility.
These meters enable automated data collection and remote monitoring, helping businesses and households optimize energy consumption. Rapid urbanization and smart grid regulations have accelerated their adoption, particularly in commercial buildings.
Government-backed incentives for energy-efficient infrastructure further drive demand. Additionally, renewable energy integration and the push for data-driven energy management contribute to their expansion. With advanced analytics and cloud connectivity, non-socket electronic sub-meters are becoming essential for Japan’s evolving energy ecosystem.
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Top Phase | Three Phase |
| Market Share in 2025 | 22.8% |
Three-phase sub-meters are witnessing rapid growth, and it is estimated to hold an industry share of 22.8% in 2025. They find extensive application in commercial and industrial spaces, where heavy electricity loads need to be efficiently distributed. With the increasing manufacturing base of Japan, increasing data centers, and commercial projects of large scale, the demand is growing.
Their capability to carry larger power loads, minimize energy losses, and accommodate smart energy management systems makes them a must-have for energy-demanding industries. The move toward renewable energy is also propelling adoption, with three-phase systems effectively managing solar and wind power distribution, maintaining stable power supply, maximizing grid performance, and minimizing energy loss in Japan's changing energy profile.
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Top Application | Residential Sector |
| Market Share in 2025 | 48.2% |
The residential sector is still the biggest area of application, forecasted to take 48.2% of the industry's share in 2025. Apartment buildings create demand with a requirement for independent energy monitoring, equitable cost splitting, and alignment with efficiency standards. As the urban population in Japan is increasing, multi-unit dwellings are increasingly using smart sub-meters for proper charging and energy saving.
Government policies favoring energy conservation and grid modernization have further boosted homeowners and developers to implement IoT-enabled sub-metering solutions. On the other hand, increasing consumer awareness and pressure toward sustainable energy consumption are driving adoption, providing efficient usage of power, cost savings, and harmonization with renewable energy sources in residential properties in Japan.
The Japan electric sub-meter market has witnessed progress in the year 2023 as increased demand for energy efficiency, smart grid integration, and energy management systems enabled by IoT has been one of the major driving forces.
Top companies like Itron Inc., Landis+Gyr, Schneider Electric, Honeywell International Inc., and others work toward boosting their presence in order to meet increased demand for advanced sub-metering solutions. Their product strategies include technological and innovative partnerships and product diversification with future next-generation metering systems for homes, businesses, and industries in mind.
Itron Inc. already completed the launch of its IoT-enabled sub-meters for real-time monitoring of energy uses in 2024, ready for smart grids. The company has also launched its AI energy analytics platform last March 2024, as reported by Smart Energy International, eventually strengthening its commitment to energy efficiency and reliability in the grid. Also, Itron formed partnerships with some Japanese utilities to implement advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) solutions.
This year's Landis+Gyr introduced an altogether fresh range of cloud-linked sub-meters that allow consumption tracking and management through the web, bringing its Japanese service network expansion for custom sub-metres to larger consumers.
In February 2024, as Metering & Smart Energy International confirmed, Landis and Gyr completed the take-over of a Japanese software company focused on energy management, enhancing its offering of integrated sub-metering.
Schneider Electric introduced EcoStruxure Resource Advisor in 2024, a cloud-based software that combines sub-metering data with advanced analytics for energy optimization. The company collaborated with local utilities to advance smart grid-compatible sub-metering solutions.
In April 2024, Schneider Electric partnered with a prominent Japanese construction company to install sub-metering systems in new commercial buildings, as noted by Energy Efficiency News. Honeywell International Inc. enhanced its Energy Manager platform in 2024, integrating sub-metering data with building automation systems to improve energy efficiency.
The company also introduced a new series of wireless sub-meters, simplifying installation in older buildings. In March 2024, Honeywell announced a collaboration with a Japanese technology firm to develop AI-driven energy management systems, as reported by Smart Cities World.
Kamstrup A/S entered the Japanese sub-metering industry in 2024, introducing a new generation of ultrasonic sub-meters known for their precision and durability in industrial environments. The company established a distribution network across Japan to ensure timely delivery and installation. In January 2024, Kamstrup announced the development of a blockchain-based energy trading platform for smart grids, as confirmed by Tech Japan.
In 2024, the Japan electric sub-meter industry witnessed significant advancements driven by technological innovation and strategic collaborations. Itron Inc. launched an AI-enabled energy analytics platform, enhancing real-time energy tracking and grid integration capabilities.
Landis+Gyr expanded its technological portfolio by acquiring a Japanese software company specializing in energy management, strengthening its ability to deliver integrated sub-metering solutions. Schneider Electric partnered with a prominent Japanese construction firm to install advanced sub-metering systems in new commercial buildings, aligning with the growing demand for smart building solutions.
Honeywell International Inc. collaborated with a Japanese technology firm to develop AI-based energy management systems, integrating sub-metering data with building automation for improved efficiency. Additionally, Kamstrup A/S introduced a blockchain-based energy trading platform, leveraging its new generation of ultrasonic sub-meters to support smart grid applications. These developments underscore the industry's focus on sustainability, digitalization, and energy efficiency, driving innovation across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors in Japan.
The Japan electric sub-meter market falls under the energy monitoring and management sector, which is itself a sub-sector of the larger electrical equipment and smart infrastructure industries. This sector is directly affected by urbanization, industrial expansion, energy efficiency regulations as well as smart grid technology advances, all of which are macroeconomic forces.
The economy of Japan is one that prides itself in technological innovation, a solid manufacturing base, and a lot of emphasis on energy sustainability. With rising electricity consumption and the government’s pledge for carbon neutrality by the year 2050, the need for energy-monitoring solutions has grown tremendously.
The old power grid coupled with the rising acceptances of renewable energy sources makes it imperative for superior metering solutions, smart sub-meters being among the most core places in Japan's energy infrastructure.
Governmental regulations such as METI's energy conservation policies and the Building Energy Efficiency Act are making the installation of IoT-enabled sub-meters compulsory for real-time energy tracking for businesses and residences. Also, the expansion of Japan's commercial sector, particularly data centers and large-scale retail, is driving demand for three-phase sub-metering solutions.
In the years to come, economic stability, digital transformation, and sustainability goals will continue to shape this sector. Strong foreign investments, infrastructure upgrades, and government incentives would further fuel the adoption of smart and AI-powered sub-metering systems to about 2035.
Growth Opportunities
Integration with Smart Grid Infrastructure
With Japan’s push for grid modernization and decentralized energy distribution, stakeholders can tap into the smart grid expansion by developing sub-meters with real-time data analytics, AI-driven insights, and blockchain-based energy transactions. Collaborations with utilities and government agencies will open new revenue streams.
Targeting Japan’s Expanding Data Center Industry
The rising demand for cloud computing, AI, and IoT has fueled rapid growth in Japan’s data center sector. Manufacturers can develop customized three-phase sub-metering solutions tailored for high-density power consumption environments, enabling precise monitoring, predictive maintenance, and compliance with Japan’s energy efficiency mandates.
Residential Smart Home Integration
As Japanese consumers embrace home automation, integrating sub-meters with smart home ecosystems (Alexa, Google Nest, and Panasonic IoT platforms) can drive adoption. Companies should partner with smart home device manufacturers to offer bundled solutions, enhancing value for residential consumers.
Strategic Recommendations
Develop AI-driven sub-meters with Predictive Maintenance
Companies should incorporate machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies, predict faults, and optimize energy use, ensuring higher adoption in industrial and commercial settings. AI-driven solutions can reduce energy costs by up to 20%, making them highly attractive.
Leverage Japan’s Subsidies for Energy-Efficient Buildings
Government incentives for zero-energy buildings (ZEBs) and energy-efficient construction present an opportunity to collaborate with real estate developers. Offering government-compliant sub-metering solutions will drive demand from new construction projects.
Expand Distribution Networks via Utility Partnerships
Partnering with Japan’s leading electric utilities and renewable energy providers will enable wider industry penetration. Bundling sub-meters with utility-led smart metering initiatives can ensure seamless adoption and integration.
By product, the industry is segmented into socket type/electromechanical sub-meters, non-socket /electronic sub-meters, and smart sub-meters.
In terms of phase, the sector is segmented into a single phase and three phases.
By application, the industry is segmented into commercial establishments, the residential sector, and the industrial sector.
Increasing electricity consumption, smart grid expansion and energy efficiency regulations are key factors contributing to the rising adoption of electric sub-meters in Japan.
Smart sub-meters offer real-time monitoring, remote access, and integration with IoT-based energy management systems, making them more efficient than traditional electromechanical meters.
Residential complexes, commercial establishments like data centers, retail chains, and industrial facilities are leading adopters due to the need for precise energy tracking and cost optimization.
Regulations such as the Building Energy Efficiency Act and incentives for smart infrastructure are driving installations, particularly in new residential and commercial developments.
These devices enable efficient integration of solar and wind energy into the grid by tracking consumption and optimizing load distribution, supporting Japan’s transition to clean energy.
Table 1: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 2: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 3: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 4: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 5: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 6: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 7: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 8: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 9: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 10: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 11: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 12: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 13: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 14: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 15: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 16: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 17: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 18: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 19: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 20: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 21: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 22: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 23: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 24: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 25: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 26: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 27: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 28: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 29: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 30: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 31: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 32: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 1: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 2: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 3: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 4: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 5: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 6: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 7: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 8: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 9: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 10: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 11: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 12: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 13: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 14: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 15: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 16: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 17: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 18: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 19: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 20: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 21: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 22: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 23: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 24: Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 25: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 26: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 27: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 28: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 29: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 30: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 31: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 32: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 33: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 34: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 35: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 36: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 37: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 38: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 39: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 40: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 41: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 42: Kanto Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 43: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 44: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 45: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 46: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 47: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 48: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 49: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 50: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 51: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 52: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 53: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 54: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 55: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 56: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 57: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 58: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 59: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 60: Chubu Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 61: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 62: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 63: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 64: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 65: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 66: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 67: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 68: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 69: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 70: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 71: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 72: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 73: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 74: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 75: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 76: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 77: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 78: Kinki Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 79: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 80: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 81: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 82: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 83: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 84: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 85: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 86: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 87: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 88: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 89: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 90: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 91: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 92: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 93: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 94: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 95: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 96: Kyushu & Okinawa Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 97: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 98: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 99: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 100: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 101: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 102: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 103: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 104: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 105: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 106: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 107: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 108: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 109: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 110: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 111: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 112: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 113: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 114: Tohoku Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 115: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 116: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 117: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 118: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 119: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 120: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 121: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 122: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 123: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 124: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 125: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 126: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 127: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 128: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 129: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 130: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 131: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 132: Rest of Japan Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
japan Tortilla Market - Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Japan Cosmetics ODM Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Yeast Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Green and Bio-based Polyol Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Natural Food Color Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025–2035
Japan Coated Fabrics Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan Barite Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan 1,4-Diisopropylbenzene Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan Compact Construction Equipment Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Social Employee Recognition System Market in Japan - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan Inkjet Printer Market - Industry Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan HVDC Transmission System Market - Industry Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA