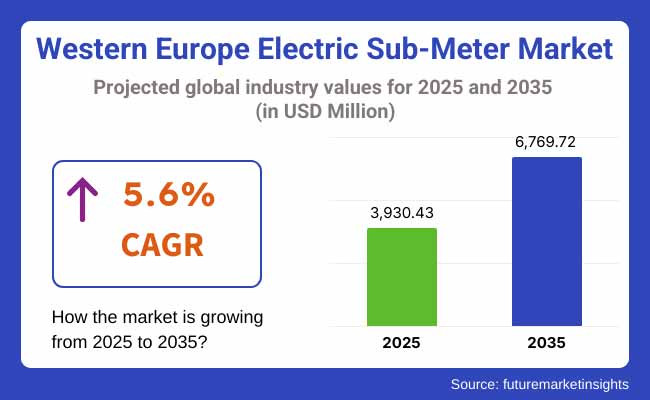
The electric sub-meter industry in Western Europe is estimated to be valued at USD 3,930.43 million in 2025. The industry is slated to expand at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. By 2035, the electric sub-meter industry will acquire a market valuation of USD 6,769.72 million.
In 2024, the Western European electric sub-meter industry grew steadily, to a projected USD 3,722.00 million. This growth was primarily fuelled by mounting energy efficiency policies, increasing electricity prices, and the extensive use of smart grid infrastructure. Germany, France, and the UK witnessed an upsurge in installations as governments encouraged finer granularity in energy monitoring for both residential and commercial purposes.
Utility firms allied with technology providers to implement high-end metering solutions, pushing real-time energy monitoring and consumption analysis. Additionally, the demand for sub-meters surged in multi-tenant complexes and industrial units as companies desired control over energy expenses.
The industry is likely to expand at a strong rate during the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. The adoption of sub-meters with IoT capabilities further accelerates the integration of energy management systems in AI-based predictive analytics.
Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholders evenly distributed across manufacturers, utility providers, policymakers, and end-users in Western Europe, the USA, and Asia-Pacific.
Regulatory Compliance & Energy Efficiency
65% of respondents identified compliance with EU energy directives and national efficiency policies as the primary driver of sub-meter adoption.
Cost Savings & Real-Time Monitoring
58% cited the ability to track and optimize energy consumption as a major factor in adopting electric sub-meters.
Regional Variance
Adoption Trends
ROI Perspectives
70% of stakeholders in the USA & Western Europe found IoT-enabled sub-meters financially viable, while only 38% in Asia-Pacific agreed.
Global Trends: 69% of manufacturers plan to expand their smart sub-meter product lines, focusing on cloud integration and AI-based analytics.
Regional Focus Areas
| Countries | Regulatory Impact & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| Germany |
|
| France |
|
| United Kingdom |
|
| Italy |
|
| Spain |
|
| Netherlands |
|
Germany's electric sub-meter industry is likely to expand at a CAGR from 2025 to 2035 is likely to be 6.2% throughout the upcoming decade. Germany has an incentive for commercial and industrial consumers to digitally connect their electricity meters under the country’s Smart Meter Rollout Law and Energy Industry Act (EnWG), creating significant demand.
The country is rapidly replacing analogue meters, aiming for 95% smart meter penetration by 2032. Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar also contribute heavily to the sub-meter industry when coupled with grid modernization efforts.
For single-phase meters, the guaranteed accuracy of the meter shall be ensured by PTB (Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt) certification, which acts as one important factor of regulation compliance. Functional IoT-enabled sub-meters are also being installed in Germany's industrial sector, which consumes around 38% of the country's electricity.
FMI opines that Germany's electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 6.2% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Italy’s electric sub-meter industry is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% between 2025 and 2035. In Italy, the Integrated Text on Electricity Measurement (TIME) regulation mandated automated metering for energy efficiency, and collects the real-time data collection required by ARERA.
The country’s large-scale rollout of second-generation smart meters (2G meters) under Enel’s initiative is a key industry driver. The government's emphasis on demand response programs and smart grid development are driving sub-meter adoption in industrial and commercial buildings. Italy also promotes sub-metering in multi-tenant homes, allowing for a fair energy bill. Manufacturers must comply with MID, and obtain CESI (Centro Electrotechnics Sperimentale Italiano) certification.
FMI opines that Italy’s electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.8% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The electric sub-meter industry in France is expected to experience a 5.5% CAGR over the next 10 years. According to the Energy Transition for Green Growth Act, sub-metering is enforced in the residential and commercial sectors, making compliance a major growth factor.
The Linky smart meter program, launched by the government in collaboration with the energy provider Enedis, is designed to replace conventional meters with automatic devices that can be controlled remotely over the next five years. The sub-metering solutions are gaining traction as integrating renewable energy and improving energy efficiency in multi-tenant buildings is on the rise.
FMI opines that France’s electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.5% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The UK is expected to surge at a CAGR of 5.7% throughout 2035. with mounting regulatory mandates and rising awareness around energy-efficient heating systems being the key drivers. The Smart Metering Implementation Programme (SMIP) established mandatory smart meter rollout to all homes and businesses throughout the UK, to be performed by energy suppliers.
The UK government’s net-zero target for 2050 is a major catalyst for sub-meter adoption in commercial and industrial sectors. Compliance with OFGEM, MID (Measuring Instruments Directive), and BS EN 50470 standards is essential for industry players. The UK’s dynamic energy pricing models and demand-response programs encourage businesses to invest in sub-meters to optimize consumption.
FMI opines that the United Kingdom electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.7% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Spain's electric-sub-meter industry will grow at a 5.3% CAGR during the upcoming decade. The Royal Decree 1110/2007 mandates remote-controlled sub-meters for all consumers consuming less than 15kW of electricity, driving the widespread adoption of sub-meters.
In a segment on energy sub-metering, the National Energy Efficiency Plan also strongly supports its adoption in industrial areas to reduce energy wastage. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with both MID 2014/32/EU and local CEM (Centro Español de Metrología) certification.
Spain’s emphasis on integrating renewables, especially in solar and wind generation, is also generating demand for distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS).
FMI opines that Spain’s electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.3% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The Netherlands is expected to experience the highest growth at a 5.9% CAGR, driven by aggressive smart meter deployment policies coupled with sustainability initiatives.
The Netherlands' focus on net-zero carbon buildings and district heating projects has increased investments in IoT-enabled sub-meters. However, consumer reluctance due to privacy concerns and data-sharing policies could slow adoption. With increasing investments in decentralized energy systems, sub-metering is expected to play a crucial role in optimizing energy sharing among communities and EV charging management.
FMI opines that the Netherlands’ electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.9% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The BENELUX region (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg) with a Compound growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4%, having Belgium and Luxembourg slightly behind the Netherlands in smart meter adoption.
The regional policies of Belgium (Flanders, Wallonia, and Brussels) lead to fragmented growth patterns, with Flanders ahead of the rest regarding smart sub-meter rollouts. Even though it's a much smaller industry, Luxembourg has enacted energy efficiency mandates that incentivize sub-metering in commercial properties. The region adheres to MID compliance and national metrology requirements for certification.
FMI opines that BENEFLUX electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.4% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The rest of Western Europe, including Austria, Switzerland, Portugal, and Nordic countries, is estimated to grow at a 5.2% CAGR, which is lower than the region's average. Although the Nordic countries take the lead when it comes to adopting renewable energy, Austria and Switzerland have tighter metering policies.
Portugal is growing with state subsidies for energy-efficient buildings. Meeting MID and national metrology institutions is still important. Yet, inconsistent policy implementation and budget constraints hinder mass adoption.
FMI opines that the electric sub-meter sales in rest of Europe will grow at nearly 5.2% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Socket type and electromechanical sub-meters will remain an important segment in traditional energy monitoring systems, especially in older buildings and industrial premises. Analogue meters are an attractive solution for basic metering requirements due to their low cost and high durability, which is why they are still widely used. However, as digital metrics continue to advance, analogue metering solutions will become increasingly outdated.
Stable Demand for Feed-Through Sub-meters Backed by Focus on Accurate Measurement of Power-Fed Loads in High-power Load Dominated Commercial and Industrial Environments When incorporated into automated energy management systems, these meters can be more intelligent, improving their effectiveness in tracking real-time energy consumption.
The current transformers are expected to grow as the need for advanced monitoring solutions increases in industries, large retail spaces and others. As energy efficiency regulations become more stringent, their ability to accurately measure high-voltage energy makes them invaluable in industrial and utility settings, as well.
Suppliers of electronic sub-meters without sockets will have to obtain a large industry share thanks to their flexible and easy integration into modern buildings. Their small footprint and adaptability for smart power grid applications will help expand their use in residential and commercial applications.
With the rise of digitalization, smart sub-meters will take the majority share of the industry. As devices that monitor real-time data, allow for remote oversight, and integrate with existing IoT platforms. These devices will become critical tools for energy-conscious consumers and operators seeking to humanize energy consumption and achieve cost savings in operations.
Single-phase sub-meters will continue as the standard for domestic and small commercial applications. A lifespan of 8,000 hours or more makes them not only cost-effective but also practical for installations, especially in apartments, small offices and retail spaces where individual energy consumption monitoring is essential. As smart home adoption is on the rise, single-phase smart sub-meters will soon be a common trend.
Three-phase sub-meters will be in higher demand for use in industrial and large commercial facilities, where high power-consumption equipment necessitates accurate load distribution and monitoring. When integrated into energy management systems, they will enable businesses to minimize wastage, and energy consumption and meet strict energy regulations.
Commercial establishments will drive demand for sub-meters as businesses prioritize energy efficiency to reduce costs. Office buildings, hotels, and mixed-use complexes will increasingly adopt smart sub-metering to track energy usage across multiple tenants and optimize billing. The rise of sustainability-focused corporate policies will accelerate this trend.
Large retail stores will integrate sub-meters into energy management systems to monitor lighting, HVAC, and refrigeration energy consumption. Supermarkets and shopping malls will particularly benefit from real-time monitoring capabilities to optimize operational efficiency and lower energy expenses.
Data centres will be a key growth segment due to their high energy consumption. With growing cloud computing and AI workloads, energy-intensive facilities will require precise sub-metering to monitor power usage effectiveness (PUE) and ensure regulatory compliance. Demand for smart, real-time energy monitoring solutions in data centres will surge as operators focus on reducing their carbon footprint.
The residential sector will see increased adoption of sub-meters, particularly in multi-tenant buildings and smart home setups. Property owners and tenants will benefit from precise energy tracking, leading to fairer billing and more energy-conscious consumption patterns. The shift toward home automation will further drive demand for smart sub-meters in residential applications.
The industrial sector will remain the largest adopter of sub-meters as manufacturers and heavy industries strive to improve energy efficiency and meet sustainability goals. With rising electricity costs and government mandates pushing for reduced carbon emissions, factories and production plants will deploy advanced sub-metering systems to monitor and optimize power distribution across operations.
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Gradual Adoption of Smart Sub-Meters: The industry witnessed steady growth as governments in Western Europe pushed for smart meter rollouts. However, adoption varied across countries due to regulatory delays and infrastructure limitations. | Mainstream Smart Metering: With stronger policy enforcement and increased investments, smart sub-meters will become standard, especially in commercial and industrial applications, driving higher industry penetration. |
| Regulatory-Driven Growth: Policies such as the EU Energy Efficiency Directive and national smart metering mandates fueled initial deployments. However, challenges related to data privacy and cybersecurity slowed adoption in some regions. | Regulation-Backed Expansion: Stricter energy efficiency laws, carbon reduction goals, and smart grid initiatives will drive faster adoption. Cybersecurity measures will evolve, making smart metering more secure and reliable. |
| Limited IoT & AI Integration: Early adoption of IoT-enabled sub-meters began, but real-time analytics and AI-based energy management solutions remained in their infancy. Most implementations were in pilot phases. | Advanced IoT & AI Applications: Widespread adoption of AI-powered analytics, predictive maintenance, and cloud-based energy monitoring will enhance efficiency. Industrial facilities and data centres will leverage AI for real-time energy optimization. |
| Dominance of Traditional Sub-Meters: Electromechanical and basic electronic sub-meters still accounted for a significant share, especially in older infrastructure where retrofitting costs were high. | Shift to Digital and Smart Solutions: The industry will see a decline in traditional sub-meters as businesses and households transition to digital, networked, and cloud-compatible energy monitoring systems. |
| Commercial & Industrial Uptake: Businesses and industrial units were the primary adopters of sub-metering solutions due to cost-saving potential. Residential adoption remained slow except in smart city projects. | Residential Expansion Alongside Industrial Growth: Increased consumer awareness and incentives for energy efficiency will drive higher sub-meter penetration in multi-tenant buildings and homes, alongside strong demand in industrial and commercial sectors. |
| Infrastructure & Supply Chain Challenges: The pandemic and global supply chain disruptions affected meter manufacturing, delaying installations and increasing costs. | Stable Supply & Faster Deployments: With improved manufacturing capabilities and localized production, supply chain bottlenecks will ease, ensuring timely sub-meter installations across Western Europe. |
| Initial Investment Barriers: Many small businesses and residential users hesitated to adopt sub-meters due to high upfront costs and uncertain ROI. | Stronger ROI Justification: Falling hardware costs, energy savings, and government incentives will encourage broader adoption, making sub-metering a more attractive long-term investment. |
| Fragmented Market Growth: Different countries in Western Europe progressed at varying speeds in terms of adoption, leading to inconsistencies in industry development. | Harmonized Expansion Across Europe: With more standardized policies and cross-border energy efficiency targets, the industry will see more uniform growth across the region. |
The electric sub-meter industry is part of the energy management and smart grid technology industry, which overlaps with industrial automation, IoT-based infrastructure, and sustainability-focused solutions. It is a major part of the overall utilities and energy efficiency sector, directly impacted by government policies, carbon reduction goals, and digital transformation efforts.
Western European electric sub-meter industry is well positioned for solid growth with surging energy costs, tougher energy efficiency regulations, and a rising need for timely consumption tracking. The governments of Western Europe are imposing stringent regulations to lower carbon emissions, boosting the mass-level adoption of smart sub-meters. Smart grids and digital energy solutions are accelerating investments, thus setting the grounds right for both industrial and commercial sectors to embrace sub-meters.
Economic instability and inflationary pressures may affect short-term investments in sub-metering technologies among small and mid-sized businesses. However, several factors such as declining hardware prices, increased energy savings, and government incentives will drive long-term industry growth. The increasing trend toward IoT-enabled and AI-powered energy monitoring solutions will further propel adoption, as companies look for data-driven energy optimization solutions.
As Europe drives toward a low-carbon economy, demand will grow for commercial properties, industrial facilities, and residential developments for sub-meters. The presence of renewables, EV charging stations, and decentralized energy systems will serve to further drive the requirement for high-end sub-metering technologies, establishing this industry as a key facilitator of energy transition in Europe.
Top players in the Western European electric sub-meter industry are competing on innovation, strategic alliances, and regional growth. With the increasing demand for smart and IoT-based sub-meters, leading players are investing heavily in AI-driven energy analytics, remote monitoring features, and cybersecurity features to make their offerings stand out. Competitive pricing continues to be a strategy, but premium brands emphasize value-driven solutions that provide predictive maintenance, real-time data analytics, and easy grid integration.
Strategic partnerships with energy utilities, smart grid technology developers, and building automation companies are driving industry penetration. Manufacturers are also enlarging production centres in Europe to minimize supply chain risks and provide compliance with increasingly complex regulatory frameworks.
Recent Key Developments
socket type/electromechanical sub-meters, non-socket/electric sub-meters and smart-sub meters
single-phase and three-phase
commercial establishments, residential sector and industrial sector
Germany, Italy, France, United Kingdom, Spain, The Netherlands, BENEFLUX and Rest of Europe
Rising energy costs, government regulations on energy efficiency, and the need for real-time consumption monitoring are key factors boosting demand.
Smart sub-meters offer real-time data tracking, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance, unlike traditional models that only record usage.
Commercial buildings, data centres, large retail stores, and industrial facilities are leading adopters due to energy optimization needs.
Stricter energy efficiency laws and carbon reduction targets are accelerating installations, especially in Western Europe.
IoT integration, AI-driven analytics, and cloud-based energy management systems are transforming energy monitoring and efficiency.
Table 1: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 2: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 3: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 4: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 5: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 6: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 7: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 8: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 9: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 10: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 11: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 12: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 13: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 14: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 15: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 16: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 17: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 18: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 19: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 20: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 21: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 22: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 23: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 24: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 25: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 26: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 27: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 28: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 29: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 30: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 31: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 32: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 33: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 34: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast By Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 35: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 36: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 37: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 38: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 39: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 40: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 41: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 42: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 43: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 44: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 45: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 46: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 1: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 2: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 3: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 4: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 5: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 6: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 7: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 8: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 9: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 10: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 11: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 12: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 13: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 14: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 15: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 16: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 17: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 18: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 19: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 20: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 21: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 22: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 23: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 24: Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 25: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 26: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 27: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 28: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 29: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 30: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 31: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 32: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 33: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 34: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 35: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 36: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 37: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 38: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 39: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 40: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 41: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 42: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 43: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 44: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 45: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 46: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 47: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 48: UK Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 49: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 50: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 51: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 52: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 53: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 54: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 55: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 56: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 57: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 58: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 59: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 60: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 61: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 62: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 63: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 64: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 65: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 66: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 67: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 68: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 69: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 70: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 71: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 72: Germany Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 73: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 74: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 75: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 76: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 77: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 78: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 79: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 80: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 81: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 82: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 83: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 84: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 85: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 86: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 87: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 88: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 89: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 90: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 91: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 92: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 93: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 94: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 95: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 96: Italy Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 97: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 98: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 99: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 100: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 101: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 102: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 103: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 104: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 105: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 106: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 107: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 108: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 109: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 110: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 111: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 112: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 113: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 114: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 115: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 116: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 117: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 118: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 119: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 120: France Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 121: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 122: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 123: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 124: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 125: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 126: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis By Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 127: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 128: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 129: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 130: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 131: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 132: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 133: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 134: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 135: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 136: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 137: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 138: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 139: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 140: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 141: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 142: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 143: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 144: Spain Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness By Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 145: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 146: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 147: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 148: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 149: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 150: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 151: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 152: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 153: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 154: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 155: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 156: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 157: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 158: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 159: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 160: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 161: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 162: Rest of Western Europe Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Western Blotting Processors Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Blotting Market is segmented by product, application and end user from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automotive Performance Tuning & Engine Remapping Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Valve Seat Insert Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Bicycle Component Aftermarket Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Automotive Load Floor IndustryAnalysis in Western Europe Forecast & Analysis 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Probiotic Supplement Market Analysis in – Growth & Market Trends from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Women’s Intimate Care Market Analysis – Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Non-Dairy Creamer Market Analysis by Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Last-mile Delivery Software Market – Growth & Outlook through 2035
Western Europe Inkjet Printer Market – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe HVDC Transmission System Market – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Conference Room Solution Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Intelligent Enterprise Data Capture Software Market - Growth & Forecast 2025-2035
Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Visitor Management System Industry Analysis in Western Europe - Market Outlook 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Base Station Antenna Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Platform Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Western Europe Event Management Software Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA