The global hydrodesulfurization (HDS) catalyst market is estimated to grow from USD 3,345.5 million in 2025 to USD 5,295.8 million by 2035, reflecting a robust CAGR of 4.7% during the forecast period. Growth is being supported by increasingly stringent fuel emission regulations, sustained demand for petroleum-derived fuels, and technological advancements in catalyst performance.
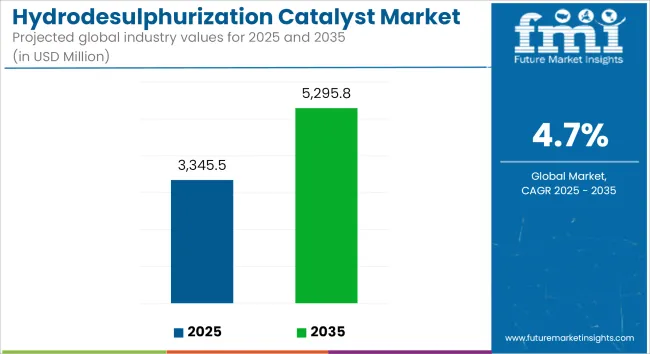
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 3,345.5 million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 5,295.8 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.7% |
HDS catalysts are being utilized in refineries to reduce sulfur content in fuels, ensuring compliance with ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) specifications and global emission mandates. Their deployment is being driven by regulatory frameworks such as Euro VI, Bharat Stage VI, and USA Tier 3, which require refiners to significantly reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from transportation fuels.
Refining operations are being upgraded with high-activity HDS catalysts that exhibit improved stability, lower deactivation rates, and extended regeneration cycles. These characteristics are enabling refiners to optimize throughput, minimize energy consumption, and reduce environmental impact. As demand for cleaner fuels grows in developing economies, new desulfurization units and grassroots refinery projects are being commissioned, particularly in Asia and the Middle East.
A resurgence in refining throughput, especially in post-refurbishment facilities, is contributing to higher catalyst consumption. Refiners are integrating advanced HDS technologies into existing setups to meet changing specifications without compromising profitability. The production of cleaner transportation fuels, including ultra-low sulfur diesel and jet fuel, is reinforcing demand for next-generation catalysts.
Technological innovation is enabling the development of nanostructured active phases, optimized pore structures, and multifunctional catalyst beds. These advancements are improving sulfur removal efficiency, reducing coke formation, and enhancing cycle longevity. Research efforts are also being directed at developing catalysts capable of processing heavier feedstocks with higher sulfur concentrations.
Operational reliability, compliance with emissions targets, and process flexibility are emerging as critical factors influencing catalyst selection. As refiners balance cost pressures with regulatory expectations, hydrodesulfurization catalysts are expected to remain integral to global refining strategies.
The HDS catalyst market is projected to grow steadily through 2035, supported by regulatory alignment, refinery modernization, and continued reliance on petroleum-based fuels in the transitional energy landscape.
The naphtha and gasoline segment is expected to maintain a solid share, contributing nearly 25% of total HDS catalyst demand in 2025 and expanding at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2035. This growth is supported by the increasing complexity of gasoline refining, where sulfur content directly affects catalytic reforming performance and octane yield.
Catalysts in this segment must facilitate deep desulfurization without negatively affecting olefins or octane levels, particularly in regions where gasoline demand continues to rise. Countries like China, India, and Saudi Arabia are aggressively enforcing fuel sulfur limits while simultaneously targeting improved fuel economy and air quality. These policy shifts are increasing the uptake of high-selectivity HDS catalysts.
Rise of hybrid vehicle fleets, which still rely on high-octane gasoline for performance, is reinforcing investment in cleaner gasoline production. Research into new catalytic materials like transition metal sulfides and mixed oxide supports is also contributing to the evolution of HDS technologies for this application segment.
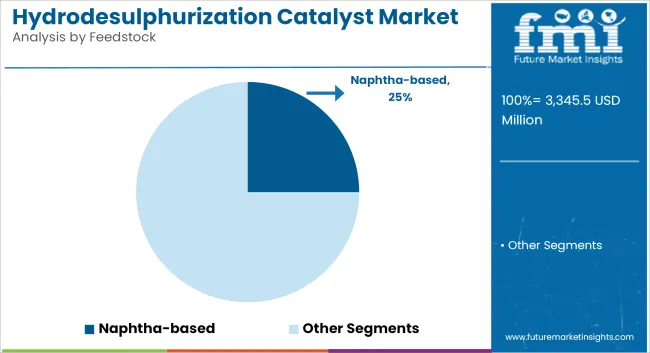
The petrochemicals industry represents the largest end-use segment for hydrodesulfurization (HDS) catalysts, accounting for over 60% of global demand in 2025, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% through 2035. This dominance is attributed to the industry's reliance on sulfur-free or ultra-low sulfur feedstocks to prevent catalyst poisoning in downstream units such as steam crackers, reformers, and aromatics extraction systems.
In petrochemical complexes, feed purification is a critical pre-treatment step. HDS catalysts are extensively used to remove sulfur from naphtha, vacuum gas oil (VGO), and other intermediate streams to ensure uninterrupted and high-yield production of ethylene, propylene, BTX (benzene, toluene, xylene), and other base chemicals. The performance of downstream catalysts and plant efficiency depends significantly on sulfur removal at the front end, placing HDS catalysts in a strategic position within the petrochemical value chain.
The expansion of petrochemical capacity in Asia (China, India, South Korea), the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, UAE), and the USA Gulf Coast is reinforcing catalyst demand. Moreover, integrated refining-petrochemical models are becoming more common, where high-throughput and feed-flexibility require robust, long-life catalysts with low deactivation rates. This growing complexity is driving investments in high-activity NiMo and CoMo catalysts tailored for hydroprocessing of cracked and sour feedstocks.

Stricter Fuel Regulations and Operational Cost Pressures
The hydrodesulphurization (HDS) catalyst industry is obstinately insisting on our ever-stricter global sulphur emissions legislations for fuels. Ultra-low sulphur requirements in regulations such as IMO 2020 and Euro VI mean refiners have to either spend to upgrade or replace their HDS units. The process however operates under high pressure with hydrogen consumption at elevated temperatures causing high energy costs and equipment wear.
Fouling of the catalyst by coke and metal deposits capping the available active sites shortens the lifetime while reducing the efficiency, necessitating more frequent regeneration or replacement. These cost burdens make compliance difficult for smaller refineries unless they make large capital investments in catalytic technology and unit retrofitting.
Cleaner Fuels, Catalyst Innovation, and Demand in Developing Regions
As countries phase out high-sulphur diesel and gasoline, demand for HDS catalysts continues to grow, despite operating challenges. To improve desulfurization at low hydrogen consumption, refineries are introducing advanced surface chemistry of catalyst systems with improved pore structure, larger specific surface area and better dispersion of active metal.
Bimetallic and nanostructured catalysts are rising as promising alternatives, promoting prolonged lifespan and poisoning resistance. Demand from transportation, urbanisation and environmental regulations in Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Africa are spurring new refinery projects and upgrades. As the world transitions away from petroleum-based fuels, HDS catalysts will remain critical for the production of compliant, low-sulphur transportation fuels.
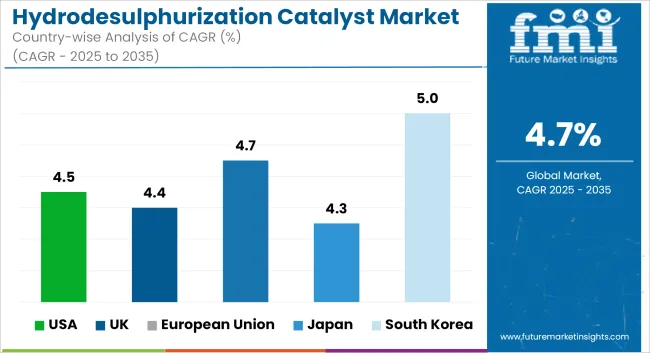
The United States hydrodesulphurization catalyst market is growing steadily owing to stringent regulations imposed by EPA for ultra-low sulphur fuels. Most common examples are upgrading hydro treating units for Tier 3 gasoline specifications or lowering SOx emissions.
USA catalyst peers are developing high-activity cobalt-molybdenum and nickel-molybdenum catalysts to show improved performance and longer cycle life. Catalysts for renewable diesel and hydro treated vegetable oil (HVO) processing are also seeing increasing demand.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 4.5% |
The United Kingdom is slowly increasing in the hydrodesulphurization catalyst market due to energy transition policies and cleaner fuel requirement. Now, fewer and far between upon their number, the little facts are held close to home, and upgrading units to better remove sulphur will be the name of the game.
Under the UK Clean Air Strategy, British refiners are moving towards stricter sulphur limits in transportation fuels. To align with energy efficiency objectives, catalyst suppliers provide customized solutions that allow lower hydrogen consumption and longer service intervals.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 4.4% |
Hydrodesulphurization catalysts are primarily dominated by the European Union, owing to Euro VI fuel standards, decarbonization efforts, and the discontinuation of high-sulphur fuels. For example, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands are rolling out modern catalyst formulations to improve desulfurization of diesel, kerosene, and naphtha streams.
EU refiners are embedding more and more mixed metal oxide catalysts in addition to nano-structured support systems to achieve higher reactivity and thermal stability. Circular economy strategies are also promoting catalyst recycling and regeneration programs throughout the region.
| Region | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| European Union | 4.7% |
The market is growing progressively as Japan promises clean air in its domain and strives for high-quality fuel production. Japan already has stringent sulphur limits in gasoline and diesel, forcing refiners to use higher-performance catalysts with longer operational lifetimes.
Japanese refineries prefer energy-saving processes in desulfurization, which minimize hydrogen consumption while ensuring high sulphur removal rates. Continued investment in synthetic fuels and alternative feedstock processing is anticipated to open new development opportunities for advanced catalyst systems.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 4.3% |
The hydrodesulphurization catalyst market in South Korea is expanding due to increasing exports of ultra-low sulphur diesel and petrochemical feedstocks. The country’s complex refining capacity and global competitiveness over the years have ensured that it has emerged a key player in producing clean fuel.
Local catalyst makers have been working on sulphur-tolerant, high-activity catalysts that would facilitate deep desulfurization and fluidized bed hydro treating. Domestic catalyst demand is also anticipated to further hike up in line with government policies aimed at tightening fine dust and sulphur oxide emissions.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 5.0% |
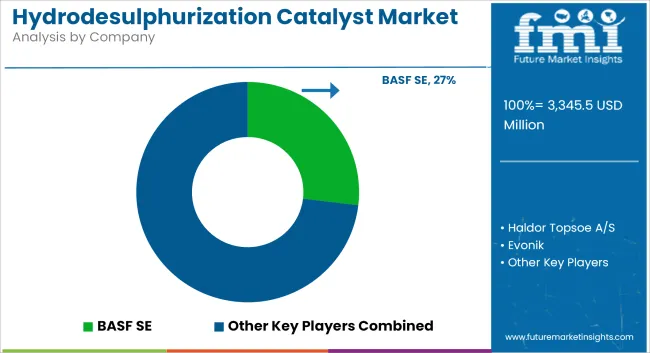
The hydrodesulfurization catalyst market is witnessing a strategic shift as competition intensifies among established catalyst manufacturers and regional players. Leading companies such as Albemarle, Haldor Topsoe, and Axens are investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced formulations that offer better activity, selectivity, and resistance to deactivation. Technologies focused on low-temperature desulfurization, high-aromatic feed processing, and longer cycle lives are gaining market preference.
Strategic partnerships between catalyst producers and refineries are also emerging, enabling the co-development of custom catalyst systems tailored to specific feedstocks and operating conditions. Meanwhile, new entrants are leveraging localized production and cost advantages to penetrate regional markets, especially in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East.
The overall market size for the hydrodesulphurization catalyst market was USD 3,345.5 million in 2025.
The hydrodesulphurization catalyst market is expected to reach USD 5,295.8 million in 2035.
The increasing enforcement of ultra-low sulphur fuel regulations, rising global demand for cleaner diesel fuels, and growing use of Co-Mo catalysts fuel the hydrodesulphurization catalyst market during the forecast period.
The top 5 countries driving the development of the hydrodesulphurization catalyst market are the USA, UK, European Union, Japan, and South Korea.
Co-Mo catalysts and diesel hydrodesulphurization lead market growth to command a significant share over the assessment period.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Residue Hydrodesulphurization Catalyst Market
Catalyst Bins Market Insights – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Biocatalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanocatalysts Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Titanium Catalyst for Polyester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Chemical Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Refinery Catalyst Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polyolefin Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
UK Refinery Catalyst Market Insights – Growth, Applications & Outlook 2025-2035
Polyurethane Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
USA Refinery Catalyst Market Report - Trends & Innovations 2025 to 2035
BDO Synthesis Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Environmental Catalysts Market Trends & Growth 2025 to 2035
Copper Bismuth Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Refinery Catalyst Market Report – Trends, Demand & Industry Forecast 2025-2035
ASEAN Refinery Catalyst Market Analysis
Aluminum-Nickel Catalyst Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Emission Control Catalyst for Small Engines Market - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Motorcycle Emission Control Catalyst Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
High-Performance Catalyst Market Trend Analysis Based on Product, End-Use, and Region 2025-2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA