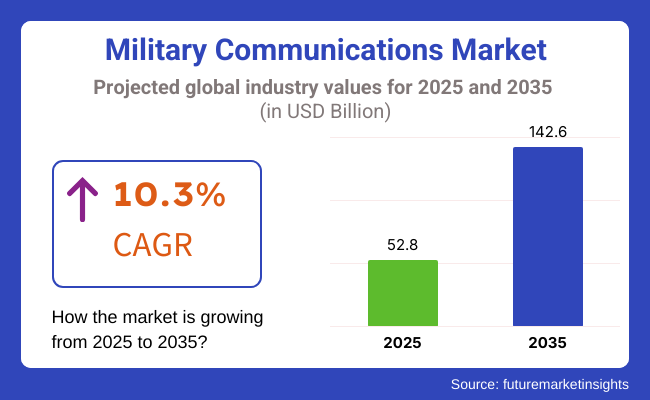
The military communications market is estimated to grow from USD 52.8 billion in 2025 to grow phenomenally to USD 142.6 billion in 2035, with a CAGR of 10.3% throughout the forecast period. This growth is partly the result of increased geopolitical tensions and the demand for safe, real-time communications options intended to improve situational awareness and operational effectiveness in contemporary military operations.
Defense communications networks are essential to facilitate secure and effective information exchange among defense forces, command centers and allied action. Asymmetric warfare tactics and next-generation threats necessitate defense institutions to invest in cutting-edge communications technologies like SATCOM, SDRs, and AI-powered cybersecurity solutions.
They facilitate reliable real-time data exchange and strengthen mission-critical coordination, intel collection and electronic warfare (EW) capabilities. 5G, unmanned vehicles, and quantum encryption integration are also transforming the military communication network, providing hardened and secure connectivity for dynamic battlefield scenarios.
There are several important factors fueling growth in the industry. Worlds across the globe are upping defense budgets to enhance command and manage structure, insight, reconnaissance, and reconnaissance (ISR) training, and battlefield network. Increasing requirements for seamless interoperability among militaries and allied nations are pushing aside the employment of standardized, next-generation communications protocols. Besides, the emerging speed of electronic warfare and cyber warfare is demanding the creation of AI-powered defense systems to detect, deter, and counter cyberattacks.
The Asia-Pacific region-mainly China, India, Japan and enormous military modernization programs - is still leading expansion, while North America and Europe maintain industry dominance through cutting-edge technology and lofty defense expenditures.
The industry is growing, but there are several hurdles to breach. It is expensive to develop and roll out secure, high-performance communications networks and, in doing so, restrict access to such networks by some countries. In addition, legacy systems tend not to have the required interoperability to communicate effectively with cutting-edge systems on military platforms.
Meanwhile, cyberattack sophistication represents significant security threats and demands relentless innovation in encryption and network defensive technologies. Bridging these challenges will involve continued investments in research and development and close cooperation between defense agencies and technology providers.
In spite of the runway that still lies ahead for the industry, with digital transformation and network resilience continuing, the defense industry remains to drive demand. 3D printing will result in customization of solutions while protecting transmissions using quantum-protected systems.
The deployment of 5G-capable battlefield networks, together with edge computing platforms, would allow military forces to decide and respond better from real-time data feeds. Global defense strategies will require escalating military communications technology to provide protected, efficient and flexible connectivity in order to allow defense forces to respond promptly and effectively to coming security challenges in the next decade.
The military communication systems segment is expected to hold a 53% share of the military communication industry in 2025. These include satellite communication (SATCOM), radar & sonar systems, tactical radio networks, and encryption technologies, all crucial for secure military operations
The swift deployment of 5G-enabled battlefield networks, AI-powered cybersecurity, and IoT-driven surveillance is driving the industry. Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman are developing next-gen SATCOM, which can transmit data immediately. At the same time, Raytheon Technologies is enhancing tactical radios with encryption capabilities to ensure secure conversations in the field. Seamless, cyber-resilient communication networks have become a top priority for governments, including the USA Department of Defense (DoD), NATO, and India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
At the same time, the services segment is expected to account for 47% of the industry by 2025. In particular, this includes network integration, cybersecurity solutions, and managed communication services, all of which are critical for protecting against growing cyber threats. Detekbacking security approaches for military network communication systems, BAE Systems, and Thales Group recently introduced an AI-powered threat detection and secure data-sharing solution.
Cloud-native military service communications are gaining momentum as well. One illustrative example of the move toward data-driven warfare is the USA Army’s TITAN program, which uses AI-generated analytics to provide real-time intelligence on the battlefield.
Defense budgets are on the rise across North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region, and growth in demand for sophisticated military communication systems and services that can support highly secure, efficient, and resilient defense operations is expected.
Four types of military communication comprise the ISR segment, which is expected to hold a 58% share in 2025. Growth of this industry is expected to be fuelled by increasing need for intelligence gathering, surveillance and reconnaissance operations in real-time. Military forces are increasing ISR systems, SATCOM, and UAVs driven by common AI technologies.
The change to networked ISR capabilities can be demonstrated with programs like the Advanced Battle Management System (ABMS) for the USA Air Force and NATO’s Alliance Ground Surveillance (AGS) capability. These ISR efforts are also sustained by defense contractors like Lockheed Martin, Boeing, and General Dynamics, who are integrating 5G, big data analytics, and autonomous data systems to support ISR activities in virtually every corner of the globe.
Military forces utilizing sensor-based surveillance along with real-time battlefield data will boost the situational awareness segment to 42% revenue share by 2025. IoT-connected devices and AI for threat detection, as well as AR for command and control interfaces, are already influencing military decision-making.
Sensor fusion technology is at the forefront of companies like Raytheon Technologies and Northrop Grumman that are creating better battlefield operating pictures (BOP). Cloud systems like the USA Army’s TITAN and DARPA’s Mosaic Warfare allow forces to share far more data far more securely and rapidly.
With multi-domain operations (MDO) being the focus of defense strategies, ISR and situation awareness will continue to lead innovations in military communications and guarantee that battlefield-nominated responses are secure and rapid and can add critical value to the mission.
The industry is growing at a fast pace due to the factors such as a result of technology improvements in secure, high-speed, and multi-domain connectivity solutions.
Ground forces need hardened communication equipment with strong encryption standards for battlefield synchronization. Naval command is engaged in high-frequency, long-range, and satellite communication in order to maintain connectivity in vast oceanic spaces.
Air command is dedicated to low-latency, high-bandwidth, real-time communications networks in the case of mission-critical operations like coordinating drones and fighter aircraft. Mobile and space & cyber defense focus on secure, encrypted networks being used, along with threat detection by AI to avoid cyber warfare.
Special operations forces require stealthy, light, and highly mobile communications systems for tactical operations. Growing dependence on satellite communications, AI-based networks, and quantum encryption technologies is transforming the future of military communications to provide unimpeded, real-time data exchange in multi-theater operations.
Contract & Deals Analysis
| Company | Contract Value (USD Million) |
|---|---|
| Lockheed Martin | Approximately USD 120 - USD 130 |
| BAE Systems | Approximately USD 90 - USD 100 |
| Northrop Grumman | Approximately USD 110 - USD 120 |
| Raytheon Technologies | Approximately USD 80 - USD 90 |
Between 2020 to 2024, the industry grew slowly due to mounting defense expenditure, geo-political uncertainties, and advancements in secure communication technologies. Military units employed software-defined radios (SDRs), satellite communications, and encrypting tactical networks to improve real-time battlefield coordination and situation awareness.
Network security and protection of data improved by the use of AI-based signal processing and cybersecurity tools. The governments spent on the development of communications infrastructure by setting up HF radios, broadband tactical networks, and anti-jam technology to enable secure communications. Interference was caused by spectrum congestion, interoperability of the allied forces, and cyberattacks on the military network. Military communication between 2025 to 2035 will be transformed with network control based on artificial intelligence, quantum-proof encryption, and 6G-based tactical networks.
Autonomous vehicles and swarms of drones will employ low-latency, real-time communications to act in unison. Laser com and direct satellite communications will enable long-range, secure communications. Artificially intelligent signal processing and blockchain-encrypted messaging will verify data and exclude intrusions. Low-power wireless communications will minimize in-field mobility impairment and network robustness against an adversarial environment.
Secure, fast, and responsive communications will enhance military effectiveness and strategic impact.
Comparative Market Shift Analysis 2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Government agencies implemented tighter cybersecurity guidelines, demanding increased Correlates of Strength encryption techniques and safe communication protocols on military networks. | AI-powered threat intelligence and quantum-resistant encryption are compelled, providing safe, real-time military communication in adversarial environments. |
| Armed forces used SDRs to facilitate adaptable, multi-band, and interoperable communication among various military branches and allied nations. | AI-based SDRs with real-time frequency adjustment and autonomous self-healing networks improve secure communication on the battlefield, minimizing signal interference. |
| Military communication with AI assistance increased situational awareness through the automation of processing data from various sensors and communication channels. | Fully autonomous military communication networks use AI to predict threats, reroute transmissions dynamically, and ensure seamless connectivity in electronic warfare environments. |
| The military used SATCOM for global connectivity, encrypted data sharing, and real-time battlefield command. | Quantum communications, anti-jam low-latency, and laser-pumped AI-supported SATCOM enable strategic battle operations and global command networks. |
| Military tested 5G-networked battlefield communication for real-time sensor fusion, unmanned aerial vehicle communication, and command posts. | Tactical 6G networks powered by AI offer instantaneous, multi-domain connectivity between soldiers, unmanned platforms, and command centers. |
| The investments in EW technologies used to detect, jam, and counter adversary communications drove the need for strong military networks. | Cognitive EW systems based on AI detect, counter, and reconfigure military communication networks autonomously to counter sophisticated cyber and signal threats. |
| IoT-enabled military devices, including wearables and unmanned systems, | AI-integrated military IoT networks provide secure, predictive analytics for troop health monitoring, logistics optimization, and smart weapon system coordination. |
The industry of is critical for military operations, providing secure and real-time exchange of data. But high infrastructure costs, such as satellite networks, encryption technologies, and maintenance, represent financial constraints. Governments and defense contractors need to spend heavy budgets on maintaining secure, resilient, and strong communication networks for military use.
Cybersecurity risks are a key issue, with military communication systems being prime candidates for cyber-attacks, espionage, and electronic warfare. Unauthorized access, data compromise, and signal jamming can compromise national security. The use of end-to-end encryption, AI-based threat detection, and secure communication protocols is essential to address security vulnerabilities.
Technological obsolescence presents a challenge, as there are constant changes in communication technologies that necessitate updates. Old systems cannot be compatible with new networks, which creates integration challenges. Military organizations need to make investments in scalable and flexible communication systems to support interoperability between various platforms and operating environments seamlessly.
Military communications is spurred by regulatory and geopolitical factors. The government regulations, procurement procedures, and conformity to international defense accords influence the industry forces. Companies have to excel at coping with complex regulatory frameworks and in building strong collaborative relationships with defense agencies in pursuit of gaining industry presence and fulfilling international norms.
Supply chain disruptions, like shortfalls in semiconductor supplies and unavailability of important components, delay production and fielding of military communications systems. Geopolitics and protectionist trade measures elevate these risks even further. Domestic manufacturing capacity, diversification of suppliers, and strategic stockpiling of crucial components mitigate these supply chain exposures.
To ensure long-term success, defense agencies and industry participants need to emphasize cybersecurity, technology innovation, and regulatory adherence. Spending on AI-based encryption, satellite-based communications networks, and secure cloud-based systems will be essential for sustaining resilience and efficiency in the developing military communications sector.
| Countries | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 8.9% |
| UK | 8.5% |
| France | 8.3% |
| Germany | 8.4% |
| Italy | 8.1% |
| South Korea | 8.7% |
| Japan | 8.1% |
| China | 9.3% |
| Australia | 8.2% |
| New Zealand | 7.9% |
The industry is transforming by leaps and bounds not only driven by increasing defense spending but also the Pentagon's fascination with cyber warfare. Top defense players such as Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, and Northrop Grumman are driving the revolution in satellite communications (SATCOM), artificial intelligence-based signal processing, and fifth-generation secure networks. The Joint All-Domain Command as well as Control (JADC2) program is aimed at creating a joint warfighting environment that enhances real-time awareness of the battlefield and operational effectiveness.
Cyber security and secure communication networks are of immediate concern. Encrypted mobile phone communications, hypersonic weapons communications systems, and AI decision-making systems are well-funded by the USA government. The USA Department of Defense collaborates with the private sector to enable effective implementation of cutting-edge technology. High-end military-grade communications systems are in demand and are growing in measure to allow for real-time data sharing and tactical connectivity requirements.
The industry is evolving at a rapid rate with investments in secure battlefield networks, AI-driven threat detection, and cyber warfare. BAE Systems, a leading British defense contractor, is leading the way in enhancing the UK military's secure communication networks. The country's focus on the utilization of satellite-based surveillance and encrypted military networks adds to operational readiness.
NATO collaborations and mutual defense initiatives propel the advancement of secure, interoperable communications networks. The UK is developing quantum-secure communications technology to counter future cyber threats. The Ministry of Defence directly funds research into autonomous communication networks, offering coordination of land, air, and sea assets in a real-time manner. Additional advanced cybersecurity innovations augment the nation's military communications network.
Robust defense expenditure, high-grade satellite networks, and cybersecurity focus boost France's industry. Thales and Airbus are some of the top vendors that facilitate innovation in secure comms tech with advanced encrypted battlefield networks and real-time data communication for military actions. AI-powered analytics propel France's modernization efforts for command and control capabilities.
With its state-of-the-art defense technology infrastructure, France integrates software-defined radios and secure mobile communications in its military. The government's emphasis on space-based military communications allows for better situational awareness and battlefield coordination. Increased defense cooperation with European allies ensures that the latest technologies are integrated into secure military communication.
Germany's industry is in a state of rapid transformation as a result of NATO obligations and increased cyber security needs. Rheinmetall as well as Hensoldt are leaders in secure comms network development based on encrypted battlefield comms and high-end tactical radios. Germany's digital transformation agenda in the defense industry focuses on AI-based communication frameworks.
Germany also envisions mobile battlefield networks and satellite-encrypted communications to enhance operational readiness. Maintenance of cyber defense capability investments also reinforces Germany's military communication network to align with the evolving security benchmarks of NATO.
Italy's industry is expanding, and the nation is investing in secure military networks and battlefield communication based on AI. Companies like Leonardo are at the forefront of encrypting tactical communication and modernizing space-based defense networks. Digital transformation efforts are being given top priority in Italy to boost secure data interchange among its defense forces.
With increasing cybersecurity risks, Italy is emphasizing the development of quantum-secure communications and encrypted mobile networks. The Italian government is forging partnerships with European nations to improve interoperability in military communications. Leverage of advanced SATCOM solutions and AI-powered battlefield coordination guarantees enhanced operational effectiveness and mission efficiency.
The South Korean industry is expanding at a high rate, driven by geopolitics and the demand for tactical network security. Hanwha Systems and LIG Nex1, two of the leading defense manufacturers, are spearheading AI-based communication systems and secure satellite communications growth. The government is investing considerably in space-based defense communications in order to boost regional security.
South Korea is building its cyber security structure, embracing quantum encryption and artificial intelligence analysis in military networks. Digital battlefield modernization, the priority sector in the nation, provides information real-time sharing and enhanced command activity. Defense networks based on 5G further support South Korea's military communication infrastructure.
Japan's military communication is also evolving with increased satellite-based defense networks, and cyber and artificial intelligence-based communication for the battlefield. Mitsubishi Electric and NEC Corporation are in the lead in developing advanced encryption-based communications products in the Japanese industry. The country's government is eager for secure marine and airspace defense communications networks.
Japan's defense modernization is based on AI-empowered intelligence systems, secure mobile communications, and instant battlefield data sharing. With mounting cyber-attacks, Japan is reinforcing military communication networks with high-level encryption and automated threat detection software. Strategic partnerships with friendly nations boost Japan's defense communications standards.
China's industry is growing at a fast rate with huge investments in secure SATCOM networks, quantum encryption, and AI-driven defense communications. The national defense market of China is controlled by Huawei and China Electronics Technology Group (CETC), which create advanced encrypted networks and cyber warfare capabilities. China's strategic focus on network-centric warfare underlines its military communications infrastructure.
The government is also heavily investing in quantum communication for enhanced cybersecurity, protecting data transmission within defense operations. AI-driven command and control systems facilitate better battlefield coordination and decision-making capabilities. As the emphasis on cyber warfare continues to grow, China continues to research and develop sophisticated encrypted military-grade communication systems.
The industry in Australia is expanding with increasing defense modernization initiatives and secure satellite network development. BAE Systems Australia and EOS Defense Systems are leaders in the creation of the nation's encrypted military communication networks. AI-driven automation is an area of interest for the Australian Defense Force, as it requires secure real-time battlefield connectivity.
Australia is integrating cyber defense measures with its defense communications networks to purchase robust and secure communications networks. SATCOM solutions expansion enhances defense surveillance and operations capabilities. With the use of AI-based command and control systems, Australia is improving its defense communications capacity to cope with new security threats.
New Zealand's industry is evolving steadily along the lines of secure digitalization and cyber-defense improvements. It is making investments in secure satellite-based communications and artificial intelligence-based cybersecurity solutions for greater national security. Datacom and Tait Communications are the leading companies in creating secure defense communications platforms.
New Zealand's defense modernization plan prioritizes interoperability with allies to facilitate effective military communication during collaborative operations. More investment in quantum cryptography and AI-defense networks increases cybersecurity strength. New Zealand's need for encrypted mobile battlefield networks enhances the coordination and readiness of armies in real time.
The industry is growing at a high rate due to higher investments in defense modernization and investments in secure communications networks. Owing to the dynamic nature of security threats in the global situation, the military forces are becoming more interested in reliable and secure communications systems so as to allow effective coordination in advanced operating conditions. Satellite-based communications, AI-based cyber protection, and next-generation tactical radios are reshaping military connectivity by providing real-time situational awareness and enhancing mission success.
To address these emerging needs, defense contractors and IT companies are making highly secure high-speed data communication systems available for battlefield and command applications. Usage of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cyber security software is growing more potent for detecting and dealing with threats, and advances in software-defined radios (SDRs) are enhancing flexibility and inter-operability across nations that have allied with them. Cloud-based networks with security and quantum encryption technology are also being designed to improve data security and operations security.
The industry is a combination of battle-tested defense titans and tech giants, and that creates competition and drives innovation in military-level communication systems. Governments across the globe are heavily investing in procurement and research initiatives to develop their defense communication infrastructure. As digital warfare and electronic threats keep changing with evolving times, ongoing innovation in reliable, high-performance communication infrastructure will be a high-priority agenda for defense organizations.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| L3Harris Technologies | 20-25% |
| Northrop Grumman | 15-20% |
| Thales Group | 10-15% |
| BAE Systems | 8-12% |
| Raytheon Technologies | 5-10% |
| General Dynamics | 4-8% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 30-38% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| L3Harris Technologies | Secure tactical radios, satellite communications, and next-gen battlefield networks. |
| Northrop Grumman | Advanced satellite-based communication and cybersecurity solutions for military operations. |
| Thales Group | Encrypted military-grade communication systems and electronic warfare solutions. |
| BAE Systems | Secure voice and data transmission solutions, AI-powered military networking. |
| Raytheon Technologies | Secure broadband connectivity, integrated communication, and missile defense systems. |
| General Dynamics | Battlefield communication infrastructure, secure tactical networking solutions. |
Key Company Insights
L3Harris Technologies (20-25%)
L3Harris is the industry leader in the military communications segment with its secure tactical radios and battlefield connectivity products. The company is expanding its encrypted satellite communications and artificial intelligence-driven cybersecurity solutions to fortify defense communication networks.
Northrop Grumman (15-20%)
Northrop Grumman is an industry leader in satellite communication and secure military networking solutions. The company's focus on next-generation space-based military communication and artificial intelligence-driven systems serves to strengthen its industry leadership.
Thales Group (10-15%)
Thales deals in secure communications of military-grade, electronic warfare, and encrypted radios. It is in the process of constructing network security and cyber security for the defense sector on an AI foundation.
BAE Systems (8-12%)
BAE Systems provides cutting-edge network solutions to the armed forces with a special focus on voice and data secure transmission. Its AI-based military networking investment provides secure real-time communication within the battlefield perimeter.
Raytheon Technologies (5-10%)
Raytheon offers military operations high-speed broadband connectivity solutions. Its integrated defense communications and missile defense network capability contributes to its industry leadership.
General Dynamics (4-8%)
General Dynamics is an expert in battlefield communications infrastructure and tactical secure networking solutions. The company's recent success in next-generation communication systems contributes to military operational performance.
Other Key Players (30-38% Combined)
The industry is categorized into systems and services.
The industry supports intelligence, surveillance & reconnaissance (ISR), situational awareness, and command & control.
The industry serves the Air Force, Land Force, and Naval Force.
The industry spans North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South East Asia, China, Japan, and the Middle East & Africa.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Component, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Component, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Component, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
The industry is expected to generate USD 52.8 billion in revenue by 2025.
The industry is projected to reach USD 142.6 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 10.3%.
Key players include General Dynamics Corporation, Airbus S.A.S., QinetiQ Group PLC, BAE Systems PLC, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Rockwell Collins Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Raytheon Company, Thales Group, and Harris Corporation.
North America and Europe, driven by rising defense modernization programs, growing investments in satellite communication systems, and increasing demand for secure tactical networks.
Satellite communication (SATCOM) systems dominate due to their ability to provide secure, long-range, and real-time connectivity for defense operations and intelligence gathering.
Explore Telecommunication Insights

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.