The global overhead cables market is poised to grow from USD 77.84 billion in 2025 to USD 134.22 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 5.6%. This sustained growth is largely attributed to global infrastructure expansion, grid modernization initiatives, and the accelerated integration of renewable energy sources.
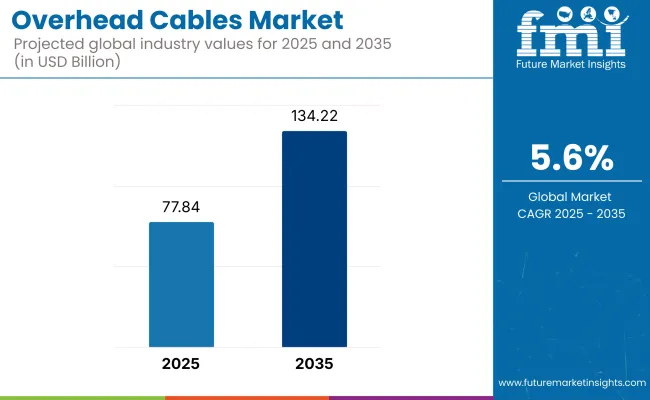
Countries like China and India dominate the demand curve due to rapid urbanization and massive electricity consumption, while mature economies such as the United States and Germany are channeling investments toward upgrading aging transmission networks. Among voltage types, high-voltage cables are set to witness the fastest growth due to their increasing use in long-distance transmission and renewable integration.
Multiple factors are driving the adoption of advanced overhead cable systems. Rising electricity demand from residential and industrial sectors, combined with the need to reduce transmission losses, is pushing utility operators to deploy high-capacity, low-loss conductors. Moreover, the integration of solar and wind energy into national grids demands cables that are both thermally efficient and environmentally robust.
Meanwhile, aluminum-alloy conductors are increasingly favored over traditional copper due to cost and weight advantages, especially in emerging economies. However, the industry continues to face challenges related to raw material price volatility, skilled labor shortages, and regulatory hurdles across regions.
Looking ahead, innovations in self-healing cables, real-time IoT diagnostics, and recyclable materials will reshape market dynamics. Smart grid deployment is expected to accelerate, particularly in North America and Western Europe, while rural electrification and grid decentralization are gaining traction in parts of Asia and Africa.
Strategic alliances, regional manufacturing hubs, and regulatory compliance will remain essential for long-term competitiveness. As countries pursue net-zero goals and energy security, the overhead cables sector is evolving from basic utility infrastructure into a critical enabler of next-gen energy systems.
Overhead cables are segmented into low, medium, and high voltage categories. While low-voltage cables are dominant in residential and suburban distribution, and medium-voltage ones serve commercial and industrial facilities, high-voltage cables are expected to see the fastest growth from 2025 to 2035.
This is due to their critical role in transmitting power across long distances, especially for utility-scale renewable energy projects and cross-border grid infrastructure. As solar and wind farms are typically located far from consumption centers, governments and utilities are investing heavily in high-voltage transmission lines to minimize energy loss and ensure stable delivery.
Moreover, ultra-high voltage (UHV) systems are gaining prominence in countries like China and the USA, further accelerating high-voltage cable deployment.
| Type Segment | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| High Voltage Cables | 6.3% |
Among residential, commercial, industrial, and utility applications, the utility segment holds the largest market share and is projected to expand the fastest over the next decade. This is driven by large-scale rural electrification programs, smart grid initiatives, and the need to integrate intermittent renewable energy sources.
As nations aim to modernize their transmission infrastructure and reduce dependency on fossil fuels, utility operators are prioritizing overhead cables that offer high capacity, reduced transmission loss, and remote monitoring capabilities. From microgrids in rural India to UHV lines in Germany, utility-scale upgrades are increasingly reliant on technologically advanced overhead cable systems.
| Application Segment | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Utility | 6.1% |
China is projected to dominate the global overhead cables market by 2035, fueled by vast infrastructure projects, smart grid rollout, and electrification across urban and rural zones. The country’s massive population and rapidly growing industrial base necessitate efficient, large-scale transmission networks.
Investments in UHV technology, government mandates for grid reliability, and expansion of cross-provincial renewable corridors further support this growth. Additionally, China’s strong domestic cable manufacturing ecosystem allows for rapid deployment and cost control, giving it a strategic advantage over other countries.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 7.0% |
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
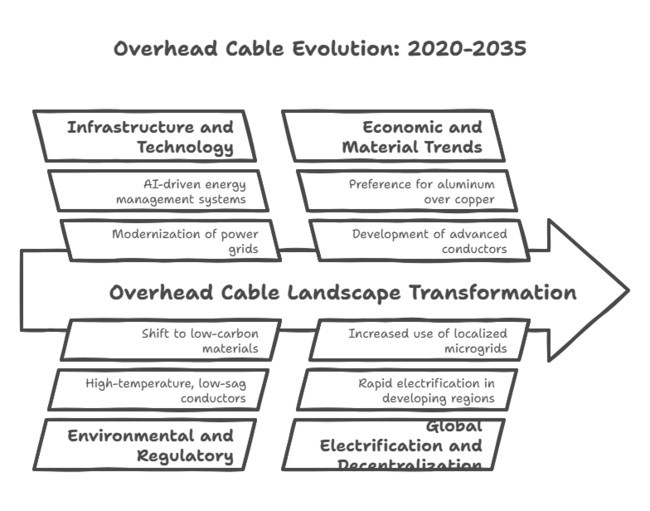
| Infrastructure Upgrades: Focus on modernizing aging power grids and expanding transmission networks. | Smart Grids & AI Integration: Adoption of AI-driven energy management systems and self-healing cables. |
| COVID-19 Impact: Initial disruptions in supply chains, followed by stimulus-driven infrastructure growth. | Digitalization & Automation: Increased deployment of sensor-embedded cables for real-time monitoring. |
| Renewable Energy Growth: Expansion of wind and solar power required enhanced transmission capabilities. | Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) Expansion: Growth in long-distance UHV transmission to support renewables. |
| Climate Resilience: Rising storms and wildfires led to increased demand for high-temperature, low-sag (HTLS) conductors. | Sustainability Focus: Shift to low-carbon, recyclable materials in cable production due to stricter regulations. |
| Material Shifts: Growing preference for aluminum over copper due to cost and weight advantages. | Higher Capacity Cables: Development of advanced conductors to support growing electricity demand. |
| Electrification in Developing Regions: Rapid expansion of power networks in Africa and Southeast Asia. | Grid Decentralization: Increased use of localized microgrids and distributed energy resources. |
Key Priorities of Stakeholders
Regional Variance
Adoption of Smart & Automated Overhead Cables
Material Preferences for Overhead Cables
Price Sensitivity & Cost Challenges
Supply Chain & Value Chain Challenges
Future Investment Priorities
Regulatory Landscape & Compliance Challenges
Conclusion: Regional Variance vs. Segment Consensus
| Regions | Key Policies & Regulations |
|---|---|
| United States |
Grid Modernization & Safety Compliance
|
| Western Europe |
Sustainability & Carbon Footprint Reduction
|
| Japan & South Korea |
Urban Infrastructure & Smart Grid Adoption
|
| Emerging Sectors |
Rural Electrification & Infrastructure Development
|
| United Kingdom |
Net Zero & Energy Transition Regulations
|
Major players in the overhead cables industry are competing fiercely on a combination of price strategies, technological advancements, strategic alliances, and internationalization. Some companies emphasize cost leadership which provides low-cost offerings to gain industry share, while others emphasize premium-quality, high-performance cables for cutting-edge grid applications.
Furthermore, key manufacturers are making alliances with utility providers, government agencies, and renewable energy companies to win large-scale infrastructure projects.
In order to sustain long-term growth, firms are using varied expansion strategies. Others are moving aggressively to increase their manufacturing presence in emerging economies such as India and other parts of Africa to address increasing electricity demand and take advantage of government-sponsored electrification initiatives. Others are pursuing mergers and acquisitions to build global reach and improve supply chain capacity.
Mergers and Acquisitions
Major Regulatory Actions
Product Launches and Partnerships
The segment for overhead cables is in the energy infrastructure and utilities industry, closely related to power transmission, telecommunications, and industrial electrification. It is influenced by global economic patterns, government policies, and technology.
With the shift towards renewable energy sources, the need for efficient and effective transmission infrastructure is on the rise. Massive investments in grid modernization, smart grids, and high-voltage power lines are driving industry growth, especially in developed economies such as the USA, Germany, and Japan.
From a macro standpoint, growing consumption of energy across emerging nations like India, China, and countries in Africa is driving infrastructure development, supplemented with government-sponsored electrification projects at the rural level.
Nonetheless, the industry contends with unpredictable fluctuations in raw materials, inflationary pressure, and distortions within worldwide supply chains affecting production cost structures. Besides this, trade rules and geo-strategic rivalries affect cross-national supply chains affecting pricing as well as the delivery of materials necessary for operations.
Overhead wires, which cover large distances, are critical for the transmission of electricity in urban, suburban, and rural locations. There are various types of cables available in the sector, such as low voltage, medium voltage, and high voltage cable types according to needs.
The United States is still investing in updating its outdated infrastructure, as it continues to be a country committed to innovation, which is driving demand for upgraded overhead cables. With a focus on sustainable energy solutions, the overhead cables sector is set to pave the way for a more resilient and interconnected electrical grid, lighting the path toward a greener future for the country.
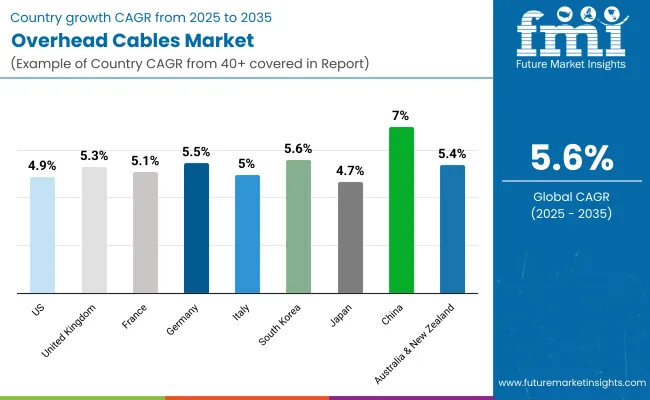
FMI projects that the United States overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 4.9% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The UK overhead cables sector is on the leading edge of technology and infrastructure. As a key enabler of efficient power transmission, the sector is pioneering renewables and sustainability. Most overhead cables are used in the same way that an underground cable would have been that they supply electricity to homes in cities and, in more rural areas, remote electricity supply.
High voltage, medium voltage, and low voltage CVT systems are among the several cable varieties that the industry covers, catering to the unique requirements of the UK's energy landscape. This emphasis on the need for infrastructure developed in a timely manner to avoid a shortage of adequate energy sources in the future.
FMI projects that the United Kingdom overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.3% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The overhead cables segment in France is part of a larger energy sector that has a strong dependence on nuclear energy and an expanding commitment to renewable energy. The transmission network that crisscrossed the country needs to be constantly upgraded to keep it efficient and reliable.
Increasing investments in smart grid technologies and interconnections with neighbouring countries are also improving cross-border electricity trade and grid stability. In line with French energy goals, where managing renewable energy sources on the grid is crucial, dynamic connections like overhead cables are needed to ensure a reliable and flexible energy supply.
FMI projects that the France overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.1% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Germany's energy transition, known as Energiewende, has significantly impacted the overhead cables industry. This transition away from fossil fuels and toward renewables such as wind and solar has resulted in a surge in demand for high-capacity transmission lines that tie generation locations, typically in the north, to industrial hubs in the south.
Since renewable energy generation becomes decentralized, it is important to widen and upgrade the transmission network. This has made it even more urgent to develop an efficient overhead cable infrastructure. Regulatory frameworks and public opposition to new transmission lines present challenges, requiring new solutions, including underground cabling in some areas.
FMI projects that the Germany overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.5% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The Italian overhead cables sector is shaped by the country's attempts to strengthen energy security and integrate renewable energy sources. The long peninsula and many islands make for special challenges in transmitting electricity around the country. Investments in high-voltage overhead cables and submarine cables are critical for regional interconnection and grid resilience.
Meanwhile, large interconnections with neighboring countries and other EU member states favor the exchange of energy between the Italian peninsula and European countries. Modernizing the transmission network, is crucial to handle the growing share of renewable energy and optimize the way energy flows across the country.
FMI projects that the Italy overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.0% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Rapid urbanization and industrialization in South Korea is driven by an increase in electricity demand, which is one of the factors responsible for the growing electricity supply created for the growth of the Overhead Cables segment in South Korea. A modern transmission infrastructure is needed in the country for smart grids and the integration of renewable energy.
Investment is also being made in high-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems, as well as expanding the transmission network to improve efficiency and decrease transmission losses. This not only coincides with South Korea's plans for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on foreign fossil energy but also with the construction of an overhead cable infrastructure which is widely spread the transition of energy to sustainability.
FMI projects that the South Korea overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.6% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The market for overhead cables in Japan is shaped by its specific geographical and seismic aspects. There is an essential requirement for transmission infrastructure that is reliable and disaster-resilient. Based on the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, Japan adjusted its energy mix to diversify, strengthening the share of the renewable energy source.
This shift requires enhancements to the transmission network to allow for more flux from variable energy inputs. To improve the longevity and performance of overhead cables, new materials and designs are being developed. Japan's dedication to technology and energy security fosters ongoing developments in its overhead cables sector, with investments in advanced materials, earthquake-resistant infrastructure, and high-temperature superconducting cables.
FMI projects that the Japan overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 4.7% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
As China's massive industrialization and infrastructure development have done, so has the country's overhead cables market. As the largest consumer of energy in the world, China has a massive population and a continually rising economy, making it an insatiable force behind the need for strong and high-efficiency overhead cable systems. It is a very mature, evolved field in the industry with global as well as domestic competition.
Overhead Cables in China Are Essential for Power Supply in Urban and Rural Areas, Ranging from High Voltage Transmission Lines to Low Voltage Distribution Networks. The Chinese overhead cables segment reflects the country's ambitious development plans and its commitment to driving progress and connectivity across its territories.
FMI projects that the China overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 7.0% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The sectors for overhead cables in Australia and New Zealand play a critical role in their strategies for modernizing energy infrastructure and incorporating renewable energy sources. Even though the two countries are on different ends of the scale in terms of geographic landscape and population density, they face unique challenges.
The long distances between urban centers and isolated communities in Australia require strong transmission networks. Investments in high-voltage transmission lines that can link renewable energy projects, like solar farms in the outback, to cities are critical.
FMI projects that the Australia and New Zealand overhead cables sales will grow at nearly 5.4% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Overhead cables market is expected to witness significant growth with rapid electrification, infrastructure upgrading, and transition to renewable energy. Countries and private sector actors are pouring money into the expansion of grids, especially in regions like Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Africa, where demand for reliable juice is increasing.
The expansion of smart grid technology also stimulates the need for more advanced, high-performance overhead cables with enhanced durability, efficiency, and real-time monitoring capabilities. The rise of renewables, including offshore wind farms and solar power plants, are also driving investments in high-voltage transmission lines. The rise of eco-friendly cables and recyclable materials is becoming a differentiator in competitive sectors sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions.
For the new companies, it has to be balanced in regards to cost, achievement and regional needs to penetrate the industry. Focusing on specialized segments such as developing lightweight, compact cables for cities or high-voltage solutions for renewable energy integration can create a competitive edge.
These contracts are essential for establishing partnerships with government agencies, energy utilities, and infrastructure developers. Furthermore, revision of supply chain through local manufacturing can also help in reduction of cost and boosting competitiveness in the sector. Compliance with regional safety and environmental regulations will therefore be among the key requirements for industry acceptance and long-term growth in mature sectors like the EU and North America.
Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, and High Voltage
Residential, Utility, Commercial, and Industrial
North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and The Middle East and Africa
He noted that factors such as increasing investment in renewable energy projects, urbanization, and modernization in the power infrastructure are fuelling demand for overhead cables.
Electricity Distribution and Transmission: For transmission and distribution of power, overhead cables are used extensively. They are also critical for industries like telecommunications, railways, construction, and manufacturing where they are the lifelines for power and data transmission.
Government safety, environmental, and efficiency regulations in the world influence material selection, design, and installation procedures. Standards such as IEC, IEEE, and various local safety regulations ensuring the reliability and longevity of overhead cable systems.
These innovations help in reducing environmental impact and increase the efficiency of overhead power lines. These updates enhance performance, durability and energy efficiency.
Infrastructure development and electrification projects are driving up demand in high-growth regions such as Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Overhead Crane Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Overhead Conductor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
HVDC Cables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Brake Cables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Aircraft cables Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Flexible Cables Market
Satellite Cables And Assemblies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Multicore Cables Market
Fire Rated Cables Market Trends - Demand, Innovations & Forecast 2025 to 2035
LASER Light Cables Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Single Core Cables Market
Fiber Optic Cables Market
Conventional Overhead Conductor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Temperature Overhead Conductor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power And Signal Cables Market
Mineral Insulated Cables Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Insulated Wires & Cables Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive Control Cables Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Power Transmission Cables Market
Submarine Optical Fiber Cables Market - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA