The Vans Market is estimated to be valued at USD 330.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 632.6 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% over the forecast period. Year-on-year growth remains steady across the forecast period, with absolute annual increases ranging from USD 22.2 billion to USD 39.7 billion. Early-stage growth, between 2025 and 2027, reflects moderate expansion, with yearly additions of around USD 22–24 billion. This aligns with baseline demand from logistics, e-commerce deliveries, and regional transportation. From 2028 onward, the annual gains increase consistently.
Between 2028 and 2030, the market adds over USD 31 billion, moving from USD 457.4 billion to USD 520.7 billion. By the final years, YoY gains reach nearly USD 40 billion, driven by electric van adoption, replacement of older fleet vehicles, and expansion in urban and intercity transport services. The YoY growth pattern is linear in absolute terms and shows no signs of contraction or volatility. Percentage-wise, the annual growth rate naturally tapers due to a growing base, yet the absolute dollar contribution rises each year. This structure confirms a stable and predictable growth trend, with consistent annual expansion driven by a mix of commercial demand, emission regulation compliance, and evolving transport needs across global markets.
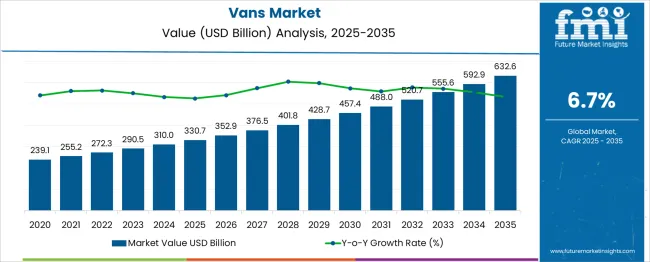
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vans Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 330.7 billion |
| Vans Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 632.6 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.7% |
The automotive vans market draws influence from five primary sectors. Around 35% of demand stems from commercial transport and delivery fleets, where cargo space, fuel efficiency, and uptime are prioritized. Passenger and multi-purpose vans account for about 25%, offering space and comfort for families, ride-share services, and airport transfers. Roughly 15% is driven by government and public fleet procurement, with vans used for law enforcement, postal services, and administrative logistics. Service-based sectors such as utilities, HVAC, and mobile repair represent another 15%, requiring custom-fit interiors for tools and equipment. The remaining 10% comes from last-mile delivery operators focused on urban mobility.
These combined segments determine product design, powertrain preference, and regional demand patterns across light commercial vehicle categories. Vans are light commercial vehicles designed primarily to carry cargo or multiple passengers through modular layouts and body configurations. Common types include panel vans with enclosed cargo areas ideal for trades and deliveries crew vans with an extra row of seating for mixed passenger cargo use passenger vans or minibuses seating between 8 and 15 people often used for shuttle and group transport Luton and box vans offering extended cargo volume over and behind the cab utility vans or mobile workshop conversions and camper or conversion vans equipped for leisure or specialized tasks Major manufacturers shaping the global van segment include Mercedes Benz with its Sprinter and Vito models Ford with the Transit and E Transit Volkswagen with Transporter, Crafter and the electric ID Buzz Hyundai, Stellantis and Nissan also play strong regional roles.
Current trends include electrification across panel van lines smart safety and ADAS integration connectivity features for fleet management modular vehicle architecture and growing demand in mobility, logistics and premium transport sectors especially in Europe North America and Asia Pacific.
The vans market is experiencing sustained growth as global logistics, urban mobility, and e-commerce sectors continue to expand rapidly. Increased demand for reliable last-mile delivery and business transport solutions has positioned vans as a core component of commercial fleet operations. Advancements in vehicle connectivity, safety technologies, and cost-efficient performance are driving adoption across both developed and emerging economies.
Infrastructural investments, especially in road networks and trade corridors, are also supporting wider deployment of vans across industries such as retail, healthcare, construction, and utility services. While the shift toward electric and sustainable transportation is underway, internal combustion engine models continue to dominate due to established fueling infrastructure and cost advantages.
Market participants are increasingly focused on optimizing fuel economy, driver comfort, and payload capacity to address evolving operational demands. Looking ahead, digital fleet management tools, vehicle automation, and emission compliance standards are expected to shape the future of the vans market and contribute to its ongoing expansion..
The vans market is segmented by vehicle, propulsion, size, end use, and geographic regions. The vehicle of vans is divided into Light commercial vans, Passenger vans, and Cargo vans. In terms of propulsion, the van market is classified into ICE, Electric, and Hybrid. Based on the size of the van market, it is segmented into Full-size, Mid-size, and Compact. The end use of the vans market is segmented into Logistics & transportation, E-commerce & retail, Public sector, Healthcare, Hospitality, and Others. Regionally, the vans industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
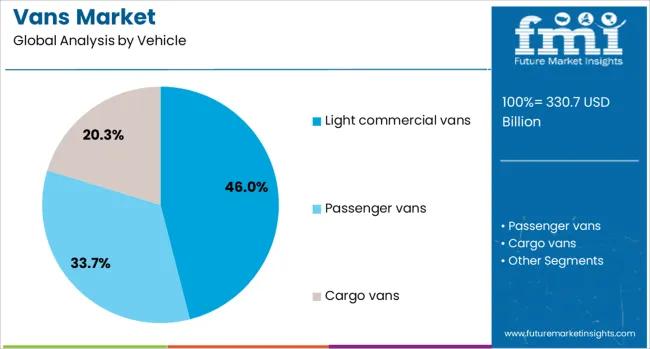
The light commercial vans segment is projected to hold 46% of the vans market revenue share in 2025, establishing it as the leading vehicle category. The increasing need for efficient and maneuverable transport solutions in urban and suburban areas has supported this segment's dominance.
Light commercial vans have been favored for their optimal balance between cargo space and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for delivery services, maintenance operations, and mobile businesses. Their lower operating costs and ease of parking have further enhanced adoption among small and medium-sized enterprises.
Manufacturers have continued to invest in upgrading cabin ergonomics, digital interfaces, and advanced driver-assistance systems to meet rising user expectations. As fleet operators prioritize quick turnaround, route flexibility, and regulatory compliance, light commercial vans have maintained a competitive edge due to their adaptability and cost-effective performance across diverse commercial applications..
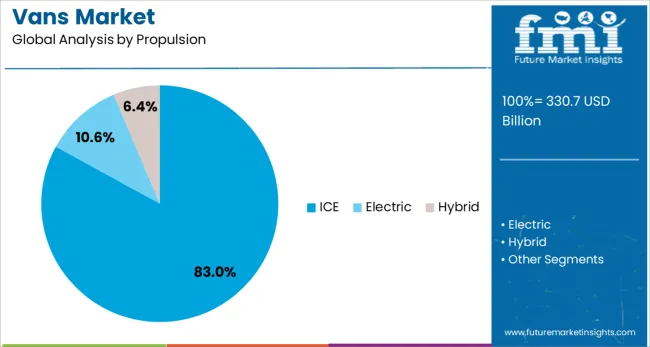
The internal combustion engine propulsion segment is expected to account for 83% of the vans market revenue share in 2025, confirming its position as the predominant propulsion type. Widespread infrastructure availability for refueling, lower upfront costs, and well-established maintenance networks have contributed significantly to the continued preference for ICE-powered vans.
Despite growing environmental awareness and policy incentives for electrification, many fleet operators have remained reliant on ICE vehicles for their longer range, payload capacity, and suitability for heavy-duty and high-mileage operations. Global oil market stability and improvements in combustion efficiency have also strengthened the operational value proposition of ICE vans.
This segment has further benefited from regional differences in emission regulations and the phased rollout of zero-emission zones. As manufacturers continue to enhance fuel economy and emission controls, ICE propulsion is projected to retain substantial market share over the near term, particularly in regions with slower EV infrastructure development..
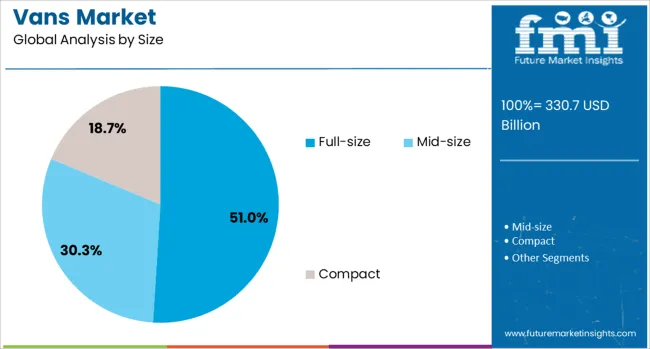
The full-size vans segment is projected to contribute 51% to the total vans market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the leading size category. This segment's growth has been driven by the demand for higher payload capacity, larger interior volume, and versatile configurations suitable for both cargo and passenger transport.
Full size vans have been increasingly adopted by logistics providers, fleet operators, and utility companies due to their robust chassis and durability in high-utilization environments. Enhanced comfort features, digital integration, and customizable layouts have made full-size vans attractive for applications ranging from mobile workshops to shuttle services.
Their capability to support a wide range of commercial functions has made them a preferred option for industries requiring dependable, high-capacity transport. Additionally, full-size models offer enhanced engine power and axle support, which are essential for long-haul and heavy-duty use cases, further solidifying their dominant role within the overall market..
Vans are being used as core fleet assets across courier, healthcare, municipal, and construction sectors, with uptake growing in alignment with short-haul logistics and urban utility demand. Their share within global light commercial vehicle (LCV) fleets has expanded due to increased model versatility, modular builds, and reduced operating costs. In Europe, vans accounted for the largest portion of commercial vehicle registrations, with similar patterns observed in the Asia Pacific and North America. Market growth has also been supported by increasing cross-border leasing for small businesses, higher asset turnover rates, and bulk orders from e-commerce logistics providers.
Last-mile fulfillment and city-centric deliveries are pushing van fleets into rapid scaling, especially in markets where urban warehousing, food delivery, and consumer electronics distribution have intensified. In 2024, 51 % of new city delivery fleets in Europe were made up of vans under 3.5 tons. South Korea, Germany, and Canada reported a 37 % surge in van demand from express logistics, while high-roof, short-wheelbase formats were favored by grocery fulfillment operators. SME-led micro-distribution networks in India and Brazil are replacing two-wheelers and three-wheelers with vans to reduce per-shipment unit costs. Fleet adaptability, better vehicle uptime, and route optimization compatibility have accelerated order conversions, especially in Tier 1 cities where fixed-route consistency and real-time tracking are being standardized by service aggregators.
The electric van segment is constrained by cost, weight, and range limitations, despite regulatory support. Average electric van prices remain 21 % higher than diesel models, discouraging uptake among price-sensitive operators. In the United States and Australia, 41 % of pilot deployments recorded payload inefficiencies due to heavy battery packs. Additionally, residual value uncertainty has reduced leasing activity by 19 % for electric LCVs across Latin America. Infrastructure issues persist, with only 1.5 public chargers per 10 vans in suburban zones. Operational planning is also impacted by long charge cycles and battery degradation risk, especially under refrigeration or incline-heavy loads. As a result, over 65 % of active SMEs in Southeast Asia continue to prefer fuel-powered vans for daily city and intercity routes.
Vehicle manufacturers are accelerating development of shared EV platforms for van manufacturing. Flexible electric chassis are being adopted in 37 % of new van models in Japan and South Korea to reduce retooling costs and offer more body-type flexibility. European firms are entering cooperative ventures with regional Tier-1 suppliers and battery integrators to offset certification and CAPEX barriers. These shared programs have reduced unit production cost by up to 18 %, boosting launch viability for electric vans under 3.5 tons. India’s fiscal leasing push for electric LCVs has seen trial uptake by food and medical logistics players, particularly in Delhi and Bangalore. Cloud-based diagnostics, predictive maintenance protocols, and preconfigured cargo utilities are being integrated into modular offerings to improve vehicle retention.
Smart telematics is being installed in 35 % of new van deliveries across Europe and South Korea. Routing software integration is already active in over 62 % of e-commerce van fleets in Canada, Mexico, and Germany. This data-driven fleet control has reduced average delivery delays by 12 % and improved asset tracking across metro service areas. In parallel, lightweighting is being addressed via aluminum structural frames and composite panels, which now feature in 24 % of newly manufactured vans. Load-optimized refrigeration and temperature-stabilized cabin configurations are gaining demand in pharma and perishable goods distribution, especially in Malaysia and Poland. Cargo customization and modular interiors are becoming standard as buyers prioritize ROI on per-kilometer costs and need high-frequency rotation within multi-client contract logistics.
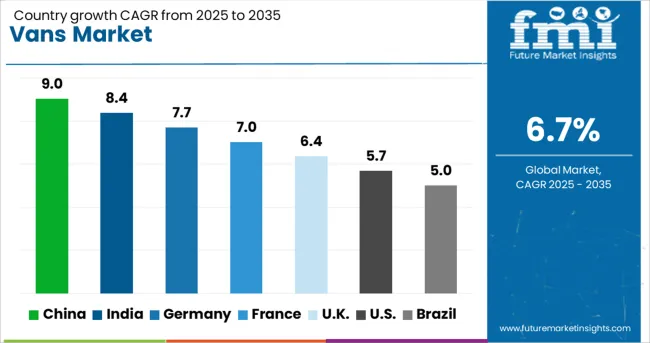
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 9.0% |
| India | 8.4% |
| Germany | 7.7% |
| France | 7.0% |
| UK | 6.4% |
| USA | 5.7% |
| Brazil | 5.0% |
The global automotive van market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% between 2025 and 2035. China leads with a 9.0% CAGR, driven by the shift to electric light commercial vehicles and growth in logistics services. India follows at 8.4%, propelled by rising demand for multi-purpose vehicles in both goods and passenger transport. Germany registers 7.7%, where modernization of urban delivery fleets and growing e-commerce contribute to market expansion. The UK records 6.4%, closely aligned with the global average, while the US grows at 5.7%, influenced by steady commercial fleet renewals. The report covers 40+ countries in total, with the top five countries included here to illustrate regional growth variations.
China maintained a dominant position in the global vans market in 2025 due to the rapid scale-up of urban logistics and intercity parcel services. Local OEMs such as SAIC Maxus and Dongfeng introduced flexible van platforms optimized for last-mile delivery, refrigeration, and utility use. The rising demand from e-commerce and express delivery firms, coupled with municipal fleet electrification policies, spurred widespread electric van adoption. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology facilitated volume production through funding and strategic partnerships. As battery supply chains matured, EV van prices reduced across commercial categories. Government pilot programs in major cities also tested AI-powered route optimization systems in electric delivery vans, accelerating digital integration into vehicle management.
India’s vans market grew steadily in 2025 as MSMEs and urban logistics operators expanded their reliance on light commercial vans. Tata Motors and Mahindra introduced electric variants targeting affordable leasing in top metros. Van utilization rose in intra-city logistics, hyperlocal deliveries, and SME-owned service fleets. The availability of road-ready electric vans under ₹15 lakh, along with expanded charging infrastructure in industrial parks, supported adoption. The government’s FAME-II extension further incentivized purchases through direct subsidies and tax rebates. Market participation increased from new EV startups in southern and western regions. Distribution and FMCG supply chains in Tier-2 cities turned to vans for efficiency, particularly for routes under 150 km.
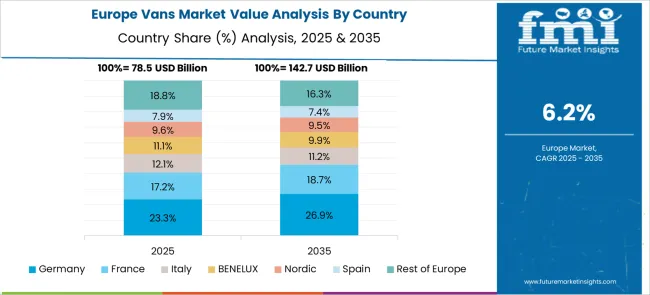
Germany’s van market performance was supported by a national emphasis on low-emission vehicles and efficient city logistics systems. Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, and Opel developed premium electric van models integrated with ADAS and connected vehicle platforms. In Berlin and Munich, city fleets prioritized fleet decarbonization, replacing diesel vans with electric alternatives via structured procurement tenders. EU fleet emission caps and carbon trading mechanisms further pushed logistics operators to opt for electric vans. Auto manufacturers aligned van production with EU Green Deal targets, scaling modular vehicle platforms for logistics and utility fleets. Charging infrastructure was upgraded in key freight corridors linking urban retail and warehousing hubs.
The UK market saw consistent demand for electric and hybrid vans in 2025, largely driven by business compliance with city emission rules and fleet decarbonization goals. Fleet managers favored leasing options to reduce upfront EV costs, with Stellantis and Ford offering van-as-a-service models for urban delivery and mobile trade professionals. Clean air zones in London, Birmingham, and Glasgow directly influenced van replacement cycles. EV adoption was also driven by government grants and congestion charge exemptions. Smaller logistics players and tradespeople adopted electric vans to maintain service access in low-emission zones, with charging networks being densified at depots and service stations across metropolitan areas.
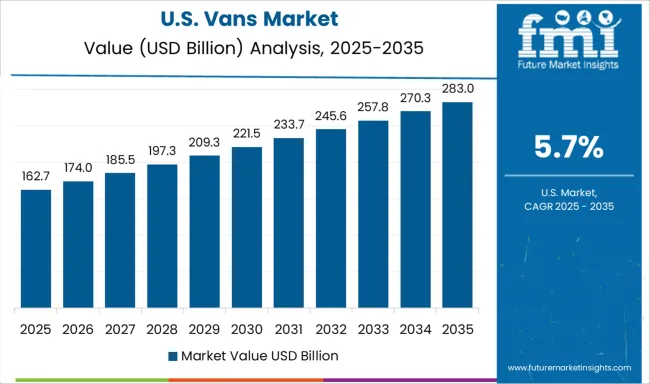
The United States vans market recorded stable growth in 2025, supported by large fleet operators initiating EV adoption across regional hubs. Rivian, GM, and Ford collaborated with logistics companies to introduce electric van pilots in California, Texas, and New York. Despite slower infrastructure expansion, government incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act enabled tax credits for commercial electric vehicle procurement. Fleets used data from trials to plan scaling strategies over a 5-year horizon. Rural and suburban demand remained dependent on internal combustion models, though urban operators began phasing in electric variants due to cost optimization and emission compliance.
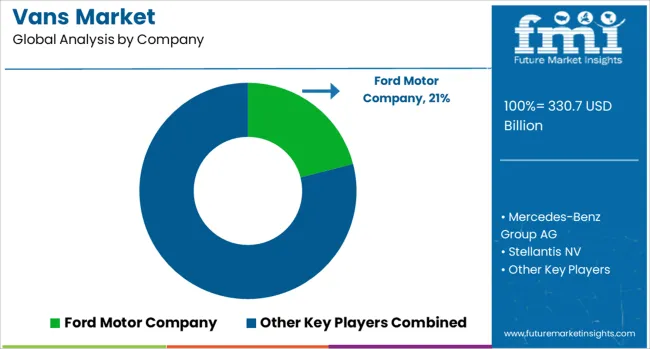
The vans market features manufacturers offering light commercial vehicles for cargo, passenger transport, and last-mile delivery services. Ford Motor Company leads with the Transit range, which is widely used in urban logistics and customizable for fleet operations. Mercedes-Benz Group AG supplies the Sprinter and Vito series, focusing on modular interiors, safety systems, and compatibility with electrified drivetrains. Stellantis NV, through brands like Peugeot, Citroën, Fiat, and Opel, provides compact and mid-size vans suited for regional transport and commercial utility across European and global markets. Toyota Motor Corporation produces vans such as the HiAce, targeting reliability in both commercial and shuttle configurations, with strong uptake in Asia-Pacific and Middle Eastern regions.
Renault Group offers the Kangoo and Master lines, designed for small business needs and available in electric variants to meet urban emission standards. Volkswagen AG markets the Transporter and Crafter vans, with configurable options for cargo, passenger, and specialized conversions, supported by digital fleet management tools. Market leadership is defined by payload capacity, fuel type flexibility, service networks, and integration of navigation, telematics, and advanced driver-assist features tailored for business use cases.
Between 2023 and 2025, the vans segment within the automobile industry shifted toward electrification, modularity, and fleet-based solutions. Ford expanded its E-Transit line across Europe and North America, targeting commercial logistics and municipal fleets. Mercedes-Benz rolled out the next-gen eSprinter in 2024, featuring customizable battery options and integrated telematics.
Rivian introduced pilot electric delivery vans beyond its Amazon deal, signaling intent to enter third-party fleet sales. In China, SAIC and BYD scaled production of electric vans for last-mile logistics. Lightweight chassis design, enhanced cargo flexibility, and software-defined fleet management platforms became central to market differentiation. Regional demand skewed toward urban logistics, cold chain transport, and electric utility conversions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 330.7 Billion |
| Vehicle | Light commercial vans, Passenger vans, and Cargo vans |
| Propulsion | ICE, Electric, and Hybrid |
| Size | Full-size, Mid-size, and Compact |
| End Use | Logistics & transportation, Ecommerce & retail, Public sector, Healthcare, Hospitality, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Ford Motor Company, Mercedes-Benz Group AG, Stellantis NV, Toyota Motor Corporation, Renault Group, and Volkswagen AG |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by vehicle type (cargo, passenger, electric/hybrid vans) and end-use (logistics, commercial, passenger transport), demand fueled by e commerce, urbanization and fleet electrification, led by Asia Pacific (~45%) with North America (~32%) catching up, innovation in EV propulsion, connected telematics, modular cargo designs. |
The global vans market is estimated to be valued at USD 330.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the vans market is projected to reach USD 632.6 billion by 2035.
The vans market is expected to grow at a 6.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in vans market are light commercial vans, passenger vans and cargo vans.
In terms of propulsion, ice segment to command 83.0% share in the vans market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Caravans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Cube Vans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mini Vans Market
Cargo Vans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Refrigerated Vans Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA