The electric vans market is estimated to be valued at USD 18.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 79.5 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.5% over the forecast period. The primary cost components in the value chain are the battery pack, electric drivetrain, vehicle chassis, and electronic control systems. Battery packs represent the largest share of production costs, accounting for a significant proportion of the total value due to the high expense of lithium-ion cells and associated thermal management systems.
Economies of scale in battery manufacturing and improvements in energy density contribute to gradual cost reductions, supporting market expansion from USD 18.8 billion in 2025 to USD 33.5 billion by 2029. Electric drivetrains, including motors and power electronics, constitute the second-largest cost element. Technological enhancements in motor efficiency and inverter design lower operational costs and enhance vehicle performance, enabling incremental market growth over the forecast period. Chassis and vehicle assembly costs remain relatively stable, while software integration for fleet management and route optimization adds a growing proportion to total expenditures. The downstream value chain involves distribution, after-sales service, and charging infrastructure deployment.
Service and maintenance networks, along with fleet electrification partnerships, contribute to incremental value capture, particularly in logistics and commercial applications. By 2035, these combined cost and value-chain dynamics underpin a market size of USD 79.5 billion, reflecting both technological optimization and strategic supply-chain management as critical factors driving profitability and adoption across global regions.
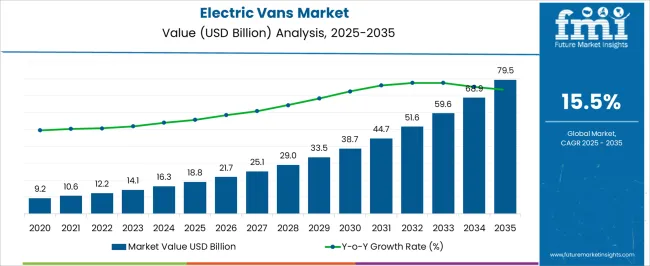
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Electric Vans Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 18.8 billion |
| Electric Vans Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 79.5 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 15.5% |
The electric vans market represents a specialized segment within the global commercial electric vehicle industry, emphasizing sustainability, efficiency, and last-mile delivery solutions. Within the broader electric vehicle sector, it accounts for about 6.3%, driven by rising demand from urban logistics, e-commerce, and fleet operators. In the commercial vehicle and light-duty transport segment, its share is approximately 5.8%, reflecting adoption for goods transport, service vehicles, and municipal operations.
Across the urban mobility and last-mile delivery market, it holds around 5.0%, supporting reduced emissions and operational cost optimization. Within the electric drivetrain and battery technology sector, it represents 4.5%, highlighting integration of high-efficiency motors, regenerative braking, and smart energy management. In the fleet management and commercial transportation solutions category, the market contributes about 3.9%, emphasizing connectivity, telematics, and route optimization for operators. Recent developments in the market have focused on battery efficiency, range extension, and fleet integration. Innovations include high-capacity lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, lightweight chassis, and energy recovery systems to enhance driving range and payload efficiency.
Key players are collaborating with logistics companies, fleet operators, and charging infrastructure providers to accelerate adoption and reduce operational costs. Adoption of modular vehicle platforms, telematics-enabled fleet management, and fast-charging solutions is gaining traction to improve utilization and operational efficiency. The incentives, government policies, and urban emission regulations are driving investment in electric vans for both public and private sector fleets.
The electric vans market is witnessing accelerated expansion, supported by the global push toward decarbonization and the widespread electrification of urban and regional transport fleets. Growing regulatory mandates targeting emissions reductions and the phasing out of internal combustion engine vehicles are encouraging fleet operators to adopt zero-emission alternatives. Technological advancements in battery energy density, coupled with declining battery costs, are making electric vans increasingly viable across various applications.
Infrastructure investments in fast-charging networks and government-backed incentives for commercial electric vehicle adoption are reinforcing market growth. Fleet operators in logistics, e-commerce, and municipal services are recognizing the total cost of ownership benefits of electric vans, especially in urban environments with high stop-and-go usage.
OEMs are also expanding their model range and production capacity to meet rising demand across light and medium-duty segments. As clean transportation becomes a global priority and electrification strategies gain momentum, electric vans are expected to become a cornerstone of last-mile and regional delivery solutions, paving the way for continued market expansion through the next decade.
The electric vans market is segmented by propulsion, range, vehicle type, battery type, and geographic regions. By propulsion, electric vans market is divided into BEV, HEV, FCEV, and PHEV. In terms of range, electric vans market is classified into Above 200 miles, Upto 100 miles, and 100 to 200 miles. Based on vehicle type, electric vans market is segmented into Commercial vehicle and Passenger vehicle.
By battery type, electric vans market is segmented into Lithium Ion, Sealed Lead Acid, and Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH). Regionally, the electric vans industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
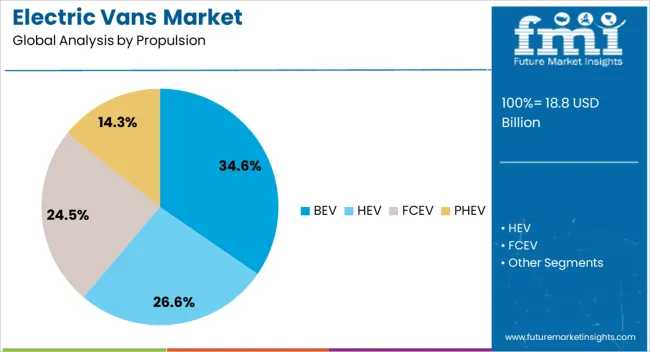
The battery electric vehicle propulsion segment is projected to account for 34.6% of the electric vans market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading propulsion type. This dominance is being driven by growing demand for fully zero-emission vehicles, supported by increasingly stringent emission standards across key regions such as Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. The absence of an internal combustion engine in BEVs simplifies vehicle architecture, reducing mechanical complexity and operational maintenance costs.
Fleet operators are prioritizing BEVs for their long-term cost savings, supported by lower fueling expenses and minimal servicing requirements. Governments and local municipalities are offering incentives, subsidies, and access to zero-emission zones, further increasing the attractiveness of BEV adoption.
Enhanced battery technologies and improvements in charging infrastructure have addressed earlier concerns related to range and downtime. As commercial and utility fleets align their operations with net-zero targets, the BEV segment is anticipated to experience consistent growth, benefiting from favorable policies and the growing preference for clean transportation solutions in high-utilization urban and regional delivery environments.
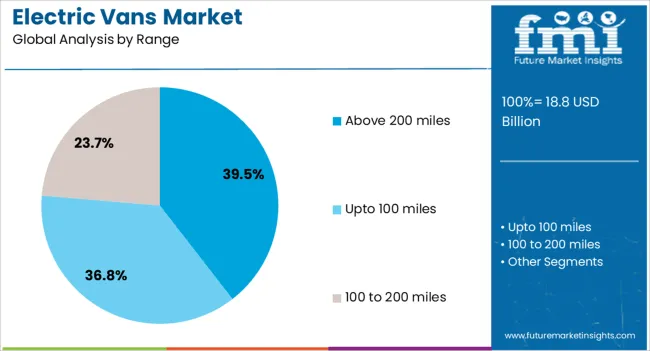
The above 200 miles range segment is anticipated to contribute 39.5% of the electric vans market revenue share in 2025, making it the most preferred range category. This leadership is being supported by improvements in lithium-ion and solid-state battery technologies, which have significantly increased energy density and allowed for longer driving ranges without compromising payload capacity. Fleet managers and logistics operators are increasingly favoring vehicles that can cover extended routes on a single charge, reducing reliance on frequent charging stops and maximizing daily operational efficiency.
The ability to service suburban and intercity delivery zones with a single full charge is driving preference for this range category. Technological developments in powertrain efficiency, regenerative braking systems, and thermal management solutions are further enhancing range performance.
As e-commerce expands and demand for reliable last-mile and regional delivery increases, electric vans capable of traveling over 200 miles are being seen as more versatile and cost-efficient options. The segment’s continued growth is expected to be supported by strategic fleet electrification plans across various industries.
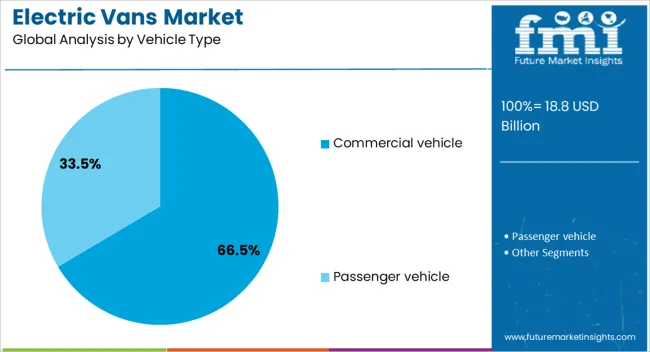
The commercial vehicle segment is expected to account for 66.5% of the electric vans market revenue share in 2025, establishing itself as the dominant vehicle type. This segment’s leadership is being driven by increasing electrification of delivery fleets, transportation services, and utility vehicles in response to environmental regulations and rising fuel costs. Businesses operating in logistics, courier services, and municipal fleets are increasingly shifting toward electric commercial vans to reduce emissions and improve operational efficiency.
The availability of various load capacities, adaptable chassis configurations, and extended driving ranges is supporting deployment across diverse commercial applications. Additionally, government procurement programs and public-private partnerships focused on clean fleet transitions are reinforcing adoption.
The total cost of ownership benefits, especially when combined with subsidies and lower maintenance expenses, are further motivating fleet operators to transition to electric models. As global cities continue to implement low-emission zones and encourage sustainable urban transport, the demand for electric commercial vans is expected to rise steadily, positioning this segment for sustained dominance in the market.
The electric vans market has experienced substantial growth driven by the increasing demand for low-emission commercial vehicles, urban delivery solutions, and fleet electrification initiatives. Electric vans provide zero tailpipe emissions, lower operational costs, and reduced maintenance compared to conventional diesel and gasoline-powered vehicles. Governments worldwide are promoting electric commercial fleets through incentives, tax rebates, and urban access regulations.
The rise of eCommerce, last-mile delivery services, and cold chain logistics has intensified demand for electric vans capable of reliable, high-frequency operation. Technological advancements in battery energy density, motor efficiency, and vehicle telematics have enhanced range, payload capacity, and fleet management capabilities. However, high upfront costs, charging infrastructure limitations, and battery degradation remain challenges, encouraging manufacturers to develop cost-effective solutions, modular designs, and efficient energy storage systems.
The adoption of electric vans is strongly influenced by government policies, incentives, and emission regulations. Urban low-emission zones, subsidies for electric fleet purchases, and tax benefits reduce the total cost of ownership for businesses. Many municipalities mandate stricter emission standards for commercial fleets, encouraging fleet operators to transition from diesel-powered vans. Funding for charging infrastructure expansion further supports market penetration. Commercial operators leverage these regulatory frameworks to lower operational expenses and improve corporate sustainability profiles. Additionally, regulatory emphasis on greenhouse gas reduction and air quality improvement has prompted collaborations between vehicle manufacturers, logistics companies, and governments to accelerate the adoption of electric vans for urban deliveries, last-mile logistics, and service fleets.
Battery and charging technology developments are central to the performance and appeal of electric vans. High-energy-density lithium-ion and solid-state batteries allow extended driving ranges while maintaining payload capacity. Fast-charging solutions reduce downtime and enable continuous fleet operation. Battery management systems and regenerative braking technology enhance efficiency and extend service life. Manufacturers are also exploring modular battery designs for easier replacement and upgrade. These technological improvements support longer delivery routes, urban logistics, and specialized applications such as refrigerated transport. Combined with telematics and route optimization software, battery innovations have enhanced operational efficiency, reliability, and overall lifecycle performance, making electric vans viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion vehicles in commercial fleets.
The expansion of e-commerce has significantly increased demand for electric vans in last-mile delivery operations. Rapid urbanization and changing consumer shopping patterns require efficient, environmentally friendly delivery solutions. Electric vans provide quiet operation and zero emissions, enabling access to urban centers with strict environmental regulations. Fleet operators benefit from lower fuel and maintenance costs, as well as government incentives supporting electrification. Specialized configurations, including cargo optimization, refrigerated units, and lightweight materials, enhance utility for diverse delivery applications. Logistics companies are deploying electric vans to optimize route efficiency, reduce carbon footprint, and improve sustainability reporting. This trend is expected to sustain market momentum across multiple urban and regional logistics networks.
Despite promising growth, the electric vans market faces challenges related to high upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure, and battery lifespan concerns. Acquisition costs remain higher than conventional vehicles, deterring some fleet operators. Uneven charging network distribution can limit route flexibility, particularly for long-haul operations. Battery degradation over time affects range and replacement costs, impacting the total cost of ownership. Manufacturers and policymakers are addressing these constraints through investment in fast-charging networks, battery leasing models, and modular designs that facilitate upgrades and replacements. Education and awareness initiatives regarding operational cost savings, environmental benefits, and performance reliability are essential to accelerate adoption and overcome infrastructural limitations.
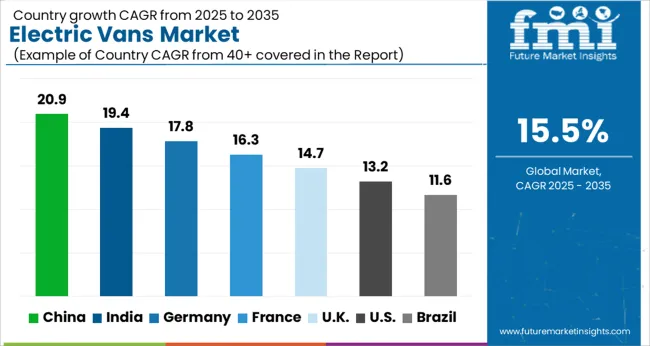
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 20.9% |
| India | 19.4% |
| Germany | 17.8% |
| France | 16.3% |
| UK | 14.7% |
| USA | 13.2% |
| Brazil | 11.6% |
The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.5% from 2025 to 2035. Germany reached 17.8%, supported by rising adoption of electric commercial vehicles and infrastructure expansion. China led with 20.9%, driven by extensive manufacturing capabilities and government incentives for zero-emission transport. India recorded 19.4%, reflecting growing urban logistics electrification and domestic EV production. The United Kingdom reached 14.7%, supported by fleet modernization initiatives and charging infrastructure development. The United States recorded 13.2%, reflecting steady integration of electric vans in commercial fleets. These regions are actively scaling, engineering, and innovating in the market. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
China is projected to grow at a CAGR of 20.9%, driven by the rapid adoption of commercial electric fleets for last-mile delivery, logistics, and urban transportation. Adoption is reinforced by government subsidies, favorable policies for new energy vehicles, and expansion of charging infrastructure in urban centers. Domestic manufacturers focus on high-capacity battery systems, energy efficiency, and connectivity features to optimize fleet operations. Integration with telematics and route management software enhances operational efficiency and reduces total cost of ownership.
India is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19.4%, supported by increasing e-commerce and urban delivery services, government incentives for electric commercial vehicles, and expanding charging networks. Adoption is reinforced by demand for low operating cost, zero-emission, and high-efficiency vans for last-mile logistics. Manufacturers are introducing electric vans with improved battery life, cargo space, and telematics integration to attract fleet operators and SMEs.
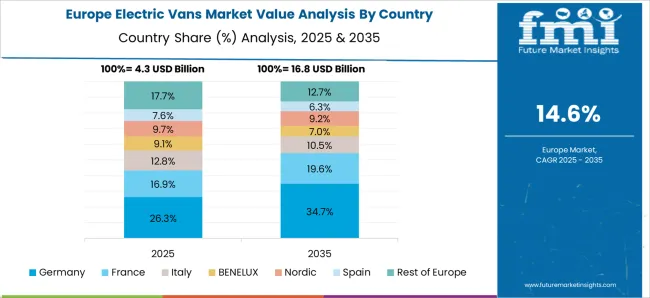
Germany is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 17.8%, driven by stringent emissions regulations, demand for sustainable commercial fleets, and rising e-commerce delivery volumes. Adoption is reinforced by electric vans offering high payload capacity, long range, and advanced telematics. Fleet operators and logistics companies prioritize operational efficiency, reduced fuel costs, and compliance with EU low emission zones.
The United Kingdom is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.7%, supported by increasing demand for electric commercial vehicles, government incentives, and emissions regulations. Adoption is reinforced by fleet operators prioritizing zero emission solutions for urban deliveries and light transport. Manufacturers emphasize high energy density batteries, payload optimization, and integration with fleet management systems to improve efficiency and reliability.
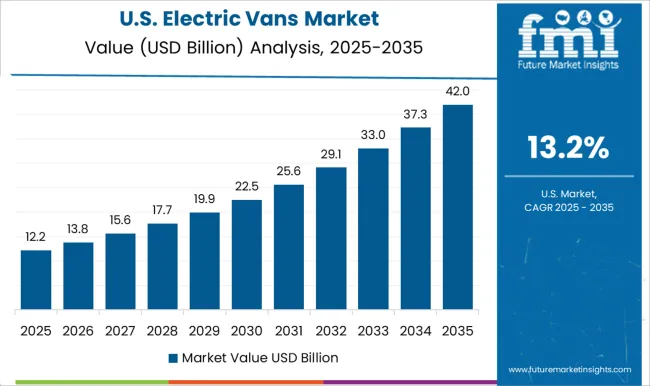
The United States is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2%, driven by adoption of electric commercial vehicles in logistics, courier services, and utility operations. Demand is reinforced by rising fuel costs, environmental regulations, and expansion of electric charging infrastructure. Manufacturers focus on energy efficient battery packs, telematics integration, and payload optimization for fleet operators. Growth is supported by increasing partnerships between EV manufacturers and delivery service providers.
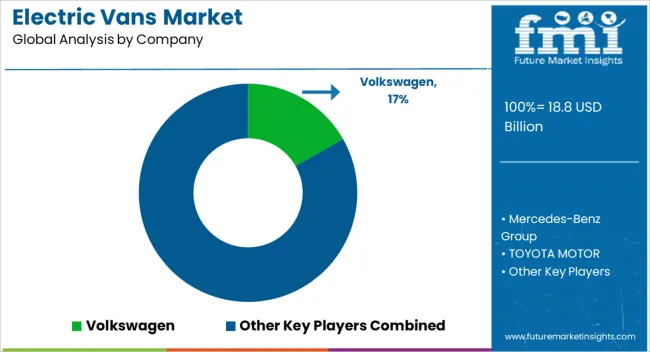
The market features a mix of established automotive giants, regional manufacturers, and innovative EV startups, focusing on commercial, logistics, and urban transport solutions. Global legacy automakers include Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz Group, Toyota Motor, Nissan Motor, Renault, Stellantis, Ford, General Motors, Hyundai, and Kia, offering a range of electric vans with high reliability, brand recognition, and global service networks.
These players emphasize battery efficiency, range, connectivity, and fleet management solutions. EV-focused newcomers and innovators such as Rivian Automotive, Arrival, Canoo, Bollinger Motors, Workhorse Group, Xos Trucks, Lordstown Motors, BYD, Maxus (SAIC Motor), and Dongfeng Motor provide modular designs, lightweight platforms, and advanced electric drivetrains targeted at urban delivery, last-mile logistics, and specialty commercial transport.
Tier-2 regional manufacturers and OEM collaborators include Mahindra Electric, Changan Automobile, Foton Motor, BAIC Motor, JAC Motors, Fuso (Daimler Truck), Groupe PSA Vans, and Nikola Corporation, supporting market penetration in Asia, Europe, and North America. Competition is shaped by battery technology, payload capacity, charging infrastructure, total cost of ownership, and fleet connectivity solutions, making both traditional automakers and EV startups critical in driving adoption and innovation.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 18.8 Billion |
| Propulsion | BEV, HEV, FCEV, and PHEV |
| Range | Above 200 miles, Upto 100 miles, and 100 to 200 miles |
| Vehicle Type | Commercial vehicle and Passenger vehicle |
| Battery Type | Lithium Ion, Sealed Lead Acid, and Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz Group, TOYOTA MOTOR, Renault, Nissan Motor, Stellantis, Rivian Automotive, Arrival, Canoo, and Bollinger Motors |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by van type and application, demand dynamics across last-mile delivery, passenger transport, and commercial fleets, regional trends in electric mobility adoption, innovation in battery efficiency, load capacity, and connectivity, environmental impact of reduced emissions and energy consumption, and emerging use cases in urban logistics, shared mobility, and sustainable fleet operations. |
The global electric vans market is estimated to be valued at USD 18.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the electric vans market is projected to reach USD 79.5 billion by 2035.
The electric vans market is expected to grow at a 15.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in electric vans market are BEV, HEV, FCEV and PHEV.
In terms of range, above 200 miles segment to command 39.5% share in the electric vans market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Electric Aircraft Onboard Sensors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Label Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Round Sprinklers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Cloth Cutting Scissors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Insulation Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Aircraft Sensors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Traction Motor Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Sensor Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Motor Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Off-Road ATVs & UTVs Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Blind Rivet Gun Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Fireplace Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Glider Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Battery Conditioners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Power Steering Motors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Motor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Gripper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Boat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Bicycle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Transmission Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA