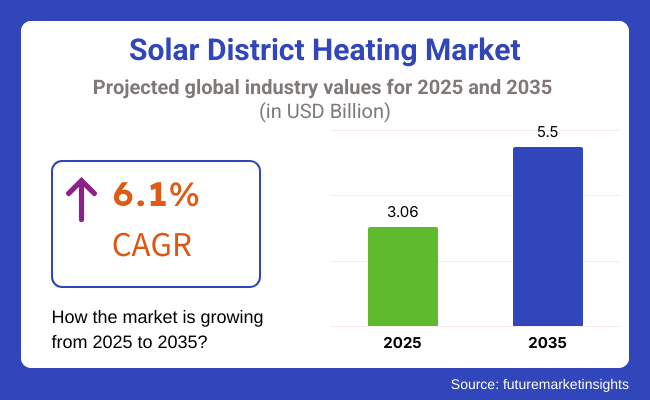
The global solar district heating market is projected to grow from USD 3.06 billion in 2025 to USD 5.5 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 6.1% over the forecast period. This expansion is being driven by aggressive clean energy policies, increasing urban energy demand, and the need to decarbonize thermal networks.
Europe has maintained a leadership position in the adoption of solar district heating (SDH) systems, with Denmark emerging as a model for other countries. According to SolarPACES, Denmark's SDH capacity exceeded 1.5 million square meters of solar collectors by 2024, supported by favorable regulations, financing mechanisms, and mandatory heat planning. Municipal utilities were mandated to prioritize renewable sources under the Danish Heat Supply Act, which accelerated deployment of large-scale solar thermal fields.
New business models are being explored to make SDH viable in diverse climate and urban density conditions. A 2024 project under the Renewable Heating and Cooling (RHC) Platform highlighted decentralized and modular plant designs, heat-as-a-service contracts, and public-private co-investment frameworks as emerging trends. As noted in the RHC report, these models have enabled the integration of solar collectors with thermal storage and auxiliary heat pumps, improving flexibility and return on investment.
ARANER, a global district energy systems developer, emphasized in a 2024 industry analysis that hybrid systems combining solar thermal with seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) and combined heat and power (CHP) units are being deployed to stabilize supply in variable demand scenarios. The company stated that “district energy networks can reduce primary energy consumption by up to 50% when powered through integrated renewable systems,” with solar heat contributing significantly to base load coverage.
In 2025, additional growth is expected from urban retrofit projects in Germany, China, and Austria, where aging gas-based district heating grids are being replaced or supplemented with solar thermal inputs. Government incentives and emissions reduction mandates under net-zero targets are further encouraging municipalities and industrial parks to adopt solar-driven heating infrastructure.
As smart grid integration and cost-optimized storage systems continue to evolve, solar district heating is anticipated to play a pivotal role in the global decarbonization of urban heat supply.
The commercial segment accounted for 37% of the global market share in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% through 2035. Demand was primarily driven by the need for space and water heating solutions in office complexes, retail centers, hotels, and educational institutions.
In 2025, government policies promoting energy-efficient building operations encouraged commercial facilities to adopt advanced heating systems equipped with control automation and emissions-reducing technologies.
Installation of hybrid and condensing systems was prioritized in newly constructed commercial buildings across Europe, Japan, and North America, in alignment with updated energy codes and building efficiency targets. Public-private partnerships and retrofit subsidies also supported the replacement of older heating units in the commercial sector, reinforcing demand stability.
Medium-scale capacity systems represented 41% of the global market in 2025 and are forecast to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% through 2035. These systems were deployed across mid-sized buildings, multi-family residential blocks, small industrial units, and institutional facilities requiring moderate heating loads.
In 2025, manufacturers focused on modular configurations that allowed scalability and ease of integration with existing infrastructure. Demand was observed in both urban and semi-urban areas where centralized utility services were limited. Product installations aligned with regional initiatives to reduce fossil fuel dependency and improve thermal efficiency in public infrastructure. Systems with digital monitoring, fault diagnostics, and zonal control features were preferred for their operational reliability and service flexibility across diverse application environments.
In district heating systems, solar thermal can collaborate instead of competing with other renewable technologies. One method that is proving to be effective is to integrate solar heat with biomass or biogas boilers where solar arrays generate heat when the sun shines, decreasing the use of biomass fuels and decreasing air pollution.
Biomass, in turn, becomes a backup during cloudy spells or peak winter demand. In another synergy-large-scale heat pumps and electric boilers-solar heat is utilized first when available, and a heat pump uses surplus wind or off-peak electricity when solar output is low. This integration allows thermal networks to act as a storage facility and balancing agent for the grid, thus helping stabilize renewable energy supply.
Solar thermal can also be combined with industrial waste heat, resulting in hybrid district heating networks that integrate multiple RE sources. (Now, some European towns are operating networks powered almost entirely by solar, biomass, geothermal and heat pumps, substantiating the possibility of all-renewable heating.)
Another major opportunity is to expand district heating infrastructure. Many cities design new networks or upgrade fossil-based systems among sustainability goals. These new-age networks are designed for enhanced renewable integration, with modular low-temperature designs. Many municipalities in Europe are preparing or building solar district heating projects, and interest is increasing in North America and Asia.
| Category | Investment Level |
|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | High |
| Germany (BEW fund, €3 billion through 2026) | High |
| France (Newheat and other private investors) | High |
| China (Large-scale installations, government push) | High |
| Middle East (Saudi Arabia’s large solar heating plant) | Medium |
| North America (Slow uptake, early pilot projects) | Low |
The USA is witnessing development of gigantic-scale renewable heat schemes with increasing urbanization and energy-efficient infrastructure requirements. Public policies and incentives have led to paradigm shifts in clean energy.
Solar collector efficiency and affordability have also become better with enhanced efficiency and reduced costs. As demand for green heat continues to grow, most residential and commercial properties are switching to green energy solutions with the vision of ending the use of fossil fuels and reducing carbon footprints.
Growth Factors in The USA
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Urbanization | Rapid urban growth necessitates efficient and sustainable heating solutions. |
| Government Initiatives | Policies supporting renewable energy adoption bolster market expansion. |
| Technological Advancements | Innovations in solar thermal technologies enhance system efficiency. |
UK focuses its efforts on developing sustainable heat networks to meet its ambitious climate neutrality goals. The government helps finance the rollout of renewable heat mass-scale networks through grants and funding programs.
Solar solutions are being integrated into more residential and commercial schemes on the premise of reducing the application of gas boilers. Public education about the virtues of renewable energy is also making the market pull.
Growth Factors in The UK
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Government Support | Initiatives offering grants and affordable loans for solar installations encourage adoption. |
| Environmental Goals | Commitment to reducing carbon emissions drives the shift towards renewable heating solutions. |
| Public Awareness | Increased awareness of sustainable energy benefits fuels market demand. |
Germany paces the world in renewable heat with strong environmental policy and advanced clean energy infrastructure to back it. Cutting-edge carbon emissions policy and aggressive climate policy have seen robust investment in solar-thermal technology. Business leadership in collector efficiency and energy storage devices drives growth in residential, commercial, and municipal markets.
Growth factors in Germany
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Environmental Policies | Strict regulations on carbon emissions promote the adoption of solar-based heating systems. |
| Technological Leadership | Advances in solar thermal technologies position Germany as a market leader. |
| Public Awareness | Growing recognition of environmental benefits and increase demand for sustainable heating solutions. |
Japan is increasingly turning to renewable sources of heat in a wide-ranging policy to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. Japan's dense, high-density urban development facilitates centralized heating schemes with energy efficiency in consumption and heat supply.
Research in advanced solar energy integration and new heat storage technology is driving overall improvement in efficiency. Growing focus on energy security and sustainability will convert into investment expansion in large-scale heating schemes over the next two years.
Growth Factors in Japan
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Security | Efforts to reduce dependence on fuels drive the adoption of renewable energy sources. |
| Urban Development | High-density urban areas benefit from centralized heating systems. |
| Technological Innovation | Continuous innovation in solar energy technologies enhance performance. |
Australia's vast solar resources are a suitable market for large thermal power systems. The government's attempts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have developed policy support and financing prospects for renewable heat projects.
Solar-heating networks are emerging as a viable alternative in industrial, commercial, and residential areas because of high energy requirements and long-term approach towards sustainability. More attention given to decarburization would tend to favor momentum in utilization of new thermal storage technologies within the next couple of years.
Growth Factors in Australia
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Abundant Solar Resources | Australia’s High solar irradiance levels make thermal-based heating highly efficient. |
| Government Policies | Supportive regulations and incentives encourage the adoption of renewable energy solutions. |
| Sustainability Goals | National commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions drive market growth. |
Global warming and burning fossil fuels are forcing societies worldwide towards cleaner forms of energy. This, in turn, has given rise to the solar district heating market. Major players in this market are Aalborg CSP, Fortum, Göteborg Energi, Kelag Energy, Keppel DHCS, Korea District Heating Corporation, Logstor, NRG Energy, Ramboll Group, RWE, Savosolar, Shinryo, Statkraft, STEAG, and Vattenfall.
These companies have shown to partake in developing and innovating in the area of solar district heating. The growth strategies adopted by these major players dictate them to focus on many aspects, such as technological innovation, strategic alliances, and investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
For example, Aalborg CSP designs integrated energy systems based on the use of concentrated solar power technology for providing efficient and sustainable heating. Fortum has partnered with Microsoft to capture surplus heat from data centers that is then directed into district heating networks to provide energy efficiency. Likewise, Göteborg Energi has teamed up with Kamstrup to implement intelligent demand-side management solutions that can optimize the utilization of energy in the city's district heating network.
ENGIE SA
ENGIE is a global leader in district energy solutions, investing in large-scale solar district heating projects across Europe, North America, and Asia. The company integrates solar thermal plants with CHP (Combined Heat and Power) and seasonal heat storage to enhance district heating efficiency. ENGIE is also involved in smart energy grid innovations, optimizing solar thermal energy utilization in urban areas.
Danfoss A/S
Danfoss is a leading supplier of district heating components and control systems, providing heat exchangers, substations, and smart heating management solutions. The company focuses on optimizing solar district heating networks, ensuring efficient distribution and minimal energy loss. Danfoss plays a key role in digitizing district heating systems, enabling real-time monitoring and automation.
Veolia Environment S.A.
Veolia is a major player in sustainable urban heating solutions, integrating solar thermal energy, industrial waste heat, and hybrid district heating grids. The company focuses on low-carbon district heating projects, implementing solar-powered and energy-recovery-based heating networks in cities across Europe and Asia.
Fortum Oyj
Fortum specializes in carbon-neutral district heating solutions, combining solar thermal, biomass, and geothermal energy. The company is actively involved in solar district heating developments in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe, integrating large-scale heat storage for year-round efficiency. Fortum is expanding its renewable district heating projects, focusing on future-proof energy systems.
Vattenfall AB
Vattenfall is a leading provider of renewable district heating, developing solar-powered heating grids and low-emission urban heating networks. The company is investing in heat storage and smart heating technologies, ensuring optimized solar energy distribution for residential and commercial applications.
By configuration, Solar District heating market can be segmented in to Centralized, Decentralized & Hybrid.
By application, Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Greenhouse Heating & Government Institutions
The capacity is another segment Small Scale, Medium Scale & Large Scale.
By region, North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia & Pacific, East Asia, Middle East & Africa.
The solar district heating market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2025 to 2035.
The solar district heating market is estimated to reach USD 3.06 billion in 2025, driven by rising investments in renewable heat networks and increasing demand for sustainable energy systems.
Germany leads due to its aggressive decarbonization policies, strong regulatory support, and early adoption of solar-based district heating infrastructure across cities.
Key growth drivers include government incentives, rising urbanization, advancements in thermal energy storage, and integration of AI for heat demand forecasting.
Top companies include ENGIE SA, Danfoss A/S, Veolia Environnement S.A., Fortum Oyj, and Vattenfall AB, among other key industry players.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by System, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 20: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 38: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 50: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 53: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 55: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 56: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Europe Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Europe Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 65: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 66: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 68: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 69: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 71: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: South Asia Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 80: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 83: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: East Asia Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 98: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 101: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: Oceania Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 106: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by System, 2018 to 2033
Figure 113: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 115: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 116: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: MEA Market Attractiveness by System, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: MEA Market Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Solar Module Recycling Service Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Tracking Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Analyzer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Aluminum Alloy Frame Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Grade Monocrystalline Silicon Rods Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Vehicle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar PV Module Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Encapsulation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Pumps Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Mobile Light Tower Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar PV Recycling Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Tracker for Power Generation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Panel Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar-Powered Active Packaging Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Panel Recycling Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar EPC Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar-Powered UAV Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Panel Cleaning Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Solar Salt Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA