The composite insulator market is expected to grow from USD 3.8 billion in 2025 to USD 7.1 billion by 2035, representing substantial growth and demonstrating the accelerating adoption of advanced composite insulation technology and power grid optimization across utility infrastructure, renewable energy systems, and high-voltage transmission sectors.
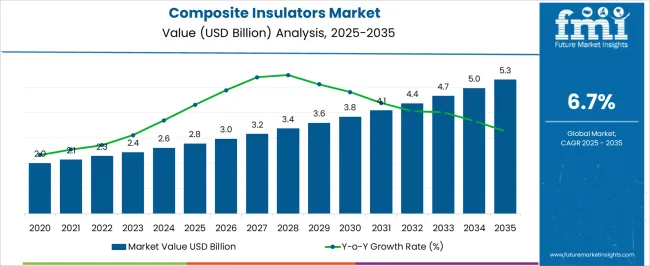
The first half of the decade (2025 to 2030) will witness the market climbing from USD 3.8 billion to approximately USD 5.2 billion, adding USD 1.4 billion in value, which constitutes 42% of the total forecast growth period. This phase will be characterized by the rapid adoption of suspension insulator systems, driven by increasing grid modernization volumes and the growing need for advanced transmission solutions worldwide. Enhanced polymer material capabilities and automated monitoring systems will become standard expectations rather than premium options.
The latter half (2030 to 2035) will witness continued growth from USD 5.2 billion to USD 7.1 billion, representing an addition of USD 1.9 billion or 58% of the decade's expansion. This period will be defined by mass market penetration of high-voltage composite technologies, integration with comprehensive smart grid platforms, and seamless compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure.
The market trajectory signals fundamental shifts in how utility facilities approach transmission optimization and electrical insulation, with participants positioned to benefit from growing demand across multiple voltage ranges and application segments.
The composite insulator market demonstrates distinct growth phases with varying market characteristics and competitive dynamics. Between 2025 and 2030, the market progresses through its technology adoption phase, expanding from USD 3.8 billion to USD 5.2 billion with steady annual increments averaging 6.5% growth. This period showcases the transition from traditional porcelain equipment to advanced composite systems with enhanced electrical performance and integrated grid monitoring becoming mainstream features.
The 2025-2030 phase adds USD 1.4 billion to market value, representing 42% of total decade expansion. Market maturation factors include standardization of insulation protocols, declining component costs for specialized equipment, and increasing utility industry awareness of composite insulator benefits reaching 90-95% operational effectiveness in transmission applications.
Competitive landscape evolution during this period features established electrical manufacturers like Siemens Energy and ABB expanding their insulator portfolios while specialty manufacturers focus on advanced polymer development and enhanced voltage capabilities.
From 2030 to 2035, market dynamics shift toward advanced smart grid integration and global infrastructure expansion, with growth continuing from USD 5.2 billion to USD 7.1 billion, adding USD 1.9 billion or 58% of total expansion.
As per Future Market Insights, a top research partner for Fortune 1000 companies, this phase transition centers on high-voltage composite systems, integration with automated transmission networks, and deployment across diverse utility and renewable energy scenarios, becoming standard rather than specialized applications. The competitive environment matures with focus shifting from basic electrical insulation capability to comprehensive grid optimization systems and integration with IoT monitoring platforms.
At-a-Glance Metrics
The market demonstrates strong fundamentals with suspension composite insulator systems capturing a dominant share through advanced electrical performance capabilities and transmission optimization. Utilities applications drive primary demand, supported by increasing grid modernization infrastructure development and high-voltage transmission requirements.
Geographic expansion remains concentrated in developed markets with established electrical infrastructure, while emerging economies show accelerating adoption rates driven by electrification initiatives and rising power transmission standards.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2025) | USD 3.8 billion |
| Market Forecast (2035) | USD 7.1 billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.5% CAGR |
| Leading Technology | Suspension Insulator Type |
| Primary Application | Utilities Segment |
Market expansion rests on three fundamental shifts driving adoption across the utilities and electrical transmission sectors.
Grid modernization creates compelling operational advantages through composite insulators that provide immediate electrical efficiency without performance degradation, enabling utility facilities to meet reliability standards while maintaining transmission capability and reducing maintenance issues.
Renewable energy integration accelerates as facilities worldwide seek advanced systems that complement traditional transmission methods, enabling precise electrical insulation and grid stability that align with industry regulations and operational efficiency standards.
High-voltage transmission enhancement drives adoption from utility facilities and power generation operations requiring effective insulation solutions that minimize electrical loss while maintaining operational performance during power transmission operations.
The growth faces headwinds from material cost challenges that vary across electrical suppliers regarding the pricing of specialized insulator equipment and polymer composite systems, which may limit adoption in budget-sensitive transmission environments. Technical limitations also persist regarding insulator capabilities and operational conditions that may reduce effectiveness in extreme voltage ranges or challenging environmental conditions, which affect electrical performance and transmission consistency.
The composite insulator market represents a specialized yet critical opportunity driven by expanding transmission infrastructure, grid modernization, and the adoption of renewable energy and smart grid platforms. The market will expand from USD 3.8B in 2025 to USD 7.1B by 2035, adding USD 3.3B in new value. Growth opportunities are concentrated around advanced suspension insulators, high-voltage technologies, transmission optimization, and smart integration capabilities.
Primary Classification: The market segments by rating into less than 11kV, 11kV to 200kV, 201kV to 400kV, 401kV to 800kV, and 800kV to 1200kV, representing the evolution from low-voltage distribution equipment to specialized transmission solutions for comprehensive grid optimization.
Secondary Classification: Voltage segmentation divides the market into high voltage, medium voltage, and low voltage sectors, reflecting distinct requirements for electrical performance, insulation compliance, and system efficiency standards.
Tertiary Classification: Product type segmentation covers pin insulators, suspension insulators, and shackle insulators, while end-use applications span commercial &industrial and utilities operations.
Regional Classification: Geographic distribution covers North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia Pacific, and Middle East &Africa, with developed markets leading adoption while emerging economies show accelerating growth patterns driven by grid expansion programs.
The segmentation structure reveals technology progression from standard insulation equipment toward specialized composite systems with enhanced electrical performance and automation capabilities, while application diversity spans from distribution operations to transmission infrastructure requiring precise voltage management solutions.
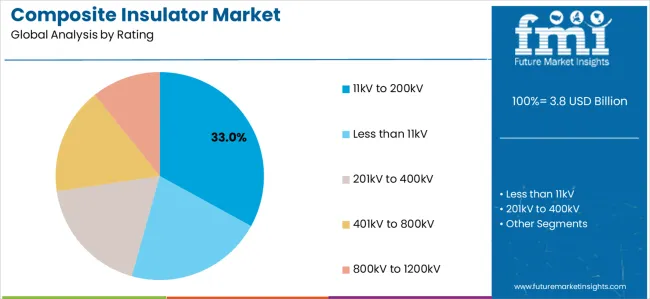
Market Position: 11kV to 200kV composite insulator systems command the leading position in the composite insulator market, holding an estimated 33% market share in 2025. These systems are favored for their advanced electrical features, including superior voltage capability, operational flexibility, and transmission optimization. This enables utility facilities to achieve optimal insulation performance across diverse medium-voltage and distribution environments, making them highly reliable for both utility and industrial applications. The segment’s growth is supported by increasing demand for efficient and high-performance insulation systems in the ongoing modernization of electrical infrastructure.
Value Drivers: The segment benefits from utility facility preference for reliable insulation systems that provide consistent electrical performance, reduced power loss, and operational efficiency optimization without requiring significant infrastructure modifications. Advanced design features enable automated grid monitoring, voltage consistency, and integration with existing transmission equipment, where electrical performance and system reliability represent critical facility requirements.
Competitive Advantages: 11kV to 200kV composite insulator systems differentiate through proven electrical stability, consistent voltage characteristics, and integration with automated grid systems that enhance facility effectiveness while maintaining optimal transmission standards suitable for diverse utility and distribution applications.
Key market characteristics:
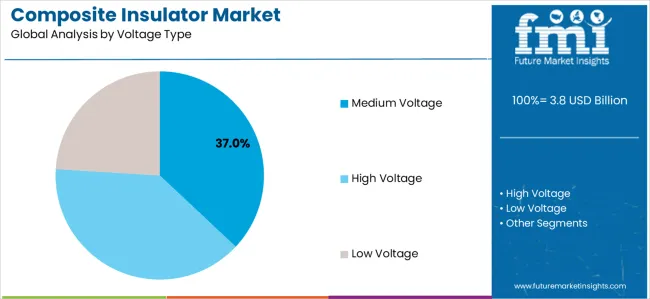
Medium voltage composite insulator systems maintain a 37% market share in the composite insulator market due to their operational efficiency and widespread application advantages. These systems are favored by facilities that require comprehensive electrical characteristics with competitive performance for both distribution and transmission applications. Market growth is primarily driven by the emphasis on grid modernization, which highlights the need for reliable insulation solutions and operational effectiveness through optimized system designs.
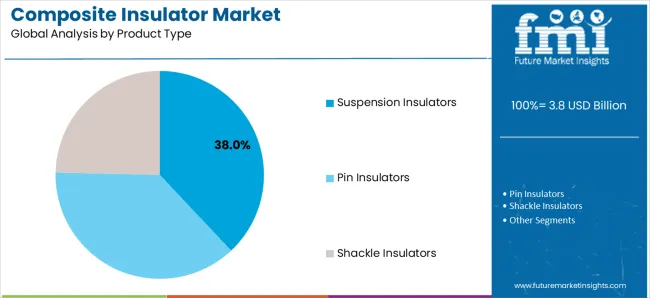
Market Position: Suspension insulators lead the market with a 38% share, representing the largest product type segment due to the extensive development of high-voltage transmission infrastructure and stringent electrical performance requirements.
Growth Drivers: Suspension insulator expansion, transmission line modernization, and voltage performance enforcement drive consistent demand for composite insulation solutions across power transmission, utility infrastructure, and grid modernization projects.
Application Scope: Suspension insulator applications span high-voltage transmission, overhead lines, substation equipment, and system upgrade projects requiring diverse electrical insulation capabilities and voltage management features.
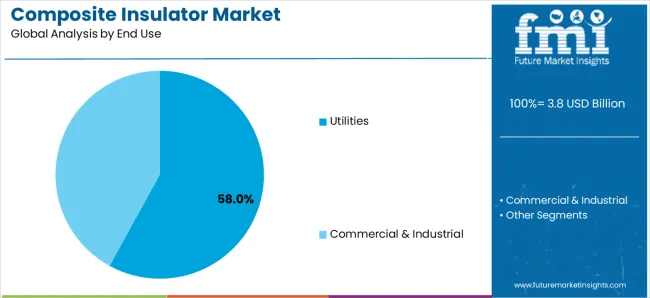
Market Position: Utilities applications lead the market with a 58% share, representing the largest end-use segment due to the extensive development of transmission infrastructure and the growing demand for electrical system reliability.
Growth Drivers: Utility sector expansion, grid modernization projects, and electrical performance optimization drive consistent demand for composite insulation solutions across power transmission, distribution networks, and infrastructure projects.
Application Scope: Utility applications span transmission lines, distribution systems, substation installations, and grid upgrade projects requiring diverse voltage capabilities and electrical performance features.
Growth Accelerators: Grid modernization infrastructure development drives primary adoption as composite insulators provide electrical transmission efficiency capabilities that enable utility facilities to meet reliability standards without excessive maintenance requirements, supporting power transmission operations and grid stability missions that require precise electrical insulation applications.
Renewable energy demand accelerates market expansion as facilities seek effective systems that minimize electrical loss while maintaining operational effectiveness during power transmission and distribution scenarios. High-voltage technology spending increases worldwide, creating continued demand for insulator systems that complement traditional transmission methods and provide operational flexibility in complex electrical environments.
Growth Inhibitors: Equipment cost challenges vary across electrical suppliers regarding the pricing of specialized insulator systems and polymer composite equipment, which may limit operational flexibility and market penetration in regions with budget constraints or cost-sensitive transmission operations.
Technical performance limitations persist regarding insulator capabilities and operational conditions that may reduce effectiveness in extreme voltage ranges, environmental contamination, or facility conditions, affecting electrical performance and transmission consistency. Market fragmentation across multiple transmission specifications and voltage standards creates compatibility concerns between different equipment suppliers and existing electrical infrastructure.
Market Evolution Patterns: Adoption accelerates in utility and renewable energy sectors where performance requirements justify insulator system costs, with geographic concentration in developed markets transitioning toward mainstream adoption in emerging economies driven by electrification initiatives and grid development.
Technology development focuses on enhanced insulator capabilities, improved electrical efficiency, and integration with automated monitoring systems that optimize transmission performance and grid effectiveness. The market could face disruption if alternative insulation technologies or transmission standards significantly limit the deployment of traditional composite equipment in utility or electrical applications.
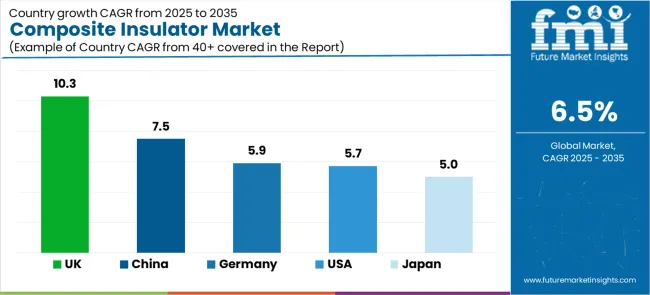
The composite insulator market demonstrates varied regional dynamics with Growth Leaders including China (7.5% growth rate) and the United Kingdom (10.3% growth rate) driving expansion through infrastructure initiatives and renewable energy development.
Steady Performers encompass Germany (5.9% growth rate), United States (5.7% growth rate), and other developed regions, benefiting from established electrical industries and advanced insulator adoption. Emerging Markets feature Japan (5.0% growth rate) and developing regions, where grid initiatives and technology modernization support consistent growth patterns.
| Country | Growth Rate (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 7.5% |
| United Kingdom | 10.3% |
| Germany | 5.9% |
| United States | 5.7% |
| Japan | 5.0% |
Regional synthesis reveals South Asian markets leading adoption through infrastructure expansion and renewable development, while North American countries maintain steady expansion supported by electrical technology advancement and grid standardization requirements. European markets show moderate growth driven by utility applications and transmission optimization integration trends.
China establishes strong market growth in the composite insulator sector, driven by aggressive infrastructure programs and ongoing advancements in renewable energy development. The country's 7.5% growth rate reflects significant government initiatives that promote the use of advanced composite insulators in transmission infrastructure and utility installations.
China’s focus on electrical technology, grid modernization, and domestic manufacturing capabilities has led to the widespread adoption of these insulators across its energy sector. Growth Concentrates in major industrial hubs, including Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangdong, where technology advancements are integrated into transmission lines and utility facilities. The development of automated grid monitoring systems and enhanced voltage capabilities is key to improving operational efficiency and supporting China’s massive energy grid.
Chinese manufacturers are increasingly focusing on producing cost-effective insulator solutions that combine the benefits of local production with advanced operational features. This, coupled with government support, facilitates the regional adoption of composite insulators across transmission, distribution, and renewable energy sectors.
Strategic Market Indicators for China:
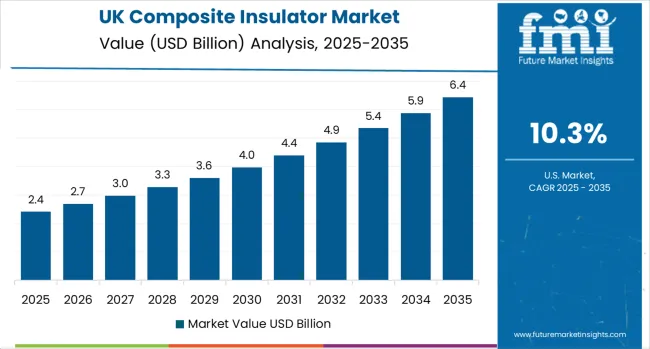
The composite insulator market holds a 10.3% growth rate, supported by government energy initiatives and infrastructure development programs that promote advanced insulator systems for utility and renewable facilities. In London, Manchester, and Edinburgh, utility facilities and renewable energy operations are implementing advanced composite insulators as standard equipment for transmission optimization and electrical insulation applications, driven by increasing government renewable investment and grid modernization programs that emphasize the importance of insulation capabilities.
British operators are adopting insulator systems that provide consistent operational performance and electrical features, particularly appealing in offshore regions where transmission efficiency and voltage standards represent critical operational requirements.
Market expansion benefits from growing electrical technology manufacturing capabilities and technology transfer agreements that enable domestic production of advanced insulator systems for utility and renewable applications. Technology adoption follows patterns established in electrical equipment, where reliability and performance drive procurement decisions and operational deployment.
Market Intelligence Brief:
Germany establishes market leadership through comprehensive electrical programs and advanced transmission infrastructure development, integrating composite insulators across utility and renewable energy applications. The country's 5.9% growth rate reflects established electrical industry relationships and mature insulator technology adoption that supports widespread use of voltage management systems in transmission and distribution facilities.
Growth concentrates in major industrial centers, including Berlin, Munich, and Hamburg, where electrical technology showcases mature insulator deployment that appeals to utility operators seeking proven transmission capabilities and operational efficiency applications.
German insulator providers leverage established distribution networks and comprehensive service capabilities, including technical support programs and performance optimization that create customer relationships and operational advantages. The market benefits from mature electrical regulations and transmission standards that mandate insulator use while supporting technology advancement and operational optimization.
Market Intelligence Brief:
United States'advanced electrical technology market demonstrates sophisticated composite insulator deployment with documented operational effectiveness in utility applications and renewable energy operations through integration with existing grid systems and transmission infrastructure. The country leverages engineering expertise in electrical technology and grid optimization integration to maintain a 5.7% growth rate. Technology centers, including California, Texas, and New York, showcase premium installations where insulator systems integrate with comprehensive transmission platforms and grid management systems to optimize electrical operations and voltage effectiveness.
American manufacturers prioritize system reliability and performance compliance in insulator equipment development, creating demand for premium systems with advanced features, including grid monitoring integration and automated voltage control. The market benefits from established electrical technology infrastructure and a willingness to invest in advanced insulation technologies that provide long-term operational benefits and compliance with international transmission standards.
Market Intelligence Brief:
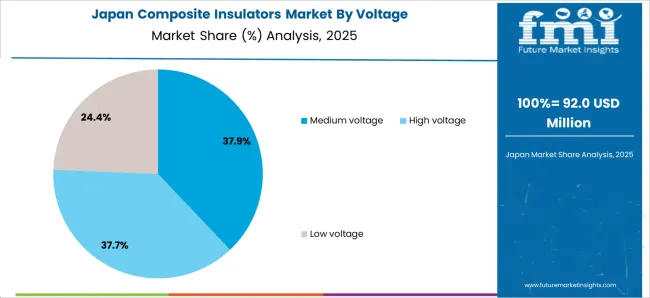
The composite insulator market expansion in Japan benefits from diverse electrical demand, including grid infrastructure modernization in Tokyo and Osaka, utility facility upgrades, and government technology programs that increasingly incorporate insulator solutions for transmission optimization applications. The country maintains a 5.0% growth rate, driven by rising electrical activity and increasing recognition of insulator technology benefits, including precise voltage control and reduced electrical interference.
Market dynamics focus on cost-effective insulator solutions that balance advanced operational performance with affordability considerations important to Japanese utility operators. Growing electrical industrialization creates continued demand for modern insulator systems in new facility infrastructure and transmission modernization projects.
Strategic Market Considerations:
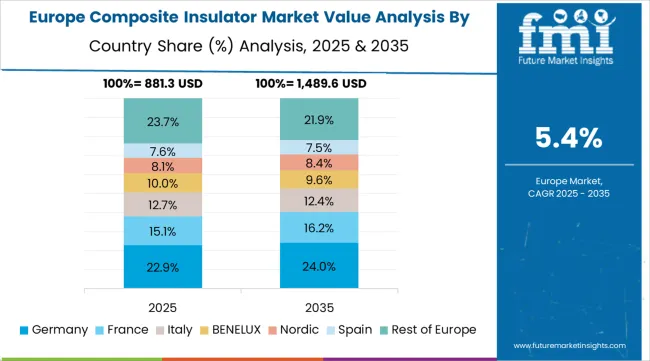
The European composite insulator market is projected to grow from USD 950 million in 2025 to USD 1.8 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period. Germany is expected to maintain its leadership position with a 26.4% market share in 2025, supported by its advanced electrical technology infrastructure and major transmission centers.
United Kingdom follows with a 20.8% share in 2025, driven by comprehensive renewable programs and electrical technology development initiatives. France holds a 17.3% share through specialized utility applications and transmission optimization requirements. Italy commands a 13.9% share, while Spain accounts for 10.2% in 2025.
Poland maintains an 8.1% share, while Russia accounts for 3.3% of the European market in 2025. The Rest of Europe region is anticipated to gain momentum, expanding its collective share from 7.5% to 8.2% by 2035, attributed to increasing electrical adoption in Nordic countries and emerging utility facilities implementing technology modernization programs.
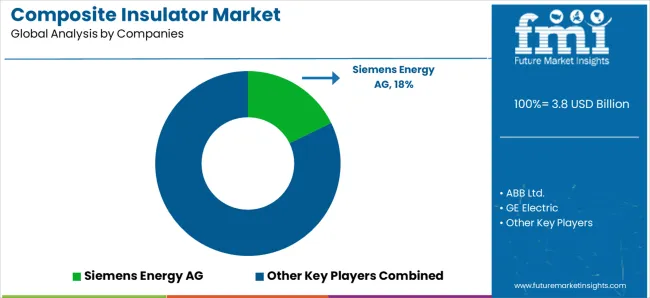
The composite insulator market operates with moderate concentration, featuring approximately 20-25 meaningful participants, where leading companies control roughly 20-25% of the global market share through established electrical industry relationships and comprehensive insulator portfolios. Competition emphasizes advanced polymer capabilities, system reliability, and transmission integration rather than price-based rivalry.
Market Leaders encompass Siemens Energy AG, ABB Ltd., and GE Electric, which maintain competitive advantages through extensive electrical technology expertise, global utility contractor networks, and comprehensive system integration capabilities that create customer switching costs and support premium pricing. These companies leverage decades of insulator technology experience and ongoing research investments to develop advanced electrical systems with precision operational control and grid monitoring features.
Technology Innovators include Lapp Insulators Group, Seves Group, and BHEL, which compete through specialized insulator technology focus and innovative operational interfaces that appeal to utility operators seeking advanced electrical capabilities and operational flexibility. These companies differentiate through rapid technology development cycles and specialized transmission application focus.
Regional Specialists feature companies like Maclean Power Systems, Olectra Greentech Limited, and TE Connectivity, which focus on specific geographic markets and specialized applications, including high-voltage systems and integrated utility solutions. Market dynamics favor participants that combine reliable insulator capabilities with advanced operational software, including precision voltage control and automatic performance optimization capabilities. Competitive pressure intensifies as traditional electrical contractors expand into insulator systems, while specialized utility companies challenge established players through innovative insulator solutions and cost-effective systems targeting specialized transmission segments.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 3.8 billion |
| Rating | Less than 11kV, 11kV to 200kV, 201kV to 400kV, 401kV to 800kV, 800kV to 1200kV |
| Voltage | High Voltage, Medium Voltage, Low Voltage |
| Product Type | Pin Insulators, Suspension Insulators, Shackle Insulators |
| End Use | Commercial &Industrial, Utilities |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia Pacific, Middle East &Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, China, Germany, India, United Kingdom, Japan, Canada, Brazil, France, Australia, and 25+ additional countries |
| Key Companies Profiled | Siemens Energy AG, ABB Ltd., GE Electric, Lapp Insulators Group, Seves Group, BHEL, Maclean Power Systems, Olectra Greentech Limited, TE Connectivity, Hitachi Energy Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by rating and voltage categories, regional adoption trends across South Asia Pacific, East Asia, and North America, competitive landscape with electrical manufacturers and utility suppliers, grid operator preferences for precision voltage control and system reliability. |
The global composite insulator market is estimated to be valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for the composite insulator market is projected to reach USD 7.1 billion by 2035.
The composite insulator market is expected to grow at a 6.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in composite insulator market are 11kv to 200kv, less than 11kv, 201kv to 400kv, 401kv to 800kv and 800kv to 1200kv.
In terms of voltage type, medium voltage segment to command 37.0% share in the composite insulator market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Analyzing Composite Insulator Market Share & Industry Trends
Composite Pin Insulator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Voltage Composite Insulators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Resin Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Roller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Paper Cans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Drums Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Textile Production Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cans Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cardboard Tube Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Cylinder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Composite Tooling Market Outlook- Share, Growth and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Composite Cardboard Tubes Market from 2025 to 2035
Composite IBCs System Market from 2025 to 2035
Market Share Breakdown of Composite Paper Cans Manufacturers
Key Players & Market Share in Composite Cylinder Production
Breaking Down Market Share in Composite Cardboard Tube Packaging
Composite Door & Window Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Composite AI Market Insights – Growth & Forecast 2024-2034

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA