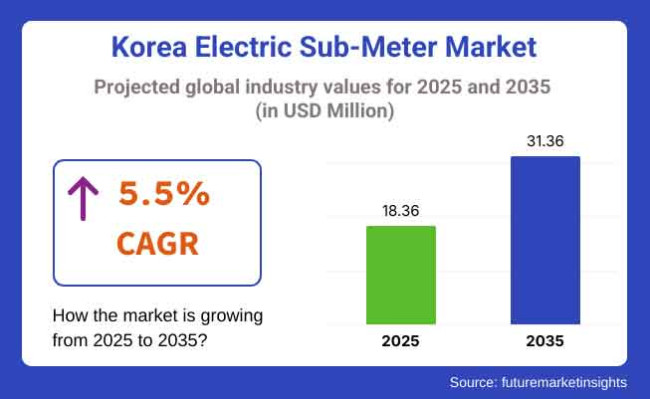
The electric sub-meter industry in Korea is poised to expand at a CAGR of approximately 5.5% throughout the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. The demand for the electric sub-meter is estimated to reach USD 18.36 million in 2025. By 2035, sales projections for this industry will surge to a valuation of USD 31.36 million.
In 2024, the Korean electric sub-meter industry experienced steady growth, driven by heightened energy awareness among consumers and tighter government regulations for energy efficiency in residential and commercial complexes.
The implementation of smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) contributed considerably, triggering demand for digital and smart sub-meters. Additionally, the industry also witnessed significant development and the retrofitting of existing buildings with sub-metering infrastructure helped drive industry expansion. Major players in the industry concentrated on innovation, combining IoT-capable meters with real-time monitoring.
The industry is expected to observe an increase in its growth pattern by the upcoming decade. The growing acceptance of energy management solutions among industrial and commercial industries will again increase demand.
Key Priorities of Stakeholders
Adoption of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Market Challenges & Future Roadblocks
Future Investment Priorities
| Regulatory Framework/Certification | Impact on the Electric Sub-Meter Market |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Management Equipment Regulation | The Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy oversees regulations to enhance energy efficiency. While electric sub-meters are not explicitly listed, products like electric fans and ranges are subject to energy efficiency standards. This indicates a governmental focus on energy-efficient appliances, potentially influencing sub-meter standards in the future. |
| High-Efficiency Appliance Certification (HEAC) | Introduced in 1996, this voluntary certification evaluates products based on energy efficiency and quality. While electric sub-meters are not currently specified, manufacturers aiming for industry competitiveness may seek this certification to demonstrate superior energy performance. |
| Electrical Safety Certification | Electrical and electronic products must comply with safety standards to be sold in South Korea. Compliance ensures that sub-meters meet national safety requirements, facilitating industry access. |
| Zero-Energy Building (ZEB) Certification | The government mandates that all new buildings over 500 m² achieve ZEB certification by 2030. This involves minimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources. Electric sub-meters play a crucial role in monitoring and managing energy consumption, aligning with ZEB objectives. |
The electric sub-meter industry in South Gyeongsang is forecasted to expand at a CAGR of 5.8%. In the industrial zones of the region, including Changwon and Gimhae, large investments are being made to implement smart energy solutions. Demand for electric sub-meters has been bolstered by government-backed initiatives encouraging energy efficiency in manufacturing hotspots. Furthermore, there is the presence of large-scale shipbuilding and automotive industries which further need accurate energy monitoring that is expected to fuel the industry growth.
The region's above-average growth is driven in part by the integration of smart grid infrastructure and the proliferation of commercial energy management systems. Businesses including manufacturers, hotels etc. are likely to target sub-metering solutions for high energy-consuming industries.
FMI opines that South Gyeongsong electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.8% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
North Jeolla, is expected to expand at a stable CAGR of 5.2% - relatively lower than the national average. This is due to a comparatively smaller industrial base. However, the government's emphasis on sustainable development for cities, many of which will be smart cities such as the one in Jeonju, is anticipated to fuel growth in the industry.
Policies that encourage the uptake of energy-efficient buildings and the integration of renewable energy are some of the main drivers. The agri-sector (greenhouse farming & food processing) is another emerging demand segment as it is also dependent on electricity.
FMI opines that North Jeolla electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.2% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
The South Jeolla region, with a strong renewable base, has seen a surge in the demand for the electric sub-meters. The South Jeolla region is slated to witness an expected CAGR of 5.3% during the projected period between 2025 and 2035. It is a powerhouse for wind and solar power projects and critical for advanced energy monitoring.
Important industrial and port cities Mokpo and Yeosu are deploying sub-metering solutions to drive logistics and manufacturing efficiencies. Growth is also being propelled by government-led smart grid projects and energy efficiency mandates for commercial buildings. Regional government initiatives to encourage electrification of public infrastructure also boost demand for sub-meters.
FMI opines that South Jeolla electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.3% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
Jeju is expected to have the maximum growth in the electric sub-meter industry with a projected CAGR of 5.0%. The government of Jeju supports energy efficiency innovations such as the deployment of sub-meters as the region is a leading smart grid testbed in Korea.
The high aspirations of the region to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030 generate a significant requirement for energy monitoring solutions. The surge in EVs, as well as renewable energy initiatives such as wind and solar farms, increases demand for sub-metering residential, commercial and industrial applications.
FMI opines that Jeju electric sub-meter sales will grow at nearly 5.0% CAGR through 2025 to 2035.
From 2025 to 2035, it is forecasted that Socket Type/Electromechanical Sub-Meters will remain relevant in Korea’s electric sub-meter industry. They are widely used in older buildings and small commercial buildings because they are rugged and simple to operate.
However, industry priorities will trend toward more advanced solutions with the continued push from the government on digitalization by the upcoming decade. Demand for electromechanical sub-meters will be driven by retrofit projects in older residential complexes and factories.
Feed-through Sub-Meters will grow at a steady rate especially in industries, and in high power consumption settings. In manufacturing plants, data centres, and logistics hubs, feed-through sub-meters are also increasingly used to measure high-voltage loads efficiently.
Due to their rugged design and proven reliability, they are well-suited for tracking energy usage in heavy-duty applications. The increase in industrial automation will further drive adoption, making these sub-meters an integral part of the changing energy management environment in Korea.
Large-scale energy monitoring in the chemical, energy, and manufacturing sectors will depend heavily on Current Transformers. As Korea advances its smart grid initiatives, high-precision current transformers marketed will exceed demands.
In commercial and industrial settings, where accurate energy measurement is essential for both cost savings and regulatory compliance, these have the potential to be remarkable. Current transformers will also remain embedded within the energy ecosystem as the installation of electric vehicle (EV) charging stations and renewable energy infrastructure continues to grow.
Non-Socket/Electronic Sub-Meters are likely to make significant growth by 2035, driven by the need for real-time energy monitoring and efficiency improvements that will position these meters prevalent in the industry.
These meters will be helpful for consumers to get more accurate digital readings. These sub-meters will be chosen in the new buildings, economy complexes, and energy-saving homes. Their simplicity of installation and convenience of use with fancy energy management systems will make them ubiquitous.
However, Traditional options will find themselves losing favour with businesses looking towards electronic sub-meters for optimal energy costs, which will continue to remain the case through industry expansion. Korea is aggressively moving toward smart grid technology, such that these advanced metering solutions will be the norm throughout residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Smart sub-meters allow for real-time energy tracking, remote access and integration with AI-based analytics to be predictive in energy management. They will be indispensable for businesses and households whose goals are to lower electricity prices and comply with demands for sustainability. The industry will continue to turn towards HPL based on the net-zero energy building and carbon reduction initiatives which only strengthen the drivers behind HPL products.
Single-phase sub-meters will remain the mainstream in the residential sector and small commercial businesses in Korea. These are the best options for apartment complexes, individual homes, and small offices due to their affordability and ease of installation. Increasing adoption of home automation and energy-saving measures will ensure single-phase sub-meter demand.
Amid Korea’s push for smart energy solutions, these meters will increasingly link to IoT-based home energy management systems, enabling homeowners to monitor and modify the amount of electricity that they use from afar.
The Three Phase Sub-Meters will be used in applications in big retail stores, factories, and data centres, where monitoring and optimal energy consumption will be required. The evolution of Korea’s manufacturing sector with Industry 4.0 technologies will require precise energy monitoring at various operational levels.
The growing number of data centers due to the rise of cloud computing and AI-based applications, will lead to a high demand for three-phase sub-meters. Furthermore, All-in-one three-phase sub-meters will play a key role in correctly metering the loads of electricity, as EV charging infrastructure continues to scale up across any country.
In Commercial Establishments, the electric sub-meters industry will experience a stable demand as businesses will increasingly opt for reducing energy use. Advanced sub-metering solutions will be increasingly deployed in hotels office buildings, and other multi-tenant properties.
Green building certifications and energy efficiency agendas will reinforce the argument for property developers to incorporate sub-meters in commercial constructions. Commercial and industrial units will increasingly adopt smart sub-meters for real-time data analytics and remote monitoring for their cost-saving initiatives.
Retail Chains, supermarkets and shopping malls are key adopters of electric sub-meter industry, as they seek to monitor and optimise energy costs in high-footfall locations. store. As the 24/7 retail revolution continues to grow, this emphasis on energy efficiency will become even more important, leading retailers to invest in smart metering technology.
Data Centers will become one of the rapidly expanding segments of the Korean electric sub-meter industry. As demand for cloud services, AI-driven computing, and edge data processing continues to grow, data centres will need innovative sub-metering systems to optimize energy consumption.
There also will be growing adoption of sub-metering solutions within the other segments for hospitals, educational institutions, and government buildings. Hospitals will focus on energy tracking to control critical medical devices, while universities will inform up-meters of power consumption throughout the campus.
These meters will be implemented by government facilities in conjunction with national energy-saving measures, in line with Korea’s mid- to long-term carbon neutrality measures. The Electric Sub-meter industry is likely to dominate the Industrial Sector including Production factories, logistics centres and processing plants will keep using high-accuracy sub-meters to track the distribution of power.
From the market perspective, as Korea aims to promote the parts of industrial automation and energy optimization, three phases of sub-meters and feed-through models will be widely used. In energy-intensive sectors like semiconductor production and heavy machinery manufacturing, they'll combine sub-meters with AI-backed analytics to gain insights into operating processes and systems to drive them more efficiently.
| 2020 to 2024 (Historical Analysis) | 2025 to 2035 (Forecast Outlook) |
|---|---|
| The industry saw moderate growth, driven by increasing energy efficiency awareness and early adoption of sub-metering solutions in commercial and industrial sectors. | The industry is expected to expand significantly, driven by government regulations, smart grid integration, and the widespread adoption of digital and smart sub-meters. |
| Traditional electromechanical and socket-type sub-meters dominated the industry, especially in older residential and commercial buildings. | Smart sub-meters and electronic non-socket sub-meters will witness the highest adoption, especially in new constructions, smart buildings, and energy-conscious industries. |
| Government policies focused on general energy efficiency improvements but lacked strict mandates for sub-metering in all sectors. | Regulatory frameworks will become more stringent, with mandates requiring smart metering solutions in commercial, industrial, and even residential buildings. |
| Industrial adoption of sub-meters was primarily concentrated in large-scale manufacturing plants and factories. | Industry 4.0 and automation will drive the need for advanced sub-metering, ensuring real-time monitoring and AI-powered predictive analytics for better energy management. |
| The residential sector had limited adoption, with sub-metering mostly used for shared electricity billing in apartment complexes. | The residential segment will see a surge in demand due to the rise of smart homes, government subsidies, and increased consumer awareness of energy consumption. |
| Data centres and technology firms began integrating sub-meters to optimize power distribution but were not a dominant segment. | The rapid expansion of cloud computing, AI-driven services, and edge data centres will make energy-efficient sub-metering a necessity in this segment. |
| The commercial sector, particularly large retail stores and hotels, showed growing interest in sub-meters for cost reduction and operational efficiency. | More businesses will invest in smart sub-meters, leveraging real-time data to optimize costs and align with sustainability goals. |
| Infrastructure developments in renewable energy and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations increased the need for precise energy monitoring. | The expansion of Korea’s renewable energy and EV infrastructure will accelerate sub-meter adoption, ensuring accurate tracking of energy distribution. |
| Regional growth was concentrated in major metropolitan areas like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon. | Secondary regions, including Jeju, South Gyeongsang, and North/South Jeolla, will see accelerated growth due to increased investments in industrialization and sustainability initiatives. |
| Industry challenges included a lack of awareness about advanced sub-metering benefits and the high initial cost of smart sub-meters. | Costs of smart sub-metering solutions will decline due to technological advancements, making them more accessible to businesses and residential users. |
The Korean electric sub-meter industry is part of the energy management and smart grid technology segment, which is an integral part of the larger electrical equipment and utilities sector. The industry is directly impacted by macroeconomic drivers like government energy policy, industrial automation, and smart city growth.
With Korea's shift toward an energy-efficient economy, the need for sophisticated sub-metering solutions is increasing, both driven by regulatory requirements and cost-saving companies. Between 2025 and 2035, economic growth, urbanisation, and industrial growth will be important factors in determining the industry.
Korea's drive for carbon neutrality in 2050 is anticipated to fuel investments in energy monitoring systems to maximize the use of electricity in residential, business, and industrial spaces. The fast growth of digital infrastructure, such as data centres and electric vehicle charging points, will also enhance the need for high-accuracy sub-metering solutions. Global supply chain variations and raw materials prices will influence pricing and availability, but technology will reduce costs.
Major companies in Korea's electric sub-meter industry are competing via pricing strategies, technological innovation, strategic collaboration, and geographical expansion. With the industry moving towards smart metering, companies are investing in high-end digital solutions, incorporating IoT and AI-based analytics in their offerings. Companies delivering affordable solutions for mass penetration, especially in the residential and industrial segments, are emerging as leaders.
To enhance industry leadership, key players are establishing collaborations with real estate developers, industrial producers, and energy service providers. Smart grid project collaborations with the government and adherence to changing regulations are also at the forefront of their plans.
Companies are also increasing manufacturing facilities and R&D spending to create more efficient, high-precision metering products. The drive to export smart sub-meters to other APAC markets is also rising, as companies ride on Korea's technological advances to gain supremacy in the wider energy management industry.
Recent Key Developments
Rising energy efficiency regulations, smart grid expansion, and growing industrialization are driving adoption.
Commercial buildings, industrial plants, data centres, and large retail stores are leading adopters.
Regulations mandating energy monitoring, sustainability goals, and smart city initiatives are accelerating usage.
Smart metering, AI-based analytics, remote monitoring, and integration with renewable energy systems are key trends.
High initial costs, supply chain disruptions, and the need for compliance with evolving energy regulations.
Table 1: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 2: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 3: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 4: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 5: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 6: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 7: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 8: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 9: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 10: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 11: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 12: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 13: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 14: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 15: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 16: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 17: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 18: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 19: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 20: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 21: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 22: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 23: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 24: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 25: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 26: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 27: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 28: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Product, 2019 to 2034
Table 29: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 30: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Table 31: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Table 32: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Forecast by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 1: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 2: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 3: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 4: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 5: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 6: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 7: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 8: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 9: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 10: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 11: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 12: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 13: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 14: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 15: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 16: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 17: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 18: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 19: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 20: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 21: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 22: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 23: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 24: Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 25: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 26: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 27: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 28: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 29: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 30: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 31: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 32: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 33: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 34: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 35: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 36: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 37: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 38: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 39: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 40: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 41: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 42: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 43: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 44: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 45: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 46: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 47: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 48: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 49: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 50: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 51: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 52: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 53: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 54: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 55: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 56: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 57: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 58: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 59: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 60: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 61: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 62: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 63: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 64: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 65: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 66: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 67: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 68: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 69: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 70: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 71: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 72: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 73: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 74: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 75: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 76: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 77: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 78: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 79: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 80: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 81: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 82: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 83: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 84: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 85: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 86: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 87: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 88: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 89: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 90: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 91: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 92: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 93: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 94: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 95: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 96: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 97: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 98: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 99: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 100: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 101: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Product, 2019 to 2034
Figure 102: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 103: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 104: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 105: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Phase, 2019 to 2034
Figure 106: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 107: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 108: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 109: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Unit) Analysis by Application, 2019 to 2034
Figure 110: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 111: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2024 to 2034
Figure 112: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product, 2024 to 2034
Figure 113: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Phase, 2024 to 2034
Figure 114: Rest of Korea Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2024 to 2034






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Electric Aircraft Onboard Sensors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Label Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Round Sprinklers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Cloth Cutting Scissors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Insulation Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Aircraft Sensors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Traction Motor Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Sensor Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Motor Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Off-Road ATVs & UTVs Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Blind Rivet Gun Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Fireplace Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Glider Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Battery Conditioners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Power Steering Motors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Motor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Gripper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Boat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Bicycle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electric Vehicle Transmission Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA