The Japan autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) treatment demand is valued at USD 85.7 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 125.3 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 3.9%. Demand is shaped by the rising burden of chronic kidney disorders among ageing populations and improved diagnosis of hereditary renal conditions. Clinical management focuses on delaying renal-function decline, controlling blood pressure, and addressing complications such as cyst growth and pain.
Kidney failure treatment represents the leading therapeutic focus due to the progressive nature of ADPKD and the continued need for dialysis planning and transplant readiness in later-stage patients. Pharmacological interventions, including vasopressin V2-receptor antagonists, are increasingly used to slow disease progression, while supportive therapies maintain electrolyte balance and cardiovascular stability.
Utilization is highest in Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kansai. These regions have better access to nephrology care, transplant facilities, and hospital systems equipped to manage advanced renal disease. Patient monitoring programmes and genetic counselling initiatives are helping to improve long-term disease outcomes and treatment continuity. Key suppliers include Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, and Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. Their portfolios focus on therapies aligned with clinical guidelines for ADPKD progression management and renal-function preservation in specialized care settings.
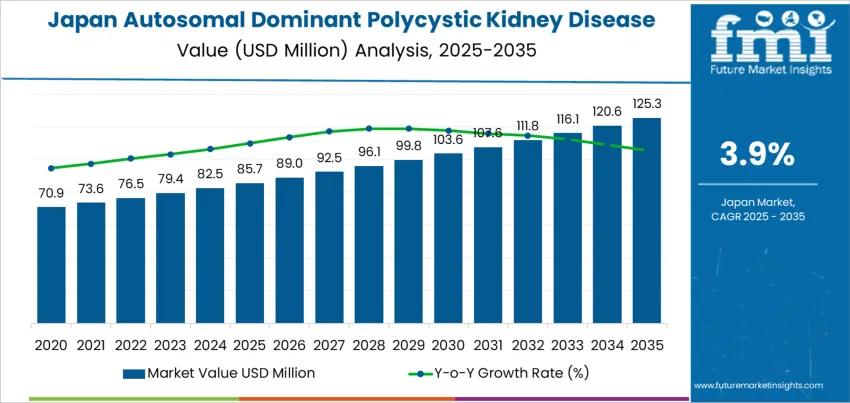
Demand for treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) in Japan shows a narrow peak-to-trough range due to the chronic and progressive nature of the condition. Peak demand is driven by diagnosed patients requiring ongoing therapy to slow kidney-function decline. Expanded nephrology screening and increased specialist referrals support stronger peaks, especially as earlier-stage detection becomes more common in urban healthcare networks. Availability of targeted therapies and structured disease-management programs also elevates treatment continuity.
Trough periods occur when undiagnosed or asymptomatic individuals delay clinical engagement. Since ADPKD progression varies widely, treatment initiation often depends on measurable functional impact, which can create periods of slower patient onboarding. Stability in clinical guidelines and limited therapy alternatives reduce rapid fluctuations, helping troughs remain relatively shallow.
The peak-to-trough pattern indicates a demand profile tied to predictable disease progression rather than external economic triggers. Peaks are supported by rising diagnostic visibility and adherence initiatives, while troughs reflect stages of delayed clinical intervention. The category maintains a steady trajectory consistent with long-term renal-care needs in Japan.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment Sales Value (2025) | USD 85.7 million |
| Japan Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment Forecast Value (2035) | USD 125.3 million |
| Japan Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 3.9% |
Demand for treatment for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan is increasing because ageing demographics and improved diagnostic practices lead to more identified cases. ADPKD is a hereditary condition that progresses over time, and many patients require long term management in nephrology and internal medicine settings. Wider access to imaging techniques such as ultrasound and CT scans enables earlier detection of kidney cysts, guiding timely therapy and regular monitoring.
Hospitals in Japan manage rising numbers of patients with chronic kidney disease, and ADPKD represents a notable share of inherited renal disorders requiring intervention. Treatment strategies focus on slowing cyst growth, controlling hypertension and preventing complications such as pain, infections and kidney function decline. Pharmaceutical advancements provide targeted therapy options that reduce disease progression risk, supporting stronger demand in specialized centers.
Home care initiatives and expanded outpatient follow up encourage sustained treatment adherence for patients seeking to avoid advanced kidney failure. Constraints include high treatment cost for targeted medications, limited awareness of genetic counseling services and later diagnosis in some families without known history. Access to specialists may vary across regions, which can delay appropriate therapeutic planning.
Demand for ADPKD treatment in Japan is shaped by structured nephrology care pathways, early detection initiatives, and aging population dynamics. Patients often require long-term symptom management including blood pressure control, renal monitoring, and treatment for complications such as cyst infection and chronic pain. Hospitals dominate care delivery due to the complexity of disease progression and need for specialized imaging and renal support systems. Increased research activity and patient education programs support accessibility to timely interventions aligned with national healthcare priorities.
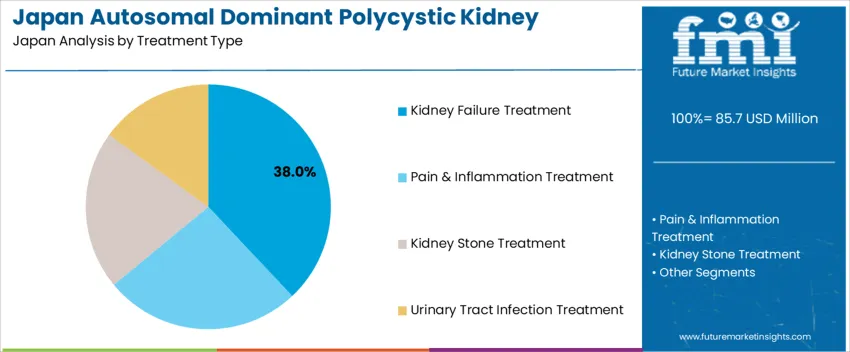
Kidney failure treatment represents 38.0%, driven by patients progressing to chronic kidney disease stages requiring dialysis evaluation and renal function preservation therapies. Clinicians prioritize pharmacologic interventions that delay cyst enlargement and kidney deterioration to reduce dependence on dialysis or transplantation. Pain and inflammation treatment accounts for 26.0%, often required to address cyst pressure and musculoskeletal complications. Kidney stone treatment contributes 21.0%, reflecting recurring nephrolithiasis in ADPKD patients that requires continuous monitoring and removal procedures. Treatment for urinary tract infections represents 15.0%, supporting prevention of cyst infection and sepsis risk in vulnerable groups. Therapeutic decisions follow Japan’s structured management guidelines emphasizing renal preservation and quality of life improvement.
Key Points:
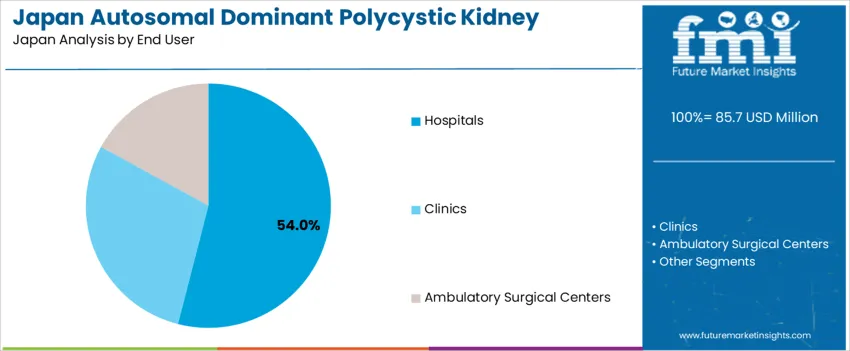
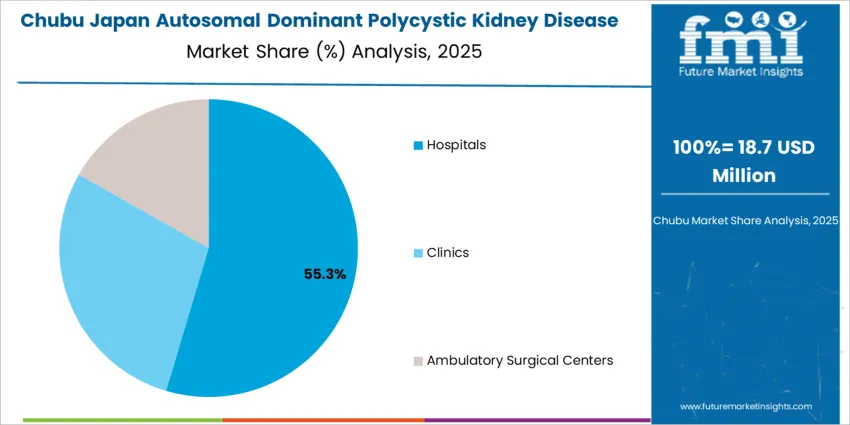
Hospitals account for 54.0%, managing advanced cases with imaging diagnostics, hemodialysis initiation, surgical consultation, and multidisciplinary nephrology oversight. Clinics represent 29.0%, supporting stable patients receiving routine medication adjustments and monitoring of blood pressure and renal markers. Ambulatory surgical centers contribute 17.0%, performing minimally invasive procedures such as cyst drainage or stone interventions without full hospitalization. Utilization patterns reflect Japan’s reliance on specialized hospital infrastructure for complex disease management while expanding community-based follow-up to improve treatment continuity.
Key Points:
Growth of early-stage disease detection, increased nephrology care access and broader use of therapies that slow cyst progression are driving demand.
In Japan, ADPKD treatment demand rises as routine imaging in health checkups identifies kidney abnormalities at earlier stages, particularly among adults in their 30s and 40s. The national insurance system supports specialist consultation and long-term monitoring, which encourages timely referral to nephrologists. Approved therapies that target cyst growth progression increase utilization among eligible patients seeking to delay dialysis or transplant. Urban medical centers in Tokyo, Osaka and Fukuoka operate dedicated renal programs that offer structured care plans including blood pressure management and kidney function monitoring. Patient organizations and hospital educators provide guidance on lifestyle adjustments that help slow disease progression, strengthening long-term engagement with treatment options.
Small patient population, treatment cost concerns and limited familiarity among non-specialist physicians restrain demand.
ADPKD affects a relatively small share of Japan’s population, which limits the number of patients actively receiving disease-modifying therapy. High medication costs can create hesitation despite insurance coverage, especially when clinical benefits must be balanced with potential side effects. General practitioners may initially misattribute symptoms such as hypertension to more common conditions, delaying specialist referral and reducing early adoption of targeted therapies. These clinical and economic barriers contribute to slower uptake in some regions.
Shift toward personalized renal-care pathways, increased integration of genetic counseling and rising demand for supportive therapies to delay renal replacement define key trends.
Hospitals are developing structured treatment pathways that align therapy choices with disease stage and patient comorbidities. Genetic counseling services are expanding to support family screening and help patients understand hereditary risk. Greater emphasis on hydration management, sodium control and liver cyst monitoring reinforces ongoing pharmaceutical adherence. Research collaborations focus on next-generation therapeutics that provide longer-term kidney protection. These trends indicate sustained, clinically guided demand for ADPKD treatment within Japan’s specialist-driven healthcare system.
Demand for ADPKD treatment in Japan is driven by improved diagnostic access, nephrology follow-up capacity, and emphasis on slowing functional decline before advanced renal impairment develops. Growth varies with regional healthcare infrastructure and patient monitoring programs. Kyushu & Okinawa show demand growing 4.8% CAGR, followed by Kanto (4.5%), Kansai (3.9%), Chubu (3.4%), Tohoku (3.0%), and the Rest of Japan (2.9%). Adoption patterns depend on genetic disease surveillance and chronic-kidney-management readiness.
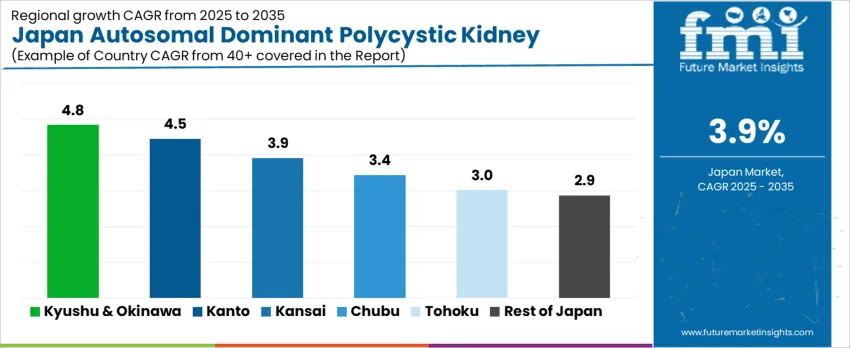
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 4.8% |
| Kanto | 4.5% |
| Kansai | 3.9% |
| Chubu | 3.4% |
| Tohoku | 3.0% |
| Rest of Japan | 2.9% |
Kyushu & Okinawa record the highest regional rise at 4.8% CAGR, supported by strengthened nephrology services and earlier diagnostic engagement for patients with a family history of polycystic kidney disease. Medical centers in Fukuoka and Kumamoto increase ultrasound and MRI evaluation frequencies to track cyst progression in at-risk adults. Care management focuses on blood-pressure stabilization and metabolic control to protect kidney function in routine follow-ups. Public healthcare networks educate patients on hydration, lifestyle consideration, and recognition of cyst-related complications requiring timely care. Hospitals maintain preparedness for monitoring interventions and route complex cases to referral nephrology units for advanced workups. Regional medical teams coordinate patient registries to support scheduling consistency. These factors contribute to rising treatment activities while maintaining structured clinical workflows associated with long-term kidney-disease management.
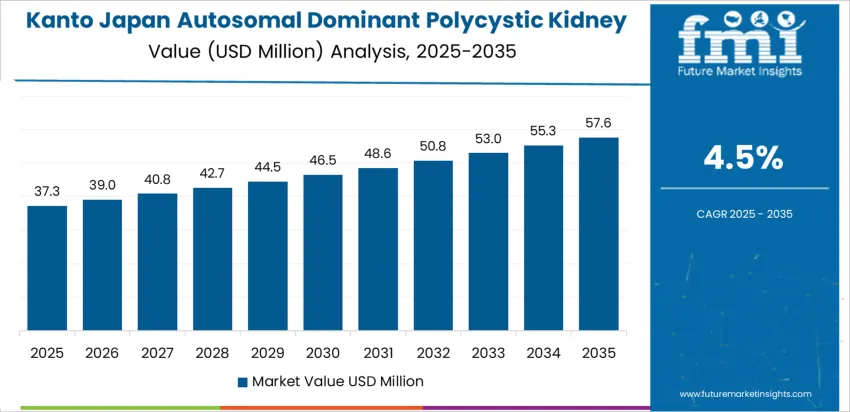
In Kanto, demand is projected to rise about 4.5% annually, reflecting the region’s concentration of tertiary nephrology centers in Tokyo, Kanagawa, and Saitama. Large hospitals expand outpatient monitoring for chronic kidney disease, integrating ADPKD-specific metrics into broader renal clinics. Blood pressure management protocols reinforce consistent medication adherence and lifestyle guidance that protects renal function. Enrollment in structured follow-up programs increases treatment regularity, especially in working-age populations who require modular appointment scheduling. Clinical record systems document disease progression and support proactive intervention. Advanced diagnostic imaging capabilities enable early confirmations when hereditary risk is present among family members. The region’s population density keeps patient flow steady and encourages greater use of risk-based screening criteria.
Kansai shows around 3.9% CAGR, linked to care models in Osaka, Kyoto, and Hyogo where kidney-function preservation forms the core of chronic disease planning. Hospital programs standardize diagnostic documentation for cyst growth trends in adults experiencing hypertension or early renal-function change. Education on lifestyle modification helps delay advanced-stage progression, reducing emergency presentations. Suburban clinics offer routine metabolic monitoring to lessen travel load for long-term patients. Shared-care arrangements ensure smooth transfer of detailed records for specialist review during escalation. Procurement teams maintain necessary support devices for imaging and renal assessments. Kansai’s structured but gradual expansion reflects stable, controlled clinical integration across community and specialist levels.
Demand in Chubu is increasing near 3.4% CAGR, influenced by Nagoya-area hospital coordination with regional clinics for scheduled evaluation of cyst progression. Outreach ensures that patients with hereditary risk receive renal-function testing before symptoms severely impact wellbeing. Clinical guidance reinforces hydration and blood-pressure control to reduce kidney strain. Case management systems track laboratory metrics and imaging intervals to prevent delayed follow-ups. Occupational health settings support awareness for working adults who may delay regular medical visits. These elements create incremental growth anchored in reliable nephrology services with moderate patient volumes across industrial and residential zones.
Tohoku reports about 3.0% yearly growth, reflecting modest but consistent expansion of renal-disease management in prefectures including Miyagi and Fukushima. Hospitals refine diagnostic triggers for patients presenting hypertension or urinary-related discomfort, ensuring imaging is applied when hereditary risk is confirmed. Rural populations require reliable scheduling along with transport coordination, so clinics aim to reduce appointment delays. Educational programs emphasize early engagement with nephrologists rather than reactive care in late stages. Procurement focuses on equipment that supports accurate tracking of renal function despite lower patient density.
Across other prefectures, demand is rising roughly 2.9% each year, driven by baseline chronic kidney disease surveillance integrated into standard primary-care services. Clinics apply structured checklists for blood pressure, kidney-function labs, and symptom progression, guiding referrals to nephrology when needed. Facilities maintain essential monitoring capacity while leveraging teleconsultation for specialty guidance. Community-level awareness ensures patients with familial history pursue periodic evaluation rather than seeking care only when complications arise. Treatment demand expands gradually as healthcare systems reduce variability in follow-up participation across smaller communities.
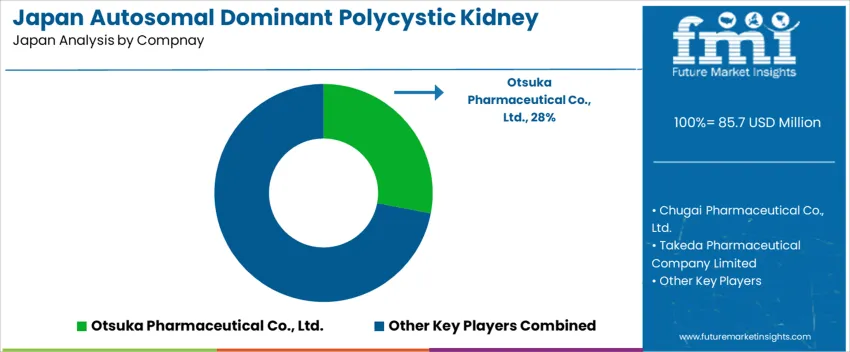
Demand for treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan is shaped by one disease-modifying agent and a broader set of supportive therapies. Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 28.0% share, driven by tolvaptan, the only pharmacological therapy that directly targets disease progression in eligible Japanese patients. Its position reflects established nephrology protocols, specialist familiarity, and structured monitoring frameworks for liver safety and electrolyte balance.
Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. contributes through antihypertensive and chronic kidney disease-related therapies used to control blood pressure and reduce cardiovascular risk in polycystic kidney disease patients. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited supports demand with agents for renal protection and associated metabolic conditions, integrated into long-term nephrology care pathways. Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited participates through blood-pressure and cardiovascular drugs that help stabilise renal function trajectories in affected adults. Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. adds treatments for anaemia and mineral-bone disorders in advanced kidney impairment, relevant to later-stage polycystic kidney disease management.
Competition in Japan centres on slowing renal function decline, controlling hypertension, managing volume status, and coordinating care across nephrology and internal medicine. Demand is concentrated in specialist centres that apply risk-based stratification to select patients for tolvaptan while using supportive therapies to manage complications over lengthy disease courses.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Treatment Type | Kidney Failure Treatment, Pain & Inflammation Treatment, Kidney Stone Treatment, Urinary Tract Infection Treatment |
| End User | Hospitals, Clinics, Ambulatory Surgical Centers |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Analysis of ADPKD patient distribution and treatment uptake across Japan; dollar spending by treatment category and healthcare setting; uptake of Tolvaptan-based therapies and supportive care; renal replacement therapy requirements including dialysis progression; integration with nephrology specialty centers and clinical research initiatives. |
The demand for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease treatment in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 85.7 million in 2025.
The market size for the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease treatment in Japan is projected to reach USD 125.3 million by 2035.
The demand for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease treatment in Japan is expected to grow at a 3.9% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease treatment in Japan are kidney failure treatment, pain & inflammation treatment, kidney stone treatment and urinary tract infection treatment.
In terms of end user, hospitals segment is expected to command 54.0% share in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease treatment in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment Market Overview - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment in USA Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Airway Disease Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Zoonotic Disease Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Acute Kidney Injury Treatment Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Crohn’s Disease (CD) Treatment Market Analysis & Forecast by Drug Type, Distribution Channel and Region through 2035
Japan Axillary Hyperhidrosis Treatment Market Insights – Size, Share & Trends 2025-2035
Th17 Driven Disease Treatment Market
Hirschsprung Disease Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs) Treatment Market Growth – Demand, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Communicable Diseases Treatment Market
Meningococcal Disease Treatment Market
APOL1 Mediated Kidney Disease Market - Demand, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Rare Neurological Disease Treatment Market Report – Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025-2035
Rare Inflammatory Disease Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Industry Share Analysis for Rare Neurological Disease Treatment Providers
Interstitial Lung Disease Treatment Market
Inherited Retinal Diseases Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Late Stage Chronic Kidney Disease Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Swine Respiratory Diseases Treatment Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA