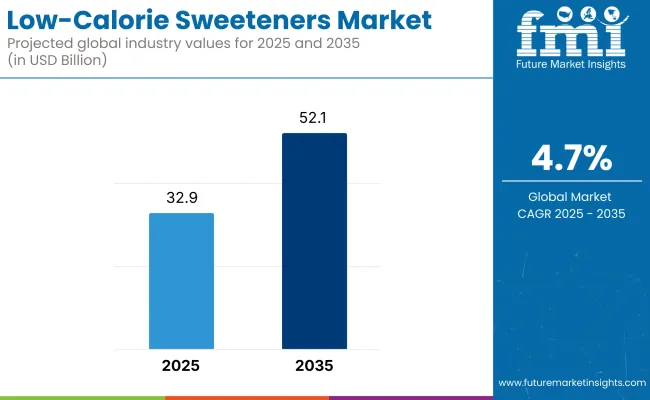
The global low-calorie sweeteners market is expected to grow from USD 32.9 billion in 2025 to USD 52.1 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 4.7%. As rates of obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and metabolic disorders climb globally, consumers and manufacturers alike are seeking strategies to reduce sugar intake.
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| Estimated Global Low-Calorie Sweeteners Market Size (2025E) | USD 32.9 billion |
| Projected Global Low-Calorie Sweeteners Market Value (2035F) | USD 52.1 billion |
| Value-based CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.7% |
Low-calorie sweeteners provide sweetness with little to no caloric contribution, offering an appealing option. Research shows that replacing sugar with sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose can lower overall calorie intake and support weight management, making them a key tool for health-conscious consumers.
Governments around the world have imposed sugar taxes and set guidelines to lower added sugar in processed foods.This has created a strong incentive for food and beverage producers to reformulate their products using low-calorie alternatives. Manufacturers are integrating sweeteners into sodas, confectionery, bakery items, dairy products, and even oral care goods expanding their placement across categories.
Innovations in sweetener formulations have significantly improved taste profiles and stability. Blended sweeteners mimic sugar’s sensory characteristics more effectively, reducing bitter aftertastes associated with earlier-generation sweeteners. Heat-stable options like sucralose are now suitable for baked products, while naturally derived sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit continue gaining traction due to clean-label trends.
On the basis of type, the stevia segment holds 38.5% share. In terms of application, the food & beverages segment accounts for 52.7% share. The Indian low-calorie sweeteners market is set to grow at 5.9% CAGR during the study period.
Following graph illustrates comparative analysis of variation of CAGR from base year (2024) to current year (2025) in global low-calorie sweetener market. In this report, realization trends of revenues are compared, which help track variation in the performance of the market for stakeholders.
| Particular | Value CAGR |
|---|---|
| H1(2024 to 2034) | 4.3% |
| H2(2024 to 2034) | 4.5% |
| H1(2025 to 2035) | 4.6% |
| H2(2025 to 2035) | 4.7% |
In H1 of the forecast period (2025 to 2035), the market will expand at a CAGR of 4.6%, and in H2 of the decade at a CAGR of 4.7%. The charts show consistent growth in the market through increasing industry adoption, and also rising R&D expenditure to create advanced low-calorie sweetener products.
Global Low-Calorie Sweetener Market will keep growing with expanding awareness towards wellness, government efforts to counter declining sugar intake, and expanding use in foods, beverages, and drugs. As consumers increasingly prefer plant-based sweeteners and clean labels, business operators will have to switch to new prospects in both as well as product reformulation.
Companies with emphasis on sustainable sourcing, flavor creation, and functional blending of ingredients will likely be best suited to capitalize on future market trends.
The low-calorie sweeteners market is segmented by type into stevia, aspartame, neotame, advantame, sucralose, saccharin, and acesulfame potassium. By source, the market includes natural and artificial sweeteners. Based on application, it covers food and beverages, bakery products, oral care products, dairy products, sauces, soft drinks, and pharmaceuticals.
Regionally, the market is divided into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Central Asia, Russia and Belarus, Balkan & Baltic Countries, and Middle East and Africa.
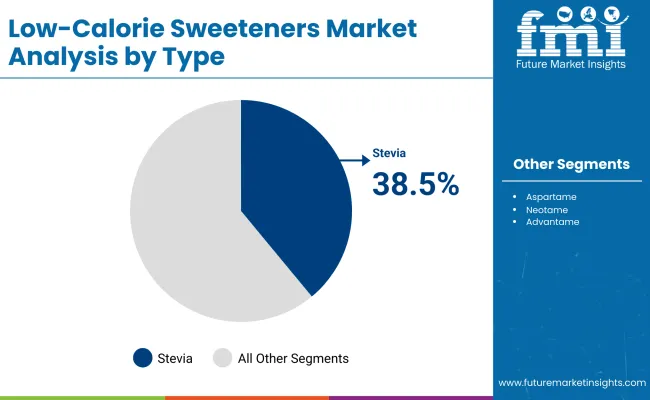
In terms of type, the stevia segment accounts for 38.5% share. Stevia is widely sold due to its natural origin, zero-calorie content, and alignment with modern consumer preferences for clean-label, plant-based, and health-conscious products.
Derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, it offers a sweet taste that is 200-300 times sweeter than sugar, allowing for minimal usage while delivering a comparable flavor profile. This makes it a preferred sugar substitute for those aiming to reduce calorie intake or manage conditions such as obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
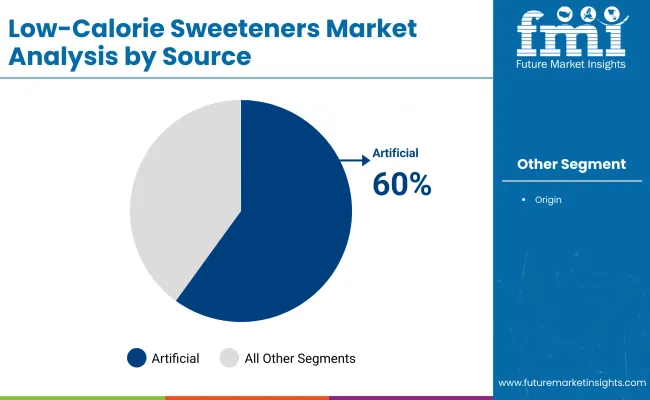
The artificial segment occupies 60% share due to their low production costs, intense sweetness (requiring minimal quantities), and high heat stability. These attributes make them ideal for large-scale use in beverages, bakery products, processed foods, and pharmaceuticals where cost and performance are critical.
Artificial sweeteners have been widely approved and used for decades by regulatory bodies like the USA, FDA, EFSA, and WHO, which has led to strong market confidence among manufacturers. Their presence in diet sodas, sugar-free gum, protein powders, and diabetic formulations has established a deep-rooted supply chain advantage and brand familiarity.
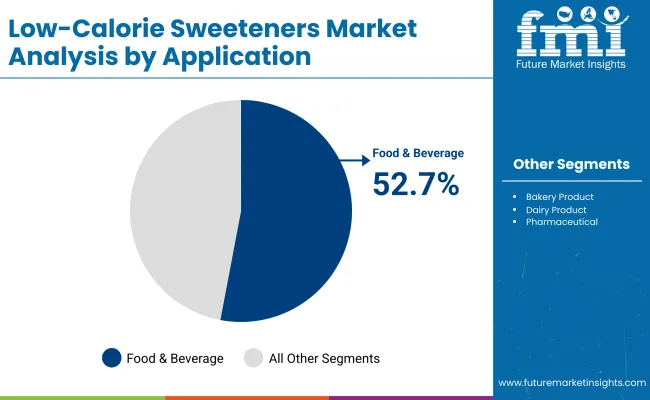
The food & beverages segment accounts for 52.7% share. Low-calorie sweeteners are widely used in the food and beverages industry due to their ability to provide sweetness without the caloric load of traditional sugar. This makes them especially valuable in a time when consumers are increasingly conscious of their sugar intake, calorie consumption, and overall health.
Rising concerns about obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders have driven food and beverage manufacturers to reformulate products with reduced or zero added sugars, making low-calorie sweeteners a critical functional ingredient.
The organised portion comprises of large global food ingredient companies and health and wellness brands, as well specialty chemicals-based companies that produce a wide range of low-calorie sweeteners (e.g., aspartame, stevia, sucralose, acesulfame K, and monk fruit).
Some of the major key players of this segment are Cargill, Tate & Lyle, Ingredion, PureCircle (a NBTY subsidiary), and DuPont. Due to their advancements in production technology, research and development, and distribution networks, these companies have the most powerful position on the market.
The organized players cater into sugar substitutes which are clean label, plant-based, non-genetically modified organism (non-GMO) and excludes artificial additives, capitalizing on heightened consumer consciousness around clean label and health products. They also devote resources to improving taste profile and mixing ratios of sweeteners to get them closer to sugar in terms of sweetness, texture and mouthfeel.
High demand for dietary, sugar-free, and low-calorie products due to the rising health concerns, such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases, in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific keeps the organised market robust in these regions.
The unorganised segment comprises of small-scale sweetener producers, regional and domestic suppliers and manufacturers of basic or traditional low-calorie sweeteners to local markets. Many of those companies focus on raw, unrefined or lower-cost sweetening agents, like honey, maple syrup and agave nectar, which less calories per serving than mainstream sugar but are not necessarily trump cards as low-calorie in relation to synthetic or heavily processed sweeteners.
Unorganised players have presence in developing regions, such as Asia, Latin America and parts of Africa, where price-sensitive consumers and small food manufacturers opt for attractive sweeteners. It is not without its challenges, though; producers must contend with constant growth, product consistency, regulatory compliance and more, yet many provide locally sourced and niche offerings that are appealing to the consumer on the lookout for a more natural or artisanal product.
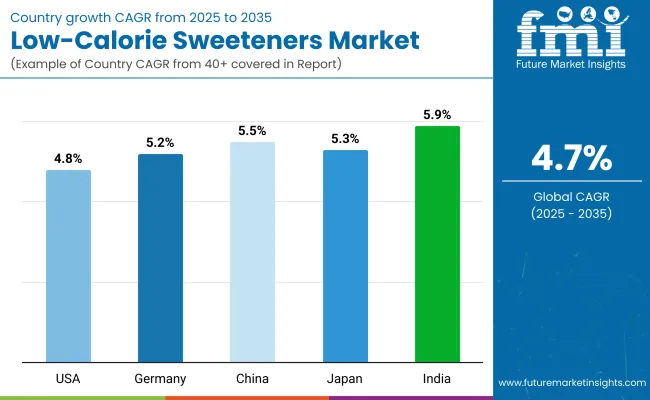
The low-calorie sweeteners market is projected to grow steadily from 2025 to 2035 across major countries. India leads with the highest CAGR of 5.9%, driven by increasing health awareness and demand for sugar alternatives. China follows closely with a CAGR of 5.5%, reflecting strong industrial and consumer adoption.
Germany and Japan show similar growth rates of 5.2% and 5.3% respectively, indicating stable market expansion in developed regions. The USA records a slightly lower CAGR of 4.8%, suggesting a more mature but still growing market. Overall, all countries demonstrate positive growth, with emerging markets showing slightly higher momentum.
| Country | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| USA | 4.8% |
| Germany | 5.2% |
| China | 5.5% |
| Japan | 5.3% |
| India | 5.9% |
Key driving factors for the USA low-calorie sweeteners market are increasing obesity rates, rising health consciousness, and stringent regulations by the FDA related to the sugar content in food products. Consumers are turning to stevia and monk fruit, natural alternatives, with a clean-label focus.
Longtime food and beverage brands, like Pepsi, have been reformulating their products to replace traditional sugar with sweeteners - including sucralose, aspartame and acesulfame potassium - to replicate the sweet taste while contributing far fewer calories. In addition, government efforts to encourage sugar-free products and impose sugar taxes have accelerated the adoption of artificial and natural sweeteners.
They are also driving the demand for low-calorie sweeteners market in China due to increasing prevalence of obesity & diabetes, increasing income levels along with urbanization. Increasing demand for glucose alternatives in beverages, dairy, and baked goods is spurring preference for healthy dietary options.
To promote the healthy diet, the Chinese Government has released the dietary guidelines to suggest a reduction in sugar, thus boosting the usage of stevia, sucralose and saccharin in food formulations. Moreover, the increasing need for low-calorie sweeteners due to the rapid growth of the functional beverages and sports drink industry is further driving the market growth.
Strong consumer inclination towards organic and natural ingredients is driving the low-calorie sweeteners market in Germany. With strict European Union regulations restricting artificial sweeteners, natural sugar alternatives including stevia and monk fruit are widely used.
The acceptance of diabetic-friendly and ketogenic diets in Germany has boosted the demand for low-calorie sweeteners with emphasis on baked items, beverages as well as dairy products. The market is also being shaped by heavy investments in innovative plant-based sweeteners and sustainable packaging.
India's low-calorie sweeteners market is witnessing tremendous growth owing to increasing urbanization, growing disposable incomes, and rising awareness regarding health hazards linked with high sugar consumption. The high demand for low-calorie sweeteners is majorly in soft drinks, dairy products, and bakery items as consumers are inclining themselves towards healthy eating options.
Indian government promoting sugar reduction policies and leading food companies are actively launching stevia & sucralose based product range. Moreover, the increasing availability of low-calorie sweeteners in online and retail stores is enhancing reach and market penetration.
The low-calorie sweeteners market is moderately consolidated, dominated by a few global giants with substantial production and R&D capabilities. Companies like Tate and Lyle, Archer Daniels Midland, Cargill Inc., and Ingredion Inc. lead the market with a broad range of sweeteners, from stevia and sucralose to artificial sweeteners, targeting food, beverage, and dietary supplement industries.
Nestlé S.A. and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. leverage their strong consumer brands to integrate low-calorie sweeteners into a variety of products. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, Celanese Corporation, and NutraSweet contribute specialized innovations, while Foodchem International focuses on supply chain and cost-effective solutions. The presence of a few major players alongside smaller innovators keeps the market competitive but not fully consolidated.
The market includes various sweeteners such as Stevia, Aspartame, Neotame, Advantame, Sucralose, Saccharin, and Acesulfame Potassium, catering to different taste preferences and dietary needs.
These sweeteners are classified as naturalor artificial, depending on their origin and processing methods.
They are widely used in food and beverages, bakery products, oral care products, dairy products, sauces, soft drinks, and pharmaceuticals, serving as sugar substitutes for health-conscious consumers.
The market is segmented as North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Central Asia, Russia and Belarus, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Middle East and Africa.
The global low-calorie sweeteners market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4.7% from 2025 to 2035.
The market is estimated to reach approximately USD 52.1 billion by 2035.
The high-intensity sweeteners segment is projected to exhibit a significant CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2035, indicating rapid growth within the market.
Key growth drivers include increasing health consciousness among consumers, rising prevalence of lifestyle diseases like obesity and diabetes, and a growing preference for natural sweeteners.
Leading companies in the market include Cargill, Incorporated; Archer Daniels Midland Company; Ingredion Incorporated; Tate & Lyle PLC; and Ajinomoto Co., Inc.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Analysis and Growth Projections for Dry Sweeteners Market
Corn Sweeteners Market Outlook - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Novel Sweeteners Market Analysis by Product Type, End Use, Application and Region from 2025 to 2035
Intensive Sweeteners Market Analysis by Nature, Type, Application, Sales Channel and Region through 2035
Fermented Sweeteners Market
Natural Malt Sweeteners Market
Peptide-based Sweetener Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Intensity Sweeteners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Next-Generation Sweeteners Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Naturally Derived Sweeteners Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High-intensity Artificial Sweeteners Market Analysis by Product Type, Form, Application Distribution Channel, and Region through 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA