The wind turbine blade market is set to increase from USD 101.6 billion in 2025 to USD 192.5 billion by 2035, advancing at a 6.6% CAGR and creating an absolute dollar opportunity of USD 90.9 billion. Rising investment in renewable energy infrastructure, coupled with global policy frameworks supporting clean power generation, is driving demand for longer, more efficient blades.
Advancements in composite materials, lightweight designs, and modular manufacturing processes are further supporting growth, enabling turbines to generate higher energy output at lower costs. The absolute dollar opportunity highlights how incremental revenue growth is distributed across regions and applications. In North America and Europe, modernization of existing wind farms and replacement of aging blades will contribute significantly to the revenue pool. Asia Pacific, particularly China and India, will account for a large portion of the opportunity due to ongoing installation of utility-scale wind projects and expansion of offshore capacity.
Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa also present incremental potential as governments push for diversification of their energy mix. By 2035, the USD 90.9 billion opportunity reflects not only new capacity additions but also aftermarket services such as blade repair, recycling, and retrofitting, making the market attractive for both manufacturers and service providers.
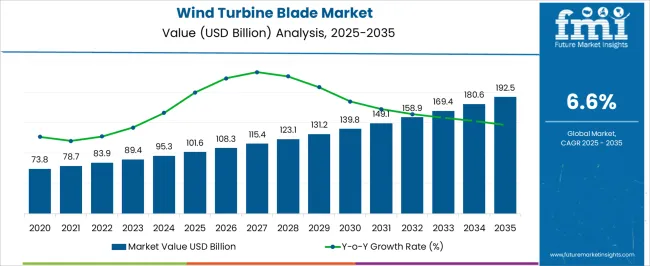
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Wind Turbine Blade Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 101.6 billion |
| Wind Turbine Blade Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 192.5 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.6% |
The wind turbine blade market is primarily driven by the renewable energy sector, which accounts for nearly 55% of the market share, as countries expand wind energy capacity to meet energy transition goals. The power generation equipment industry contributes around 20%, integrating blades into utility-scale projects. Offshore wind development represents about 12%, with growing investments in large turbines requiring advanced blade designs. Composite materials manufacturing accounts for close to 8%, supporting the supply of lightweight, durable blade components. The remaining 5% comes from research institutions and specialized engineering firms, where innovation in aerodynamics and materials drives blade efficiency improvements.
The wind turbine blade market is growing with innovations in size, materials, and recycling solutions. Blades exceeding 100 meters are being developed to increase energy capture and improve efficiency in offshore projects. Composite materials, including carbon fiber and advanced resins, are gaining use for strength and reduced weight. Digital twin technology and AI-driven simulations are enhancing design optimization and predictive maintenance.
Manufacturers are focusing on recyclable blade solutions to address end-of-life challenges. Collaborations between turbine producers, research institutions, and governments are accelerating advancements. Rising global demand for clean energy and expansion of offshore wind farms are fueling market adoption.
The market in 2025 is being shaped by technological advancements in blade design, improved aerodynamics, and materials innovation that enhance energy capture and durability.
Government policies promoting clean energy deployment and investment in wind infrastructure are accelerating demand for high-performance turbine blades. Manufacturers are focusing on scalable production capabilities and optimized designs to cater to both onshore and offshore projects, meeting the growing capacity requirements of utility providers.
Increasing replacement needs for aging turbines and ongoing development of larger rotor diameters are also contributing to market momentum. The emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices, recyclability of blade materials, and integration with digital monitoring systems is expected to strengthen market growth further, ensuring blades remain efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with evolving energy transition goals.
The wind turbine blade market is segmented by material, application, capacity, size, and geographic regions. By material, wind turbine blade market is divided into Glass Fiber and Carbon Fiber. In terms of application, wind turbine blade market is classified into Onshore and Offshore. Based on capacity, wind turbine blade market is segmented into 3 – 5 MW, 3 MW, and > 5 MW. By size, wind turbine blade market is segmented into 31 – 60 m, ≤ 30 m, 61 – 90 m, and ≥ 90 m. Regionally, the wind turbine blade industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
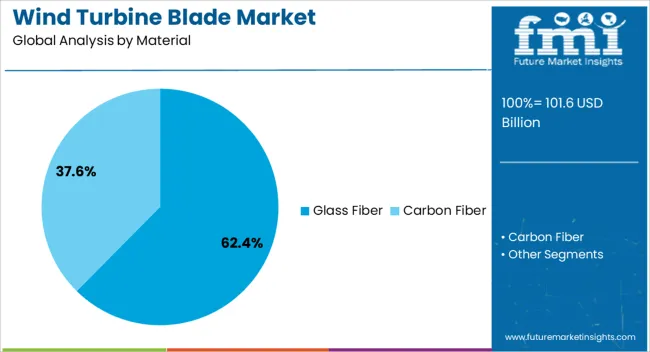
The Glass Fiber material segment is projected to account for 62.4% of the Wind Turbine Blade market revenue in 2025, establishing it as the dominant material choice. This leadership is being driven by the balance of high strength-to-weight ratio, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturing flexibility that glass fiber offers.
The segment’s growth has been supported by its ability to withstand varied environmental conditions while maintaining structural integrity over long operational lifespans. Its compatibility with advanced resin systems and suitability for complex blade geometries have enabled widespread adoption in both large-scale manufacturing and specialized turbine applications.
Additionally, the relative affordability of glass fiber compared to alternative composites has made it a preferred option for large utility-scale projects, supporting lower levelized cost of energy The ease of mass production and proven track record in global wind farms further reinforce its position as the material of choice in the market.
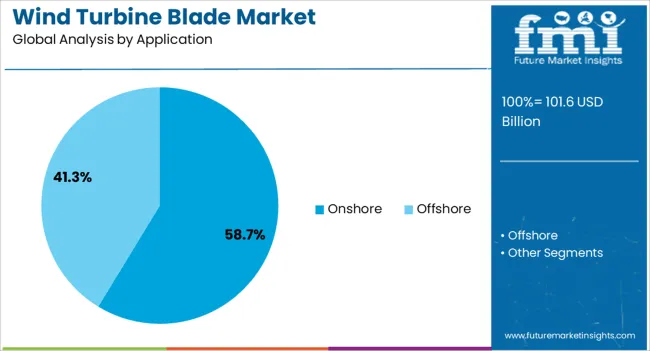
The Onshore application segment is anticipated to hold 58.7% of the Wind Turbine Blade market revenue in 2025, making it the leading application area. This dominance is being attributed to the established infrastructure, lower installation costs, and faster project development timelines associated with onshore wind farms.
Supportive government policies, competitive auction pricing, and growing investment from both public and private sectors in land-based renewable energy generation have fueled the segment’s expansion. The reduced logistical complexity compared to offshore projects has facilitated quicker deployment and scalability of onshore wind capacity.
Continuous improvements in turbine efficiency and blade design have further enhanced the output of onshore installations, making them a cost-effective option for meeting renewable energy targets The consistent global demand for onshore wind, particularly in regions with favorable wind resources and accessible grid connections, is expected to maintain the segment’s leading position.
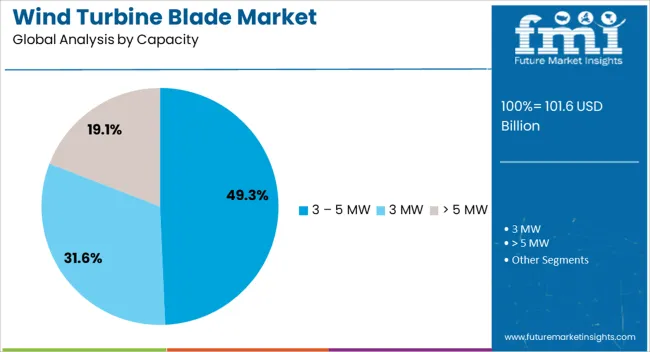
The 3 – 5 MW capacity segment is expected to account for 49.3% of the Wind Turbine Blade market revenue in 2025, marking it as the most significant capacity category. The optimal balance between power output, cost-efficiency, and suitability for a wide range of onshore and offshore environments is driving this prominence.
Turbines within this capacity range offer strong energy yields without the heightened logistical and structural challenges of larger capacity models. The segment’s adoption has been supported by its versatility in addressing both utility-scale and community-level energy projects.
The ability to integrate advanced blade designs and materials within this capacity range has further enhanced performance and operational reliability. Additionally, the 3 – 5 MW range aligns well with grid stability requirements and offers a favorable return on investment for developers, ensuring sustained demand in diverse markets worldwide.
The wind turbine blade market is expanding due to growing renewable energy investments and rising wind power capacity installations. Global revenue crossed USD 16.5 billion in 2024, with an expected CAGR of 6.6 % from 2025 to 2035. Asia Pacific holds 45% share, led by China and India, due to large-scale onshore and offshore wind projects. Europe accounts for 30%, driven by offshore installations in the UK, Germany, and Denmark. North America contributes 20%, supported by USA onshore wind capacity expansion. Blades above 60 meters dominate installations, accounting for 55% of demand. Lightweight composite materials, extended rotor diameters, and offshore adoption drive global blade manufacturing growth.
Large-sized turbine blades above 60 meters account for 55% of installations, driven by the need for higher power output and efficiency. Offshore projects increasingly use blades above 80 meters, delivering higher capacity factors. Composite materials, including carbon fiber and glass fiber, contribute 70% of blade manufacturing due to high strength-to-weight ratio and durability. Asia Pacific leads with 45% share, focusing on utility-scale wind farms in China and India. Europe contributes 30%, emphasizing offshore capacity expansion. North America accounts for 20%, driven by USA wind corridor development. Lightweight, large-diameter blades improve turbine performance, reduce levelized cost of energy, and strengthen global adoption.
Technological advancements in blade design focus on aerodynamics, durability, and manufacturing efficiency. Modular blade construction reduces transport costs by 10–15%. Advanced resin infusion and automated fiber placement improve structural integrity and reduce defects. Coatings with erosion resistance extend blade lifespan by 20–25%, lowering maintenance costs. Asia Pacific emphasizes cost-effective production of large-scale blades for onshore and offshore projects. Europe invests in next-generation offshore designs with improved performance in high-wind environments. North America integrates smart sensors for predictive maintenance. These innovations enhance reliability, reduce lifecycle costs, and support large-scale adoption of wind turbine blades globally.
Onshore projects account for 70% of blade installations due to lower costs and easier logistics, while offshore projects represent 30% with higher-capacity turbines. Offshore blades exceed 80–100 meters, designed for 8–12 MW turbines, primarily in Europe and Asia Pacific. Asia Pacific leads with 45% share, with China and India deploying large onshore farms. Europe contributes 30%, with the UK and Germany focusing on offshore expansion. North America holds 20%, emphasizing the USA onshore projects across Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. Rising investment in hybrid onshore-offshore projects and extended rotor diameters is expanding the use of turbine blades across global wind power capacity additions.
Wind turbine blades face challenges from high manufacturing costs, logistics, and recycling concerns. Blades above 80 meters require specialized facilities and transport, raising logistics costs by 12–18%. Composite materials like carbon fiber increase blade production costs by 20–25%. Offshore projects require complex installation vessels and heavy-lift cranes, increasing deployment expenses. Recycling of composite blades remains limited, with 85% of decommissioned blades sent to landfills. Asia Pacific mitigates costs through domestic production, while Europe invests in blade recycling technologies. North America emphasizes modular blade design to reduce logistics barriers. Despite these efforts, costs, logistics, and recycling remain adoption challenges globally.
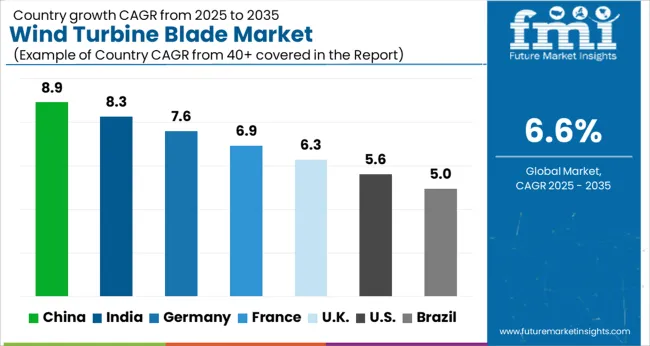
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 8.9% |
| India | 8.3% |
| Germany | 7.6% |
| France | 6.9% |
| UK | 6.3% |
| USA | 5.6% |
| Brazil | 5.0% |
In 2025, the wind turbine blade market is projected to expand at a global CAGR of 6.6% through 2035, driven by increasing renewable energy investments, government-backed clean power initiatives, and technological improvements in blade design and materials. China leads at 8.9%, 34.8% above the global benchmark, supported by BRICS-led expansion in wind farm installations, large-scale manufacturing capacity, and export-oriented production. India follows at 8.3%, 25.8% above the global average, reflecting strong growth in renewable energy projects, rising domestic manufacturing, and increasing investments in offshore and onshore wind capacity. Germany records 7.6%, 15.2% above the benchmark, shaped by OECD-backed innovation in composite materials, advanced blade engineering, and strong policy support for renewable integration. The United Kingdom posts 6.3%, 4.5% below the global rate, with demand influenced by offshore wind projects, regional manufacturing, and selective adoption in onshore applications. The United States stands at 5.6%, 15.2% below the benchmark, with steady growth in wind power capacity, domestic blade production, and modernization of existing turbines. BRICS economies drive overall market expansion, OECD countries focus on efficiency and advanced technologies, while ASEAN nations contribute through emerging renewable energy installations.
China wind turbine blade market is expanding at 8.9% CAGR, above the global 6.6%, supported by aggressive offshore and onshore wind installations. In 2024, more than 69 GW of new wind capacity was added, and approximately 55% of it utilized domestically manufactured blades. Leading producers including Goldwind, MingYang, and Envision invested in longer composite blades exceeding 120 meters to enhance efficiency. Demand is rising due to grid expansion, regional energy policies, and large-scale offshore projects near Guangdong and Jiangsu provinces. Material innovation using carbon fiber composites has improved blade lifespan by 10%.
India wind turbine blade market is advancing at 8.3% CAGR, higher than the global 6.6%, supported by renewable energy initiatives and capacity additions across Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. In 2024, India commissioned over 5.5 GW of wind capacity, with local firms such as Suzlon and Inox Wind increasing blade production efficiency. Government-backed auctions stimulated procurement of longer blades to improve plant load factors. Export activity also grew, with India supplying around 14% of global blade exports to Africa and Southeast Asia. The adoption of hybrid designs combining fiberglass and carbon fiber has improved performance in medium-wind zones.
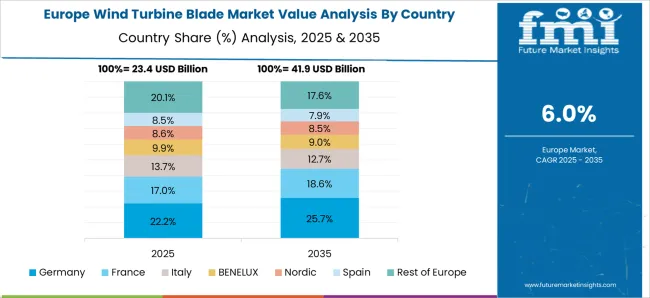
Germany wind turbine blade market is increasing at 7.6% CAGR, stronger than the global 6.6%, with emphasis on repowering older wind farms and expanding offshore installations in the North Sea and Baltic Sea. In 2024, the country added 4.2 GW of capacity, and about 35% came from offshore projects requiring specialized blades. Leading companies such as Siemens Gamesa and Nordex improved blade aerodynamics, reducing noise emissions and enhancing efficiency. Repowering initiatives replaced blades on turbines over 15 years old, increasing demand for medium-to-large blades. The share of lightweight composite blades grew due to their ability to extend operating lifespans in challenging climates.
United Kingdom wind turbine blade market is advancing at 6.3% CAGR, close to the global 6.6%, driven by offshore wind farm development in the North Sea. In 2024, the UK added 3.1 GW of offshore wind capacity, making it one of the largest offshore markets globally. Blade manufacturers such as LM Wind Power and Siemens Gamesa expanded production for offshore-specific designs exceeding 100 meters. Local initiatives are promoting carbon fiber usage to reduce weight and improve durability under harsh marine conditions. Policy incentives such as Contracts for Difference (CfD) auctions created favorable conditions for large-scale blade deployment.
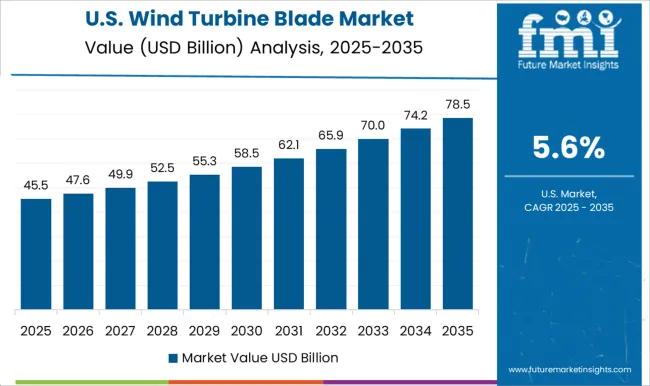
United States wind turbine blade market is expanding at 5.6% CAGR, below the global 6.6%, reflecting a mature but steadily growing industry. In 2024, 6.5 GW of wind capacity was added, primarily concentrated in Texas, Oklahoma, and Iowa. Domestic blade manufacturers including GE Vernova and TPI Composites invested in larger onshore blades above 80 meters to optimize performance in wide plains. Tax incentives under the Inflation Reduction Act accelerated procurement, while offshore projects in New York and Massachusetts boosted demand for extra-large blade models. Recycling programs for older blades gained momentum, aiming to repurpose 15% of decommissioned blades into construction materials.
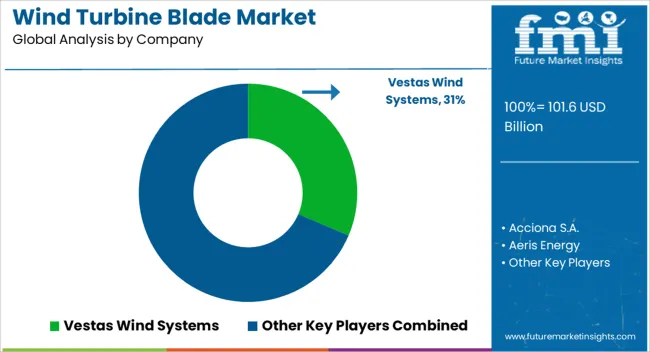
The wind turbine blade market is highly competitive, driven by the rapid expansion of wind energy capacity globally and the demand for longer, lighter, and more efficient blades. Market competition is shaped by blade material (composite, fiberglass, carbon fiber), size, aerodynamic design, durability, cost, and manufacturing capabilities. Companies differentiate through advanced materials, optimized aerodynamics, modular designs, and innovations that enhance energy capture and reduce maintenance requirements.
Key players such as LM Wind Power (GE Renewable Energy), Siemens Gamesa, Vestas, Nordex, Suzlon, TPI Composites, Mingyang Smart Energy, Goldwind, Enercon, and CSIC Haizhuang dominate the market by offering high-performance, durable, and technologically advanced wind turbine blades. Strategic collaborations with turbine manufacturers, energy project developers, and regional suppliers are leveraged to strengthen market presence. Regional and emerging players compete by providing cost-effective, lightweight, and customizable blades tailored to local wind conditions. The market is moderately consolidated, with leading companies focusing on innovation, material efficiency, production scale, and after-sales support to maintain market share and meet the growing demand for renewable energy solutions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 101.6 Billion |
| Material | Glass Fiber and Carbon Fiber |
| Application | Onshore and Offshore |
| Capacity | 3 – 5 MW, 3 MW, and > 5 MW |
| Size | 31 – 60 m, ≤ 30 m, 61 – 90 m, and ≥ 90 m |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Vestas Wind Systems, Acciona S.A., Aeris Energy, EnBW, Enercon GmbH, Gamesa Corporacion Technologica, Hitachi Power Solutions, LM Wind Power, MFG Wind, Nordex SE, Siemens AG, Sinoma Wind Power Blade Co. Ltd, Suzlon Energy Ltd., and TPI Composites SA |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by blade type and installation, demand dynamics across onshore and offshore projects, regional trends in renewable power expansion, innovation in composite materials and blade length, environmental impact of decommissioning and recycling, and emerging use cases in hybrid energy systems and repowering projects. |
The global wind turbine blade market is estimated to be valued at USD 101.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the wind turbine blade market is projected to reach USD 192.5 billion by 2035.
The wind turbine blade market is expected to grow at a 6.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in wind turbine blade market are glass fiber and carbon fiber.
In terms of application, onshore segment to command 58.7% share in the wind turbine blade market in 2025.
Explore Similar Insights

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA