About The Report
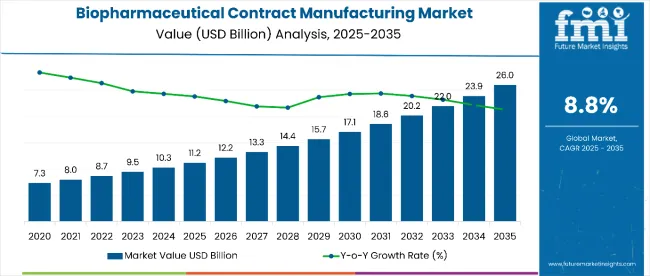
The biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is projected to grow from USD 11.23 billion in 2025 to USD 26.93 billion by 2035 at a CAGR of 8.8%. Growth is being driven by limited in-house capabilities and the rising complexity of biologics. Mammalian-based expression systems will account for 72.5% of global market share in 2025. Increased adoption of outsourced services is linked to the specialized requirements of monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and gene therapies. China, India, and Japan projected as the fastest-growing regions over the forecast period.
Infrastructure expansion and strategic partnerships have been prioritized. Thermo Fisher Scientific announced on 14 April 2025 the expansion of its biologics facility in Hangzhou, China, to meet regional demand. These investments have been driven by increasing volume requirements and a shift toward cell and gene therapy pipelines. Sartorius reported in its 2025 white paper the commercial-scale integration of single-use bioreactors to accelerate clinical and commercial output.
Complex batch processes, high capital barriers, and inconsistent regulatory standards have limited capacity scale-up in some markets. According to the Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing and Quality Alliance on 2 May 2025, global alignment of quality frameworks remains incomplete. Still, the USA FDA’s 2025 CMC guideline revision has supported contract manufacturers in meeting accelerated approval timelines. By 2035, mammalian systems will remain dominant, while microbial-based platforms gain adoption for cost-sensitive biologics.
Leading CMOs are actively pursuing vertical integration to offer end-to-end capabilities, from early-phase development to commercial-scale production. This model reduces time-to-market and regulatory friction for biopharma clients. Lonza, Samsung Biologics, and WuXi Biologics have each announced modular facility frameworks in 2025 that enable flexible scaling and multi-product handling. This trend is reshaping the competitive landscape by favoring CMOs that can align with the rapid iteration cycles of mRNA platforms and personalized cell therapies. Meanwhile, mid-sized firms are differentiating through niche expertise-such as high-potency APIs or fill-finish services-rather than competing on volume.
| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size, 2025 | USD 11.23 billion |
| Market Size, 2035 | USD 26.93 billion |
| Value CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.8% |
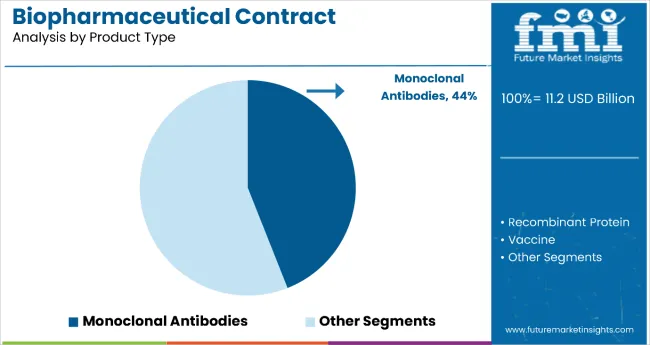
Monoclonal antibodies hold the dominant position with 44.0% of the market share in the product type category within the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market. This leadership is driven by monoclonal antibodies' exceptional therapeutic versatility and their widespread applications across oncology, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
mAbs offer superior specificity in targeting disease-causing proteins while minimizing off-target effects, making them highly effective therapeutic interventions that have revolutionized modern medicine.
The segment's dominance is reinforced by the increasing complexity of monoclonal antibody production, which requires specialized manufacturing expertise and advanced infrastructure that many pharmaceutical companies prefer to outsource.
The growing pipeline of mAb-based therapies and the expansion into biosimilar manufacturing following patent expirations further drive demand for contract manufacturing services. As precision medicine continues to advance and regulatory pathways for biologics become more streamlined, the monoclonal antibodies segment is positioned to maintain its market leadership through continued innovation in therapeutic applications and manufacturing optimization.
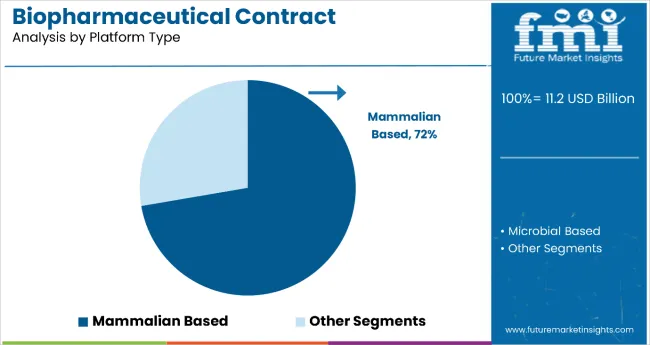
Mammalian-based platforms dominate the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market with 72.3% of the market share in the platform type category. This substantial leadership is attributed to mammalian expression systems' superior ability to produce complex biologics with proper protein folding, post-translational modifications, and glycosylation patterns that are essential for therapeutic efficacy.
Mammalian cell lines, particularly CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells, have become the gold standard for producing monoclonal antibodies and other complex biologics due to their similarity to human cellular machinery.
The segment's dominance is reinforced by mammalian systems' proven track record in regulatory approvals and their ability to produce biologics that closely mimic natural human proteins. While mammalian-based manufacturing requires higher capital investment and operational costs compared to microbial systems, the superior product quality and regulatory acceptance justify the premium pricing.
As the biopharmaceutical industry continues to focus on complex therapeutics including antibody-drug conjugates and advanced protein therapies, the mammalian-based platform segment is expected to maintain its dominant position through continued technological advances in cell line development and bioprocessing optimization.
The United States will retain its position as the dominant profit pool in the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, with revenue projected to rise from USD 3.95 billion in 2025 to USD 8.41 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 7.8%. The USA continues to house the most mature biologics innovation ecosystem globally, with over 45% of global late-stage biologic trials headquartered domestically. This fuels sustained clinical and commercial outsourcing demand, particularly in monoclonal antibodies, ADCs, and cell therapies. Further, regulatory alignment is strong: the USA.
FDA’s 2025 overhaul of CMC guidance reduced pre-approval inspection bottlenecks and incentivized sponsor-CDMO alignment early in the development lifecycle. Also, CDMOs operating within major biotech corridors-Massachusetts, California, and North Carolina-benefit from local talent density, proximity to sponsors, and favorable infrastructure. However, operational risks include rising wage inflation across biomanufacturing roles and regional variations in GMP audit standards. Additionally, ESG compliance costs may pressure EBITDA margins as California, in particular, enforces tighter environmental controls. Despite these headwinds, USA based CDMOs are expected to maintain high capacity utilization levels, benefiting from multi-year manufacturing agreements and lifecycle production of high-margin biologics.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 3.95 | 7.8% |
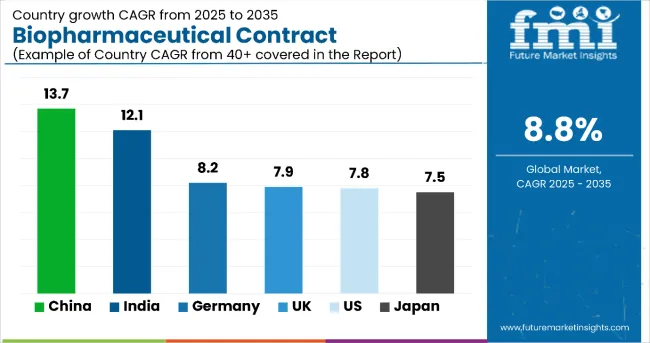
China is expected to be the fastest-expanding national market in the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing landscape, scaling from USD 0.91 billion in 2025 to USD 3.32 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 13.7%. China’s government-backed “Biotech 2030” framework has made biomanufacturing a priority sector, offering tax relief, land access, and soft capital to CDMOs investing in GMP-compliant infrastructure. Regulatory transformation is proving pivotal. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has aligned its technical review framework with ICH guidelines, creating cross-border trust in Chinese CDMO output.
Domestic biopharma demand is intensifying-China now leads globally in new IND filings for biosimilars and PD-1 inhibitors. Infrastructure in Suzhou, Shanghai, and Guangzhou is rapidly scaling, with regional CDMOs expanding their mammalian cell capacity and investing in single-use bioreactor lines. Risk factors include quality inconsistencies among smaller players and fragmented GMP audit standards between provinces. Nonetheless, foreign sponsors are increasingly sourcing early-stage and biosimilar manufacturing from China to benefit from 30-40% cost advantages. With regulatory credibility rising and internal biologics consumption booming, China is forecast to capture a growing share of global outsourcing mandates.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.91 | 13.7% |
Germany remains the cornerstone of biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing in Western Europe, with the market estimated to expand from USD 0.88 billion in 2025 to USD 1.94 billion by 2035, registering a steady CAGR of 8.2%. Three fundamentals underpin its trajectory. First, Germany hosts some of the EU’s most advanced biomanufacturing infrastructure, anchored by a strong legacy in chemical engineering and pharmaceutical scale-up. CDMOs in cities like Munich, Heidelberg, and Frankfurt are heavily invested in mammalian and microbial systems, positioning them to service monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and biosimilars. Second, Germany benefits from an export-oriented biologics economy.
Over 60% of its CDMO output is destined for global supply chains, supported by mature logistics and stringent EU-GMP compliance. Third, regulatory stability and access to high-skill labor continue to enhance the investment climate. However, downside risks persist. Energy volatility, particularly since 2022, remains a cost-management challenge for temperature- and pressure-sensitive biomanufacturing processes. Additionally, wage inflation in Germany’s technical sectors may compress long-term margins. Even so, high trust in German GMP standards, combined with the country’s central location within EU pharma logistics, ensures it remains a preferred outsourcing destination for USA. and Japanese sponsors seeking access to EMA-aligned production pathways.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.88 | 8.2% |
Japan’s biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is poised for solid expansion, growing from USD 0.76 billion in 2025 to USD 1.56 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 7.5%. The outlook is supported by several regulatory and structural levers. Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has increased alignment with ICH harmonization protocols, particularly in process validation and biologics licensing, making it easier for multinational sponsors to engage Japanese CDMOs. Japan’s aging population and corresponding biologics demand, especially in oncology and autoimmune disorders, are triggering more domestic outsourcing as local biotechs and pharma firms reduce capital expenditure on in-house facilities.
Japanese CDMOs enjoy a reputation for high precision and low deviation rates, particularly in aseptic fill-finish operations and microbial fermentation. Challenges remain. Japan faces acute labor shortages in biomanufacturing, particularly outside major hubs like Tokyo and Osaka, and cost competitiveness is often eclipsed by regional peers in South Korea and China. However, Japan’s CDMOs continue to win long-term contracts from global sponsors focused on quality-sensitive therapeutic segments. The overall growth trajectory is stable, with rising demand for complex biologics and steady investment in modular capacity enhancements.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.76 | 7.5% |
India is rapidly consolidating its position as a global cost-efficiency hub for biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing, with the market expected to grow from USD 0.72 billion in 2025 to USD 2.26 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 12.1%. Three strategic enablers shape this growth. India’s existing strength in generic drug manufacturing is being leveraged into biologics, with major CDMOs in Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Pune investing heavily in bioreactor capacity and single-use systems. Regulatory reforms under the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) have streamlined GMP certification and technology transfer processes, reducing onboarding time for international sponsors.
India's labor and utility cost advantages remain unparalleled, with 30-40% savings over Western CDMOs, enabling it to win early-stage, scale-up, and biosimilar mandates from global biotech firms. However, challenges remain: regulatory harmonization with ICH continues to lag in consistency, and perception risks around quality compliance persist-especially for sterile fill-finish operations. Nonetheless, several top-tier Indian CDMOs have secured USA FDA and EMA approvals, boosting global confidence. As biologics penetration rises in domestic therapy areas (oncology, autoimmune, diabetes), internal demand is also beginning to complement export-led growth, reinforcing India’s dual-role value in the outsourcing value chain.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.72 | 12.1% |
The United Kingdom continues to deliver stable, innovation-led performance in the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing sector, with the market forecast to grow from USD 0.69 billion in 2025 to USD 1.47 billion by 2035, representing a CAGR of 7.9%. The UK’s appeal rests on three foundational strengths. First, proximity to Oxford-Cambridge-London’s “Golden Triangle” offers CDMOs high-density access to early-stage biotech pipelines and translational medicine programs, enabling fast technology transfer and pilot-scale production.
Second, the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has proven agile post-Brexit, updating GMP frameworks to remain competitive with EMA and FDA pathways while offering localized regulatory support. Third, the government’s Life Sciences Vision (2021-2031) earmarked over GBP 1 billion in incentives for advanced therapy manufacturing, catalyzing investment in viral vector, plasmid DNA, and mRNA infrastructure. However, the post-Brexit operating environment still creates frictions, especially in cross-border clinical trial sourcing and batch release logistics. Wage inflation and energy costs are further pressuring margin structures. Despite this, the UK remains a high-trust environment for quality-sensitive manufacturing-particularly for oncology and cell therapies-making it an attractive destination for global sponsors seeking reliability over scale.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.69 | 7.9% |
South Korea is emerging as a strategic biopharmaceutical manufacturing powerhouse in Asia, with its contract manufacturing market projected to grow from USD 0.61 billion in 2025 to USD 1.52 billion by 2035, registering a strong CAGR of 9.5%. South Korea is home to global CDMO giants-most notably Samsung Biologics and Celltrion-who have aggressively expanded their biomanufacturing campuses with ultra-large-scale capacity and advanced automation. These firms offer one of the lowest cost-per-gram benchmarks globally for mammalian-based biologics, making Korea highly competitive in high-volume, late-stage commercial manufacturing.
The Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) has consistently aligned its biologics regulations with ICH standards, giving international sponsors confidence in both product quality and regulatory predictability. The Korean government offers robust fiscal incentives and infrastructure grants under its “K-Bio” initiative, which targets biopharma as a strategic export industry. Challenges include rising labor costs in Incheon and Busan and increasing competition from China in early-stage manufacturing. Nonetheless, South Korea remains favored for complex biologic production, particularly by USA and EU sponsors who value its track record in scale, compliance, and time-to-market performance.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.61 | 9.5% |
France is steadily consolidating its position as a key node in the Western European biopharmaceutical outsourcing network, with the market expected to expand from USD 0.59 billion in 2025 to USD 1.18 billion by 2035, marking a CAGR of 7.2%. The outlook is supported by a triad of strategic factors. First, the French government’s Health Innovation 2030 plan includes EUR 7.5 billion in funding for life sciences R&D and manufacturing, which has enabled several mid-size CDMOs to modernize their facilities and expand mammalian cell culture capabilities.
Second, France's stringent adherence to EMA GMP protocols, combined with an experienced regulatory workforce, continues to make it a low-risk jurisdiction for European and global sponsors. Third, its central location within the EU allows seamless access to pan-European supply chains. However, challenges remain. France’s labor environment is tightly unionized, leading to higher wage rigidity and slower workforce scale-up compared to peers like Ireland or the Netherlands. Energy prices have also been volatile, particularly for temperature-sensitive bioproduction. Still, the combination of high trust, government backing, and strong pharma-academic linkages ensures that France will retain its relevance, particularly for high-value clinical production and technology transfer projects.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.59 | 7.2% |
Brazil is steadily emerging as Latin America’s most promising biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market, forecast to grow from USD 0.47 billion in 2025 to USD 1.13 billion by 2035, registering a CAGR of 9.1%. Three core factors underpin this trajectory. First, Brazil’s regulatory authority-ANVISA-has strengthened its biologics review and GMP inspection processes, accelerating alignment with global standards and boosting confidence among multinational sponsors. Second, demand for biologics in Brazil’s public healthcare system (SUS) is rising sharply, driven by national tenders for oncology, diabetes, and autoimmune treatments.
This has prompted local CDMOs to expand fill-finish capacity and invest in upstream mammalian cell culture infrastructure. Third, the Brazilian government offers fiscal incentives and import duty waivers for technology transfer and local manufacturing partnerships, making Brazil an attractive base for sponsors aiming to localize production for regional access. Key risks include currency volatility and occasional procurement delays in public sector contracts, which can affect short-term cash cycles. Additionally, Brazil’s logistics infrastructure-while improving-still lags behind global benchmarks in cold-chain resilience. Nonetheless, with a population of over 200 million and a deepening biologics pipeline, Brazil is becoming a strategic node for Latin American contract manufacturing scale-up.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.47 | 9.1% |
Mexico is gaining traction as a secondary manufacturing hub in the Americas, with the biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market expected to expand from USD 0.42 billion in 2025 to USD 0.95 billion by 2035, translating to a CAGR of 8.4%. Three structural drivers are fueling this growth. First, proximity to the United States and integration under USMCA trade protocols make Mexico an ideal nearshore option for North American sponsors seeking cost-effective GMP capacity without offshore regulatory complexity.
Second, COFEPRIS, Mexico’s health regulatory agency, has intensified its international collaboration and now participates in the Pan American Network for Drug Regulatory Harmonization, improving sponsor confidence in quality systems. Third, local CDMOs are moving up the value chain-from packaging and secondary processes to upstream biologics manufacturing-supported by investment from regional conglomerates and global firms. Constraints persist: while labor costs remain attractive, skills shortages in cell culture and analytical development are a known bottleneck. Infrastructure gaps in power reliability and specialized logistics infrastructure also temper rapid expansion. Even so, Mexico’s regulatory gains and geographic advantage are expected to solidify its role as a fast-growing biomanufacturing alternative within the Western Hemisphere.
| 2025 Value (USD billion) | CAGR 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| 0.42 | 8.4% |
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Estimated Market Size (2025) | USD 11.23 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 26.93 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.9% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019 to 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Report Parameter | Revenue in USD billion |
| By Platform Type | Mammalian-Based and Microbial-Based |
| By Product Type | Monoclonal Antibodies, Recombinant Protein, Vaccine, Insulin, Growth Factor, Interferons, Others |
| By Application Type | Clinical and Commercial |
| By Therapeutic Area Type | Autoimmune Diseases, Oncology, Metabolic Diseases, Ophthalmology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Infectious Diseases, Neurology, Respiratory Disorders |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, China, Germany, Japan, India, United Kingdom, South Korea, France, Brazil, Mexico |
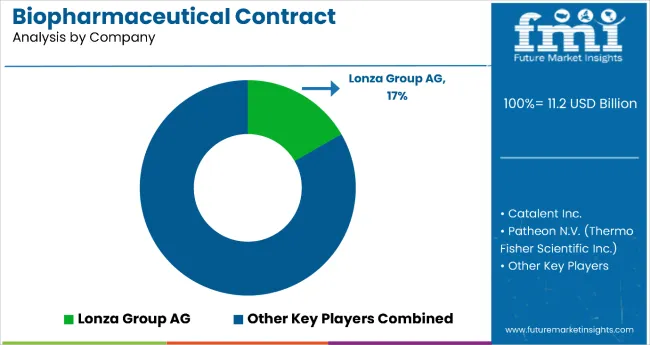
| Key Players | Samsung Biologics, Lonza Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific ( Patheon ), WuXi Biologics, Catalent Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim BioXcellence , Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies, AGC Biologics, Avid Bioservices , Rentschler Biopharma |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by value, market share analysis by region, and country-wise analysis |
The industry is segmented into Mammalian-Based and Microbial-Based manufacturing platforms.
The industry is segmented into Monoclonal Antibodies, Recombinant Protein, Vaccine, Insulin, Growth Factor, Interferons, and Others.
The industry is categorized into Clinical and Commercial applications.
The industry is segmented into Autoimmune Diseases, Oncology, Metabolic Diseases, Ophthalmology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Infectious Diseases, Neurology, Respiratory Disorders, and Others.
The industry is studied across North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia and Pacific, East Asia, and the Middle East & Africa.
The biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing industry is expected to reach USD 11.23 billion in 2025.
The biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing industry is projected to grow to USD 26.93 billion by 2035.
The biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing industry is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 8.8% from 2025 to 2035.
Oncology, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases are among the leading therapeutic areas driving outsourcing demand.
Key companies include Samsung Biologics, Lonza Group, Thermo Fisher Scientific (Patheon), WuXi Biologics, Catalent Inc., and Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2019 to 2034
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 9: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 10: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 13: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 14: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 15: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 16: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 17: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 18: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 19: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 20: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 21: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 22: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 23: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 24: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 25: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 26: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 27: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 28: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 29: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 30: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 31: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 32: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 33: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 34: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 35: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 36: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2019 to 2034
Table 37: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 38: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Table 39: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Table 40: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 6: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2019 to 2034
Figure 7: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 8: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 9: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 10: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 11: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 12: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 13: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 14: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 15: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 16: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 17: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 18: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 19: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 20: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 21: Global Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 22: Global Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 23: Global Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 25: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2024 to 2034
Figure 26: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 27: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 29: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 30: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 37: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 38: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 39: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 40: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 41: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 42: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 43: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 44: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 45: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 46: North America Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 47: North America Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 48: North America Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 49: North America Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 50: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 53: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 56: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 57: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 58: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 59: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 60: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 61: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 62: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 63: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 64: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 65: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 66: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 67: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 68: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 69: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 70: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 71: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 72: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 73: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 74: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 75: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 76: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 77: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 78: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 79: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 80: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 81: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 82: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 83: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 84: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 85: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 86: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 87: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 88: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 89: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 90: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 91: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 92: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 93: Western Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 94: Western Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 95: Western Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 96: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 97: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 98: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 99: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 100: Western Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 101: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 102: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 103: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 104: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 105: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 106: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 107: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 108: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 109: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 110: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 111: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 112: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 113: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 114: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 115: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 116: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 117: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 118: Eastern Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 119: Eastern Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 120: Eastern Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 121: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 122: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 123: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 124: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 125: Eastern Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 126: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 127: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 128: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 129: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 130: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 131: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 132: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 133: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 134: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 135: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 136: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 137: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 138: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 139: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 140: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 141: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 142: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 143: South Asia and Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 144: South Asia and Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 145: South Asia and Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 146: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 147: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 148: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 149: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 150: South Asia and Pacific Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 151: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 152: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 153: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 154: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 155: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 156: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 157: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 158: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 159: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 160: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 161: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 162: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 163: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 164: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 165: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 166: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 167: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 168: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 169: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 170: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 171: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 172: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 173: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 174: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 175: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 176: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 177: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 178: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 179: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 180: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 181: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2019 to 2034
Figure 182: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 183: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2024 to 2034
Figure 184: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Platform Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 185: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 186: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 187: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 188: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 189: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 190: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application Type , 2019 to 2034
Figure 191: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 192: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 193: Middle East and Africa Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2019 to 2034
Figure 194: Middle East and Africa Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 195: Middle East and Africa Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 196: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Platform Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 197: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Product Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 198: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Application Type , 2024 to 2034
Figure 199: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Therapeutic Area Type, 2024 to 2034
Figure 200: Middle East and Africa Market Attractiveness by Country, 2024 to 2034






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Contract Dose Manufacturing Market
Global IVD Contract Manufacturing Market Trends – Size, Forecast & Growth 2024-2034
Biologics Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biosimilar Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Orthopedic Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Pharmerging Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nutraceutical Contract Manufacturing Services Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
High Potency API Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Pharmaceutical Solid Dosage Contract Manufacturing Market
High-Potent Oral Solid Dosage Contract Manufacturing Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Contractual Cleaning Services Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2026 to 2036
Contract Lifecycle Management Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2026 to 2036
Contract Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2026 to 2036
Manufacturing on Demand for Medical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biopharmaceutical Fermentation Excipients Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Manufacturing Scale Electrostatic Precipitator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Contract Logistics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Manufacturing Logistics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Market Analysis - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Contract Furniture Market Analysis by Product Type, End-users, Distribution Channel, and Region from 2025 to 2035.

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.