The global electrical steel market is valued at USD 47.8 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 88.9 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period. Demand is being supported by increased production of energy-efficient transformers, expansion in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, and investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
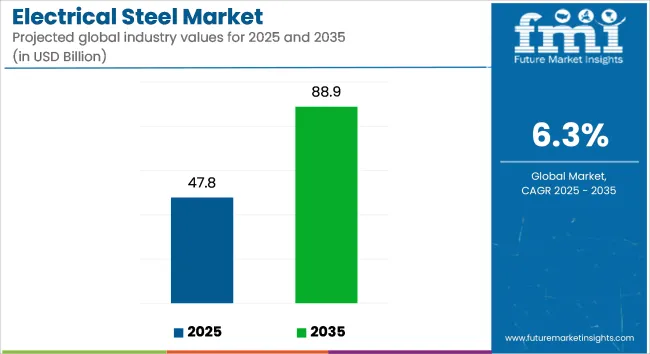
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry size (2025E) | USD 47.8 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 88.9 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.3% |
Electrical steel is used in magnetic cores of transformers, generators, and motors to reduce core losses and enhance energy efficiency. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), transformers utilizing grain-oriented electrical steel (GOES) have been associated with a projected 15% reduction in global electricity transmission losses by 2030. Utilities and transmission network operators are progressively phasing in GOES-based high-efficiency cores to comply with energy performance directives.
In the transportation sector, non-grain-oriented electrical steel (NGOES) is being incorporated into EV traction motors due to its superior magnetic permeability and efficiency at varying frequencies. Tesla’s 2024 investor disclosure reported a 20% reduction in motor core losses through the deployment of advanced NGOES in high-performance EVs. With global EV production expected to exceed 30 million units annually by the early 2030s, material usage per vehicle is projected to increase, prompting procurement shifts among OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers.
Electrical steel is also being used in wind turbine generators, solar inverter cores, and hydroelectric systems. BloombergNEF projected global wind capacity additions to surpass 150 GW annually by 2030. As onshore and offshore turbine installations scale, core materials with optimized magnetization properties are being selected to improve load factor reliability and grid integration.
R&D activity among electrical steel producers is intensifying, with emphasis on high-silicon variants, domain-refined grades, and advanced lamination coatings to reduce eddy current and hysteresis losses. Production lines are being upgraded for thin-gauge GOES to serve ultra-high-efficiency transformers required in HVDC transmission systems.
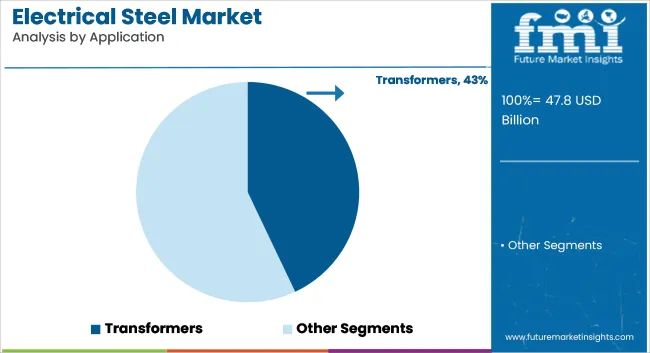
The transformer segment to hold approximately 43% of the global electrical steel market share in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% through 2035. Electrical steel is a key material in the cores of power and distribution transformers, where it enhances magnetic flux density while minimizing core losses.
With rising demand for grid reliability, renewable energy integration, and rural electrification, transformer manufacturing is increasing across Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Latin America. Non-grain-oriented and grain-oriented electrical steels are being engineered for lower hysteresis loss, improved permeability, and reduced eddy currents. Investments in smart grids, substation upgrades, and cross-border transmission infrastructure continue to reinforce transformer-related demand for advanced electrical steel grades.
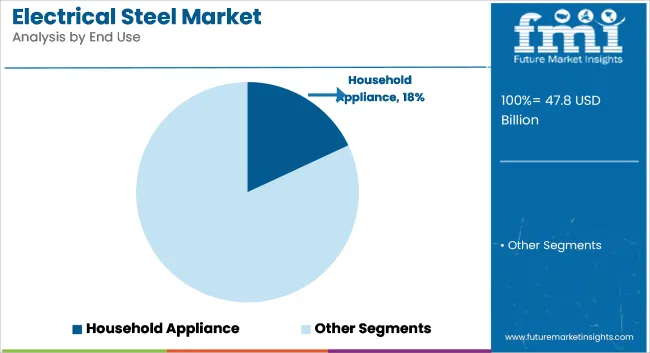
The household appliances segment is estimated to account for approximately 18% of the global electrical steel market share in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2035. Electrical steel is widely used in the motors and cores of washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, and induction cooktops. The material's magnetic properties help reduce energy consumption and improve device performance.
With increasing demand for inverter-based and energy-labeled appliances, especially across emerging economies, the role of electrical steel in ensuring quieter, longer-lasting, and more efficient appliances is expanding. Manufacturers are also focusing on reducing thickness and optimizing silicon content in electrical steel to meet evolving standards under programs such as ENERGY STAR and BEE (India). As electrification in residential sectors grows, household appliances will continue to be a reliable downstream market for electrical steel.
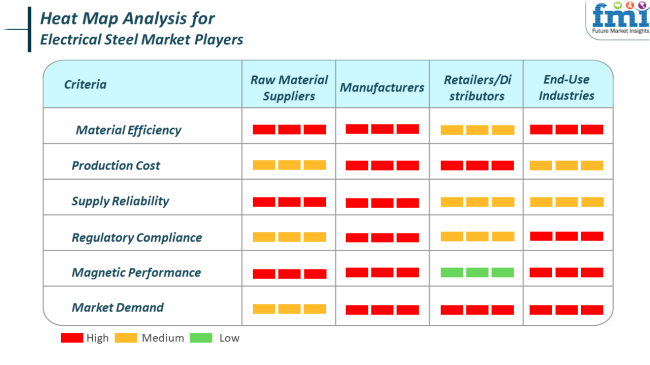
The industry addresses high technical standards and performance requirements, especially in energy and automotive applications. Both raw material suppliers and manufacturers prioritize material efficiency, magnetic performance, and reliability in supply since these dimensions have a direct bearing on conductivity and transformer or core performance (red). Meanwhile, manufacturers focus on production costs and compliance with regulations, which is a balancing act between technological standards as well as environmental and safety standards.
With regard to production costs and industry demand, retailers/distributors rely on this for inventory turnover and competitive pricing. As such, end-use industries, such as automotive and energy, show the following preferences concerning magnetic performance, material efficiency, and related regulations: these directly tie into energy savings and system longevity overall.
Various risks within the industry impact its stability and growth. The most common among these risks is that of industry risk, particularly because of global demand swings. Industry mainly depends on factors like automobiles (electric vehicles mostly), energy (transformers and motors), and construction. Weaknesses in these areas, irrespective of the cause, such as economic recession, geopolitical instability, or energy policy change, lessen the demand for product.
The market is also subject to price fluctuations of raw materials, specifically iron ore and coking coal; this directly influences manufacturing costs and profit margins, especially amongst less price-powerful companies. Operational risks arise from the necessary capital intensity and technical complexity associated with product production. The entire production process, particularly that of grain-oriented (GO) electrical steel as well as non-grain-oriented (NGO) electrical steel, demands stringent control coupled with quality assurance.
Any disruption in the manufacturing processes on account of equipment failure or supply chain bottlenecks, as well as a shortage of labor, might cause a delay in delivery, increased costs, or loss of customer loyalty. Moreover, the technological expertise needed to keep up with the latest efficiency and magnetic property standards stiffens pressure on relatively smaller or novice entrants into this industry.
There are high regulatory and trade risks as well. The steel industry is usually one of the most tariffed, duty-imposed, and anti-dumping sectors, which affects its trade flow and leads to increased costs for importers and exporters. For example, the USA tariffs on steel imports have changed the prices and availability of product used in transformers, which is concerning utility companies. Also, environmental regulations regarding carbon emissions, waste disposal, and energy use are becoming stiffer. Heavy modifications in production facilities or changes in materials used would incur high costs.
On account of the environment and sustainability, markets will feel greater pressure on the ecological footprint of steel production during this time. Steel manufacture is extremely energy-intensive and is, therefore, a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
As ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) factors are increasingly becoming important to investors and regulators alike, the adoption of greener technology is what companies will have to show, as will responsibly sourcing and recycling practices. Nonconformity towards sustainability expectations would mean reputational damage or loss of key investment funds.
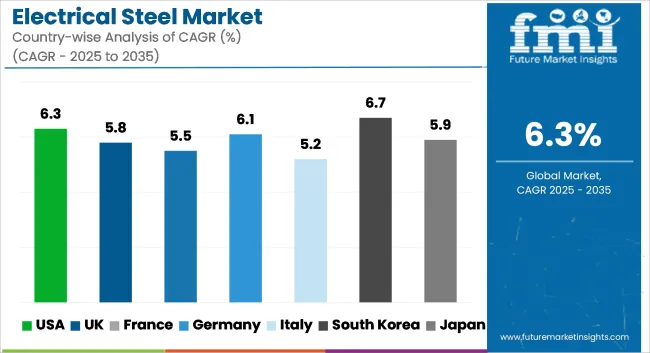
| Countries | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 6.3% |
| UK | 5.8% |
| France | 5.5% |
| Germany | 6.1% |
| Italy | 5.2% |
| South Korea | 6.7% |
| Japan | 5.9% |
| China | 7.4% |
| Australia | 5.3% |
| New Zealand | 4.9% |
The USA electric steel industry will grow at a CAGR of 6.3% during 2025 to 2035, with growing investments in renewable energy infrastructure and powering the grid with modernization. Increasing demand for efficient motors and electric transformers is compelling domestic consumption vigorously. Moreover, policy efforts to popularize electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid systems are also fuelling the industry further.
Dominant producers like AK Steel, Cleveland-Cliffs Inc., and United States Steel Corporation are top industry players that are aggressively expanding their capacity. Increased usage of electric powertrains in vehicle applications is also fueling demand for non-grain-oriented electrical steel. In contrast, the grain-oriented ones continue to play a critical role in applications involving power transmission and distribution.
The UK industry is expected to grow with a CAGR of 5.8% through the forecast period, which is largely driven by the demand for cleaner forms of energy consumption and electric transport. The focus on minimizing carbon emissions has led to a relentless demand for energy-saving electrical parts in industrial as well as commercial applications.
Major industry players like Tata Steel, UK, and Liberty Steel are concentrating on cutting-edge production techniques and strategic collaborations to meet increasing domestic needs. Wind turbine installation and EV charging stations are driving demand for products globally, particularly transformers and inductors that energize renewable energy grids.
France's industry is anticipated to expand at a 5.5% CAGR during 2025 to 2035. The country's energy policy of decarbonization and sustainable nuclear power is propelling demand for product. Increased investment in smart grid technology and electric mobility are also fueling industry forces ahead.
Companies like ArcelorMittal and Aperam are industry leaders in industry growth through innovation and capacity expansion. The product is increasingly being used in applications like power transformers and high-performance motors for domestic upgrading and the growing EV base.
Germany is expected to experience a CAGR of 6.1% in the industry between 2025 and 2035. The strong automotive industry, combined with the high level of focus on energy conversion and industrial electrification, is driving up the use of high-quality magnetic materials. Energy-efficient motor cores and renewable energy infrastructure are some of the industry drivers for consumption.
Industry players such as Voestalpine and Thyssenkrupp are increasing R&D activities to produce high-quality products that can meet changing technological demands. Use in EV production, wind energy equipment, and power transformers is driving robust industry growth.
Italy's industry is likely to expand at a CAGR of 5.2% over the forecast period, with industrial automation trends and increasing grid modernization initiatives. Expansion of the national electrification agenda, particularly in public transport and renewable energy generation, is fueling material demand.
Industry leaders like Marcegaglia and Acciaieried'Italia are leading by integrating production activities and diversifying product lines. Increased emphasis on grain-oriented electrical steel for transformer cores and non-grain-oriented electrical steel for electric motors will enhance industry stability.
The South Korean industry is expected to register a 6.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035, fueled by the electronics and the automotive industry's technological superiority. The spread of EVs and the growth of smart grids are considerably propelling the use of high-performance products.
Major players such as POSCO and Hyundai Steel are using innovation and sustainability to increase capacity. Increasing local demand from domestic customers and foreign buyers for high-grade electrical machinery and automotive uses is stimulating the production of higher grades of grain and non-grain-oriented steel.
Japan's industry is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period, supported by robust demand from the industrial machinery and automotive sectors. Initiatives to minimize energy losses and maximize equipment efficiency are influencing the selection of materials for applications in motors and generators.
Players like Nippon Steel Corporation and JFE Steel are emphasizing precision manufacturing to meet strict performance standards. The rising use of products in high-frequency motors of EVs and robotics is propelling industry growth in domestic and export markets.
China will also lead the industry, with a growth rate of 7.4% during the forecast period. Key growth drivers include long-term industrialization, mass-scale adoption of EVs, and comprehensive replacement of national power infrastructure. Government policies on emissions reduction through carbon neutrality and energy efficiency are also driving demand.
Large producers such as Shougang Group and Baowu Steel Group are expanding capacity and investing in advanced processing technologies. Uses in segments such as grid enhancement, electric mobility, and energy-efficient appliances are propelling a diversified and healthy industry.
The Australian industry will expand at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2025 to 2035, with constant innovation in renewable energy schemes and rising electrification of rural and remote regions. There is a rising need for efficient transformers and motors, and initiatives are being made to modernize infrastructure.
Imports and partnerships with global suppliers are enabling industry growth. Key stakeholders are observing the use of products in applications that are synergistic with the nation's net-zero objectives, especially in solar and wind infrastructure and clean transportation networks.
New Zealand is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% through the forecast period in the industry. Strategic energy reforms and decarbonization policies for the transport segment are adding demand. Demand for efficient transformer and motor systems is picking up pace with utilities and manufacturing sectors.
Imports and collaborations are meeting local markets with international suppliers, whereas domestic production sites are constrained. Uses in power grid refurbishment, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and green building technology are driving future industry potential for products.
The electrical steel market is highly consolidated, with major players like Nippon Steel, POSCO, and ArcelorMittal dominating production capacities. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced electrical steel grades that meet evolving industry requirements. For instance, Nippon Steel’s March 2025 launch of Ultra-Loss-Core GOES targets high-voltage transformer applications, offering a 12% reduction in energy loss compared to conventional grades. POSCO expanded its NGOES production in February 2025 to cater to the booming EV motor market in South Korea and beyond.
The industry is segmented into grain-oriented electrical steel and non-grain oriented electrical steel.
The industry is categorized into inductors, motors, and transformers.
The industry is segmented into automobile, manufacturing, energy, household appliance, and others.
The industry is divided into North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Middle East and Africa.
The market is estimated to be worth USD 47.8 billion in 2025.
Market sales are expected to reach USD 88.9 billion by 2035, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient motors, transformers, and electric vehicle components.
China is witnessing fastest growth at a CAGR of 7.4%, supported by rapid industrialization and expansion in power infrastructure and electric mobility.
Non-grain oriented electric steel is widely used.
Key companies in the market include Novolipetsk Steel, Voestalpine Stahl GmbH, POSCO, Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation, ThyssenKrupp AG, JFE Steel Corporation, CogentPower, ArcelorMittal SA, Aperam SA, Baosteel Group, AK Steel Holding Corp, and Allegheny Technologies, Inc.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Electrical Steel Coatings Market 2025-2035
Stainless Steel Electrical Cabinet Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Enclosure Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Sub Panels Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Testing Services Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Testing Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrically Conductive Adhesives Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrically-Driven Heavy-Duty Aerial Work Platforms Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrically Actuated Micro Robots Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrically Conductive Coating Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Conduit Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Safety Personal Protection Equipment (PPE) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Steering Column Lock Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Coil Tester Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Electrical Fuses Market Analysis – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Electrical Digital Twin Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Electrical Bushings Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Electrical Insulation Materials Market Trends 2024 to 2034
Electrical Label Market Demand & Industry Applications 2024 to 2034
Electrical Service Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA