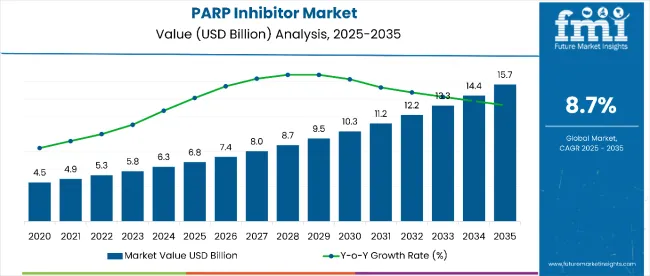
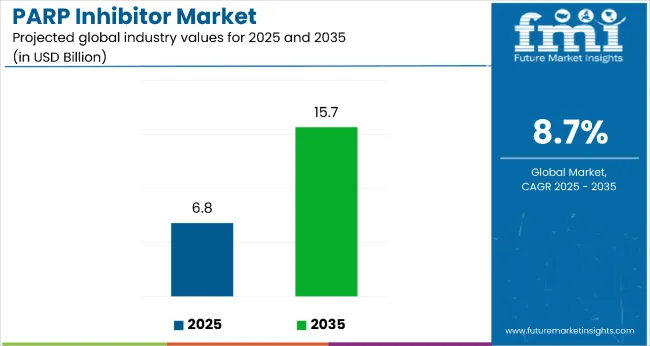
The PARP inhibitor market is estimated to be valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 15.7 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% over the forecast period. Increasing awareness of targeted cancer therapies, advancements in biomarker-driven treatment, and expansion into rare cancer indications are fueling market growth. Adoption of combination therapies with immunotherapy and chemotherapy is also contributing to market expansion.
The substantial expansion is fueled by increasing adoption of targeted cancer therapies, especially for ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. The market is also gaining momentum from expansion into rare cancer indications and the integration of precision medicine techniques such as biomarker-driven patient selection. Regulatory support, increasing patient awareness, and the rise of combination therapies further accelerate the adoption of PARP inhibitors, contributing to steady market growth across global regions.
By 2030, the market is expected to reach around USD 10.3 billion, with an incremental growth of about USD 3.5 billion during the first half of the decade. The remaining USD 5.4 billion growth is anticipated in the latter half, illustrating balanced development over the forecast period. Innovations in combination treatment regimens, enhanced patient stratification, and expanded approvals for new PARP inhibitors are key drivers shaping this trajectory. Overall, the market outlook remains positive, supported by therapeutic advancements that improve treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
The market holds an 86.2% share within the targeted cancer therapies segment, driven by its proven efficacy in treating BRCA-mutated and homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) cancers. It accounts for around 83.9% of the ovarian cancer treatment market, supported by strong clinical data and growing patient adoption. The market contributes nearly 38% to the overall oncology therapeutics landscape, bolstered by increasing use in breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. It holds close to 24% of the precision medicine segment, where biomarker-driven patient stratification strengthens its position. The share in the global targeted therapy market is about 20%, highlighting its expanding role in multimodal cancer treatment regimens.
The market is evolving with new combination therapies enhancing treatment outcomes and expanding indications into rare cancers. Pharmaceutical companies are investing in next-generation PARP inhibitors and companion diagnostic developments. Collaborations with healthcare providers and increased regulatory approvals are accelerating market penetration. Furthermore, growing awareness among clinicians and patients, along with rising accessibility through reimbursement policies, support broader adoption. These dynamics are reshaping the oncology treatment landscape and positioning PARP inhibitors as a key pillar of personalized cancer care.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Estimated Value in 2025 (E) | USD 6.8 billion |
| Forecast Value in 2035 (F) | USD 15.7 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.7% |
The market is growing significantly due to multiple converging factors driven by advances in cancer treatment and precision medicine. One of the primary reasons is the increasing prevalence of cancers such as ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers, which are responsive to PARP inhibitor therapy. These inhibitors target tumors with specific genetic mutations, particularly BRCA1 and BRCA2, exploiting vulnerabilities in cancer cells by blocking DNA repair pathways, leading to enhanced treatment efficacy.
Additionally, advances in biomarker-driven patient stratification and genetic testing have improved the identification of eligible patients who are most likely to benefit from PARP inhibitors, thereby expanding the addressable patient population. Increasing awareness among healthcare professionals and patients about the benefits of targeted therapies has also contributed to higher adoption rates of PARP inhibitors.
The market is segmented by drug type, indication, distribution channel, and region. By drug type, the market is categorized into Olaparib, Niraparib, Rucaparib, and Talazoparib. Based on indication, the market is divided into ovarian cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer. In terms of distribution channel, the market is segmented into hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online pharmacies. Regionally, the market is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia and Pacific, East Asia, and the Middle East & Africa.
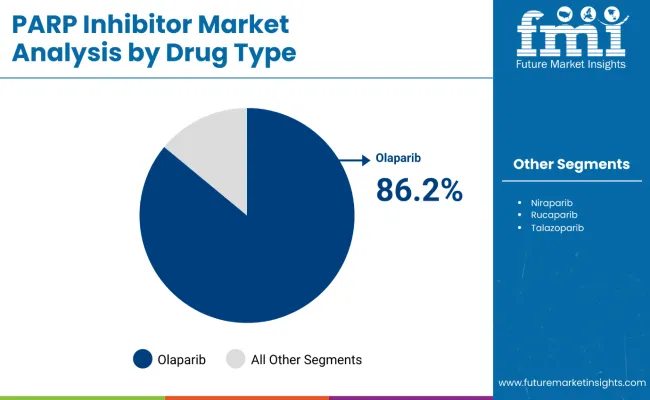
The most lucrative segment within the PARP inhibitor market by drug type is Olaparib, which is projected to hold an overwhelming market share of 86.2% in 2025. Olaparib’s market dominance is attributed to its status as the first FDA-approved PARP inhibitor and its broad-spectrum applicability across multiple cancer indications, particularly ovarian and breast cancer. The drug’s proven clinical efficacy in extending progression-free survival and overall survival bolsters physician confidence and patient demand.
Olaparib's success is further enhanced by multiple regulatory approvals worldwide, comprehensive reimbursement coverage, and a strong clinical trial pipeline expanding its indications, including use in non-BRCA mutated cancers with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD). Its flexible administration and favorable safety profile also contribute to its competitive edge.
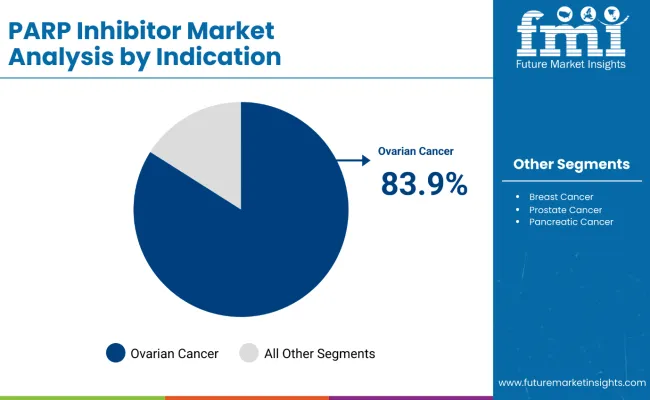
The most lucrative segment by indication in the PARP inhibitor market is ovarian cancer, commanding a dominant market share of 83.9% as of 2025. This segment’s prominence is driven by the high incidence and significant unmet medical need associated with ovarian cancer, which is one of the most common gynecologic malignancies worldwide. Historically, ovarian cancer treatment options have been limited, positioning PARP inhibitors like Olaparib as breakthrough therapies that substantially improve progression-free survival for patients, especially those with BRCA mutations or homologous recombination deficiency (HRD).
The strong clinical validation of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer has led to widespread adoption, robust reimbursement policies, and accelerated regulatory approvals across major markets. Furthermore, ongoing trials are exploring expansions into earlier-stage ovarian cancer and maintenance therapies, which are expected to boost usage and market growth further. Compared to other indications like breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers, ovarian cancer remains the primary revenue driver, benefiting from a combination of high patient volumes, compelling efficacy data, and progressive treatment paradigms, solidifying its position as the most lucrative indication segment in the PARP inhibitor market.
From 2025 to 2035, the PARP inhibitor market is propelled by increasing adoption of targeted cancer therapies that improve patient outcomes by exploiting DNA repair weaknesses in tumors. Advances in biomarker-driven precision medicine have allowed clinicians to better identify eligible patients, enhancing treatment efficacy and safety. This precision approach positions PARP inhibitors as essential components in personalized oncology regimens, expanding their clinical use across ovarian, breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancers.
Pharmaceutical Innovation and Regulatory Support Driving Market Growth
Rising pharmaceutical innovation is a primary growth catalyst for the PARP inhibitor market. Continuous investment in clinical trials exploring combination therapies with immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and novel agents is broadening treatment options and patient populations. Regulatory agencies are providing accelerated pathways and wider approvals, facilitating faster market access. Manufacturers offering robust clinical evidence and improved drug profiles, such as reduced side effects and enhanced potency, stand to capture sustained demand.
Advancements in Combination Therapies and Precision Oncology
Integration of combination regimens and companion diagnostic testing further enhances market expansion opportunities. The development of next-generation PARP inhibitors with improved selectivity and efficacy, combined with advancements in genomic testing, is optimizing therapeutic outcomes. These trends underscore the evolving paradigm of precision oncology, positioning PARP inhibitors as vital, growing pillars in modern cancer treatment with strong regulatory and clinical support.
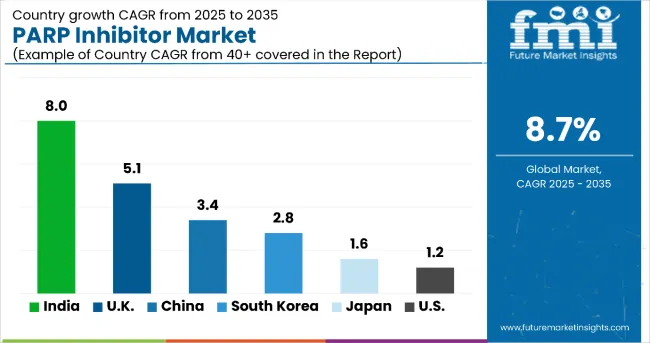
| Country | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|
| India | 8.0 |
| United Kingdom | 5.1 |
| China | 3.4 |
| South Korea | 2.8 |
| Japan | 1.6 |
| United States | 1.2 |
The market shows diverse growth across countries. India leads with an 8% CAGR driven by expanding healthcare access and rising cancer awareness. The UK follows at 5.1%, supported by strong NHS backing and advanced biomarker testing. China and Germany both grow steadily around 3-3.4%, fueled by healthcare investments and regulatory reforms. South Korea has moderate growth at 2.8%, backed by government initiatives and insurance coverage expansion. Japan’s market grows modestly at 1.6% due to regulatory strictness and an aging population. The US shows the slowest growth at 1.2%, influenced by market maturity and high treatment costs, despite being an innovation leader.
The report covers an in-depth analysis of 40+ countries; six top-performing OECD countries are highlighted below.
Revenue from PARP inhibitor in the United Kingdom is expanding steadily with a CAGR of 5.1%. The NHS’s emphasis on advanced targeted cancer therapies and early diagnosis programs supports robust market growth. Access to innovative biomarker testing has improved patient stratification, enhancing treatment effectiveness and growing therapy adoption. Regulatory agility and reimbursement frameworks facilitate faster approvals and patient access. Strong collaboration between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers accelerates clinical trial activities. Increasing public and physician awareness about precision oncology also drives demand. Investments in personalized medicine infrastructure have strengthened treatment delivery. Overall, the UK market remains a vital hub for PARP inhibitor innovation and deployment.
Demand for PARP inhibitor in China is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.4%, fueled by expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising cancer incidence. Government policies encouraging domestic innovation and importation of novel therapies support increasing availability. The growing middle class with enhanced healthcare affordability stimulates demand for advanced oncology treatments. Improvements in diagnostic capabilities and wider access to genomic testing facilitate personalized treatment adoption. Expansion of cancer care centers across urban and rural regions enhances patient reach. Investments from key pharmaceutical players are scaling manufacturing and clinical development. Regulatory reforms accelerate market entry for new PARP inhibitors. These factors collectively drive steady output expansion in the Chinese PARP inhibitor market.
Demand for PARP inhibitor in South Korea is growing at a CAGR of 2.8%, marked by high adoption within an advanced healthcare framework. Government initiatives focusing on innovation in cancer treatment emphasize early detection and targeted therapies. Pharmaceutical collaborations with research institutions enhance clinical trial success rates and drug development. Availability of companion diagnostic tests optimizes patient selection, bolstering treatment outcomes. Insurance coverage improvements allow broader patient access to PARP inhibitors. Aging demographics increase cancer patient populations, creating demand growth. Digital health solutions aid patient monitoring and compliance. These structural developments position South Korea’s market for steady expansion.
Demand for PARP inhibitor in Japan demonstrates moderate growth at 1.6% CAGR, shaped by stringent regulatory standards alongside strong demand driven by an aging population. The country’s meticulous approval process ensures drug safety and efficacy, fostering clinician confidence. Increasing use of precision oncology and biomarker testing enhances targeted treatment utilization. High healthcare standards and insurance coverage support consistent patient access. Pharmaceutical companies focus on innovation in drug delivery and combination therapies to meet evolving treatment needs. Research investments by domestic firms underpin ongoing market development. Patient awareness campaigns promote earlier diagnosis, further supporting the market. These dynamics contribute to a balanced growth trajectory for Japan’s PARP inhibitor sector.
Revenue from PARP inhibitor in the USA, with a CAGR of 1.2%, is characterized by extensive pharmaceutical research and widespread adoption of precision medicine. High investment in clinical trials drives innovation in combination therapies and next-generation PARP inhibitors. Advanced genomic testing facilitates effective patient stratification, improving therapeutic outcomes. Despite high treatment costs and regulatory complexities moderating rapid uptake, reimbursement programs enable access for many patients. Increasing collaboration between biotech startups and large pharma accelerates drug development pipelines. Growing awareness among oncologists and patients supports market growth. Digital health technologies improve patient adherence and monitoring. This expansion pattern highlights the US as a crucial, dynamic market for PARP inhibitors.
Revenue from PARP inhibitor in India is experiencing rapid growth with an estimated CAGR of 8%, driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing cancer awareness. Rising government healthcare initiatives promote early detection and personalized medicine adoption. Greater availability of genomic testing and diagnostic facilities supports precision oncology treatments. Growing affordability and insurance penetration increase patient access to PARP inhibitors. Pharmaceutical companies are expanding local production capacities and clinical trial activity to meet demand. Increased collaboration with global firms enhances technology transfer and innovation. The rise of oncology specialty centers across urban and semi-urban areas increases treatment reach. These factors collectively fuel a surge in market output and expansion.
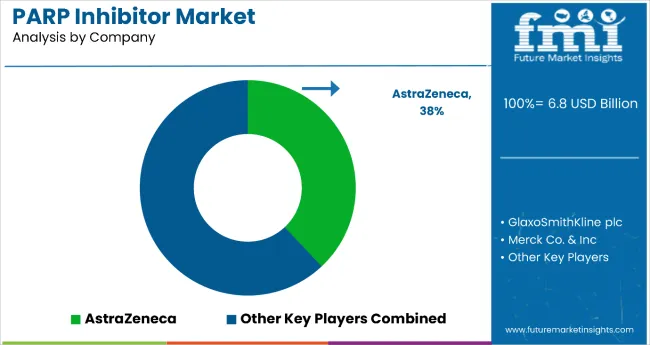
The PARP inhibitor market is a rapidly growing segment of the oncology therapeutics landscape, driven by increasing demand for targeted cancer therapies that focus on DNA repair mechanisms. Key players in the market include AstraZeneca plc, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie Inc., and Clovis Oncology, Inc., each contributing to the development and commercialization of PARP inhibitors for various cancer types, particularly ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.
AstraZeneca, with its leading PARP inhibitor Olaparib (Lynparza), has been at the forefront of the market, offering a widely adopted treatment option for ovarian cancer and expanding into other indications like breast cancer and prostate cancer. GlaxoSmithKline is advancing Veliparib, focusing on combination therapies to enhance its effectiveness in treating solid tumors and hematologic cancers.
Merck & Co., through its PARP inhibitor Rucaparib (Rubraca), is making significant strides, particularly in ovarian cancer, and is exploring its potential in combination therapies for broader oncology applications. AbbVie, in collaboration with ImmunoGen, is focusing on EPC-119, its investigational PARP inhibitor for treatment-resistant cancers. Clovis Oncology is another important player, with its PARP inhibitor Rucaparib approved for use in ovarian cancer and prostate cancer, aiming to expand its use across various cancer types.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units (2025) | USD 6.8 billion |
| Drug Type | Olaparib, Niraparib, Rucaparib, Talazoparib |
| Indication | Ovarian Cancer, Breast Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer |
| Distribution Channel | Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia and Pacific, East Asia, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, United Kingdom, Germany, China, India, Japan, South Korea, France, Canada, Brazil, Australia, and 40+ countries |
| Key Companies Profiled | AstraZeneca plc; GlaxoSmithKline plc; Merck & Co., Inc.; AbbVie Inc.; Clovis Oncology, Inc. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales segmented by drug type and indication, growing adoption of precision oncology, expansion of companion diagnostic testing, increasing use of combination therapies, evolving regulatory approvals, and rising patient awareness of personalized treatment strategies |
The global PARP inhibitor market is estimated to be valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2025.
The market size for PARP inhibitors is projected to reach USD 15.7 billion by 2035.
The PARP inhibitor market is expected to grow at an 8.7% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
Olaparib is projected to lead in the PARP inhibitor market with 86.2% market share in 2025.
In terms of indication, ovarian cancer is projected to command 83.9% share in the PARP inhibitor market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
FcRn Inhibitors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
CGRP Inhibitors Market Trends - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Global KRAS Inhibitor Market Analysis – Size, Share & Forecast 2024-2034
PCSK9 Inhibitor Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
SGLT2 Inhibitors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
SGLT2 Inhibitors Treatment Market Overview – Trends & Growth 2024-2034
NF-KB Inhibitors Market
Mould Inhibitors Market
Kinase Inhibitors For Cancer Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Kinase Inhibitor in Autoimmune Diseases Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Enzyme Inhibitors Market
Galectin Inhibitor Therapeutics Market
Paraffin Inhibitors Market
Corrosion Inhibitors Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Checkpoint Inhibitor Refractory Cancer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Market – Trends, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Mouse RNase Inhibitor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Proton Pump Inhibitors Market Insights - Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025 to 2035
Angiopoietin Inhibitors Therapeutic Market
Oilfield Scale Inhibitor Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA