The Korea aircraft ground support equipment market is anticipated to be valued at USD 124.52 million in 2025. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% during the forecast period and reach a value of USD 220.9 million in 2035.
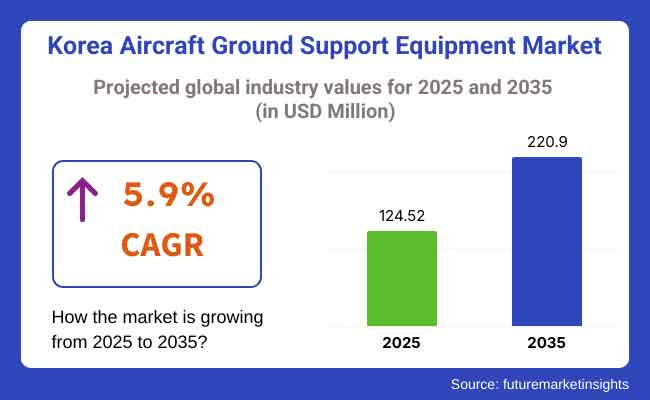
In 2024, the Korea aircraft ground support equipment market experienced steady expansion, reaching an estimated USD 117.7 million. Some of the key drivers of demand were expanding air traffic, airport modernization, and the availability of electric and hybrid GSE solutions responding to stringent environmental regulations.
South Gyeongsang and North Jeolla provinces came out as prominent adopting industries, induced by airport infrastructure investments and government policies enabling sustainable aviation practices. The proliferating use of e-commerce also added strength to the demand for cargo-handling equipment.
Looking forward to 2025 and beyond, the industry is anticipated to maintain its pace with a CAGR of 5.9%. The shift toward autonomous GSE with AI integration is thought to pick up speed towards enhancing operational efficiency and reducing turnaround time. Fleet expansion of airlines in Korea will further necessitate advanced ground support solutions.
By 2035, the forecast puts the industry in excess of USD 220.9 million, showing strong investments directed toward next-generation GSE technologies and joint implementation through regulations.
A recent survey conducted by FMI with key stakeholders in the Korea aircraft ground support equipment market revealed several crucial industry trends and challenges. A clear majority of respondents, i.e. airport authorities, manufacturers of the equipment, and airline operators, have emphasized the growing industry inclination toward electric and hybrid GSE.
Regulatory pressure to cut carbon emissions and reduce fuel dependency has profiled this transition, with over 60% of stakeholder actors indicating plans to invest in sustainable equipment within the next five years. However, high initial costs and lack of infrastructure remain significant impediments to mass adoption.
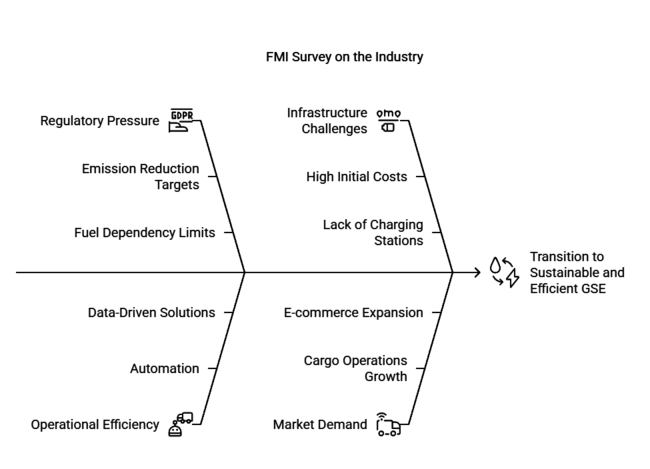
Operational Efficiency is another key point. Stakeholders emphasize automation and data-driven maintenance solutions. AI-integrated fleet management systems are gaining interest in the Korean aviation field as airlines pursue optimizing turnaround times and reducing discretionary equipment failures. Such trends align with an industry-wide movement toward predictive maintenance, with real-time data analytics used to reduce downtime and maintain operational reliability.
In this respect, there was also interest from stakeholders to standardize technology adoption across various airports to provide for seamless interoperability of ground support solutions.
The survey also revealed increasing demand for specialized GSEs to support the growth of cargo operations. More than 55% of stakeholders foresee a rapid year-on-year increase in demand for advanced cargo-handling equipment. This includes high-load capacity transporters and automated baggage-handling systems amid the continuous expansion of e-commerce and global trade.
Government incentives for enhancing GSE manufacturing were also cited, as reliance on imported machinery remains a major hurdle.
To gain a deeper understanding of Korea’s GSE industry dynamics and emerging opportunities, connect with FMI for exclusive insights and tailored consultation.
Government policies and regulations are shaping the Korean aircraft ground support equipment market, with a focus on efficiency, sustainability, and safety. More stringent emissions regulations, certification of GSE as a requirement, and financial incentives are all accelerating the transition to electric GSE and the adoption of international standards concerning safety in aviation.
Government Regulations & Mandatory Certifications in South Korea
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Consistent growth based on post-pandemic recovery and increasing air travel demand. The rise in investments in airport infrastructure facilitated industry growth. | Increased growth is driven by technology advancements, automation, and sustainability programs, along with growing airport expansion activities. |
| Phase-by-phase adoption of smart GSE solutions, with minimal rollout of AI- and IoT-based equipment. | Widespread implementation of AI-driven, IoT-based, and fully automatic GSE for optimizing efficiency and decreasing turnaround time. |
| Partial transition to electric GSE, with hybrid variants gaining popularity. Minimal infrastructure for mass electrification. | Mass transition to electric and hybrid GSE based on stricter environmental regulations and enhanced charging infrastructures. |
| Adoption of international safety and efficiency standards, with a moderate drive towards sustainability initiatives. | Regulatory policies focusing more on greener and zero-emission GSE, complemented by increased safety and efficiency regulations. |
| Focused on upgrading current airport GSE fleets for enhanced operational efficiency. | The industry is expected to see higher investments in AI-driven, automated, and eco-friendly ground-handling solutions to meet future aviation demands. |
| Industry dominance by established domestic as well as foreign players, focusing on product reliability and cost competitiveness. | More competitive with increased investments in innovation, digitalization, and environmental technologies, inviting new industry players. |
Airport service equipment dominates the Korea Aircraft Ground Support Equipment (GSE) market, ensuring seamless airport operations. Investments in de-icing vehicles, refuelers, and lavatory units are improving efficiency and safety. Rising air traffic is pushing Korean airports to modernize, incorporating automation and smart technology. Better equipment makes turnaround times shorter, minimizes delays, and better serves passengers.
Higher international and domestic flights create good opportunities for GSE manufacturing and supply. Operational efficiency is further boosted by digital monitoring and predictive maintenance integrated into the equipment in the air. As the aviation sector develops in Korea, the existence of airport service equipment remains a major factor in guaranteeing reliability and nurturing the long-term growth of the industry.
Rental ground support equipment in the Korea Aircraft GSE market is gaining acceptance as airlines and airports are opting for flexible and cost-efficient modes of operation. Owning fleets that function only through short-term leasing helps operators to adjust their fleets with changing demand things for the seasons without needing to engage in any hefty capital investment.
Ground support equipment rental serves Korean airports' purpose of using such well-maintained, modern equipment to meet environmental and safety requirements as they change over time.
The trend promotes sustainability, with consequent reduction of waste and maintenance costs. Leasing provides carriers and ground handlers with greater financial freedom. With increasing competitive pressures, renting GSE is a strategic opportunity allowing operators to optimize their operations and comply with strict performance and efficiency requirements.
Electricity-free GSE still dominates the Korean Aircraft GSE market, accounting for nearly half of the demand in the industry. At airports where adequate electric infrastructure is not present, diesel- and hydraulic-powered equipment play a vital role. These are the workhorses of ground handling operations, especially in aircraft towing and cargo operations. As stricter emissions rules take effect, producers enhance fuel economy and hybridization.
Such a shift in low-emission technology complements non-electric equipment sustainability objectives without reducing functional performance. Substitute power systems are being adopted slowly in Korean airports. Yet, non-electric GSEs remain essential to areas where high-performance applications necessitate them, ensuring efficiency and quick response within the constantly changing system that includes Korean airport infrastructure.
The commercial segment is on a growth-trend in the Korea Aircraft GSE market, given the increasing passenger and cargo traffic. For operational efficiency, automation, AI-based logistics, and real-time baggage tracking are among features that Korean airports install. Smart passenger boarding, electric ground vehicles, and advanced cargo loaders are features of ground support in-streamlining. Investments in digitalization, self-service check-ins, and infrastructure modernization for sustainability drive future trends in commercial aviation.
The future holds very good for the commercial aviation industry, as airlines continue to increase their fleet and enhance service. Ground support operations continue to evolve to meet these growing fleets and improve services. Advanced technology transformation will guarantee that operations will be efficient, reliable, and follow regulations, thus making its status as a vital engine of the nation's growing aviation industry in Korea.
The Korea aircraft ground support equipment market has experienced significant growth in 2024, driven by the expansion of airport infrastructure, increasing air traffic, and a strong focus on sustainability. Notable players such as JBT Corporation, TLD Group, Textron GSE, Toyota Industries Corporation, and Tug Technologies Corporation have been actively undertaking strategies for establishing their footprint while targeting increasing demand for advanced GSE solutions.
In 2024, JBT Corporation continued to lead the Korean GSE industry with a 28% market share, generating an estimated revenue of USD 70 million out of the total market size of USD 250 million. The company has focused on increasing electric and hybrid GSEs because of strict environmental requirements in Korea. In addition, JBT has also introduced intelligent telematics systems to monitor and conduct predictive maintenance of its equipment in real-time, thereby facilitating operational efficiency for airport operators. JBT also won a major contract with Incheon International Airport, supplying electric baggage handling systems and de-icing equipment for aircraft, thereby solidifying its position further.
TLD Group, a leading global manufacturer of GSE, holds a 24% share of the Korean market, generating an estimated revenue of USD 60 million in 2024. In line with the operation for green airports across the world, TLD initiated its newly launched electric tow tractors and ground power units in 2024. TLD has also partnered collaboratively with local distributors to improve after-sales service and shorten delivery times. TLD is embracing innovative new solutions as part of their strategy to contract for Gimpo and Jeju, which are regional airports.
Textron GSE, a subsidiary of Textron Inc., held a 20% share of the Korean GSE market in 2024, generating revenue of USD 50 million. The company recently launched a new range of GSE that is compact and lightweight, being ideally suited to the smaller footprint requirements of most Korean airports.
Textron has also ventured into areas including remote diagnostics and fleet management software, thus making strides in streamlining the customer experience. In this context, Textron GSE announced a partnership for the supply of electric baggage carts and pushback tractors with a Korean aviation services provider, as reported by Aviation Pros in March 2024. The partnership gave a lot more basis for Textron's presence in the region.
The company holds a 16% share of the Korean GSE market, generating USD 40 million in revenue. With strong endorsement from its innovative electric vehicle technologies, Toyota has developed a new set of battery-powered GSE-like aircraft refuelers and cargo loaders in 2024. Besides that, it has expanded its service network across Korea to provide timely maintenance and support for its equipment.
This made Toyota the preferred choice for domestic airlines and airport operators due to the company's strong and positive brand reputation and emphasis on sustainability.
Tug Technologies Corporation, industry share-12%, revenue share-USD 30 million, has recently been in aggressive pursuit of growth in Korea. In 2024, Tug Technologies launched the latest range of hybrid GSE-powered by diesel and electric combined.
The Korea aircraft ground support equipment market is heavily influenced by macroeconomic factors such as air traffic growth, infrastructure investments, technological advancements, and regulatory policies. The aviation industry witnessed continued growth between 2020 and 2024 as recovery in global travel from the pandemic is on the rise, while numerous governments are intensifying efforts for modernization in airport facilities.
Passenger demand and increasing cargo shipments urged airlines and airports to invest in efficient Ground Support Equipment (GSE) that can smooth operations and reduce delays.
The industry is expected to experience rapid development from 2025 to 2035, driven by rising air travel demand, sustainability initiatives, and digital transformation. Korean Green New Deal would push for more electrification in GSE that reduces carbon emissions as well as improve airport efficiency through advanced automation, AI-based logistics, and IoT-enabled equipment.
Gradual rise in inflow of foreign investments and partnerships in the Korean aviation sector will ultimately contribute to infrastructure development, paving way for competitive growth.
The main challenges are attributed to economic fluctuations, global supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical stability. However, the government stimulus and sustainability policies are expected to minimize such occurrences and create a scenario that would ensure the long-term expansion of Korea's Aircraft GSE industry.
Growth Opportunities
Expansion of Electrified GSE
Korea’s Green New Deal incentivizes electric and hybrid GSE adoption. Stakeholders should invest in battery-powered pushback tugs and charging stations at Incheon and Gimhae airports. This strategic move enhances sustainability compliance, reduces emissions, and strengthens industry positioning for long-term competitiveness.
Automation & AI Integration
AI baggage handling, as well as autonomous GSEs, can transform airport logistics. Collaborating with Korean AI companies to design self-driving baggage carts and robotic refueling systems could enhance efficiency, lower labor costs, and cut aircraft turnaround times, responding to the increasing demand for automated ground support solutions.
Expansion into Regional Airports
Secondary airports like Muan and Ulsan are undergoing expansion, presenting untapped opportunities for GSE providers. Forming early partnerships with regional authorities ensures that there is an opportunity for supply contracts in sophisticated ground handling equipment, hence supporting the growth of Korea's aviation infrastructure as well as adequate development of regional air traffic.
Strategic Recommendations
Strengthen Digital Integration for Operational Efficiency
Investing in GSE equipped with IoT technology and AI diagnostics can provide substantial operational efficiency benefits. Companies ought to devise predictive maintenance solutions that will help reduce downtime, prolong asset life, and minimize unexpected failures. Partnership with airport authorities in order to integrate smart fleet management systems will yield real-time insight, optimize resource use, and improve overall productivity in ground handling.
Enhance Aftermarket Services
Predictive maintenance using IoT sensors differentiates providers in Korea’s competitive aviation industry. Airlines prioritize GSE suppliers with strong service networks to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency. Positive maintenance solutions increase operational efficiencies with greater reliability on GSE, culminating in customer loyalty and partnerships.
Local Manufacturing & Partnerships
Collaborating with Korean manufacturers serves to eliminate import costs and guarantee compliance for locally produced GSE with KS Certification. The formation of joint ventures will lead to faster entrance to the industry, resilient supply chains, and enhanced customized equipment that will adequately meet the needs of regional airport operational demands.
In terms of equipment, the industry is segmented into airport service, cargo loading, and passenger services.
By ownership, the sector is segmented into leased GSE, owned GSE, and rental GSE.
In terms of power, the industry is segmented into electric, hybrid, and non-electric.
By application, the sector is segmented into commercial and defense.
Increasing air traffic, airport expansion projects, and sustainability regulations are key factors boosting the adoption of advanced ground support equipment across major and regional airports.
Policies like the Korean Green New Deal and MOLIT’s emission standards are encouraging airports and airlines to transition toward zero-emission ground support equipment through financial incentives and regulatory mandates.
Airport service equipment, including refuelers, de-icing vehicles, and ground power units, holds the largest share due to its critical role in ensuring smooth airport operations and aircraft turnaround efficiency.
Automation is enhancing efficiency through AI-powered baggage handling systems, autonomous pushback tugs, and robotic refueling, helping airports reduce labor costs and improve operational precision.
Yes, aircraft ground support equipment in Korea must meet local safety and environmental standards. Domestically produced equipment requires KS Certification, while imported units must comply with KC Mark regulations.
Table 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 39: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 40: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 41: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 42: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Application, 2018 to 2033
Table 43: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 44: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Table 45: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 46: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Table 47: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Table 48: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 16: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 20: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 23: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 24: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 35: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 36: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 37: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 40: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 41: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 44: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 45: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 48: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 55: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 60: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 61: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 64: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 65: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 66: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 68: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 73: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 84: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 85: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 86: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 88: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 93: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 96: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 97: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 106: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 108: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 113: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 115: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 116: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 117: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 120: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 121: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 126: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Equipment, 2018 to 2033
Figure 133: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 135: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 136: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Ownership, 2018 to 2033
Figure 137: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 140: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Power, 2018 to 2033
Figure 141: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 144: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Application, 2018 to 2033
Figure 145: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 146: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Equipment, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Ownership, 2023 to 2033
Figure 149: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Power, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Application, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Korea Automotive Performance Tuning and Engine Remapping Service Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Smart Home Security Camera Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Bicycle Component Aftermarket Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Isomalt Industry – Market Trends & Industry Growth 2025 to 2035
Korea Probiotic Supplement Industry – Industry Insights & Demand 2025 to 2035
Korea Calcium Supplement Market is segmented by form,end-use, application and province through 2025 to 2035.
The Korea Non-Dairy Creamer Market in Korea is segmented by form, nature, flavor, type, base, end-use, packaging, distribution channel, and province through 2025 to 2035.
Korea Women’s Intimate Care Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Korea Conference Room Solution Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Visitor Management System Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea fiber optic gyroscope market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Event Management Software Market Insights – Demand & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Submarine Cable Market Insights – Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Last-mile Delivery Software Market in Korea – Trends & Forecast through 2035
Korea HVDC Transmission System Market Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Base Station Antenna Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Smart Space Market Analysis in Korea-Demand & Growth 2025 to 2035
Korea Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Platform Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea I2C Bus Market Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA