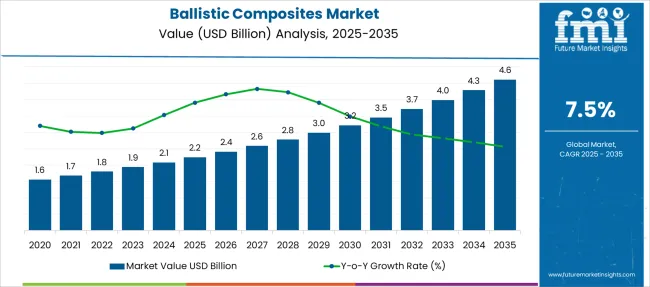
The Ballistic Composites Market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 4.6 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% over the forecast period.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Ballistic Composites Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 2.2 billion |
| Ballistic Composites Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 4.6 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 7.5% |
The ballistic composites market is expanding steadily, driven by heightened global focus on defense modernization, law enforcement safety, and rising geopolitical tensions. Demand for lightweight, high-performance materials that provide superior ballistic protection without compromising mobility is accelerating adoption across military and civilian applications.
Innovations in fiber technology and composite engineering have led to materials with improved strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing protection levels while reducing fatigue for end users. As asymmetric warfare and urban combat scenarios increase, there is a growing requirement for advanced body armor, vehicle protection systems, and structural reinforcements.
Furthermore, increasing investments in homeland security, rising defense budgets, and active procurement of next-generation protective gear are supporting long-term market growth. With continuous advancements in fiber technology and multi-material hybrid composites, the market is poised to witness sustained innovation and robust demand across various operational domains.
The ballistic composites market is segmented by fiber type, product, and application and geographic regions. By fiber type of the ballistic composites market is divided into Aramid Fiber-Based, Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, and Others. In terms of product of the ballistic composites market is classified into Polymer Matrix Composite, Ceramic Matrix Composite, and Metal Matrix Composite (MMC).
Based on application of the ballistic composites market is segmented into Body Armor, Vehicle Armor, Ballistic Plates and Inserts, Ballistic Helmets and Shields, and Others. Regionally, the ballistic composites industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
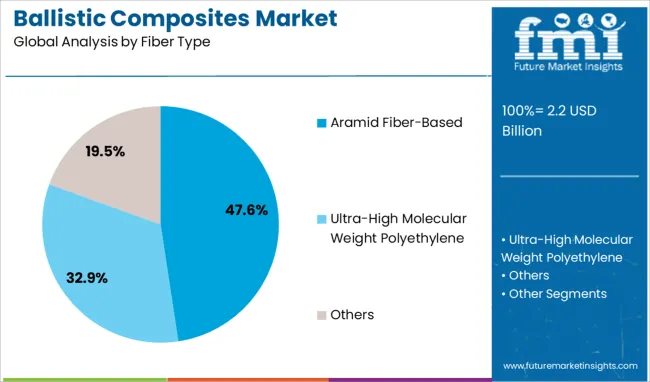
The aramid fiber-based segment leads the fiber type category with a 47.6% market share, driven by its superior mechanical strength, high thermal stability, and lightweight characteristics. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Twaron are extensively utilized due to their proven performance in absorbing and dispersing impact energy, making them ideal for ballistic protection.
Their resistance to cuts, abrasions, and chemical degradation further enhances their utility in critical environments. As demand rises for advanced materials that offer both flexibility and durability, aramid fiber-based composites remain the material of choice across military and law enforcement sectors.
Increasing procurement of advanced personal protection equipment and armored solutions continues to reinforce the segment’s dominance. The segment is expected to maintain momentum as new processing technologies and multi-layered composite architectures optimize the protective capabilities of aramid-based solutions.
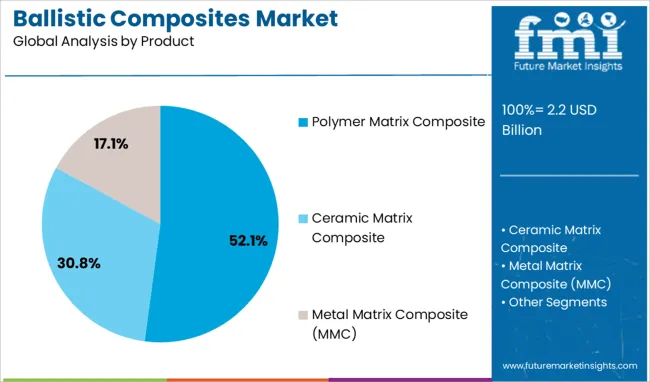
The polymer matrix composite segment holds the highest share within the product category at 52.1%, attributed to its widespread application in flexible and rigid armor systems. These composites provide excellent energy absorption, corrosion resistance, and manufacturing versatility, making them suitable for helmets, shields, and vehicle panels.
Their ability to be tailored for specific performance requirements through reinforcement with high-performance fibers such as aramid or UHMWPE has contributed to their popularity. The segment is also benefiting from a strong pipeline of innovations focusing on thermoplastic matrices that offer recyclability and improved impact tolerance.
The use of polymer matrix composites in both personal and structural protective systems is expected to expand further due to their favorable strength-to-weight ratios and integration potential with emerging technologies. As militaries and defense contractors increasingly emphasize modular, lightweight armor solutions, the segment’s leadership is likely to persist.
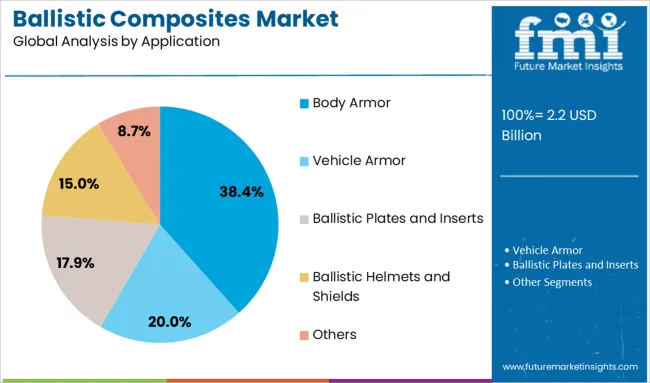
The body armor segment commands a 38.4% share in the application category, driven by its critical role in safeguarding personnel in military, law enforcement, and security operations. Demand is being fueled by rising global security threats, cross-border conflicts, and the need for advanced protective solutions for frontline responders.
Body armor made with ballistic composites offers enhanced protection against bullets, fragments, and blunt force, while significantly reducing weight compared to traditional metallic options. The segment has seen continuous evolution with the development of soft and hard armor systems that meet various threat level standards, improving operational flexibility.
Procurement programs across multiple countries, coupled with modernization initiatives and an increasing number of private security personnel, are sustaining strong demand. The emphasis on soldier survivability and lightweight armor kits will further anchor this segment’s relevance in the ballistic composites market.
The ballistic composites market is expanding steadily, driven by increasing global demand for lightweight protection in military, law enforcement, aerospace, and civilian applications. Aramid fibers and ultra‑high molecular weight polyethylene dominate as reinforcement materials. Polymer matrix composites represent the largest segment. Growth is strongest in vehicle and body armor sectors, especially in North America and Asia-Pacific, with continuous adoption in helmets, shields, and armored vehicles.
Manufacturers face lengthy and costly validation protocols before deploying ballistic composites. These materials must meet rigorous standards for penetration resistance, multi-hit performance, and weight limits. Certification bodies define region-specific requirements, particularly for soldier protection gear and armored vehicles.
Each composite design and layering structure may require customized testing, increasing development cycles. Suppliers also must ensure consistent quality across batches under variable raw material inputs.
This slows resolution of new fiber‑matrix combinations, such as hybrid aramid/UHMWPE systems, and delays introduction of next-generation materials. Smaller firms without internal validation capabilities must depend on external labs, further adding lead time.
Rising procurement of armored vehicles and tactical transport opens key opportunities. Vehicle armor accounted for roughly 40 percent of total market revenue in 2024 and remains the largest end-use segment. Increasing cross-border threats and regional defense upgrades across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific fuel armored vehicle demand.
Hybrid composites and lightweight panels enable better protection-to-weight ratios for military fleets. Aerospace and naval platforms also require modular panels for blast resistance and crew safety. Expanding civilian applications, such as armored transport for VIPs, accompany rising local unrest. Suppliers who offer tailored panel systems or retrofit kits for specific vehicles gain competitive advantage against traditional metallic armor solutions.
A clear trend in this market is the use of hybrid fiber systems that combine aramid, UHMWPE, and sometimes glass fibers in layered structures. These systems offer a balance of flexibility, durability, and energy absorption. Manufacturers are improving impact dispersion by alternating fiber orientations or combining materials within the same matrix.
Polymer resins used in these composites have also improved in their adhesion, transparency, and resistance to degradation. The result is lighter and more effective armor solutions for body protection, shields, and vehicle panels. Some developers are also integrating smart layers for tracking damage or providing visual wear indicators.
As defense buyers seek more adaptable and ergonomic armor designs, the ability to customize fiber content and layout becomes a key differentiator. Hybrid systems support these evolving performance requirements without sacrificing form or function.
The production of ballistic composites involves costly raw materials such as high-strength fibers and specialized polymer matrices. These inputs are often imported and priced based on global supply constraints. The manufacturing process itself demands controlled environments, precision layering, and specialized equipment.
Consistency across batches is critical, as any variation can compromise protective performance. For smaller manufacturers or budget-conscious buyers, these factors make ballistic composites less accessible compared to traditional solutions. Civilian security markets and developing regions may favor lower-cost materials even if they are heavier or less effective.
Until production becomes more cost-efficient or materials are locally sourced, the high expense of composite armor will remain a barrier in broader adoption. This limits market penetration in low-to-mid-tier applications that are price sensitive or lack long-term procurement funding.
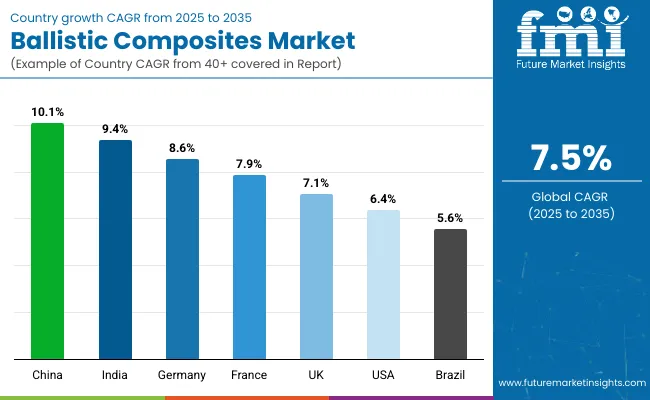
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 10.1% |
| India | 9.4% |
| Germany | 8.6% |
| France | 7.9% |
| UK | 7.1% |
| USA | 6.4% |
| Brazil | 5.6% |
The global ballistic composites market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% through 2035, supported by increased application in defense gear, armored vehicles, and aerospace shielding. Among BRICS nations, China leads with 10.1% growth, driven by expanded defense manufacturing and procurement of lightweight protective systems.
India follows at 9.4%, where domestic fabrication has been promoted through military modernization programs and law enforcement upgrades. In the OECD region, Germany reports 8.6% growth, supported by advanced materials processing and structured supply contracts with defense contractors.
The United Kingdom, at 7.1%, shows sustained demand in personal armor, marine composites, and tactical vehicle reinforcement. The United States, at 6.4%, reflects steady growth through standardized military adoption and commercial ballistic applications. Market evolution has been shaped by ballistic resistance standards, layering protocols, and fiber-reinforcement specifications. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
Significant progress has been recorded in the ballistic composites market across China, which has expanded at a 10.1% CAGR, driven by heightened material requirements in military, aerospace, and protective gear applications. Increased procurement has taken place by domestic defense contractors, where lightweight armor plating has been prioritized.
Composite variants such as aramid fibers and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene have been adopted across tactical vests and vehicle armor panels. Production hubs in Jiangsu and Guangdong have scaled their integration of thermoplastic composites into ballistic helmets and shields.
Civil law enforcement units have also influenced local demand with orders for anti-fragmentation gear. Performance consistency under multi-impact conditions has been emphasized through internal testing and batch standardization. Export volumes for finished armor parts have grown toward markets in Asia and Eastern Europe, supporting full-cycle domestic manufacturing lines.
A rising trend in the use of ballistic composites in India has contributed to a 9.4% CAGR, fueled by expanded deployments in defense mobility and personnel protection programs. Composite inserts for bulletproof jackets and tactical shields have been produced using locally sourced glass fibers and imported aramid variants.
Government-backed initiatives in indigenous armor manufacturing have reinforced demand across public-sector ordnance factories and private security equipment firms. Civil security forces have placed orders for lighter yet impact-resistant vests suitable for rapid response operations.
Modular plating systems featuring multi-layer composites have been introduced for paramilitary use in border zones. Collaborations with defense research units have led to field trials involving hybrid weaves and laminated structures. Steady procurement from logistics and convoy protection divisions has been facilitated through supplier networks located in Pune and Hyderabad.
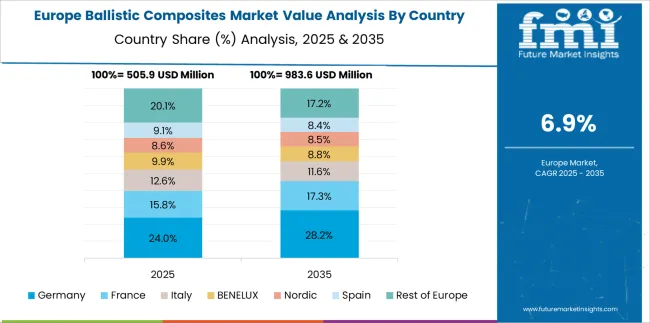
Within Germany, a 8.6% CAGR has been maintained in the ballistic composites market, propelled by persistent innovation in vehicle armor and aerospace shielding solutions. Adoption has been focused on combining rigidity and low areal density in ballistic panels used in military transport systems and personal gear.
Aramid-carbon hybrid composites have found application in lightweight ballistic doors and protective barriers. Aerospace contractors have sourced ballistic-grade laminates for cockpit protection in rotorcraft and fixed-wing aircraft. Local testing facilities in North Rhine-Westphalia and Saxony have validated composite resilience under NATO-standard trials.
Collaboration between material scientists and defense manufacturers has emphasized thermal stability and multi-strike endurance. Demand from police tactical units has remained strong for portable shields and compact body armor fitted with modular composite plates.
Expansion in the ballistic composites market across the United Kingdom has occurred at a 7.1% CAGR, supported by structured investments in tactical protective solutions and export-grade armor components. Defense suppliers have used glass-reinforced thermoset composites in riot control shields and lightweight ballistic panels.
Metropolitan police forces have specified requirements for low-profile vest inserts and multi-threat protection systems, influencing domestic design standards. Collaborative frameworks with aerospace firms have promoted inclusion of ballistic-rated components into airborne crew seats and fuselage panels.
Portable ballistic barriers assembled with folding composite frames have seen increased deployment across special response teams. Independent testing services in Hampshire and South Yorkshire have provided certification for law enforcement-ready gear. Supply chains based in Birmingham and Cardiff have managed distribution of semi-finished parts and laminated sheets.
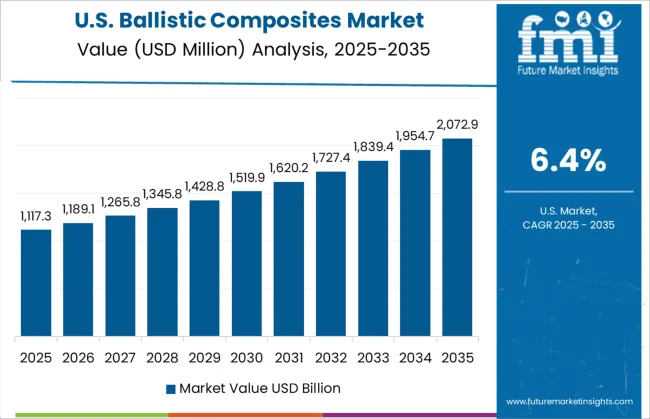
The United States has shown a 6.4% CAGR in the ballistic composites market, with consistent demand across defense, homeland security, and vehicle armoring industries. Extensive use has been reported in composite plates, aircraft seat protection, and mine-resistant vehicle flooring systems. Multi-hit and fragmentation resistance has driven the adoption of ceramic-fiber hybrid inserts.
Manufacturers in Michigan and Texas have maintained high-volume outputs of aramid-reinforced armor panels supplied to military bases and federal agencies. Police departments have transitioned toward modular vest systems embedded with flexible composite shields. Defense contractors have ordered advanced composites for use in unmanned ground vehicles and aircraft body inserts. Field testing has been emphasized by the Department of Defense for gear intended for urban and counter-insurgency operations.
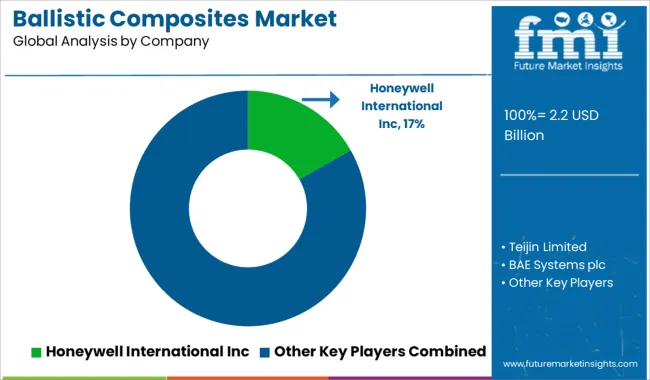
The ballistic composites market is led by a select group of companies that specialize in high-strength, lightweight protective materials designed to resist extreme impact and projectile threats. Honeywell International Inc. holds a strong position with its Spectra® fiber technology, widely used in body armor, helmets, and vehicle protection systems due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
Teijin Limited, through its Twaron® and Endumax® product lines, provides para-aramid fibers that are integral in ballistic panels and anti-fragmentation solutions. BAE Systems plc integrates advanced composites into defense platforms, offering customized armor systems for military vehicles and personnel protection.
DuPont de Nemours Inc., a pioneer in aramid fiber development, remains a key player with its globally recognized Kevlar® brand, which continues to set performance benchmarks in ballistic resistance. DSM Dyneema offers Dyneema®, a high-modulus polyethylene fiber known for its ultra-lightweight ballistic protection used in both military and law enforcement sectors.
Morgan Advanced Materials supplies composite armor solutions for ground forces and naval applications, while 3M Company supports personal protective equipment with engineered materials that combine impact resistance and comfort. Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics Corporation and Koninklijke Ten Cate BV offer vehicle and structural armor composites, balancing flexibility and performance under high-velocity threats.
Emerging and specialized suppliers such as MKU Limited, ArmorSource LLC, and Revision Military focus on innovation in helmet and body armor design. Gurit Holding AG, Barrday Inc., and TPI Composites, Inc. bring deep composites expertise, enabling tailored protection solutions for aerospace, defense, and transport sectors.
On Apr 30, 2025, BAE Systems awarded Integris Composites a contract to supply ballistic protection systems for CV90 IFVs used by multiple European nations. The expansion reinforces Integris's role as a strategic supplier in armored vehicle production and reflects strong performance in composite defense manufacturing.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 2.2 Billion |
| Fiber Type | Aramid Fiber-Based, Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, and Others |
| Product | Polymer Matrix Composite, Ceramic Matrix Composite, and Metal Matrix Composite (MMC) |
| Application | Body Armor, Vehicle Armor, Ballistic Plates and Inserts, Ballistic Helmets and Shields, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Honeywell International Inc, Teijin Limited, BAE Systems plc, DuPont de Nemours Inc, DSM Dyneema, Morgan Advanced Materials plc, 3M Company, Saint-Gobain Performance Plastics Corporation, Koninklijke Ten Cate BV, Gurit Holding AG, MKU Limited, Barrday Inc, TPI Composites, Inc, ArmorSource LLC, and Revision Military |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by ballistic composite type including aramid fiber-based, UHMWPE-based, polymer-ceramic, and metal matrix composites; by application in vehicle armor, body armor, helmets & face protection; and by geographic region including North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific; demand driven by rising defense and law enforcement spending, escalating security threats, and need for lightweight protection; innovation in hybrid fiber matrices, additive manufacturing, and embedded sensor systems; costs influenced by raw fiber material prices, complex processing technologies, and certification standards. |
The global ballistic composites market is estimated to be valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2025.
The market size for the ballistic composites market is projected to reach USD 4.6 billion by 2035.
The ballistic composites market is expected to grow at a 7.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in ballistic composites market are aramid fiber-based, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene and others.
In terms of product, polymer matrix composite segment to command 52.1% share in the ballistic composites market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Ballistic Protection Material Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ballistic Floatation Vest Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ballistic Protective Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ballistic Protection Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ballistic Protection Scanners Market
Geocomposites Market
Dental Composites Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Marine Composites Market
CF PEEK Composites Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
APAC Biocomposites Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Plastic Composites Market
Advanced Composites Market Trends - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Industry Share Analysis for Advanced Composites Companies
Structural Composites Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Automotive Composites Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Composites Market Size, Growth, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Graphene Nanocomposites Market 2025 to 2035
Carbon Fiber Composites for Prosthetics Market 2025-2035
Metal Matrix Composites Market
Polyurethane Composites Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA