The Biobased Polypropylene PP Size Market is estimated to be valued at USD 45.4 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 70.6 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% over the forecast period.
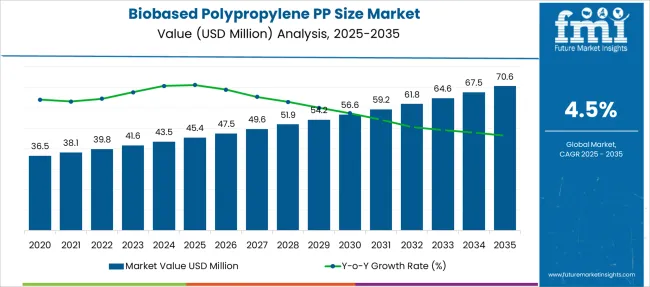
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Biobased Polypropylene PP Size Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 45.4 million |
| Biobased Polypropylene PP Size Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 70.6 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.5% |
The biobased polypropylene market is gaining momentum as industries shift towards sustainable materials that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Growing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures have accelerated the adoption of biobased polymers as alternatives to conventional plastics.
Biobased polypropylene offers the benefits of traditional polypropylene, such as durability and versatility, while reducing carbon footprint. Increasing demand from various end-use sectors, including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods, is driving market expansion.
Technological advancements in production processes have improved the performance and cost competitiveness of biobased polypropylene. Manufacturers are also focusing on enhancing material properties to meet specific application requirements. With sustainability becoming a key priority globally, the biobased polypropylene market is expected to see steady growth. Segmental expansion is anticipated to be led by the injection molding application, which dominates due to its widespread use in producing complex and high-strength components.
The biobased polypropylene pp size market is segmented by application and geographic regions. By application of the biobased polypropylene pp size market is divided into Injection, Textile, Films, and Others. Regionally, the biobased polypropylene pp size industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
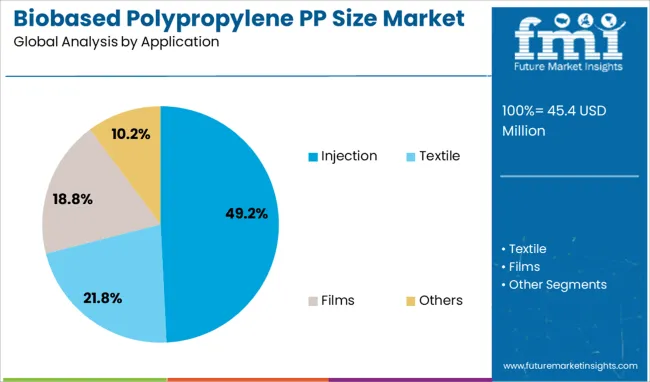
The injection molding application segment is projected to account for 49.2% of the biobased polypropylene market revenue in 2025, establishing it as the leading application. This growth is attributed to the versatility of injection molding in manufacturing a wide range of products with precise dimensions and consistent quality.
The injection process allows for efficient production of complex shapes and lightweight components, which are highly valued in the packaging and automotive sectors. Biobased polypropylene’s compatibility with injection molding equipment has facilitated its rapid adoption.
The cost-effectiveness and scalability of injection molding make it suitable for mass production. As demand for sustainable materials increases across various industries, the injection molding application segment is expected to maintain its dominant position in the biobased polypropylene market.
The bio‑based polypropylene market is growing as brand owners, packaging firms, and automakers seek renewable carbon alternatives. Produced from feedstocks like sugarcane or cellulosic biomass, bio‑PP offers identical properties to conventional polypropylene with lower lifecycle greenhouse emissions without compromising recyclability. Injection molding in packaging and automotive applications is the dominant use case. Feedstock sourcing efforts and regulatory support in regions such as Europe and Asia‑Pacific are expanding market reach, while cost remains a key barrier to commercial-scale adoption.
Production of bio‑based polypropylene comes with significantly higher costs than fossil‑derived PP. Converting biomass feedstocks via fermentation or catalytic conversion adds extra processing steps, which raise capital, energy, and operating expenses. Specialized infrastructure and certification systems are needed to meet mass‑balance or renewable attribution standards. Until economies of scale emerge, most producers cannot compete on price in bulk applications such as commodity packaging or consumer goods. Many end users prioritize per‑unit cost, especially in high‑volume contexts. Limited production volume and reliance on specific agricultural feedstocks exacerbate cost disparity. Until alternative feedstocks like algae or agricultural residues are commercialized, cost remains a major constraint on adoption, especially in emerging markets or sectors with tight material budgets.
Consistency of input biomass affects production reliability. Bio‑PP relies on feedstocks such as sugarcane, corn, vegetable oils or cellulosic biomass. Seasonal variation, weather events, and agricultural competition can disrupt supply volume and quality. Changes in moisture content, ash levels or sugar concentrations require process adjustment and may impact final resin properties. Producers working with multiple feedstock types must invest in feedstock pretreatment, blending systems and quality control to ensure uniform output. Supply shortages or price spikes add risk to long‑term contracts with OEMs or packaging brands. Geographic dependency and limited feedstock sourcing networks further constrain stability. Until diversified biomass sources are integrated into plant operations, feedstock unpredictability remains a significant operational challenge.
Demand for bio‑based polypropylene is expanding in packaging and automotive sectors. In injection molding for packaging applications, brands seek bio‑PP to meet renewable carbon targets without altering processing methods. The automotive segment values bio‑PP for lightweight interior and exterior components, helping reduce vehicle mass and meet environmental commitments. Some vehicle makers are piloting bio‑PP in door panels, dashboards, and bumpers. Market activity in Europe, Asia‑Pacific and North America is supported by government incentives and corporate feedstock mandates. Manufacturers that offer drop‑in resin grades compatible with existing molding lines are gaining acceptance. Collaborative partnerships between resin producers and end users accelerate tailored development and scale adoption in strategic application areas.
Lack of harmonized standards for labeling, certification and feedstock attribution limits confidence in bio‑PP. Mass‑balance approaches allow mixing conventional and bio feedstock, but regional regulations vary on accepted claims. Inconsistent certification protocols across Europe, North America and Asia complicate global marketing. Without consumer-grade or industry-wide verification, some bio-based claims may be questioned by end users or regulators. Regulatory uncertainty slows procurement decisions, especially among sustainability‑driven brands wary of greenwashing. Producers must navigate multiple jurisdictional frameworks to meet renewable content mandates. Until uniform certification and labeling protocols are established across major regions, hesitation among purchasers may limit growth and value creation for bio‑PP offerings.
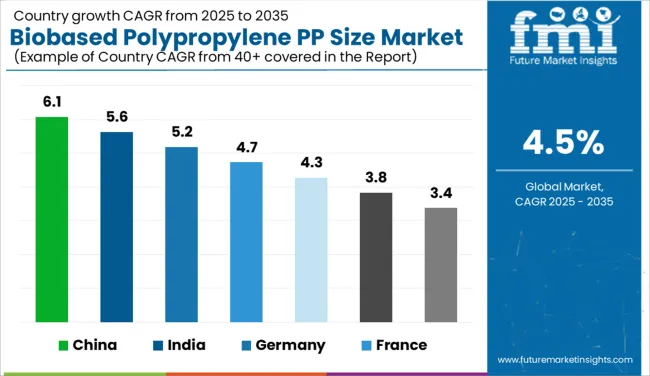
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 6.1% |
| India | 5.6% |
| Germany | 5.2% |
| France | 4.7% |
| UK | 4.3% |
| USA | 3.8% |
| Brazil | 3.4% |
The global biobased polypropylene market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% through 2035, supported by increasing adoption in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods. Among BRICS nations, China leads with 6.1% growth, driven by expanded biopolymer processing and domestic end-use manufacturing. India follows at 5.6%, where the shift toward alternative feedstocks in flexible packaging and molded components has supported production. In the OECD region, Germany reports 5.2% growth, reflecting established polymer capabilities and steady use in durable goods. The United Kingdom, at 4.3%, has maintained demand across specialty applications in household and medical-grade products. The United States, at 3.8%, remains a stable market, where procurement preferences and lifecycle performance metrics are guiding integration. Biocontent verification, material substitution guidelines, and resin certification protocols have shaped market expansion. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
An increasing shift toward renewable raw materials has led to a 6.1% CAGR in the biobased polypropylene (PP) size market in China. Industrial packaging sectors have integrated bio-PP into extrusion and thermoforming applications to meet performance benchmarks. Bulk usage has been seen across food containers and automotive components due to the lightweight yet durable nature of bio-PP. Public procurement programs have included criteria favoring reduced emissions during the product lifecycle, which has benefited biobased inputs. Key provinces, including Jiangsu and Guangdong, have recorded higher volumes due to the concentration of chemical manufacturing hubs. Machine compatibility and scalability of bio-PP pellets have been demonstrated across existing polymer processing lines. Packaging converters and OEMs have invested in transition kits that accommodate modified bio-polymers. Market participation has been influenced by research collaboration and access to imported bio-naphtha.
Rapid interest in polymer alternatives has resulted in a 5.6% CAGR for the biobased polypropylene (PP) size market in India. Bio-PP has been incorporated into rigid packaging, caps, and film applications by local manufacturers focusing on alternate resin sourcing. Small-to-mid-size converters have favored material blends compatible with current injection molding lines. Usage has also been noted in textiles and household storage items, where strength-to-weight ratio and odor resistance are critical. Government-backed pilot initiatives in New Delhi and Hyderabad have assessed bio-PP’s feasibility at a commercial scale. Logistics providers have adopted bio-PP crates for internal material movement across warehouses and distribution centers. Support has been extended through regional manufacturing clusters working with bio-feedstock suppliers. Efforts to diversify polymer inputs have been seen in private-label consumer product packaging as well.
Established processing lines in Germany have enabled a 5.2% CAGR in the biobased polypropylene (PP) size market. Bio-PP has been utilized in durable consumer goods, interior automotive components, and injection-molded items across manufacturing sectors. Technical feasibility and existing mold compatibility have made adoption relatively seamless for legacy processors. Regulatory support for carbon-reduction in polymers has influenced procurement policies across federal institutions and retail suppliers. Recyclability with standard PP streams has contributed to higher acceptance across distribution networks. Industrial users have benefited from consistent melt flow index parameters that match fossil-based PP standards. Demand has also been observed in pilot-scale packaging projects led by regional innovation centers. Certification standards such as ISCC Plus and EN 13432 have been referenced by buyers for validation of origin.
In the United Kingdom, increased consideration for non-petroleum polymers has contributed to a 4.3% CAGR in the biobased polypropylene (PP) size market. Adoption has occurred in product segments where drop-in bio-based alternatives are preferred over redesigning production lines. Specialty retailers and contract manufacturers have initiated trials for bio-PP containers and trays. Major interest has been seen among eco-focused brands launching limited-edition product runs using alternative polymers. Cost comparisons with virgin PP have affected volume uptake but not experimentation. Educational institutions and product design hubs have launched collaborative workshops around the functional equivalence of bio-PP. Local manufacturers have explored short-run applications in cosmetics packaging and dispenser assemblies. End-use feasibility in healthcare-grade applications is currently being tested in select laboratories and niche producers.
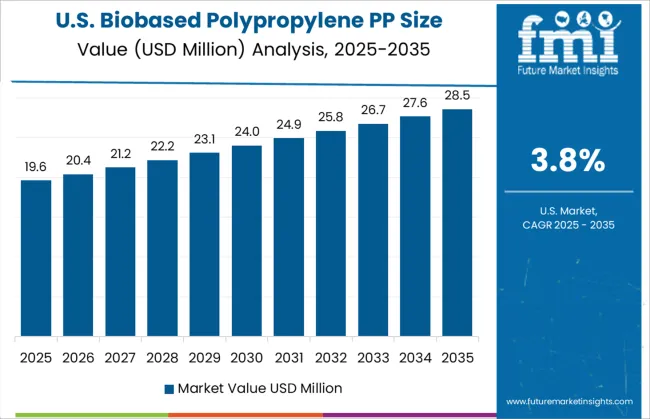
In the United States, a 3.8% CAGR has been recorded in the biobased polypropylene (PP) size market due to gradual material substitution efforts. Commercial packaging sectors have evaluated bio-PP for thermoformed clamshells, bottle caps, and caps and closures across FMCG portfolios. Corporate sustainability targets have spurred pilot-scale usage in personal care and food-contact applications. Barriers involving raw material cost and infrastructure alignment have moderated the pace of widespread adoption. Academic consortia and chemical engineering research centers have supported regional material trials. Small-scale molding units have adopted bio-PP pellets where regulatory trials permit use in non-critical applications. Import reliance for bio-based feedstock remains high, although domestic startups are exploring fermentation-based production. Certification and material traceability systems are increasingly integrated into supply chain audits.
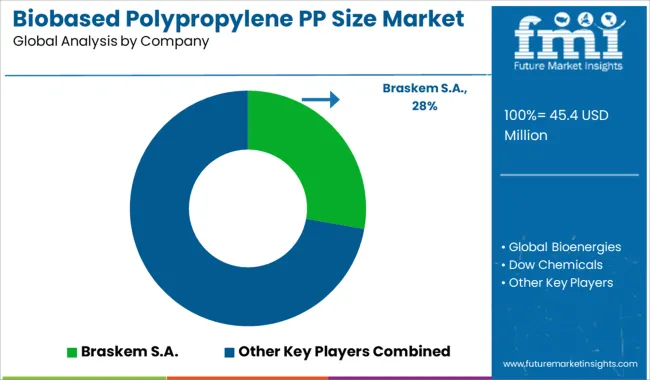
The biobased polypropylene (PP) market is emerging as a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil-derived polypropylene, with demand increasing across automotive, packaging, consumer goods, and textiles. Braskem S.A. is the most prominent and established supplier, leveraging sugarcane-based feedstocks to produce bio-PP with identical performance properties to petroleum-based resins, enabling drop-in compatibility in existing manufacturing processes.
The company’s integrated biopolymer value chain and large-scale production capacity give it a dominant position in global markets. Global Bioenergies, though primarily focused on isobutene production, is expanding its capabilities into bio-derivatives suitable for polypropylene synthesis. Their proprietary fermentation technologies allow the conversion of renewable feedstocks into hydrocarbon monomers, paving the way for bio-PP applications across various sectors. Dow Chemicals is involved in the development and commercialization of biobased polymers through strategic partnerships, targeting automotive interiors and packaging applications with low carbon footprint materials.
Trellis Earth Products, Inc. contributes to the North American market with biobased thermoplastics that incorporate renewable content, offering partial PP replacements in disposable foodservice items and rigid packaging. Biobent Polymers, a USA-based innovator, has developed bio-composite polypropylene blends using agricultural byproducts such as soy, which reduce reliance on petroleum without compromising structural performance. As the biobased PP market continues to expand, these suppliers are focusing on reducing production costs, increasing bio-content ratios, and aligning product performance with regulatory and brand-owner sustainability demands, especially in automotive lightweighting and FMCG packaging applications.
On September 16, 2024, Braskem America launched WENEW™, a bio-circular polypropylene made from used cooking oil, certified under ISCC Plus. It matches conventional PP in performance and targets food packaging, snack-film, and QSR markets. On May 6, 2025, Braskem marked 15 years of its I’m green™ bio-based line with a 37% expansion at its Triunfo, Brazil plant. Green ethylene capacity increased to 275,000 t/year, capturing ~159,000 t CO₂ annually.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 45.4 Million |
| Application | Injection, Textile, Films, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Braskem S.A., Global Bioenergies, Dow Chemicals, Trellis Earth Products, Inc., and Biobent Polymers |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by bio-based polypropylene type including homopolymer, random copolymer, and impact copolymer, by application in packaging films, automotive interiors, consumer goods, textiles, and medical items, and by geographic region including North America, Europe, and Asia‑Pacific; demand driven by sustainability mandates and lightweighting requirements; innovation in sugarcane and cellulosic feedstocks, melt‑mass polymerization, and mass‑balance certification; costs influenced by higher feedstock and process costs versus petro PP; and emerging use cases in mono-material recyclable packaging, bio-PP textiles, and low-carbon automotive components |
The global biobased polypropylene PP size market is estimated to be valued at USD 45.4 million in 2025.
The market size for the biobased polypropylene PP size market is projected to reach USD 70.6 million by 2035.
The biobased polypropylene PP size market is expected to grow at a 4.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in biobased polypropylene PP size market are injection, textile, films and others.
In terms of , segment to command 0.0% share in the biobased polypropylene PP size market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Biobased And Synthetic Polyamides Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biobased Degreaser Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biobased Biodegradable Plastic Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Biobased Propylene Glycol Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Biobased Transformer Oil Market
Polypropylene Woven Bag and Sack Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Polypropylene Yarn Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Polypropylene Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Polypropylene Corrugated Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Polypropylene Random Copolymers Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Trends - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Market Share Distribution Among Polypropylene Woven Bag and Sack Manufacturers
Polypropylene Screw Caps Market
Polypropylene Film Market
Polypropylene Fibre Market
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Foamed Polypropylene Films Market Growth - Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Surgical Polypropylene Mesh Market
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) Foam Market 2025 to 2035
Demand for Polypropylene in EU Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA