A valuation of USD 352.7 million in 2025 is expected to advance to USD 662.3 million by 2035, reflecting a 6.5% CAGR. Growth through 2025 to 2030 is projected to add USD 124.0 million, driven by wider adoption of film coating lines at seed processors and consistent demand from cereals, oilseeds, and high-value horticulture.
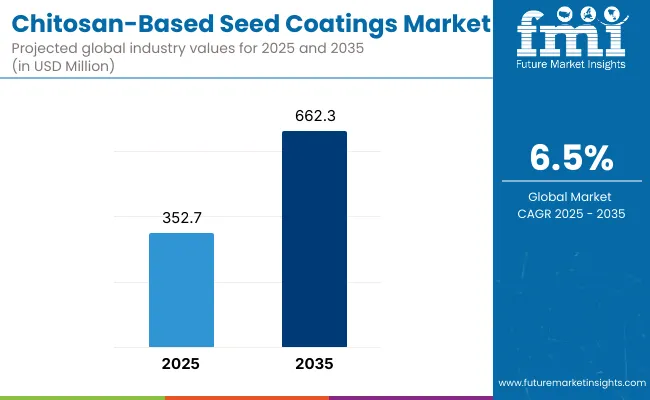
Chitosan-based Seed Coatings Market Key Takeaways
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Chitosan-based Seed Coatings Market Estimated Value In (2025E) | USD 352.7 Million |
| Chitosan-based Seed Coatings Market Forecast Value In (2035f) | USD 662.3 Million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.5% |
During 2030 to 2035, an additional USD 185.6 million in value is anticipated as polymer encapsulation scales, fermentation-derived grades expand availability, and stress-tolerance use cases mature for drought and salinity management. Uptake is set to be reinforced by the agronomic benefits of chitosan-antimicrobial activity, improved germination, and elicitation of plant defense pathways-while compatibility with biologicals and micronutrient packages strengthens positioning in integrated seed treatment stacks.
In the USA, a steady upgrade cycle at commercial seed treaters underpins demand, whereas China and India are forecast to accelerate on the back of mechanization, hybrid seed penetration, and climate resilience policies. Regulatory comfort with shell-derived inputs is expected to persist, while fungal fermentation-derived chitosan gains favor in markets emphasizing traceability and non-animal sourcing. Digital agronomy and e-commerce channels are likely to broaden access for mid-sized growers, sustaining a balanced mix of direct contracting and distributor-led sales.
Expansion is being enabled by agronomic efficacy, sustainability alignment, and manufacturing innovation. Chitosan’s intrinsic antimicrobial and elicitor properties have been validated across crops, supporting seed protection against pathogens while priming plant defenses. Compatibility with nutrient delivery and biological actives has improved stand establishment and early vigor, translating to yield stability-critical under weather variability.
Manufacturing advances, including tighter deacetylation control and molecular-weight tailoring, have enhanced film integrity and adhesion, reducing dust and improving meterability in commercial treatment equipment. Polymer encapsulation has elevated dose precision for high-value horticulture, while fermentation-derived chitosan offers a scalable, non-marine alternative valued in markets prioritizing traceability.
Climate stress episodes are increasing adoption of stress-tolerance coatings for drought and salinity, particularly in South Asia and East Asia. As distributors integrate advisory services and digital ordering, access for small and mid-sized growers has improved, reinforcing recurring demand across seed replacement cycles.
Segmentation spans type, source, coating method, crop type, application functionality, end user, distribution channel, and region, each mapping to distinct agronomic needs and go-to-market models. Polymeric coatings lead on breadth of use; shell-derived sources dominate on availability, while fermentation-derived options rise with traceability demands.
Film coating remains the operational default for cereals and oilseeds, whereas polymer encapsulation is favored in precision horticulture. Seed protection is prioritized in disease-prone geographies; stress-tolerance and nutrient delivery accelerate in climate-exposed belts. Commercial farmers and seed processors anchor demand, with direct B2B contracts prevailing and online platforms scaling for smaller lots.
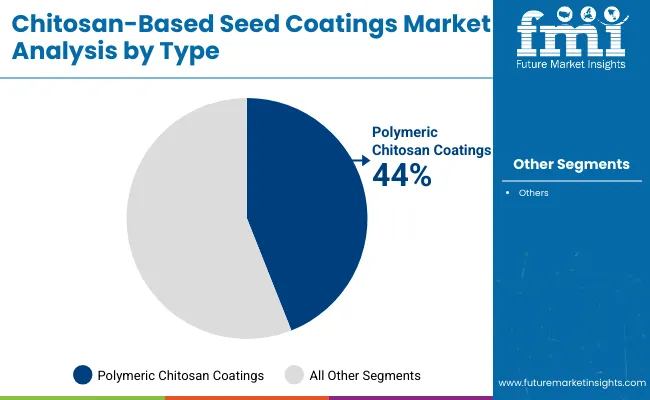
The type segment is led by polymeric chitosan coatings, which accounted for 44% of the market in 2025. Their dominance is attributed to strong film-forming ability, adhesion, and compatibility with other seed treatment actives such as micronutrients, fungicides, and biological inoculants. Polymeric grades are widely favored by commercial seed processors for cereals, grains, and oilseeds, where uniform coverage, dust reduction, and durability are crucial.
In contrast, oligomeric chitosan coatings are increasingly adopted in high-value seed lots due to their smaller molecular weight, which supports faster plant uptake and seed priming. Blended chitosan coatings, integrating biopolymers and nutrients, are emerging as the fastest-growing category, reflecting the industry’s shift toward multi-functional treatments that combine protection with germination enhancement. Overall, polymeric coatings remain central to large-scale agriculture, underpinning both efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
| Type | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Polymeric Chitosan Coatings | 44.00% |
| Others | 56.00% |
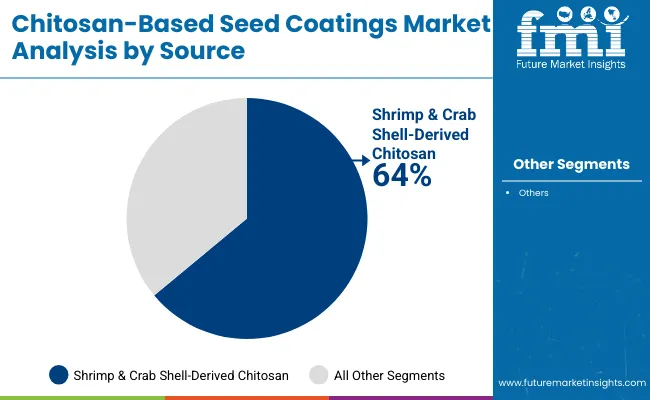
The source segment highlights the enduring importance of shrimp and crab shell-derived chitosan, which accounted for 64% of the market in 2025. This category remains dominant because of established supply chains, cost competitiveness, and scalability, particularly in regions with abundant marine processing industries.
Seed processors favor shell-derived chitosan for its reliable antimicrobial properties and consistent performance in film coating applications. However, environmental and sustainability concerns are creating momentum for alternatives. Fungal fermentation-derived chitosan is growing rapidly at a CAGR above 9%, driven by increasing demand for non-animal sourcing, traceability, and circular bioeconomy policies in Europe and East Asia.
Squid and other marine sources contribute modestly but serve niche regional markets. The combination of legacy infrastructure for shell-derived chitosan and innovation in fermentation-derived grades ensures a diversified sourcing mix moving forward.
| Source | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Shrimp & Crab Shell-Derived Chitosan | 64.00% |
| Others | 36.00% |
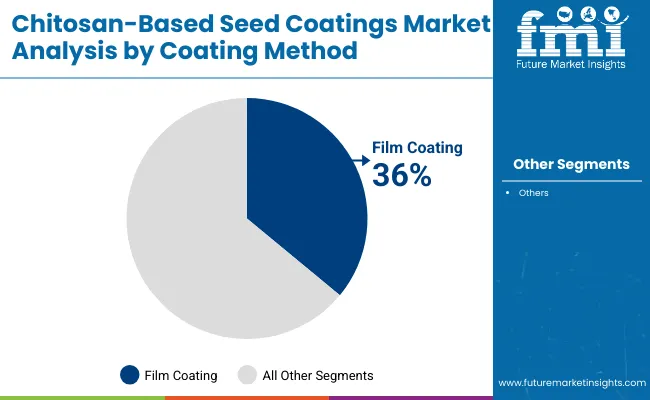
Film coating is expected to remain the leading coating method, holding 36% share in 2025. Its continued dominance is based on operational efficiency and adaptability to high-throughput commercial seed treating equipment. Film coating ensures uniform application, dust control, and low active ingredient loading, making it the standard choice for large-volume crops such as cereals, grains, and oilseeds.
It is cost-effective and well-aligned with existing seed treatment lines. Polymer encapsulation, however, is projected to expand at the fastest rate, particularly in horticultural and high-value crop markets, due to its ability to deliver precise dosing, controlled release, and compatibility with multiple actives. Pelleting and encrusting remain specialized methods suited for small seeds, improving flowability and precision planting. Collectively, coating methods reflect a balance between efficiency, precision, and crop-specific needs.
| Coating Method | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Film Coating | 36.00% |
| Others | 64.00% |
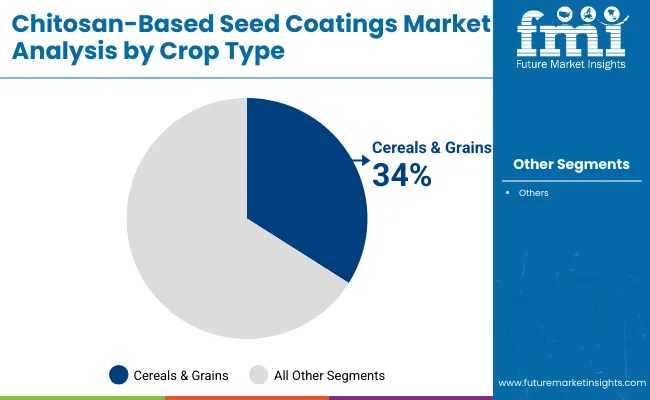
Cereals and grains dominate the crop type segment, representing 34% of market share in 2025. Their leadership is linked to the vast global seeding area, strong mechanization, and the importance of stand establishment in crops like wheat, rice, corn, and barley. Commercial farmers increasingly rely on seed coatings to enhance germination, improve vigor, and protect against soil-borne pathogens.
Fruits and vegetables are projected to grow fastest, driven by the high economic returns of quality seeds and the importance of vigor and disease suppression in intensive farming systems. Oilseeds and pulses sustain steady demand, especially in North and South America, where soybean and canola acreage is significant. Turf and ornamentals represent niche markets, but adoption is growing in controlled environments. This distribution highlights cereals’ centrality while underscoring diversification into higher-value crops.
| Crop Type | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Cereals & Grains | 34.00% |
| Others | 66.00% |
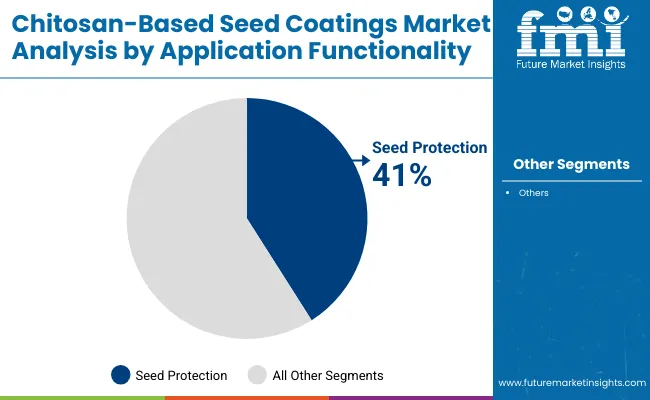
Seed protection was the leading application functionality in 2025, accounting for 41% of market share. Its dominance stems from chitosan’s inherent antimicrobial and antifungal properties, which help seeds resist pathogens and enhance survival during early growth stages. Farmers and seed processors prioritize this functionality as it directly impacts stand establishment and overall yield potential.
Nutrient delivery and germination boosting, grouped under seed enhancement, are expanding rapidly in high-value crops, where precision in early growth can translate into premium returns. Stress tolerance applications, including coatings for drought and salinity resistance, are becoming increasingly relevant as climate variability intensifies in South Asia and East Asia. This functionality spectrum shows how chitosan-based coatings are not just protective but also enablers of plant performance under diverse agronomic conditions.
| Application Functionality | Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Seed Protection | 41.00% |
| Others | 59.00% |
Driver - Efficacy plus stack compatibility will broaden agronomic use
Chitosan’s dual action as both an antimicrobial and a plant defense elicitor is expected to underpin its growing role in seed treatment. By reducing pathogen load and stimulating systemic resistance, seeds achieve stronger establishment and improved resilience against soil-borne stress. In addition, compatibility with micronutrients, microbial inoculants, and biostimulants enables chitosan to be integrated into stacked recipes, thereby delivering multi-functional value.
This flexibility makes it highly attractive to seed processors and commercial farmers seeking cost-effective solutions that enhance vigor and early root development. The expansion of polymer encapsulation techniques further strengthens dose accuracy for high-value horticulture, reinforcing ROI-driven adoption. Collectively, these attributes position chitosan as more than a protective agent, instead as a versatile enabler of next-generation integrated seed treatment platforms.
Restraint - Feedstock variability and specification control will pressure margins
Supply dependence on marine waste streams such as shrimp and crab shells exposes producers to variability in quality, seasonal fluctuations, and uneven deacetylation profiles. Such inconsistency increases the need for advanced processing controls to achieve uniform viscosity and molecular weight distributions, both critical to coating performance.
Although fungal fermentation-derived chitosan offers a more consistent alternative, it remains costlier, limiting its short-term substitution in volume-driven markets. Smaller seed processors may struggle to maintain consistent coating performance across seed lots, as capital-intensive equipment and rigorous QA protocols are needed to ensure homogeneity.
Margins are therefore likely to be pressured, with cost volatility in raw materials and stringent customer specifications elevating entry barriers. This restraint is projected to create opportunities for consolidation, favoring suppliers that can guarantee reliable quality and sustainable sourcing.
Trend - Climate resilience, traceability, and fermentation sourcing will reshape adoption
Agriculture’s exposure to extreme weather patterns is intensifying interest in seed coatings that mitigate abiotic stress. Chitosan-based coatings designed for drought, salinity, and temperature resilience are projected to see wider adoption, particularly in South Asia and East Asia where crop losses from climate variability are frequent.
Beyond functionality, buyers are placing emphasis on traceability and sustainability, which is boosting demand for fermentation-derived chitosan that offers non-animal sourcing and transparent production processes. This aligns with food industry and export requirements, especially in Europe and Japan.
Simultaneously, digital agronomy and online agri-commerce platforms are reshaping distribution, making premium coatings accessible to mid-sized and smallholder farmers. Together, these shifts indicate that chitosan will increasingly serve as a climate-smart, transparent, and digitally enabled solution within the global seed coating landscape.
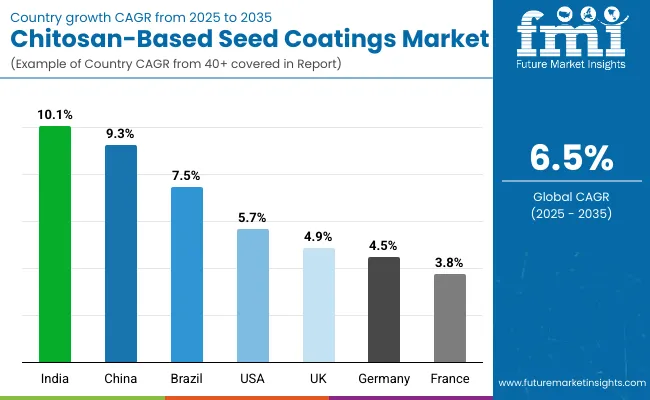
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 9.3% |
| India | 10.1% |
| Germany | 4.5% |
| France | 3.8% |
| UK | 4.9% |
| USA | 5.7% |
| Brazil | 7.5% |
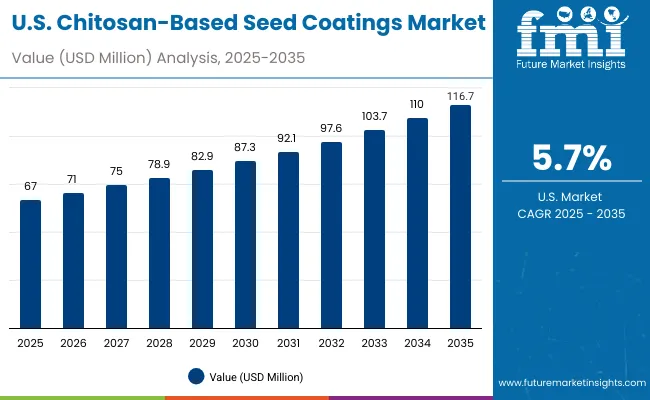
| Year | USA Chitosan-based Seed Coating Market (USD Million) |
|---|---|
| 2025 | 67.0 |
| 2026 | 71.0 |
| 2027 | 75.0 |
| 2028 | 78.9 |
| 2029 | 82.9 |
| 2030 | 87.3 |
| 2031 | 92.1 |
| 2032 | 97.6 |
| 2033 | 103.7 |
| 2034 | 110.0 |
| 2035 | 116.7 |
A steady scale-up in commercial seed treating capacity is anticipated to support demand as seed processors prioritize uniform coverage, dust control, and easy meterability. Film coating is expected to remain the operational default for cereals and oilseeds, while polymer encapsulation is set to expand in vegetable and specialty seed lines where dose precision and multi-active loading are valued.
Chitosan’s antimicrobial and elicitor properties are being positioned as a complementary layer within stacked recipes that include micronutrients, microbial inoculants, and synthetic protectants, improving stand establishment and early vigor.
Distributor agronomy programs and direct B2B contracts are projected to anchor go-to-market models, with digital ordering simplifying replenishment for medium-sized farms. As sustainability reporting tightens, interest in fermentation-derived grades is likely to grow among processors serving food and seed companies with strong ESG targets, even as shell-derived supply remains the volume backbone.
Robust expansion is projected as hybrid seed penetration, mechanization, and climate resilience programs converge to raise treatment intensity per seed lot. Film coating will likely dominate high-throughput cereals and maize, while polymer encapsulation gains in horticulture and protected cultivation, reflecting the need for precise dosing and controlled release.
Chitosan’s role in disease suppression and vigor enhancement is being integrated with micronutrients and microbial inoculants to address early-season stress. Supply chains for shell-derived chitosan are mature, yet pilot adoption of fermentation-derived grades is expected in export-oriented segments that emphasize traceability.
Provincial extension services and distributor networks are anticipated to expand training on coating quality, dust standards, and equipment calibration, improving performance consistency. E-commerce sales of input packs for smallholders are likely to rise, broadening access to premium treatments.
Fastest growth among key countries is expected as mechanization spreads, certified seed usage increases, and climate variability intensifies demand for stress-tolerance solutions. Commercial farmers and organized seed processors are projected to expand film coating for cereals and pulses, while polymer encapsulation gains momentum in high-value horticulture due to precise dose delivery and compatibility with multi-active stacks.
Chitosan’s antimicrobial benefits and elicitor action are being positioned to improve emergence uniformity and early vigor under heat and intermittent moisture stress. Direct B2B contracting with seed companies is likely to dominate large volumes, while agri-ecommerce platforms expand access for mid-size growers with advisory-led bundles. Fermentation-derived chitosan is expected to find early adopters in export-linked horticulture that values non-animal sourcing and traceability.
A quality-centric market posture is anticipated as seed processors prioritize compliance, dust minimization, and stable coating performance across lots. Film coating is expected to remain the baseline, with increased use of chitosan blends that integrate micronutrients or biopolymers to improve emergence uniformity in cereals, oilseeds, and sugar beet.
Precision agriculture programs and on-farm stewardship requirements are likely to favor low-dust, high-adhesion formulations that maintain planter hygiene. OEM partnerships for calibration and QA protocols should reinforce consistency, while fermentation-derived chitosan garners attention among processors serving sustainability-led customers. Although overall growth remains moderate, share retention is projected through higher specification products and exporter-grade consistency.
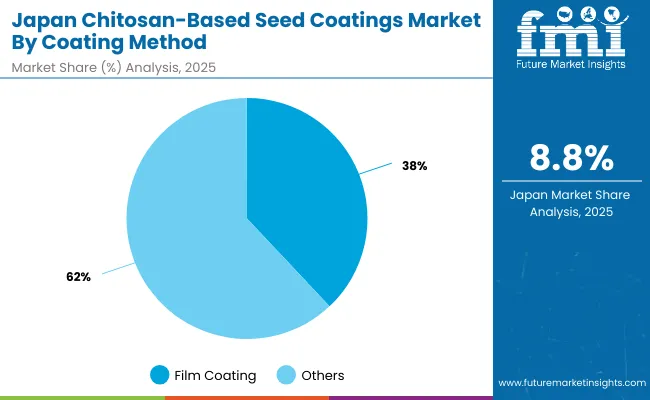
Japan’s chitosan-based seed coating market is structured around multiple coating methods, with film coating leading at 38% share in 2025. Film coating remains widely used for cereals, rice, and bulk vegetable crops because of its cost efficiency and ease of integration into existing seed treating systems. However, polymer encapsulation, with 28% share, is forecast to grow fastest at 8.8% CAGR, reflecting Japan’s emphasis on high-value horticulture and precision agriculture. Encapsulation provides controlled release, dose accuracy, and the ability to integrate multiple actives-qualities increasingly demanded in greenhouse and nursery cultivation.
Pelleting and encrusting maintain specialized roles, supporting seed flowability, planter calibration, and uniform seed sizing in vegetables and flowers. Collectively, Japan’s coating method mix illustrates a balance between established, large-volume film coating and innovation-led encapsulation that supports premium crop sectors.
| Coating Method | Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Film Coating | 38% |
| Others | 62% |
| Coating Method | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Film Coating | 6.2% |
| Others | 7.3% |
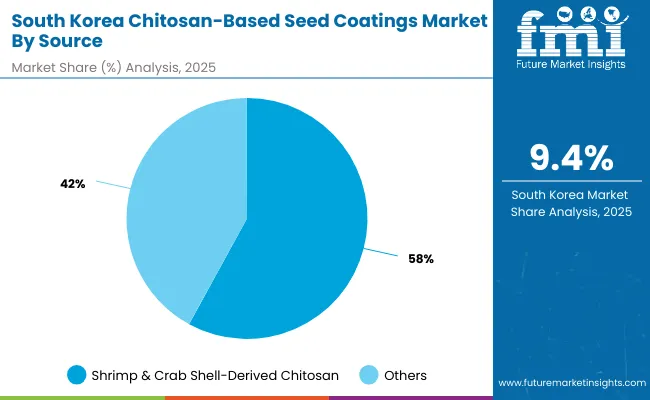
South Korea’s chitosan-based seed coating market is led by shrimp & crab shell-derived chitosan, holding 58% share in 2025, supported by established supply chains and lower production costs. This source dominates applications in cereals and maize, where large volumes and cost efficiency are priorities.
However, the most dynamic growth is projected for fungal fermentation-derived chitosan, which already accounts for 36% of the market and is expected to expand at a robust 9.4% CAGR. This reflects South Korea’s strong emphasis on sustainability, traceability, and innovation within its advanced agricultural ecosystem.
Fermentation-derived grades are gaining traction in horticulture, greenhouse crops, and export-oriented segments where non-animal sourcing is valued. Squid and other marine sources, though smaller at 6% share, contribute to niche applications but lack scalability. Together, these trends position South Korea as a leader in transitioning toward high-spec, sustainable chitosan sourcing.
| Source | Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Shrimp & Crab Shell-Derived Chitosan | 58% |
| Others | 42% |
| Source | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Shrimp & Crab Shell-Derived Chitosan | 6.00% |
| Others | 7.50% |
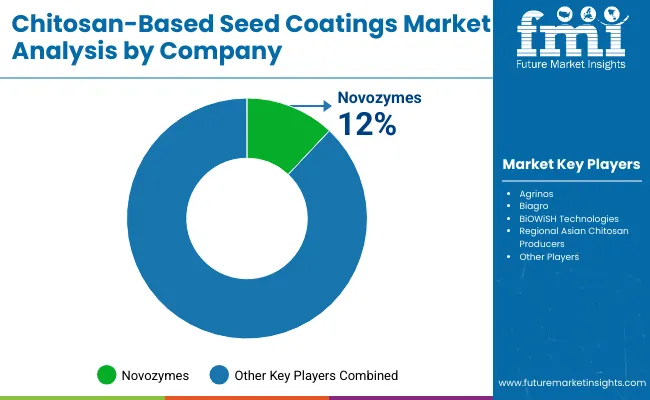
| Company | Global Market Value Share, 2025 |
|---|---|
| Novozymes (via Microbial & Biocontrol Portfolio) | 12.0% |
| Others | 88.0% |
The competitive environment in the Chitosan-Based Seed Coatings Market is characterized by a small group of global players supported by regional specialists and research-focused enterprises. Novozymes, leveraging its microbial and biocontrol portfolio, is assessed as the leading participant with a 12% global value share in 2025. Its advantage stems from integrated solutions combining chitosan with microbial inoculants and biostimulants, aligning with the industry’s preference for stackable seed treatment products.
Alongside Novozymes, companies such as Agrinos, Biagro, and BiOWiSH Technologies are pursuing differentiated offerings in biopolymer blends and encapsulation technologies. Regional producers in Asia, particularly in China and India, are expanding shell-derived chitosan capacity, benefiting from abundant marine by-products and cost-efficient processing. Innovation is also occurring among niche European firms that specialize in fermentation-derived chitosan, targeting sustainability-conscious buyers with non-animal sourcing credentials.
Competitive advantage is increasingly shifting toward firms capable of ensuring consistency in molecular weight distribution, dust reduction, and compatibility with advanced application equipment. With climate resilience and traceability gaining traction, companies that can pair high-performance coatings with transparent sourcing are expected to capture premium market positions, while smaller participants may face consolidation pressures.
Key Developments in Chitosan-based Seed Coating Market
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size, 2025 | USD 352.7 Million |
| Market Size, 2035 | USD 662.3 Million |
| Absolute Growth (2025 to 2035) | USD 309.6 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.50% |
| Value Added 2025 to 2030 | ~USD 124.0 Million |
| Value Added 2030 to 2035 | ~USD 185.6 Million |
| Type (2025) | Polymeric Chitosan Coatings lead (44% share) |
| Source (2025) | Shrimp & Crab Shell-Derived Chitosan leads (64% share) |
| Coating Method (2025) | Film Coating leads (36% share) |
| Crop Type (2025) | Cereals & Grains lead (34% share) |
| Application Functionality (2025) | Seed Protection leads (41% share) |
| End User (2025) | Commercial Farmers lead (44% share) |
| Distribution Channel (2025) | Direct Sales lead (58% share) |
| Key Growth Regions (CAGR) | South Asia & Pacific (9.0%) , East Asia (8.1%) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | USA, UK, Germany, France, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Brazil |
| Key Companies Profiled | Novozymes, Agrinos, Biagro, BiOWiSH Technologies, regional Asian chitosan producers |
| Additional Attributes | Climate-resilient coatings; compatibility with microbial inoculants; non-animal fermentation-derived sourcing; dust control and meterability ; e-commerce enablement |
The market is valued at USD 352.7 million in 2025.
The market is expected to reach USD 662.3 million by 2035.
The market is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 6.5%.
Polymeric Chitosan Coatings are projected to dominate with a 44% share in 2025.
South Asia & Pacific (9.0% CAGR) and East Asia (8.1% CAGR) are expected to witness the fastest growth rates.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Seed Paper Bag Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Processing Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Biostimulants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Health Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Additives Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Coating Material Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Packaging Market Analysis – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Binders Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Market Share Breakdown of Seed Cracker Manufacturers
Seed Polymer Market
Seed Testing Services Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2018-2028
Teaseed Cake Market – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
The Linseed Oil Market is Analysis by Nature, Product Type, Application, and Region from 2025 to 2035
Rapeseed Protein Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Flaxseed Gum Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapeseed Oil Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Analysis and Growth Projections for Hempseed Milk Business
Rapeseed Meal Market Analysis by Type, Application, Nature, and Region Through 2035
Assessing Rapeseed Protein Market Share & Industry Trends

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA