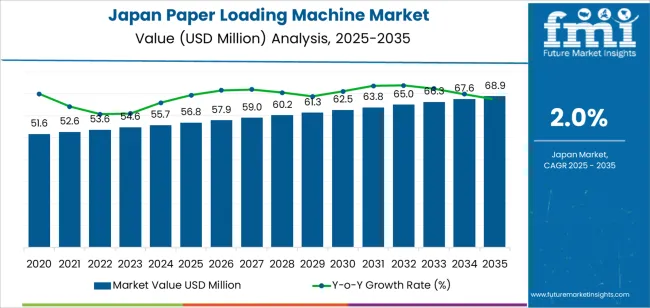
The demand for paper loading machines in Japan is valued at USD 56.8 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 68.9 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 2.0%. Demand is supported by steady utilization across printing facilities, packaging converters, bookbinding units, and commercial document-processing centers that rely on precise and continuous material handling.
Growth is shaped by gradual automation upgrades in mid-sized printing operations, wider use of high-speed feeders in packaging workflows, and ongoing improvements in accuracy, jam-reduction systems, and multi-format handling. These enhancements encourage reinvestment among established users. Roll loading machines remain the leading product type as high-volume press environments prioritize tension stability, continuous feeding, and reduced manual intervention. Automated and semi-automated loading systems continue expanding as facilities replace aging equipment to improve workflow continuity, operator safety, and predictable throughput.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kansai represent the highest-growth regions due to the strong presence of commercial printing hubs, packaging facilities, logistics centers, and institutional document-processing units. These regions also benefit from established distributor networks, spare-part channels, and technical-service availability that support installation, calibration, and lifecycle maintenance. Key manufacturers include IHI Machinery and Furnace Co., Ltd., Kawanoe Zoki Co., Ltd., Shin-Ei Machinery Co., Ltd., Oji Engineering Co., Ltd., and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Machinery Systems, Ltd., supplying roll, sheet, and web-fed loading systems to a wide range of printing and converting environments in Japan.
Growth contribution in Japan’s paper-loading-machine segment is driven primarily by steady utilization across printing, packaging, and commercial document-processing facilities. The largest contribution comes from routine industrial demand, where paper-handling equipment supports continuous workflow in publishing houses, office-supply manufacturers, and logistics documentation centers. These operations rely on stable production volumes, creating a predictable contribution baseline. A second contribution comes from automation upgrades within small and mid-sized printing shops. As facilities replace manual loading with semi-automated or fully automated systems, incremental adoption adds to year-to-year growth. These upgrades occur gradually because procurement follows equipment-lifecycle timelines, which helps maintain a consistent but measured contribution.
Technological refinement provides another steady layer. Improvements in feed accuracy, jam-reduction systems, and multi-format handling increase operational efficiency, encouraging periodic reinvestment among established users. This supports additional contribution without introducing volatility. Institutional demand from administrative centers, universities, and government printing units forms a smaller but stable component of the index. Procurement in these settings depends on scheduled equipment replacement and compliance with workflow-standardization requirements.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Paper Loading Machine Sales Value (2025) | USD 56.8 million |
| Japan Paper Loading Machine Forecast Value (2035) | USD 68.9 million |
| Japan Paper Loading Machine Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 2.0% |
Demand for paper loading machines in Japan is increasing because printing facilities, packaging plants and document-processing centers seek automated systems that improve handling efficiency and reduce manual labour. These machines support high-speed loading of paper stacks into printers, cutters and finishing equipment, which aligns with Japan’s focus on precision and productivity in industrial operations. Commercial printers, bookbinding companies and office-equipment service providers rely on automated loading to maintain consistent throughput and reduce paper jams that disrupt workflow.
Growth in e-commerce packaging and printed-label production also contributes to wider adoption in regional factories. Improvements in compact machine design and user-friendly controls make automated loading practical even for mid-sized facilities with limited floor space. Constraints include high initial investment for advanced systems, maintenance requirements for continuous operation and integration challenges with older printing equipment. Some small printing shops continue using manual loading due to cost sensitivity or low production volume. Fluctuations in paper demand across commercial printing segments may also delay equipment upgrades.
Demand for paper loading machines in Japan is shaped by the needs of printing plants, packaging converters, bookbinding facilities, and newspaper production units that rely on stable material handling systems. These machines support efficient transfer of rolls or sheets into high-speed presses, laminators, and finishing lines. Japanese operations emphasize precision alignment, reduced manual intervention, and consistent feed quality to maintain print accuracy and limit downtime. Requirements vary by substrate type, production volume, and equipment configuration, influencing machine selection across facilities.
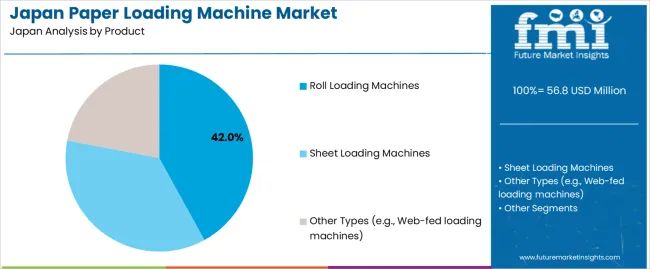
Roll loading machines represent 42.0%, driven by their use in Japan’s newspaper printing, flexible packaging, and large-format press environments. These machines support continuous unwinding, controlled tension, and accurate roll placement required for long-run operations. Sheet loading machines account for 36.0%, used in commercial printing, bookbinding, and sheet-fed packaging applications where precise stacking and feeding are essential. Other machine types, including web-fed loading systems, represent 22.0%, serving specialized converting lines and labeling operations. Product distribution reflects Japan’s mix of high-speed roll-based workflows and mid-volume sheet-based production, each requiring stable material transfer, reduced setup time, and consistent feed alignment.
Key points:
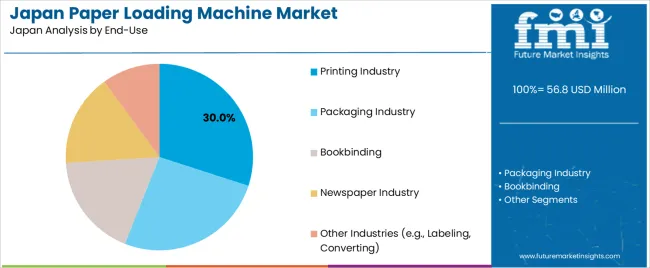
The printing industry accounts for 30.0% of demand, supported by Japan’s commercial print houses, newspaper facilities, and digital press operations requiring precise material handling. Packaging represents 26.0%, covering folding cartons, flexible packaging, and label production that depend on repeatable feeding accuracy. Bookbinding contributes 18.0%, where sheet handling influences trimming, folding, and binding quality. The newspaper industry accounts for 16.0%, maintaining roll-loading needs for continuous high-speed press runs. Other industries represent 10.0%, including labeling and converting operations that use customized loading systems. End-use distribution reflects Japan’s established printing base and ongoing modernization across packaging and binding workflows.
Key points:
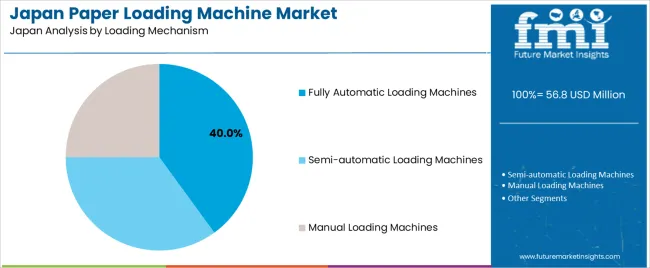
Fully automatic loading machines represent 40.0%, reflecting Japan’s reliance on automation to improve handling accuracy, reduce labor, and support continuous production. These systems integrate alignment sensors, lift mechanisms, and automated repositioning to maintain consistent feeding across long shifts. Semi-automatic machines account for 35.0%, used in facilities balancing automation with operator oversight, particularly in mid-volume print and packaging operations. Manual loading machines represent 25.0%, applied in small workshops or low-volume environments where flexibility outweighs speed. Mechanism distribution reflects Japan’s shift toward automated handling to support production stability, operator safety, and predictable throughput in industrial environments.
Key points:
Growth of high-volume commercial printing, increased automation in packaging and rising labour shortages in manufacturing are driving demand.
In Japan, paper loading machines gain traction as commercial printing companies in Tokyo, Osaka and Aichi automate feeding operations to support continuous production of brochures, instruction manuals and transactional documents. Packaging manufacturers supplying food, cosmetics and consumer goods use automated loading systems to handle cartons, labels and specialty paper forms with greater precision. Labour shortages in printing and converting plants accelerate adoption because automated loaders reduce manual handling and improve shift productivity. Regional mail-processing centers also use paper loading equipment to support bulk envelope preparation for administrative and financial institutions.
High equipment cost, limited floor space in older facilities and slow replacement cycles restrain demand.
Japanese printing shops operating in dense urban areas often run in compact buildings with limited space for new automated feeders, reducing feasibility of installation. Paper loading machines require significant upfront investment, and many small or family-operated print shops hesitate to upgrade unless production needs clearly justify the cost. Replacement cycles remain long because Japanese operators maintain machinery carefully and prefer to extend the life of existing systems. These financial and spatial limitations create stable but moderate expansion across the sector.
Shift toward compact automated feeders, increased integration with digital printing lines and rising demand from e-commerce packaging operations define key trends.
Manufacturers are developing compact paper loading units designed for tight production floors, enabling easier adoption among mid-sized print and converting operations. Digital printing lines used for short-run packaging, variable data printing and on-demand marketing materials increasingly integrate automated loaders to improve workflow speed. E-commerce growth in Japan drives packaging suppliers to automate carton and insert handling, reinforcing demand for reliable and adjustable loading equipment. These trends support a gradual move toward higher automation levels in Japan’s printing and packaging industries.
Demand for paper loading machines in Japan is shaped by printing facilities, packaging plants, paper-processing workshops, and distribution centers that rely on automated or semi-automated systems to handle paper rolls, sheets, and bundled materials. Growth reflects regional concentrations of printing operations, logistics hubs, document-processing centers, and paper-related manufacturing. Kyushu & Okinawa lead at 2.4%, followed by Kanto (2.2%), Kansai (2.0%), Chubu (1.7%), Tohoku (1.5%), and Rest of Japan (1.4%).
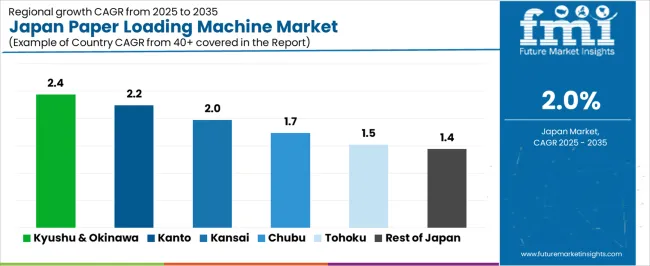
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 2.4% |
| Kanto | 2.2% |
| Kansai | 2.0% |
| Chubu | 1.7% |
| Tohoku | 1.5% |
| Rest of Japan | 1.4% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 2.4% CAGR, supported by stable activity in printing services, packaging units, and document-processing facilities. Prefectures such as Fukuoka and Kumamoto maintain medium-scale printing clusters requiring mechanical loading systems to handle sheet stacks and paper rolls used in commercial print jobs. Regional logistics centers use paper loading machines for sortation areas and packaging workflows that require consistent feeding of paper-based materials.
Local administrative offices and business-service firms continue processing physical documents, sustaining demand for small to mid-capacity machines. Equipment suppliers across Fukuoka maintain routes for installation, service, and replacement parts. Tourism in Okinawa supports printing demand for brochures, guides, and hospitality materials, increasing the need for reliable paper-handling equipment in commercial shops.
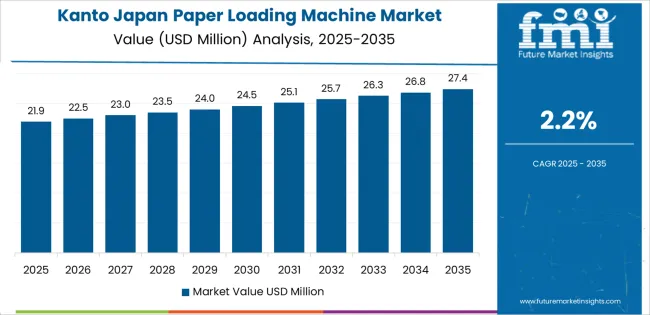
Kanto grows at 2.2% CAGR, driven by dense commercial printing, large back-office operations, and active distribution hubs across Tokyo, Kanagawa, and Saitama. Tokyo’s printing houses rely on automated paper loading for brochures, books, marketing material, and administrative documents processed at high volume. Corporate service centers use loading machines to support document reproduction tasks requiring steady input feeding. Logistics facilities across Saitama and Chiba rely on paper-handling equipment to process packaging inserts, labels, and printed order slips. Paper distributors in Kanagawa maintain consistent demand for equipment that improves workflow efficiency during sorting and bundling. Commercial print operators replace older machines to support continuous production cycles.
Kansai grows ata 2.0% CAGR, supported by printing networks, packaging producers, and administrative centers across Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe. Printing facilities in Osaka depend on paper loading machines for booklets, catalogues, and commercial print runs. Kyoto’s educational and institutional sectors generate consistent document-processing needs, increasing reliance on automated paper feeders. Packaging plants use paper loaders for box liners, inserts, and protective sheets in assembly workflows. Kobe’s industrial districts adopt mid-capacity loading systems to manage document output and packaging operations in mixed-use facilities. Regional distributors maintain reliable inventories of paper-handling equipment suitable for varied workloads.
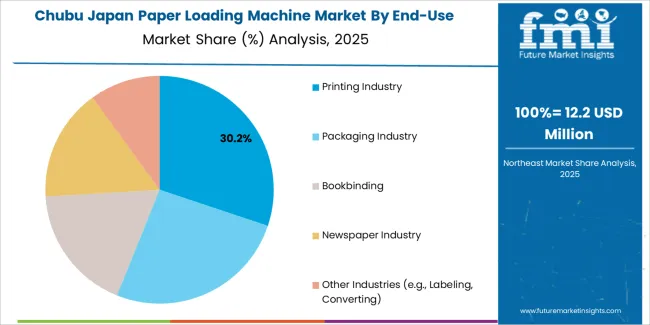
Chubu grows at 1.7% CAGR, shaped by manufacturing-linked packaging, regional printing operations, and corporate administrative centers across Aichi, Shizuoka, and Nagano. Packaging suppliers rely on paper loading machines to support assembly lines for product labeling, cushion materials, and documentation inserts. Commercial printing units in Nagoya use automated feeders for catalogues, manuals, and high-volume print batches. Manufacturing firms integrate paper-handling systems for documentation, quality tags, and packaging paperwork. Shizuoka’s presence in paper production contributes to downstream handling needs in local processing sites.
Tohoku grows at 1.5% CAGR, influenced by moderate printing activity, packaging operations, and public-sector documentation workflows across Miyagi, Fukushima, and Aomori. Print shops use loading machines to maintain continuous input for administrative documents, educational materials, and commercial print tasks. Packaging units rely on paper-handling systems to prepare inserts and protective sheets for regional manufacturing exports. Public offices maintain steady use of paper-based records, sustaining demand for small and mid-capacity loaders. Local distributors provide equipment tailored for modest production scales.
Rest of Japan grows at 1.4% CAGR, supported by small printing houses, municipal offices, local packaging units, and business service providers. Smaller print shops rely on compact paper loaders to manage brochures, forms, and local advertising materials. Regional packaging facilities use loaders for protective sheets and documentation inserts. Administrative centers maintain physical-record processing, supporting ongoing equipment needs. Equipment distributors provide compact models suited for lower-volume operations.
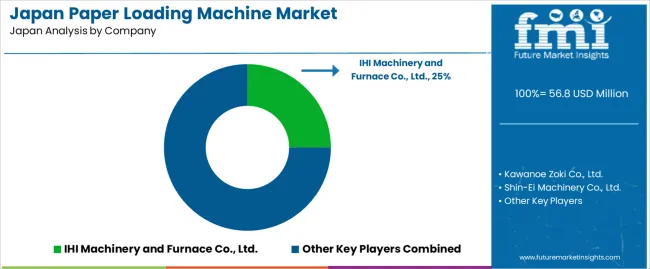
Demand for paper-loading machines in Japan is shaped by domestic paper-machinery manufacturers that supply equipment to large integrated paper mills, specialty-paper facilities, and packaging-paper producers. IHI Machinery and Furnace Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 25.0% share, supported by controlled mechanical-handling design, stable load-transfer performance, and long-standing relationships with major Japanese paper groups. Its systems provide consistent reel handling, reliable positioning, and dependable maintenance support.
Kawanoe Zoki Co., Ltd. maintains strong participation with automated loading equipment integrated into tissue, printing-paper, and board-production lines. Its machines offer predictable operating stability, straightforward maintenance, and compatibility with Japanese mill layouts. Shin-Ei Machinery Co., Ltd. adds capacity through compact and mid-scale paper-handling systems used in regional mills and converters.
Oji Engineering Co., Ltd. supports loading operations within large industrial paper facilities, providing equipment engineered for continuous-duty environments. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Machinery Systems, Ltd. contributes through reel-handling and logistics equipment paired with its broader pulp-and-paper machinery portfolio. Foreign suppliers, including ANDRITZ, Valmet, and Voith, serve high-capacity mills requiring advanced automation, especially for new production lines and modernization projects. Competition in Japan centers on mechanical reliability, automation integration, safety compliance, alignment accuracy, and long-term service availability within paper-production environments that demand continuous, precision-driven material handling.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Product | Roll Loading Machines, Sheet Loading Machines, Other Types (e.g., Web-fed loading machines) |
| End-Use | Printing Industry, Packaging Industry, Bookbinding, Newspaper Industry, Other Industries (e.g., Labeling, Converting) |
| Loading Mechanism | Fully Automatic Loading Machines, Semi-automatic Loading Machines, Manual Loading Machines |
| Machine Size/Capacity | Medium-sized Machines, Large-sized Machines, Small-sized Machines |
| Automation Level | Automated Loading Machines, Smart/Connected Loading Machines (Industry 4.0 integration), Conventional Loading Machines |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | IHI Machinery and Furnace Co., Ltd., Kawanoe Zoki Co., Ltd., Shin-Ei Machinery Co., Ltd., Oji Engineering Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Machinery Systems, Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type, end-use sector, loading mechanism, machine size, and automation level; regional industrial adoption patterns across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; influence of automation upgrades in printing, packaging, and newspaper industries; integration of IoT/Industry 4.0 features such as predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics; competitive landscape of domestic machinery manufacturers; rising demand for high-speed loading systems in commercial printing and converting operations. |
The demand for paper loading machine in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 56.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the paper loading machine in Japan is projected to reach USD 68.9 million by 2035.
The demand for paper loading machine in Japan is expected to grow at a 2.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in paper loading machine in Japan are roll loading machines, sheet loading machines and other types (e.g., web-fed loading machines).
In terms of end-use, printing industry segment is expected to command 30.0% share in the paper loading machine in Japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Paper Loading Machine Market Trend Analysis Based on Product, End-Use, Loading Mechanism, Machine Size/Capacity, Automation Level and Regions 2025 to 2035
Machine Glazed Paper Industry Analysis in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Paper Machine Systems Market
Paper Cup Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Competitive Overview of Paper Cup Machine Market Share
Paper Making Machines Market
Machine Glazed Paper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Machine Glazed Paper Industry Analysis in Asia Pacific Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Machine Glazed Paper Industry Analysis in Western Europe Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Machine Glazed Paper Industry Analysis in Korea Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Key Players & Market Share in Machine Glazed Paper Industry
Kraft Paper Machine Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Micro Flute Paper Market Analysis – Size, Share & Industry Trends 2025-2035
Paper Core Cutting Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Paper Napkin Making Machine Market Analysis, Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Machine Glazed Kraft Paper Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Paper Napkins Converting Machines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Top Loading Cartoning Machine Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Corrugated Paper Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Competitive Overview of Corrugated Paper Machine Market Share

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA