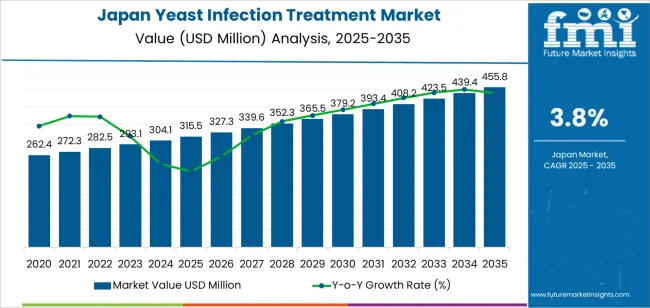
The Japan yeast infection treatment demand is valued at USD 315.5 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 455.8 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 3.8%. Demand is influenced by sustained utilization of antifungal therapies across outpatient clinics, women’s health practices, and pharmacies. Increased diagnosis of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, broader awareness of self-managed treatment options, and stable prescription volumes for first-line antifungals support continued uptake. Ageing demographics and greater screening in primary-care settings also contribute to treatment demand.
Azoles lead the treatment landscape. These drugs are preferred for their established efficacy, broad-spectrum antifungal action, and widespread clinical use in both prescription and OTC formulations. They remain the standard therapy for acute and recurrent infections, with consistent demand from hospital, clinic, and retail pharmacy channels.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilization due to population density, concentration of medical facilities, and strong distribution networks for pharmaceutical products. These regions also maintain extensive retail pharmacy presence and active women’s health service providers, supporting consistent access to antifungal treatments. Key suppliers include Sato Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kowa Company, Ltd., Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc., and Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd. These companies provide azole-based formulations, combination therapies, and OTC antifungal products used in clinical and self-care management of yeast infections.
Growth momentum in Japan’s yeast-infection-treatment segment advances at a steady and predictable pace across the forecast horizon. The early period shows consistent momentum supported by routine clinical demand, wider availability of over-the-counter antifungal products, and stable consultation rates across primary-care and gynecology settings. Increased awareness of self-care options and improved diagnostic access in pharmacies and clinics help sustain a uniform rise during the initial years.
Mid-period momentum continues at a similar rhythm as treatment protocols remain well established and product categories mature. Incremental improvements in topical and oral formulations support steady adoption without creating sharp year-to-year shifts. Utilization patterns remain stable because infection prevalence and seasonal variation are relatively predictable, producing limited volatility in clinical and retail demand.
In the later period, momentum remains positive but becomes more uniform as the therapeutic landscape stabilizes. Replacement demand and periodic product refinements contribute to incremental gains, though annual changes narrow as prescriber preferences and consumer habits converge. The overall momentum profile reflects a controlled expansion pattern, shaped by consistent clinical need, mature treatment options, and stable distribution across Japan’s healthcare and retail channels.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Yeast Infection Treatment Sales Value (2025) | USD 315.5 million |
| Japan Yeast Infection Treatment Forecast Value (2035) | USD 455.8 million |
| Japan Yeast Infection Treatment Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 3.8% |
Demand for yeast infection treatment in Japan is increasing because more patients seek timely management of vulvovaginal candidiasis and related fungal conditions. Factors such as ageing, higher diabetes prevalence, increased antibiotic use and lifestyle changes contribute to recurrent infections, which strengthens demand for antifungal creams, oral medications and diagnostic services. Greater awareness of women’s health encourages early consultation and purchase of over-the-counter options for mild to moderate symptoms.
Hospitals and clinics also diagnose more cases due to improved screening and wider use of PCR and culture-based testing. E-commerce and pharmacy chains expand access to topical azoles and supportive products, which further supports steady demand. Constraints include cautious use of antifungals to avoid resistance, limited awareness of proper treatment duration among some users and reluctance to seek care for recurrent infections. Mild symptoms are sometimes self-managed with home remedies, which slows adoption of formal treatment in certain cases.
Demand for yeast infection treatment in Japan reflects clinical management practices for genital, oral–esophageal, and invasive fungal conditions. Treatment selection depends on infection severity, patient history, and response to antifungal medication. Indication patterns show how Japanese healthcare facilities address both routine mucosal infections and more complex systemic cases requiring specialized care. Route-of-administration choices indicate how clinicians balance convenience, absorption, and treatment intensity across outpatient and inpatient settings. These patterns outline how antifungal therapy supports symptom control, eradication of fungal overgrowth, and prevention of recurrence in both acute and chronic presentations.
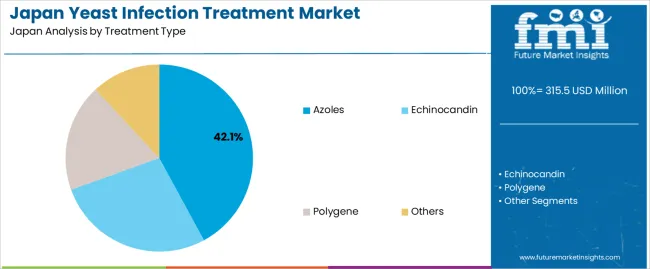
Azoles hold 42.1% of national demand and represent the leading treatment class in Japan. These agents are widely used for genital and oral candidiasis because they provide broad antifungal activity and consistent clinical response. Echinocandin accounts for 27.4%, used primarily for invasive infections requiring hospital-based monitoring or when azole resistance is observed. Polygene represents 18.6%, supporting cases requiring alternative mechanisms of action. Other treatments account for 11.9%, covering supplementary antifungal options. Treatment-type distribution reflects Japanese prescribing preferences, resistance patterns, and the need for flexible therapy across mild and severe presentations.
Key drivers and attributes:
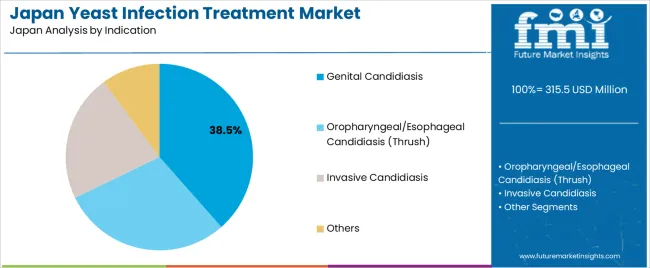
Genital candidiasis holds 38.5% of national demand and represents the most common indication treated in Japan. Cases are addressed in outpatient clinics and women’s health departments, where rapid symptom control is prioritized. Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis accounts for 29.3%, occurring in patients with immunosuppression, chronic illness, or medication-related susceptibility. Invasive candidiasis represents 22.1%, requiring intensive medical attention, blood culture monitoring, and hospital-based therapy. Other indications hold 10.1%, spanning dermal and secondary fungal complications. Indication distribution reflects Japanese outpatient care patterns, ageing demographics, and immune-related conditions influencing susceptibility to fungal infections.
Key drivers and attributes:
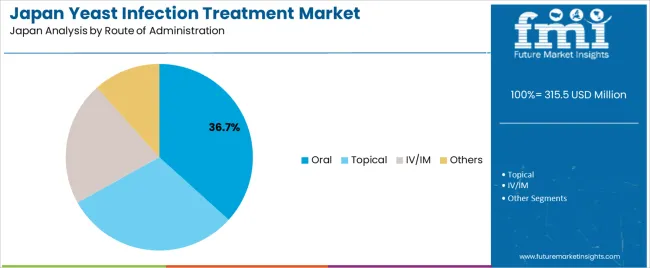
Oral treatment holds 36.7% of national demand and represents the leading administration route in Japan. Tablets and capsules support convenient dosing, stable absorption, and suitability for mild to moderate infections treated in outpatient settings. Topical treatment accounts for 30.2%, widely used for genital and cutaneous candidiasis requiring localized action. IV/IM administration represents 21.5%, applied to invasive or severe infections requiring controlled dosing in hospital environments. Other routes account for 11.6%, covering specialized formulations. Administration-pattern distribution reflects Japanese treatment protocols balancing convenience, targeted delivery, and intensive care for severe presentations.
Key drivers and attributes:
Higher diagnosis rates in women’s health clinics, increased OTC antifungal use and growing attention to self-care among working women are driving demand.
In Japan, demand for yeast infection treatments rises as gynecology clinics conduct more routine examinations through municipal health programs and employer-supported checkups. Working women in urban regions such as Tokyo and Osaka increasingly seek fast relief options available through pharmacies, where OTC antifungal creams and suppositories are commonly stocked. Pharmacists play a central advisory role in Japan’s retail health ecosystem, encouraging early treatment of mild symptoms. Seasonal humidity, common in Kanto and Kyushu, contributes to recurring cases, further increasing reliance on topical azoles and combination therapies. These factors sustain treatment demand across both clinical and retail channels.
Reluctance to discuss intimate-health symptoms, limited awareness of recurrent infection management and conservative prescribing patterns restrain growth.
Many women in Japan remain hesitant to seek prompt medical attention due to cultural discomfort around discussing intimate issues, which delays diagnosis and reduces early treatment uptake. Awareness of long-term management strategies for recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis remains limited outside specialist clinics, lowering adherence to multi-step regimens. Physicians in Japan often prefer narrower treatment options and may avoid switching to newer formulations unless symptoms persist, slowing broader introduction of alternative antifungals. These behavioural and clinical patterns contribute to moderate, steady rather than rapid growth in demand.
Shift toward low-irritation formulations, increased pharmacy-based counselling and expanding digital women’s health services define key trends.
Manufacturers in Japan are offering mild, fragrance-free antifungal products tailored to sensitive-skin users, reflecting consumer preference for gentle formulations. Chain pharmacies in metropolitan areas expand consultation spaces, allowing pharmacists to guide patients on correct dosing and symptom differentiation. Digital women’s health platforms and teleconsultation services are gaining traction, providing discreet access to gynecological advice and prescription pathways. Educational campaigns on recurrent infection management, often delivered through apps used by young women, are improving treatment consistency. These trends indicate a gradual strengthening of yeast infection treatment adoption across Japan’s healthcare and retail landscape.
Demand for yeast infection treatment in Japan is increasing through 2035 as healthcare providers manage recurrent fungal infections, rising awareness of women’s health, and broader access to over-the-counter antifungal products. Hospitals, gynecology clinics, and community pharmacies supply topical and oral treatments used for candidiasis and related conditions. Aging populations, chronic-disease prevalence, and antibiotic usage patterns contribute to steady regional demand. Differences in healthcare-facility density, patient awareness, and pharmacy networks shape growth rates. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 4.7%, followed by Kanto (4.3%), Kinki (3.8%), Chubu (3.3%), Tohoku (2.9%), and Rest of Japan (2.8%).
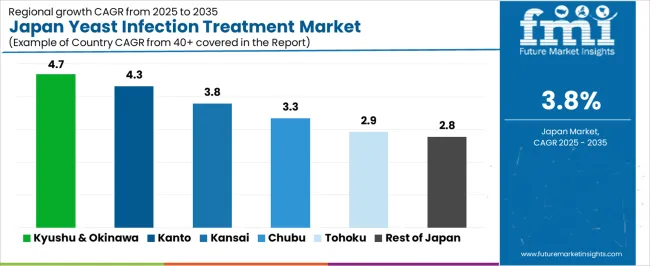
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 4.7% |
| Kanto | 4.3% |
| Kinki | 3.8% |
| Chubu | 3.3% |
| Tohoku | 2.9% |
| Rest of Japan | 2.8% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 4.7% CAGR, supported by widespread pharmacy availability, regional women’s-health programs, and consistent outpatient demand across Fukuoka, Kumamoto, Nagasaki, Kagoshima, and Okinawa. Clinics manage frequent candidiasis cases linked to humidity, antibiotic use, and chronic conditions. Gynecology centers in Fukuoka provide structured care using topical azoles, oral antifungal medication, and recurrence-prevention guidance. Community pharmacies sell over-the-counter formulations preferred for mild cases, increasing accessibility for patients seeking early treatment. Okinawa’s subtropical climate contributes to steady seasonal incidence, supporting sustained product turnover. Primary-care centers incorporate yeast-infection care within routine women’s-health consultations.
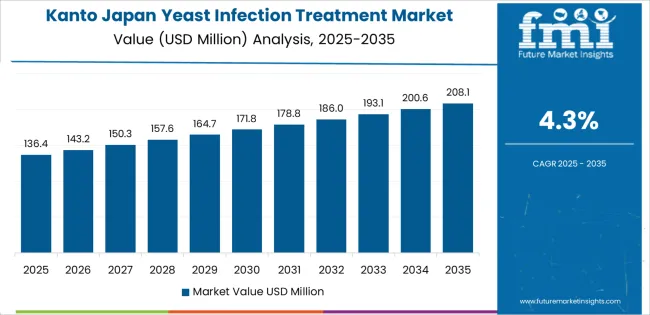
Kanto grows at 4.3% CAGR, driven by large healthcare networks, dense populations, and high pharmacy accessibility across Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, Saitama, and Ibaraki. Urban clinics treat significant numbers of yeast-infection cases related to stress, antibiotic exposure, and chronic health conditions. Gynecology departments rely on topical azoles, oral antifungals, and diagnostic procedures to address symptomatic and recurrent cases. Pharmacies in metropolitan districts offer a broad selection of OTC treatments that support early self-management. Public-health programs promote awareness of women’s hygiene and preventive practices.
Kinki grows at 3.8% CAGR, supported by regional hospital systems, preventive-care participation, and strong pharmacy networks across Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo, Nara, Wakayama, and Shiga. Clinics treat yeast infections linked to antibiotic usage, metabolic disorders, and lifestyle-related factors. Gynecology departments in Osaka and Kyoto adopt evidence-based treatment protocols using topical and oral antifungals. Pharmacies maintain steady sales of OTC creams, suppositories, and antifungal washes. Preventive-care initiatives in Hyogo and Nara encourage routine consultations for women experiencing recurrent infections.
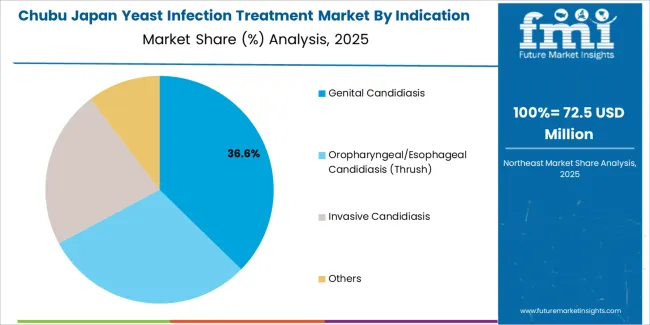
Chubu grows at 3.3% CAGR, influenced by regional healthcare access, outpatient care patterns, and consistent pharmacy distribution across Aichi, Shizuoka, Gifu, Mie, and Nagano. Clinics in Aichi provide antifungal therapies for patients experiencing recurrent or treatment-resistant infections. Pharmacies in Shizuoka and Mie supply OTC creams and oral formulations for symptomatic relief. Healthcare providers in Nagano incorporate yeast-infection management into routine women’s-health consultations. Public-health centers promote preventive hygiene practices targeting women across rural and suburban areas.
Tohoku grows at 2.9% CAGR, shaped by aging populations, rural healthcare reliance, and moderate OTC-treatment use across Miyagi, Aomori, Fukushima, Akita, Iwate, and Yamagata. Public hospitals treat fungal infections associated with chronic illnesses and long-term medication use. Clinics use topical and oral antifungals for outpatient management. Pharmacies supply basic OTC antifungal products for mild cases. Rural populations rely on primary-care centers for diagnosis and follow-up. Local health programs encourage awareness of yeast-infection symptoms and early-treatment behaviors.
Rest of Japan grows at 2.8% CAGR, supported by local clinics, small hospital networks, and stable pharmacy access across prefectures outside major regional hubs. Healthcare providers treat yeast infections as part of routine women’s-health services. Pharmacies maintain consistent turnover of OTC antifungal creams and oral agents. Rural communities rely on multipurpose clinics for diagnosis and treatment. Public-service centers offer educational materials on preventive hygiene and self-management.
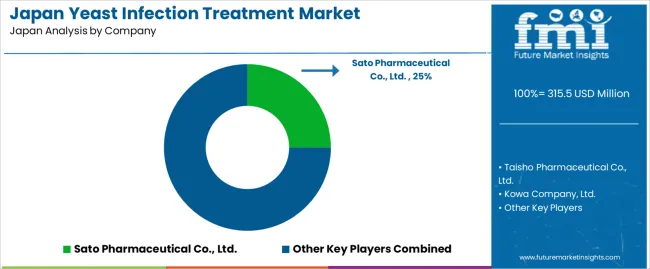
Demand for yeast-infection treatment in Japan is shaped by domestic pharmaceutical companies with established OTC channels, women’s-health portfolios, and nationwide pharmacy distribution. Sato Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 25.0% share, supported by controlled production of miconazole products designed for self-care treatment. Its formulations provide consistent dosage accuracy and stable symptom-relief performance, and its long-standing pharmacy presence reinforces strong consumer recognition.
Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. maintains significant participation through antifungal OTC treatments aligned with Japan’s self-medication practices. The company’s distribution coverage ensures reliable availability across urban and regional pharmacies, and its products offer predictable absorption and steady therapeutic action. Kowa Company, Ltd. contributes steady volume with topical antifungal solutions used in mild to moderate cases. Its formulations emphasize stable application properties and reliable tolerability, supporting adoption in community pharmacies.
Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. supports domestic demand with women’s-health OTC treatments that provide controlled release and consistent adherence to local regulatory requirements. Its established supply networks allow stable access for clinics and retail channels. Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd. maintains a smaller but visible presence with select antifungal offerings distributed through Japanese pharmacy chains, providing formulations with verified safety and stable therapeutic profiles.
Competition in Japan centres on formulation stability, symptom-relief consistency, regulatory conformity, packaging suitability for self-care, and dependable pharmacy distribution. Demand remains steady as Japanese consumers continue to prefer OTC azole-based treatments with predictable effectiveness, accessible dosing formats, and reliable availability across nationwide retail networks.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Treatment Type | Azoles, Echinocandin, Polygene, Others |
| Indication | Genital Candidiasis, Oropharyngeal/Esophageal Candidiasis (Thrush), Invasive Candidiasis, Others |
| Route of Administration | Oral, Topical, IV/IM, Others |
| Form | Tablets/Capsules, Creams/Ointments, Powders, Others |
| Distribution Channel | Retail Pharmacies/Drug Stores, Hospital Pharmacies, Online Sales, Specialty Stores, Others (Hypermarkets/Conventional Stores) |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Sato Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kowa Company, Ltd., Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by treatment type, indication, administration route, dosage form, and distribution channel; regional demand variations across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of antifungal therapy manufacturers; developments in azole resistance, novel topical and systemic antifungals, and rapid-diagnosis support tools; integration with hospital infection-control programs, community pharmacies, online pharmaceutical retailing, and patient self-care segments in Japan. |
The demand for yeast infection treatment in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 315.5 million in 2025.
The market size for the yeast infection treatment in japan is projected to reach USD 455.8 million by 2035.
The demand for yeast infection treatment in japan is expected to grow at a 3.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in yeast infection treatment in japan are azoles, echinocandin, polygene and others.
In terms of indication, genital candidiasis segment is expected to command 38.5% share in the yeast infection treatment in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Yeast Infection Treatment Market by Drug Type, Distribution Channel, End User, and Region, 2025 to 2035
Japan Yeast Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Yeast Infection Diagnostics Market Report - Demand, Trends & Industry Forecast 2025 to 2035
Global Eye Infections Treatment Market Report - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Systemic Infection Treatment Market
Japan Axillary Hyperhidrosis Treatment Market Insights – Size, Share & Trends 2025-2035
Norovirus Infection Treatment Market
Japan Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs) Treatment Market Growth – Demand, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Pork Tapeworm Infection Treatment Market Trends – Demand & Innovations 2025 to 2035
Toxoplasmosis Infection Treatment Market
Salivary Gland Infection Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Staphylococcal Infection Treatment Market
Coxsackievirus Infections Treatment Market – Growth & Drug Innovations 2025 to 2035
Intra-Abdominal Infection Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Varicella Zoster Infection Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Treatment Market (UTI) Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand for Burns Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Helicobacter Pylori Infections Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Global Antibiotic-Resistant Infections Treatment Market Analysis – Size, Share & Forecast 2024-2034
Demand for Water Treatment System in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA