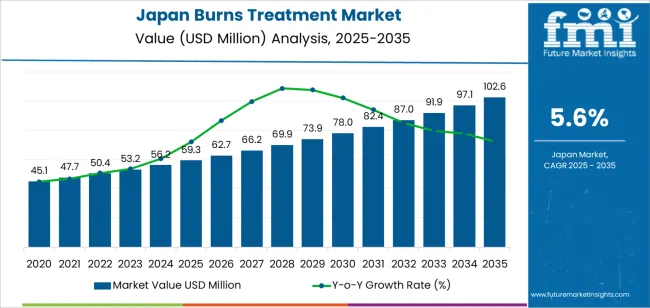
The Japan burns treatment demand is valued at USD 59.3 million in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 102.6 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 5.6%. Demand is shaped by the continued incidence of thermal, scald, chemical, and electrical burns across residential, industrial, and community environments. Increased utilization of advanced wound-care protocols in hospitals and outpatient centres also supports expansion. Greater emphasis on early intervention, pain management, infection prevention, and scar reduction contributes to broader adoption of specialized burn-care products. Integration of evidence-based clinical pathways in emergency and reconstructive care adds further momentum.
Wound care dressings lead the treatment landscape. These dressings are selected for moisture balance, antimicrobial support, exudate control, and suitability across superficial to deep-partial-thickness injuries. Adoption is reinforced by improvements in hydrocolloids, alginates, foams, silicone-based materials, and advanced bioactive dressings designed for faster epithelialization and reduced dressing-change frequency.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilization due to the concentration of emergency care units, specialized burn centers, and multidisciplinary wound-care teams. These regions also maintain strong procurement systems and structured clinician-training programmes that support consistent use of modern burn-care products. Key suppliers include Smith & Nephew plc, Mölnlycke, 3M Healthcare, Coloplast, and ConvaTec Japan K.K. These companies provide dressings, topical agents, negative-pressure wound therapy units, and related solutions used across acute burn management, reconstructive treatment, and long-term wound-care rehabilitation.
Growth momentum in Japan’s burns-treatment segment shows a steady and uniform trajectory through the forecast horizon. Early-period momentum is supported by broader adoption of structured burn-care protocols, increased availability of specialized treatment units, and integration of improved wound-care materials. Hospitals continue to refine clinical pathways, which strengthens utilization of topical agents, advanced dressings, and supportive therapies. This creates a consistent rise in treatment demand with limited variability.
Mid-period momentum maintains a similar pace as burn-care practices stabilize across major medical centers. Adoption of enzymatic debridement, regenerative materials, and infection-control solutions remains steady, supporting predictable year-to-year activity. Growth during this phase benefits from incremental improvements rather than sudden shifts, reflecting the routine and essential nature of burn-care services.
In the later period, momentum remains positive but becomes more uniform as the therapeutic landscape matures. Replacement cycles for equipment and sustained use of advanced dressings provide incremental gains, though annual changes narrow as adoption levels across hospitals converge. The momentum profile indicates consistent expansion with limited volatility, shaped by stable clinical demand, structured care pathways, and gradual technology refinement within Japan’s healthcare system.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Burns Treatment Sales Value (2025) | USD 59.3 million |
| Japan Burns Treatment Forecast Value (2035) | USD 102.6 million |
| Japan Burns Treatment Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 5.6% |
Demand for burns treatment in Japan is rising because hospitals and specialized centers manage a steady number of thermal, scald and contact-related injuries, particularly among older adults and workers in manufacturing environments. Japan’s ageing population experiences slower wound healing and higher risk of complications, which increases the need for advanced dressings, antimicrobial therapies and grafting materials. Medical institutions also invest in improved wound-care protocols, including bioactive dressings, cultured skin substitutes and moisture-retention treatments that support faster recovery and lower infection rates.
Growth in outpatient wound-care services and rehabilitation programmes further increases the use of specialized burns-management products. Constraints include high cost of advanced therapies, limited availability of specialized burn units in rural regions and the need for trained personnel to manage complex cases. Some facilities rely on standard dressings due to budget limits or limited clinical capacity, which slows adoption of newer techniques.
Demand for burns treatment in Japan reflects the range of interventions provided across hospitals, specialized burn units, and outpatient clinics. Treatment choice depends on wound depth, infection control needs, healing progression, and facility resources. Japan’s clinical practices emphasize early assessment, moisture balance, and prevention of complications arising from severe injuries. Degree-of-burn distribution shows how patients present with different severity levels linked to domestic accidents, occupational injuries, and seasonal exposure risks. These patterns outline how facilities incorporate dressings, therapy systems, and medications into treatment protocols that support safe recovery, reduce infection probability, and stabilize tissue response across diverse patient groups.
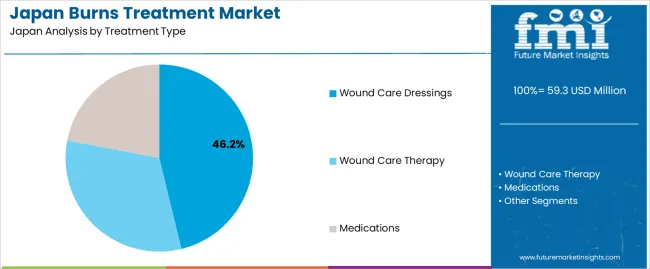
Wound care dressings hold 46.2% of national demand and represent the leading treatment category across Japanese medical facilities. They support moisture control, barrier protection, and early-stage healing for first- and second-degree injuries commonly treated in emergency departments and outpatient units. Wound care therapy accounts for 31.8%, covering debridement routines, negative-pressure systems, and specialized techniques used for deeper burns requiring extended clinical supervision. Medications represent 22.0%, including topical antimicrobials, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory preparations used to manage pain and infection risk. Treatment-type distribution aligns with Japanese protocols that prioritize staged management, infection prevention, and wound stability during early recovery.
Key drivers and attributes:
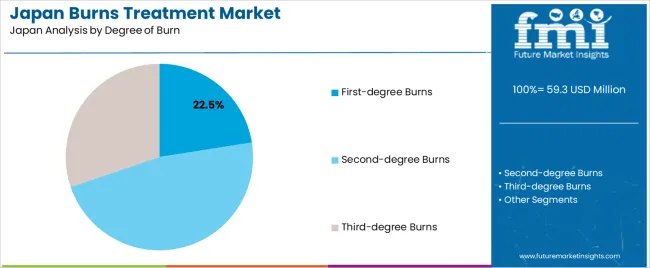
Second-degree burns hold 47.3% of national demand and represent the most frequently treated burn category in Japan. These injuries require structured care involving dressings, hydration management, and infection monitoring to support re-epithelialization. First-degree burns account for 22.5%, involving superficial injuries commonly treated with protective dressings and short clinic visits. Third-degree burns represent 30.2%, requiring comprehensive intervention including surgical debridement, skin grafting, and prolonged follow-up. Burn-degree distribution reflects domestic accident patterns, workplace incidents, elderly care considerations, and seasonal hazards. Clinical response times, facility capacity, and multispecialty coordination guide treatment decisions across Japanese healthcare settings.
Key drivers and attributes:
In Japan, burns treatment demand is shaped by the country’s ageing population, where older adults experience higher risk of scald injuries and cooking-related accidents, particularly in single-person households common in urban prefectures. Industrial facilities in Kansai, Kanto and Chubu, which host large manufacturing clusters, report steady cases of chemical and thermal burns requiring specialized care. Japan’s healthcare system maintains a network of designated burn units within university hospitals, increasing access to specialized treatment and advanced wound-care materials. Municipal emergency services also provide rapid triage, supporting timely intervention and improved survival outcomes, thereby increasing long-term care needs.
Many regional hospitals face shortages of plastic and reconstructive surgeons trained in burn management, which limits capacity outside major cities such as Tokyo and Osaka. Advanced dressing materials, including bioactive scaffolds and moisture-retentive films, carry higher procurement cost that can burden hospital budgets under the National Health Insurance system. Adoption of newer biologic therapies and engineered skin substitutes is gradual, partly due to cautious clinical evaluation practices and limited availability of specialized application teams. These constraints reduce the pace of expansion in specialized burns treatment across Japan.
Japanese hospitals are expanding use of hydrofiber and silver-based dressings favored for infection control and moisture regulation, especially in high-risk elderly patients. Tele-wound monitoring systems are being introduced to support follow-up care in rural regions where travel to major burn centers is difficult. Rehabilitation centers in Japan report rising demand for long-term scar-management services, including pressure garments and laser therapy, reflecting higher survival rates and patient focus on functional and cosmetic recovery. These trends indicate a broadening scope of burns care across acute, outpatient and rehabilitation settings in Japan.
Demand for burns treatment in Japan is rising through 2035 as hospitals, emergency departments, and specialized wound-care units expand capacity for managing thermal, scald, and contact burns. Japan’s aging population, industrial workplaces, and household accident patterns contribute to consistent treatment needs across regions. Medical facilities increasingly rely on advanced wound dressings, grafting techniques, antimicrobial products, and rehabilitation-focused protocols. Regional demand varies according to hospital concentration, emergency-care infrastructure, and local injury profiles. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 7.0%, followed by Kanto (6.5%), Kinki (5.7%), Chubu (5.0%), Tohoku (4.4%), and Rest of Japan (4.2%).
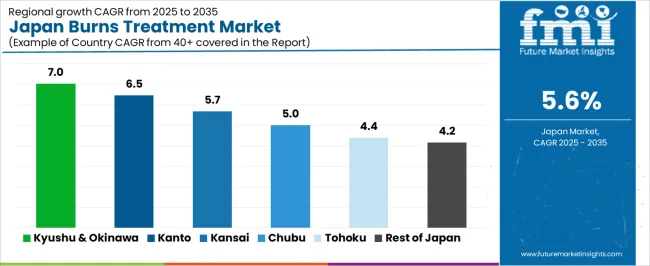
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 7.0% |
| Kanto | 6.5% |
| Kinki | 5.7% |
| Chubu | 5.0% |
| Tohoku | 4.4% |
| Rest of Japan | 4.2% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 7.0% CAGR, driven by the region’s broad medical network, higher incidence of household scald injuries among elderly residents, and the presence of industrial operations around Fukuoka, Kumamoto, and Kagoshima. Hospitals in Fukuoka manage significant emergency caseloads that include thermal and flame-related burns requiring acute care, advanced dressing applications, and infection-control protocols. Regional facilities support long-term recovery through rehabilitation programs for mobility, skin elasticity, and scar management. Local clinics use hydrogel, silicone-based, and collagen-support dressings for outpatient follow-ups. Okinawa relies on regional medical centers for surgical interventions, including grafting and debridement procedures.
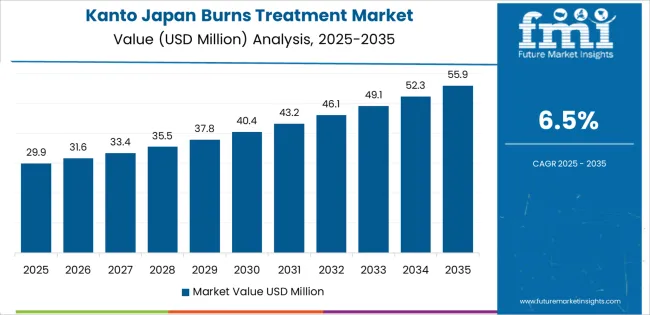
Kanto grows at 6.5% CAGR, supported by dense hospital networks, high population concentration, and large numbers of emergency-care centers across Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, Saitama, and Ibaraki. Urban districts see frequent minor burns from household cooking, workplace contact incidents, and scald injuries among older adults. Major hospitals operate specialized burn units equipped for intensive wound management, graft procedures, and fluid-resuscitation protocols. Clinics manage long-term outpatient needs using silicone sheets, hydrogels, and antimicrobial dressings. Health-check facilities increasingly incorporate patient-education programs on home safety, reducing recurrence. Metropolitan hospitals upgrade capacity for pediatric burn management and reconstructive support.
Kinki grows at 5.7% CAGR, supported by regional emergency-care capacity, industrial-area safety demands, and established burn-management protocols across Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo, Nara, Wakayama, and Shiga. Osaka’s major hospitals manage diverse burn types, including flame injuries, electrical accidents, and scald incidents. Clinics provide follow-up care involving moisture-retentive dressings, silicone therapy, and antimicrobial materials. Kyoto and Hyogo hospitals integrate surgical options for deeper burns and grafting needs. Workplace injuries in manufacturing zones contribute to steady caseloads requiring specialized assessment and occupational recovery support. Elderly households across Nara and Wakayama show increased scald-related outpatient visits.
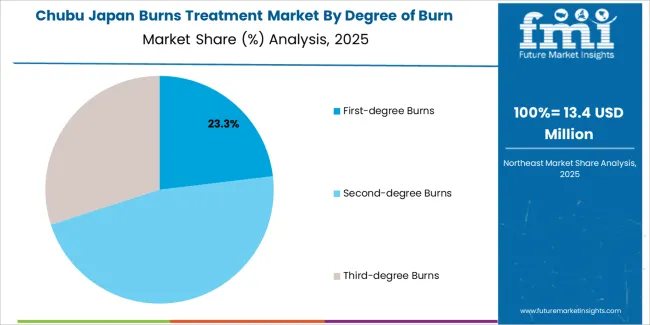
Chubu grows at 5.0% CAGR, influenced by industrial-workplace exposure, household cooking accidents, and steady emergency-care activity across Aichi, Shizuoka, Gifu, Mie, and Nagano. Aichi’s industrial clusters contribute to contact and thermal injuries requiring fast treatment and specialized dressing applications. Hospitals in Shizuoka and Gifu expand burn-management capacity with wound-cleaning protocols, debridement support, and antimicrobial care. Clinics across Nagano use advanced dressing materials to handle mild and moderate burns in outpatient settings. Coastal communities in Mie report stable annual caseloads involving scald and flame injuries, increasing reliance on regional emergency units.
Tohoku grows at 4.4% CAGR, shaped by regional climate, heating-related accidents, household injuries, and reliance on public hospitals across Miyagi, Aomori, Fukushima, Akita, Iwate, and Yamagata. Colder months increase indoor heating-equipment accidents, leading to minor burns and scald injuries. Public hospitals manage moderate and severe burns requiring specialized wound-care protocols and prolonged observation. Rural communities rely on portable care solutions and outpatient clinics offering hydrogel, foam, and silicone-support dressings. Prefectural medical programs promote prevention awareness targeting elderly households. Rehabilitation services address long-term functional recovery for deeper injuries.
Rest of Japan grows at 4.2% CAGR, supported by smaller hospital networks, community-level medical centers, and consistent outpatient activity across prefectures outside major metropolitan zones. Regional hospitals manage household scalds, cooking-related contact burns, and minor flame injuries using standard wound-care protocols. Clinics provide follow-up support with modern dressings and scar-care materials for gradual healing. Elderly populations contribute to steady demand due to higher burn susceptibility. Local health services incorporate safety education into community programs. Rehabilitation facilities assist in functional recovery for moderate burns requiring longer-term care.
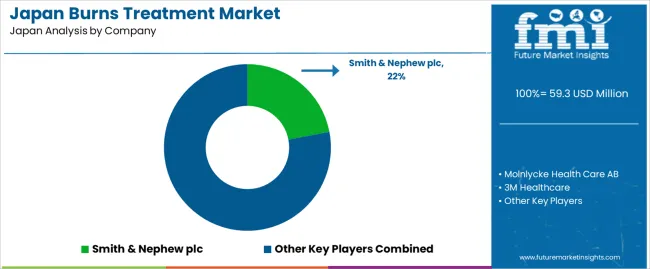
Demand for burns treatment in Japan is shaped by wound-care suppliers with established clinical channels, local regulatory approvals, and structured distribution to hospitals and specialized burn units. Smith & Nephew plc holds an estimated 22% share, supported by controlled production of silver dressings, bioactive coverings, and negative-pressure systems used widely in Japanese acute-care settings. Its products offer stable moisture management and predictable handling characteristics suited to partial- and full-thickness burns.
Mölnlycke maintains strong adoption through silicone dressings and absorbent foams designed for atraumatic removal and consistent exudate control. These materials are commonly used in Japanese burn units seeking stable adhesion and reduced discomfort during dressing changes. 3M Healthcare contributes broad utilization with antimicrobial dressings and synthetic skin-substitute technologies that provide reliable bacterial-load reduction and sustained coverage for graft sites.
Coloplast supports domestic demand with moisture-balancing dressings and flexible adhesive systems suited to sensitive burn tissue, emphasizing controlled absorption and secure placement. ConvaTec Japan K.K. adds depth through hydrofiber and antimicrobial products offering steady fluid management and compatibility with long-duration wear requirements in inpatient and outpatient care.
Competition across this segment centers on exudate control, antimicrobial effectiveness, dressing-change comfort, graft-site compatibility, and dependable supply across hospital networks. Demand remains steady as Japanese clinicians prioritize advanced wound-care materials that support controlled healing conditions, limit infection risk, and maintain stable coverage throughout varied burn-severity treatments.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Treatment Type | Wound Care Dressings, Wound Care Therapy, Medications |
| Degree of Burn | First-degree Burns, Second-degree Burns, Third-degree Burns |
| End User | Hospitals, Burn Centers, Ambulatory Surgical Centres, Outpatient Wound Clinics |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Smith & Nephew plc, Mölnlycke, 3M Healthcare, Coloplast, ConvaTec Japan K.K. |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by treatment type and burn degree; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of advanced wound care and burn management suppliers; developments in antimicrobial and bioengineered dressings, negative-pressure therapy, and biologic treatments; regulatory and reimbursement influences on product uptake; integration with hospitals, specialised burn centres, emergency and trauma services, and outpatient rehabilitation programs. |
The demand for burns treatment in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 59.3 million in 2025.
The market size for the burns treatment in japan is projected to reach USD 102.6 million by 2035.
The demand for burns treatment in japan is expected to grow at a 5.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in burns treatment in japan are wound care dressings, wound care therapy and medications.
In terms of degree of burn, first-degree burns segment is expected to command 22.5% share in the burns treatment in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan Axillary Hyperhidrosis Treatment Market Insights – Size, Share & Trends 2025-2035
Japan Biliary Tract Cancers (BTCs) Treatment Market Growth – Demand, Trends & Forecast 2025-2035
Demand for Water Treatment System in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Endometriosis Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Demand for Yeast Infection Treatment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
japan Tortilla Market - Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Japan Cosmetics ODM Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA