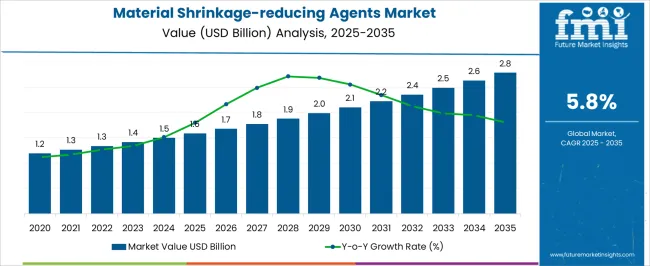
The material shrinkage reducing agents category is projected to rise from USD 1.6 billion in 2025 to USD 2.8 billion in 2035 at a CAGR of 5.8%. The market growth curve shape appears steady and compounding, with values stepping from 1.6 to 1.8, 2.0, and 2.2 before reaching 2.8. Adoption is being encouraged across concrete admixtures for crack control, slab curling mitigation, and dimensional stability in cementitious systems. Use in precast elements, flooring, tunnels, and water retaining structures is being prioritized.
The curve should be read as durable, underpinned by performance specifications that favor predictable shrinkage reduction and service life. From 2029 onward, the curve inclines at a measured pace as dosing control, field trials, and QA QC programs are embedded in ready mixed concrete and precast manufacturing. Alcohol based and polymeric chemistries are being paired with water reducers and superplasticizers to preserve workability while limiting capillary tension that drives drying shrinkage.
Procurement decisions are being guided by warranty terms, test data on shrinkage strain, and compatibility with fibers, silica fume, and supplementary cementitious materials. In an opinionated reading, growth looks grounded in specification wins and replacement cycles, not hype, with suppliers rewarded for technical service and consistent batching performance.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Material Shrinkage-reducing Agents Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 1.6 billion |
| Material Shrinkage-reducing Agents Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 2.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.8% |
The material shrinkage reducing agents segment is estimated to account for about 7% of the concrete admixtures market, roughly 5% of the construction chemicals market, close to 6% of the cement and concrete additives market, nearly 3% of the ready mix concrete market, and around 4% of the precast concrete market. Taken together, these proportions aggregate to approximately 25% across the listed parent categories. This footprint is viewed as meaningful because shrinkage reducers serve as a direct lever for controlling drying shrinkage, early age cracking, and slab curling, which drives lifecycle performance in pavements, floors, and precast elements.
Influence has been reinforced by specifications that target joint spacing, restrained shrinkage limits, and tighter crack width criteria. In practice, selection is guided by dosage efficiency, compatibility with superplasticizers, water cement ratio targets, and finishing windows, with glycol ether based and polymeric chemistries favored for predictable shrinkage strain reduction. It is argued that SRAs deliver superior value where repair risk and downtime penalties are material, such as distribution centers, cold rooms, water tanks, and architectural precast panels. Demand has been supported by ready mix producers and precasters seeking stable mixes that limit remedial work and warranty claims.
Testing protocols around ASTM and EN methods, coupled with ring tests and free drying benchmarks, have been used to validate performance and de-risk project delivery. On balance, shrinkage reducing agents should maintain a solid share within these parent markets, as contractors and owners prioritize crack control and dimensional stability to secure durable concrete outcomes.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market is witnessing consistent growth, driven by rising demand in construction and infrastructure projects requiring high durability and minimal cracking. These agents are increasingly being adopted to enhance concrete performance by reducing drying shrinkage, improving long-term structural integrity, and lowering maintenance costs. Advancements in formulation technologies are enabling the development of shrinkage-reducing agents that deliver improved workability and compatibility with various cement types and admixtures.
Growing investments in urban development, particularly in high-rise structures, industrial facilities, and transportation infrastructure, are stimulating demand for advanced concrete additives. The market is also benefiting from stricter building codes and quality standards in multiple regions, encouraging contractors and ready-mix producers to incorporate shrinkage-reducing agents for enhanced performance.
Rising awareness of lifecycle cost savings and the extended service life of concrete structures further supports adoption. As construction activity expands in both developed and emerging markets, the industry is expected to see steady growth, with manufacturers focusing on high-performance formulations and environmentally sustainable solutions to meet evolving market needs.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market is segmented by product type, chemical composites, application, end use industry, and geographic regions. By product type, material shrinkage-reducing agents market is divided into Liquid shrinkage-reducing agents, Powder shrinkage-reducing agents, and Others. In terms of chemical composites, material shrinkage-reducing agents market is classified into Polyethers, Polyalcohols, Glycols and Glycol Ethers, Surfactants, and Others. Based on application, material shrinkage-reducing agents market is segmented into Ready-mix concrete, Precast concrete, Self-consolidating concrete, High-performance concrete, Shotcrete, Mortars and grouts, and Others.
By end use industry, material shrinkage-reducing agents market is segmented into Residential construction, Commercial construction, Infrastructure development, Industrial construction, Water containment structures, and Others. Regionally, the material shrinkage-reducing agents industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
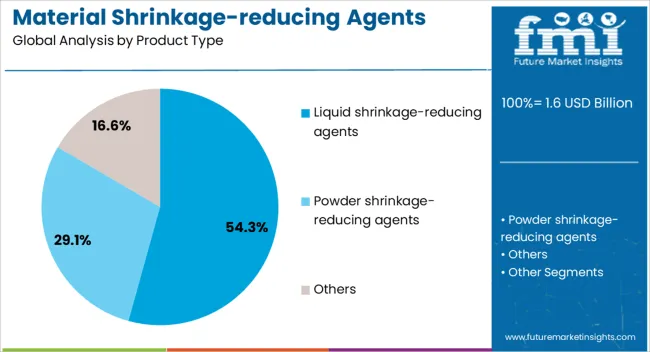
The liquid shrinkage-reducing agents segment is projected to hold 54.3% of the material shrinkage-reducing agents market revenue share in 2025, making it the dominant product type. This leadership is attributed to its ease of mixing, rapid dispersion in concrete mixtures, and compatibility with existing batching processes. Liquid formulations offer superior control over dosage accuracy, ensuring consistent performance across varying site conditions.
They are widely preferred in large-scale projects where uniformity and quality control are critical, as they enable faster integration during production without the need for specialized equipment. Enhanced efficiency in reducing capillary tension during the drying phase contributes to minimized cracking and improved structural longevity.
The segment is also benefiting from increased use in high-performance and self-compacting concrete applications, where precise admixture control is essential. As infrastructure projects grow in complexity and scale, the demand for liquid shrinkage-reducing agents is expected to remain strong, driven by their proven effectiveness, operational convenience, and ability to meet stringent construction quality standards.
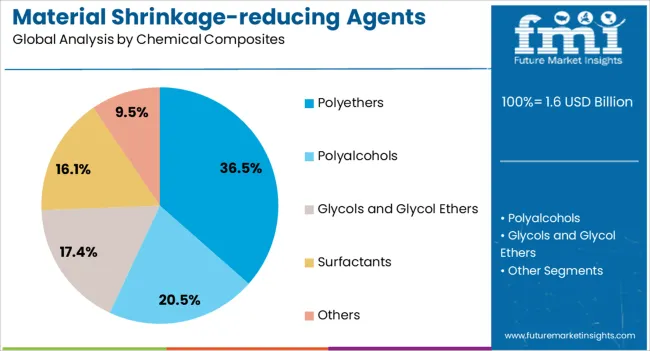
The polyethers application segment is anticipated to account for 36.5% of the material shrinkage-reducing agents market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as a key application area. Polyether-based agents are valued for their high efficiency in reducing surface tension within concrete pore solutions, effectively limiting shrinkage during the curing process. Their chemical stability ensures performance consistency across a range of environmental conditions, making them suitable for diverse geographic markets.
The segment is also benefiting from advancements in chemical synthesis, enabling the production of polyethers with enhanced dispersion properties and longer-lasting effects. Adoption is being further supported by their compatibility with a wide range of cementitious systems, including blended cements and supplementary cementitious materials.
As construction projects increasingly prioritize durability and lifecycle performance, polyether-based shrinkage-reducing agents are expected to see sustained demand. The combination of technical reliability, adaptability to modern concrete mixes, and compliance with evolving construction standards reinforces their competitive position in the market.
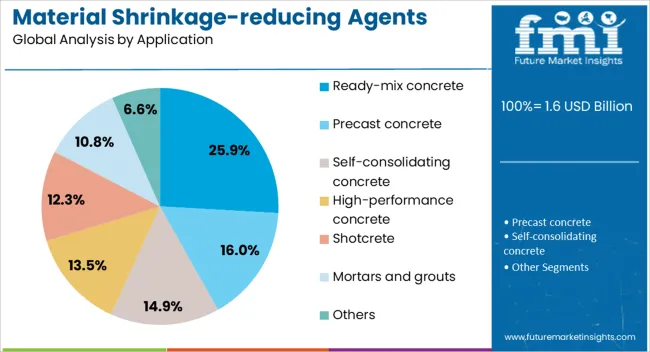
The ready-mix concrete application segment is expected to represent 25.9% of the material shrinkage-reducing agents market revenue share in 2025, establishing itself as a significant end-use category. This prominence is being driven by the increasing reliance on ready-mix solutions for large-scale infrastructure, commercial, and residential projects, where consistent quality and performance are essential.
Shrinkage-reducing agents in ready-mix concrete play a critical role in minimizing drying shrinkage, preventing surface cracking, and enhancing durability in high-stress structural applications. Their use allows concrete producers to meet stringent project specifications while optimizing production efficiency and delivery timelines.
The segment’s growth is also supported by the rising popularity of sustainable construction practices, as shrinkage-reducing agents contribute to longer service life and reduced repair needs With urbanization and industrialization continuing to expand worldwide, the demand for ready-mix concrete incorporating advanced admixtures is projected to increase, securing the segment’s role as a key contributor to the overall growth of the material shrinkage-reducing agents market.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market is projected to expand as crack control, dimensional stability, and surface flatness are prioritized across concrete and mortar applications. Demand is being reinforced by industrial floors, precast elements, and high-spec slabs where curling and microcracking must be mitigated. Opportunities are expected in data center pads, cold-joint repairs, and screeds under resilient flooring. Trends point toward polyol and glycol ether chemistries, combo packs with water reducers, and dosage guidance embedded in mix design software. Challenges remain around cost-per-cubic-meter justification, proof under variable curing, and uneven specification practices across regions.
Demand has been reinforced by industrial flooring, distribution hubs, aircraft hangars, hospitals, and parking structures where early-age drying shrinkage and restrained movement cause curling, crazing, and joint spalling. Material shrinkage-reducing agents are being specified in ready-mix concrete, site-batched mortar, and self-leveling underlayments to lower capillary tension, reduce autogenous shrinkage, and ease tensile stress development. Precast producers have favored SRAs in wall panels, façade cladding, and utility vaults because dimensional accuracy and reduced rework are prized on fast schedules. Owners of data centers and laboratories have insisted on flatter slabs that protect epoxy coatings and precision equipment, which keeps SRA adoption resilient even when cement content is optimized. In an opinionated view, SRAs should be treated as insurance against costly slab remediation. When paired with proper joint layout, fiber reinforcement, and moisture control, the additive has delivered fewer callbacks and a more predictable floor finish.
Opportunities have been opened in precast yards where differential moisture loss and thermal swings create fit-up issues at erection. SRAs are being positioned in segmental bridges, metro tunnel segments, and architectural precast to limit edge cracking and maintain tight tolerances. Flooring contractors have specified SRAs in pumpable screeds beneath vinyl, rubber, and wood because moisture-related debonding risk is lowered. Repair mortars and grouts used on cold joints, patching, and anchor bedding have benefited from reduced shrinkage, which protects bond lines around dowels and post-installed bars. Packaging with superplasticizers, internal curing agents, and shrinkage-compensating admixtures has created tailored mixes for high-performance concrete and self-consolidating concrete. In our opinion, the most profitable route lies in turnkey specifications that bundle mix design support, on-site slump and temperature checks, and ASTM-compliant ring tests, allowing contractors to defend budgets with measurable crack width outcomes.
Trends have centered on low-odor polyol systems and glycol ether blends tuned for water-cement ratio ranges common in ready-mix and precast plants. Hybrid packages that combine SRA with mid-range water reducers or set controllers are being adopted to keep workability while controlling shrinkage. Mix design software and e-ticketing platforms are starting to include SRA dosage libraries linked to ambient temperature, relative humidity, and target drying shrinkage values per ASTM C157. Contractors have preferred compatibility with silica fume, slag cement, and limestone cements to avoid segregation or finishing issues. Field verification via ring tests, slab-on-grade mockups, and embedded strain gauges is trending to validate expected shrinkage strain reduction. From an opinionated perspective, practical wins are delivered by clear finishing guidance, joint spacing recommendations, and curing plans that match the chemistry, rather than by headline shrinkage reduction claims printed on data sheets.
Challenges are posed by cost justification where SRA pricing must compete with thicker slabs, tighter joint spacing, or extra reinforcement as alternative crack mitigation paths. Dosage sensitivity has created variability when water addition, temperature swings, or aggressive finishing disrupt expected performance. Standards alignment remains uneven, with specifications referencing assorted test methods for drying shrinkage, restrained ring behavior, and surface curling that do not always correlate. Compatibility concerns with air entrainment, calcium chloride exposure, or colored architectural mixes have slowed approvals. Supply chain constraints for select glycols and specialty polyols have been noted by admixture blenders. In our view, credible success depends on preconstruction trials, moisture control during curing, and transparent life-cycle cost models that quantify reduced callbacks. Without disciplined field practices and clear submittals, the market will continue to face pushback from value engineering and lowest-bid procurement.
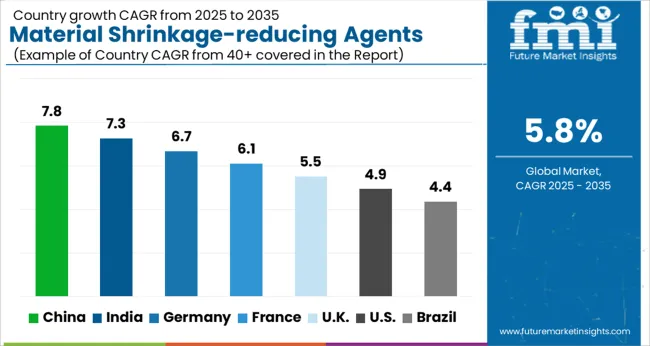
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.8% |
| India | 7.3% |
| Germany | 6.7% |
| France | 6.1% |
| UK | 5.5% |
| USA | 4.9% |
| Brazil | 4.4% |
The global material shrinkage-reducing agents market is projected to grow at 5.8% from 2025 to 2035. China leads at 7.8%, followed by India 7.3% and France 6.1%; the United Kingdom 5.5% and United States 4.9% follow. Demand is being pulled by ready-mix concrete, precast elements, polished floors, and joint-controlled industrial slabs where drying shrinkage and crack width limits are scrutinized. Polyether and glycol-ether SRAs, often paired with shrinkage-compensating blends, are being specified to stabilize dimensional change, improve flatness, and protect floor coverings. Europe favors tight conformance with EN test methods and low-VOC profiles, while Asia emphasizes cost-effective dosing and broad contractor training. The USA market advances steadily through spec-driven adoption in data centers, distribution hubs, healthcare, and education projects seeking predictable slab behavior and reduced remedial work. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top markets are shown here for reference.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market in China is expected to expand at 7.8%. Growth is being supported by large logistics floors, high-bay warehouses, and expansive precast operations that demand controlled drying shrinkage and reliable joint spacing. Domestic construction-chemical producers have scaled polyether-based SRA portfolios, while hybrid dosing with shrinkage-compensating admixtures is being adopted for thick sections and long-bay slabs. Ready-mix networks are standardizing QC around GB/ASTM/EN references, with slab flatness, curling, and crack maps used as field benchmarks. Architectural concrete for façades and public works is benefiting from improved surface integrity and reduced crazing under aggressive curing regimes. In our view, pricing leverage from local raw materials and broad contractor education will keep China in a leadership position across industrial, municipal, and commercial footprints where dimensional stability is prioritized.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market in India is projected to grow at 7.3%. Uptake is being driven by industrial parks, metro depots, data-center slabs, and healthcare facilities where crack-width limits and floor flatness targets are enforced. Local blenders are extending SRA lines compatible with PCE water-reducers to maintain workability at low w/c ratios. Moisture-sensitive floor coverings in malls and offices are pushing SRAs into toppings and self-leveling underlayments, cutting post-installation claims. Contractors are adopting mock-up slabs to calibrate curing, saw-cut timing, and SRA dosage, improving predictability under varying site conditions. With state-led infrastructure and private warehousing in expansion mode, steady migration toward spec-based admixture packages is expected to anchor demand through the forecast window.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market in France is anticipated to rise at 6.1%. Demand is being shaped by premium architectural concrete, precast façades, and renovation of civic buildings where dimensional stability and surface appearance are scrutinized. Broader use of blended cements (CEM II/CEM III) is influencing shrinkage profiles, prompting specifiers to adopt SRAs to balance drying behavior without raising water content. CE-marked admixtures with documented EN 12617-4 results, low odor, and tight VOC profiles are being prioritized. Flooring contractors report fewer callbacks on curling and tile debonding when SRAs are paired with disciplined curing and moisture testing. In our assessment, France will continue to emphasize compliant, high-performance admixture systems that protect aesthetics and reduce remedial grinding or injection work across public and commercial programs.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market in the UK is forecast to expand at 5.5%. Growth is centered on distribution sheds, healthcare refurbishments, and education projects guided by TR34, BS 8204, and client-issued crack-width criteria. SRAs are being embedded in mixes for joint-controlled slabs, polished concrete, and toppings under resilient floor finishes. Import-led supply is common, though distributors are holding more project-specific stock to hedge weather and pour sequencing. Specifiers favor SRA packages that maintain finishability at low w/c while limiting drying curl and restraint-induced cracking. With framework agreements and repeatable mix designs, adoption is likely to progress steadily as contractors pursue predictable slab behavior and reduced snag lists at practical completion.

The material shrinkage-reducing agents market in the United States is expected to grow at 4.9%. Adoption is being led by data-center pads, big-box distribution, hospitals, and higher-education buildings where ACI guidance on slab-on-ground and crack control is closely followed. SRAs are being combined with internal-curing fines, optimized aggregates, and PCE water-reducers to hold shrinkage while preserving set time and finish. Polished-concrete programs report improved joint performance and reduced curling where SRAs are specified with disciplined curing. Owners are seeking fewer callbacks from tile and resilient floor failures, making SRAs attractive in underlayments and toppings. With spec-driven procurement and strong installer know-how, a measured but durable trajectory is indicated as project teams trade small admixture premiums for lower remedial costs and tighter schedules.
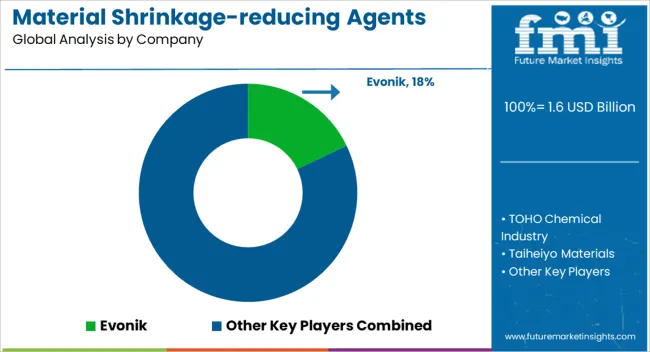
Competition in material shrinkage-reducing agents has been shaped by brochures that turn mix design risk into clear, line-item assurances. Evonik, Sika Group, GCP Applied Technologies, and MasterLife position liquid SRAs that target drying and autogenous shrinkage with dosage windows near 0.5 to 1.5% by weight of cement. Claims focus on crack width moderation, slab curling control, and joint spacing confidence. Data sheets foreground ASTM C157 reductions, often presented as up to double-digit % improvements at equal water-cement ratio. Compatibility with polycarboxylate superplasticizers is stated plainly, with notes on air content and set time drift. Precast and slab-on-ground use cases are separated, with distinct tables for early strength retention and finishability. Brochures from TOHO Chemical Industry and Taiheiyo Materials emphasize cement-friendly chemistries and low-odor handling for plants with enclosed batching. NOF America highlights polyalkylene-glycol backbones and stable performance in mixes rich in slag or fly ash. Aezis and Belith compete through powder SRAs for dry-mix mortars, where storage stability and easy dosing win attention.
Strategy has rested on documentation density, not slogan work. Leading brochures show side-by-side mixes with shrinkage strain curves, 7 and 28 day strengths, and joint layout guidance tied to measured % reduction. Crack risk calculators appear with inputs for slab thickness, restraint, and temperature swing. Service notes cover pump pressure, retempering tolerance, and finish timing so crews do not chase surprises. Field sheets cite saw-cut timing and curing practice to keep gains banked.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 1.6 Billion |
| Product Type | Liquid shrinkage-reducing agents, Powder shrinkage-reducing agents, and Others |
| Chemical Composites | Polyethers, Polyalcohols, Glycols and Glycol Ethers, Surfactants, and Others |
| Application | Ready-mix concrete, Precast concrete, Self-consolidating concrete, High-performance concrete, Shotcrete, Mortars and grouts, and Others |
| End Use Industry | Residential construction, Commercial construction, Infrastructure development, Industrial construction, Water containment structures, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Evonik, TOHO Chemical Industry, Taiheiyo Materials, Sika Group, Aezis, NOF America, Belith, GCP Applied Technologies, and MasterLife |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by chemistry type (glycol ether, polycarboxylate, polymeric blends), Dollar sales by application (ready mix, precast, grouts, screeds), Dollar sales by form (liquid, powder), Trends in shrinkage control for high strength and mass concrete, Role in mitigating autogenous and drying shrinkage and cracking, Regional usage across Asia Pacific, Europe, North America. |
The global material shrinkage-reducing agents market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the material shrinkage-reducing agents market is projected to reach USD 2.8 billion by 2035.
The material shrinkage-reducing agents market is expected to grow at a 5.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in material shrinkage-reducing agents market are liquid shrinkage-reducing agents, powder shrinkage-reducing agents and others.
In terms of chemical composites, polyethers segment to command 36.5% share in the material shrinkage-reducing agents market in 2025.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Material Rack Correction Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Material Handling Integration Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Material-Based Hydrogen Energy Storage Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Material Tester Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Material Handling Equipment Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Material Handling Monorails Market
Biomaterial Tester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biomaterial In Surgical Mesh Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Biomaterial Market Analysis – Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Metamaterial Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
PET Material Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Metamaterial Absorbers Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanomaterial Supercapacitors Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Nanomaterials Market Insights - Size, Share & Industry Growth 2025 to 2035
Competitive Overview of PET Material Packaging Market Share
Tire Materials Market Insights – Size, Trends & Forecast 2025–2035
Mono-material Packaging Market Analysis: Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Case Material Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Mono Material Pump Market Analysis - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Bulk Material Handling System Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA