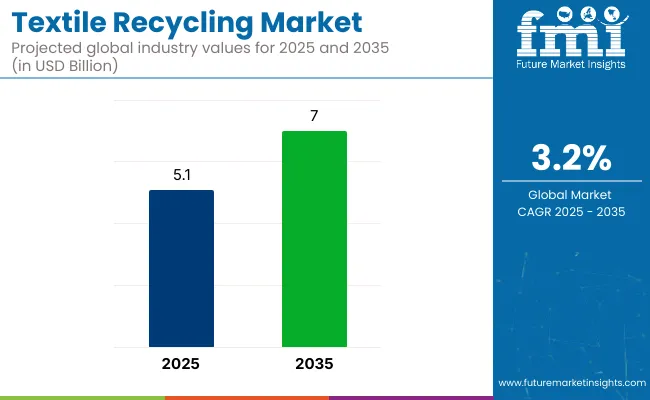
The global textile recycling market is projected to grow from approximately USD 5.1 billion in 2025 to USD 7.0 billion by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.2% over the forecast period.
Growth is being driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues, expanding regulatory frameworks around waste management, and rising demand for circular economy models in the fashion and textile industries.
Market momentum has been influenced by the implementation of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs and mandatory textile waste collection initiatives in several European and North American countries. These policies have placed greater accountability on manufacturers and brands to manage the full lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life processing.
As a result, many global apparel companies have begun incorporating higher volumes of post-consumer and post-industrial recycled fibers into their product lines to meet compliance targets and consumer expectations.
Recycling technologies have continued to evolve. Mechanical recycling methods have become more refined, allowing for greater retention of fiber integrity during processing. In parallel, chemical recycling techniques for synthetic textiles, particularly polyester and blended fibers, have progressed through pilot and early commercial phases.
Companies such as Renewcell and Infinited Fiber Company have advanced chemical processes for cellulose regeneration, enabling the conversion of worn textiles into high-quality inputs suitable for mainstream apparel production.
Despite technological progress, several challenges persist. High operating costs, inconsistent quality of collected textile waste, and a lack of regionally distributed recycling infrastructure continue to limit scale. In emerging markets, informal waste collection systems dominate, which restricts traceability and contaminant control.
However, partnerships between fashion brands and waste management providers are emerging to streamline textile recovery and improve material sorting.
Investment in automated sorting systems, AI-based material recognition, and closed-loop production models is expected to increase as pressure builds on brands to meet sustainability commitments. Fashion retailers are also launching take-back schemes and incentivized collection programs to boost raw material supply for recycling.
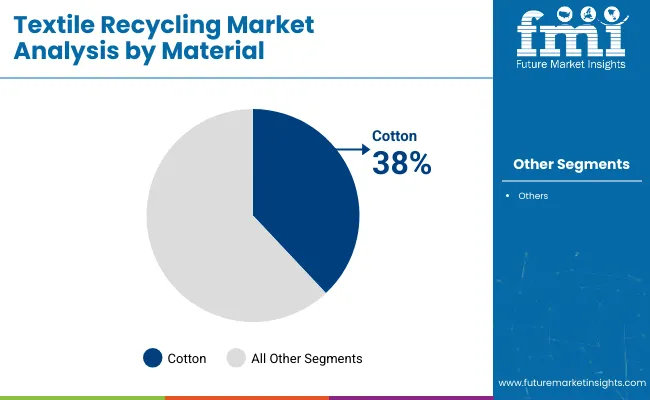
Cotton is projected to account for approximately 38% of the global textile recycling market share in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.1% through 2035. Cotton waste is generated in high volumes from post-consumer garments and pre-consumer cutting scraps. It is commonly recycled into insulation, wiping cloths, yarns, and nonwoven fabrics.
While fiber length degradation during mechanical recycling remains a challenge, advancements in chemical recycling and fiber regeneration technologies are enhancing recovery efficiency. The rise of sustainable fashion and increasing brand commitments to circular textile programs are expected to sustain cotton’s relevance in recycled textile value chains.
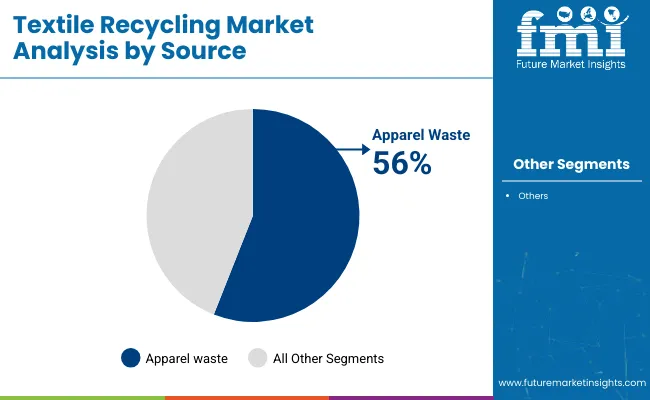
The apparel waste segment is estimated to hold approximately 56% of the global textile recycling market share in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.3% through 2035. This category includes post-consumer clothing, manufacturing offcuts, and unsold inventory diverted from landfill or incineration. Rising volumes of fast fashion, coupled with low garment utilization rates, have made apparel a significant contributor to textile waste. Governments and industry coalitions are launching take-back programs and extended producer responsibility (EPR) frameworks to improve collection and recovery rates.
As awareness of environmental impacts increases and recycling infrastructure improves, apparel waste is expected to remain a consistent input stream for textile recyclers globally.
The textile recycling industry in the United States is expected to grow steadily due to increasing awareness of sustainability and government initiatives promoting circular economy practices. However, the country faces challenges such as high operational costs and a fragmented recycling infrastructure.
The demand for recycled textiles is rising, especially in the fashion and home furnishing sectors, driven by corporate sustainability goals. Investments in advanced sorting and processing technologies will help improve efficiency in the coming years.
FMI opines that the United States textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.8% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.29 billion by 2035.
The UK textile recycling industry is projected to witness moderate growth, supported by strong government policies and consumer preference for eco-friendly products. The rising demand for sustainable fashion, combined with stricter waste management regulations, will drive industry expansion.
Additionally, collaborations between fashion brands and recycling firms are expected to enhance the adoption of recycled fibers. Challenges such as inconsistent waste collection systems still exist but are being addressed through technological advancements.
FMI opines that the United Kingdom textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.9% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.26 billion by 2035.
Germany is expected to have one of the highest growth rates in the textile recycling industry due to its well-established waste management infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. The country is a leader in circular economy initiatives, with strong support from both the government and private sector.
The adoption of advanced chemical recycling methods and AI-based textile sorting systems is further driving industry growth. Germany's high recycling rates and strong corporate commitments to sustainability will continue to drive industry growth.
FMI opines that Germany’s textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.5% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and are expected to reach USD 0.96 billion by 2035.
France is making significant progress in textile recycling, backed by stringent sustainability policies and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs. The country has banned the destruction of unsold textiles, pushing brands to invest in recycling solutions. Increased funding for textile waste management and innovative fiber recovery techniques will boost industry growth. Increasing consumer awareness is further driving demand for recycled and upcycled clothing.
FMI opines that the France textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.4% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.80 billion by 2035.
Italy’s textile recycling industry is benefiting from the country’s strong fashion and textile industries, which are increasingly embracing sustainability. Luxury and fast fashion brands are incorporating recycled materials into their production processes, while government initiatives are encouraging the development of circular economy models. However, Challenges such as a fragmented recycling infrastructure and high costs remain, which necessitates increased investment in technology and logistics by industry stakeholders.
FMI opines that the Italy textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.1% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.66 billion by 2035.
Australia and New Zealand are witnessing a gradual shift towards textile recycling, driven by government regulations and consumer demand for sustainable fashion. Both countries are investing in textile recovery programs and partnerships between fashion brands and recycling firms. However, logistical challenges due to their geographic location and lack of large-scale infrastructure may limit growth. Increased innovation in fiber recycling technologies is expected to improve industry prospects.
FMI opines that the Australia & New Zealand textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.7% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.32 billion by 2035.
China is emerging as a major player in the textile recycling Industry, supported by strong government policies aimed at reducing textile waste. The country’s vast manufacturing sector is integrating recycled materials into production, and advanced recycling technologies are being rapidly adopted.
Additionally, growing environmental awareness among consumers and stricter waste management regulations are accelerating Industry growth. Despite challenges like illegal textile waste dumping, increased investments in sustainable practices are expected to drive significant progress.
FMI opines that the China textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.8% a CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.49 billion by 2035.
South Korea’s textile recycling Industry is expanding as the country implements stricter sustainability regulations and promotes circular economy initiatives. Advanced textile processing technologies and AI-driven waste sorting systems are enhancing recycling efficiency.
Additionally, fashion brands are increasingly using recycled fibers, supported by government incentives. One of the key challenges is the high cost of textile collection and processing. Continued investment in research and development will be crucial for industry expansion.
FMI opines that South Korea's textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.37 billion by 2035.
Japan’s textile recycling industry is progressing steadily, driven by strong environmental consciousness and government-led sustainability initiatives. The country has a well-developed recycling infrastructure, but the adoption of textile recycling in mainstream fashion remains slow.
Traditional waste disposal methods still dominate, limiting the growth of textile recycling in Japan. However, rising interest in circular fashion and new developments in fiber-to-fiber recycling technology could help accelerate industry adoption in the long run.
FMI opines that the Japanese textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.9% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.28 billion by 2035.
The textile recycling market in India is well-positioned to grow significantly, fueled by increasing awareness of sustainability. India has prioritized circular economy and waste management initiatives due to the substantial amount of textile waste it generates annually from both domestic consumption and export production. With the government encouraging EPR in textiles and organized collection of textile waste systems, the market is witnessing substantial progress.
Finally, the development and acceleration of new fiber-to-fiber recycling technologies, particularly for cotton and polyester, are underway. Several startups and established players are working on mechanical and chemical recycling processes to transform textile waste into reusable fiber. Despite these challenges, collaborations between fashion brands, recyclers, and policymakers are helping steer the industry back on course.
FMI opines that the Indian textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 4.0% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.53 billion by 2035.
The industry is concentrating on expanding fiber recovery and promoting circularity in textile production. Substantial investments are being directed toward innovative recycling technologies, including wet spinning and chemical regeneration, to convert pre- and post-consumer textile waste into reusable fibers.
Efforts are underway to industrialize textile-to-textile recycling, especially for complex fabrics like polyester-cotton blends. Additionally, there is growing demand for traceable recycled textiles, prompting brands to introduce products that provide verified sustainability credentials.
Textile recycling helps reduce landfill waste, conserves natural resources, lowers carbon emissions, and supports a circular economy by reusing materials for new products.
Commonly recycled materials include cotton, polyester, wool, polyamide, and blended fabrics. Advanced technologies also enable the recycling of synthetic fibers.
Challenges include high processing costs, contamination of materials, limited infrastructure, and difficulties in sorting blended fabrics for efficient recycling.
Mechanical recycling shreds and reprocesses textiles without altering their structure, while chemical recycling breaks fibers down into raw materials for higher-quality reuse.
Industries such as fashion, home furnishings, automotive, and sportswear benefit from textile recycling by incorporating sustainable materials into their products.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Textile Waste Recycling Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Textile Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Textile Machine Lubricants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Textile Based pH Controllers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Textile Transfer Paper Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Textile Colorant Market – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Textile Flooring Market Trends & Growth 2025 to 2035
Textile Tester Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Textile Colors Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Textile Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) Market Insights - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Textile Staples Market Size & Trends 2025 to 2035
Textile Auxiliaries Market Trends 2024-2034
Textile Printing Ink Market
Geotextile Tube Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
Agri Textiles Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Asia Textile Chemicals Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Agro textiles Market
Carbon Textile Reinforced Concrete Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Ceramic Textile Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Digital Textile Printing Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA