The AI-based driving systems (L2 to L5) market is valued at USD 2.35 billion in 2025 and will advance to nearly USD 8.7 billion by 2035, recording a CAGR of 14% with a multiplying factor of about 3.7x.
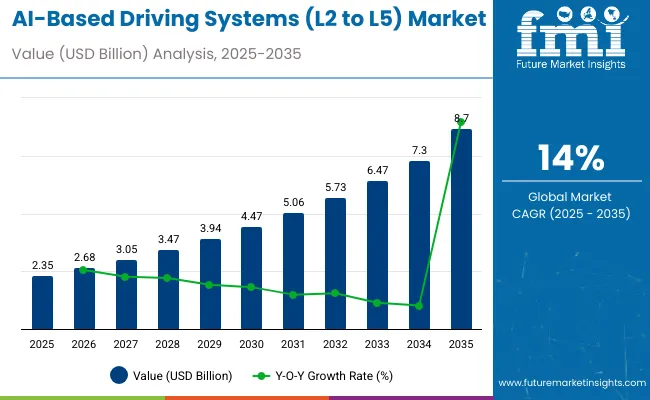
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 2.35 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 8.7 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14% |
Examining the growth rate volatility index reveals that market expansion is not uniform across the forecast horizon. Early years, from 2025 to 2028, reflect stronger growth momentum as pilot programs and premium vehicle integration accelerate adoption in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. Higher penetration of L2 and L3 systems contributes to a more stable trajectory during this phase, with demand closely tied to regulatory approvals and consumer readiness.
Between 2028 and 2032, volatility becomes more pronounced as scaling of L4 systems encounters infrastructure challenges, regional policy differences, and uneven consumer acceptance. Growth may decelerate temporarily in certain regions while others advance more quickly, leading to fluctuations in the index. Toward 2033 to 2035, volatility stabilizes again as regulatory clarity, cost reduction in sensors and processors, and higher fleet integration drive broader adoption across passenger and commercial vehicles. The analysis highlights that while long-term growth remains strong, manufacturers must prepare for short-term fluctuations and align strategies to manage cyclical shifts in adoption pace.
The AI-based driving systems market, covering levels 2 through 5, is supported by several upstream industries. Automotive OEMs represent around 34%, as integration of driver assistance and autonomous stacks is becoming a standard feature in new vehicles. Semiconductor and sensor suppliers contribute approximately 26%, providing lidar, radar, cameras, and dedicated AI processors. Software and algorithm developers account for about 21%, driving perception, decision-making, and control systems. Connectivity and telecom services hold close to 11%, enabling V2X communication, over-the-air updates, and fleet coordination. Aftermarket, validation, and service providers make up the remaining 8%, covering retrofits, simulation, and compliance testing.
The AI-based driving systems market is transitioning from pilot projects toward commercial deployment. Level 2 and 2+ systems remain dominant, with adoption surpassing 50% of new premium vehicles in 2024, while Level 3 functionality is gradually entering luxury and fleet segments. Hardware costs are declining, with lidar module prices dropping by nearly 20% year-on-year, accelerating wider integration. Investment in AI software is expanding steadily, with simulation platforms reducing validation costs by up to 30% for OEMs. Partnerships between automakers, sensor manufacturers, and cloud providers are strengthening, supporting scalable solutions for urban mobility. Level 4 testing fleets continue to expand, setting the groundwork for eventual large-scale commercialization.
Market expansion is supported by rising integration of advanced driver assistance systems, connected vehicle platforms, and demand for autonomous technologies across passenger and commercial vehicles. Level 2 systems currently dominate with more than 65% share, while Level 3 adoption is expanding in premium vehicles. Level 4 and Level 5 deployment is expected to grow steadily after 2030 as infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and sensor technologies mature. North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific represent the largest markets with ongoing pilot programs, consumer adoption, and heavy investment in automotive AI platforms.
AI based driving systems are gaining momentum due to their ability to reduce road accidents and enhance driving convenience. Level 2 solutions such as adaptive cruise control and lane keeping assistance are already common in mid to high range passenger vehicles. Level 3 technologies enable conditional automation, reducing driver workload by automating highway driving and traffic congestion handling. These systems enhance safety by minimizing human error which accounts for nearly 90% of road accidents. Growing demand for automated logistics fleets and premium passenger cars is accelerating adoption. In my view, AI powered driving systems are no longer just a luxury feature, they are becoming a core requirement in vehicle safety and performance.
Opportunities are emerging as Level 3 systems gain regulatory approval in several markets and begin commercial rollout. Automakers are integrating conditional automation into high-end passenger vehicles, setting the stage for mass adoption by 2030. Level 4 solutions for urban shuttles, robo taxis, and commercial delivery vehicles are attracting investment, particularly in North America and Asia. Development of AI driven decision making, real time mapping, and sensor fusion is strengthening the potential of these systems. From my perspective, the aftermarket services, software updates, and subscription based autonomous features will become an additional revenue stream for automakers and technology providers, expanding profitability.
AI based driving systems are converging with connected mobility platforms to enable vehicle to everything communication. This integration allows predictive decision making by linking cars with traffic signals, road infrastructure, and other vehicles. Cloud enabled AI algorithms continuously update driving models, improving accuracy and safety. Automakers are focusing on building AI chipsets, sensor fusion algorithms, and over the air software update capabilities to strengthen autonomous driving. In my opinion, vehicles equipped with AI and connectivity will redefine transport efficiency, reduce congestion, and enable new services such as shared autonomous fleets and urban mobility platforms.
Despite strong growth potential, deployment of Level 4 and Level 5 systems is constrained by inadequate infrastructure, high system costs, and regulatory complexity. Advanced sensors such as lidar and high performance AI processors significantly raise vehicle costs, limiting adoption to premium segments. Road infrastructure in emerging markets is often insufficient to support fully autonomous driving, delaying rollout timelines. Cybersecurity risks related to connected AI systems also present a significant challenge. In my assessment, manufacturers and policymakers must work together to lower costs, standardize regulations, and develop smart infrastructure. Without coordinated action, widespread adoption of high level AI driving systems will face delays.
The AI-Based Driving Systems Market in 2025 is shaped by automation levels from L2 to L5, integration of advanced sensors, and adoption across passenger and commercial fleets. Level 2 systems hold the largest share at 40%, followed by Level 3 at 28% and Level 4 at 20%. Software drives 34% of the component segment, while sensors represent 27%. Passenger vehicles dominate with 46% share, followed by commercial vehicles at 32%. BEVs lead propulsion with 38%, while OEMs account for 36% of end-user demand. Companies including Tesla, NVIDIA, Waymo, BMW, Mobileye, and Cruise are actively shaping deployment strategies. Growth is powered by data-driven algorithms, sensor fusion, and demand for safer, more efficient driving systems.
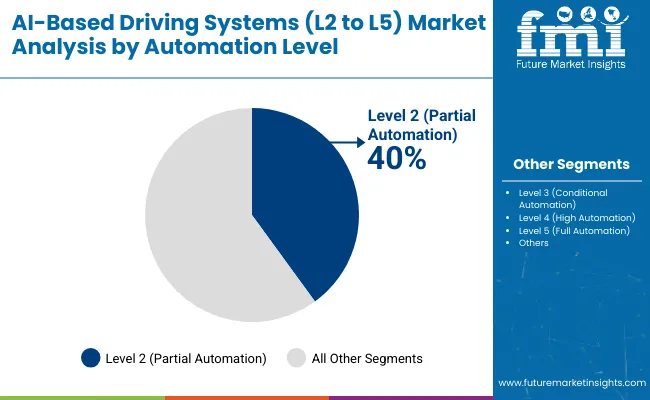
Level 2 systems dominate automation with 40% share, providing partial assistance features such as adaptive cruise control, lane keeping, and automated braking. Level 3 holds 28%, where conditional automation enables drivers to disengage under specific conditions, with brands like Mercedes-Benz, Audi, and Honda leading development. Level 4 systems contribute 20%, allowing high automation in geo-fenced zones, largely tested by Waymo and Cruise in robo-taxi programs. Level 5 accounts for 12%, targeting full automation with no human intervention, still in pilot phases by Tesla, Baidu Apollo, and AutoX. Market adoption progresses gradually from assisted driving to full autonomy, supported by advances in AI hardware, regulatory adaptation, and infrastructure readiness.
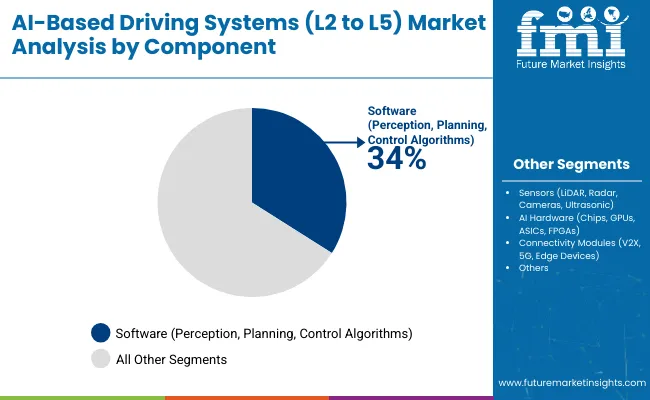
Software dominates components with 34% share, covering perception, motion planning, and control algorithms. Tesla, NVIDIA, and Mobileye provide leading AI-driven software stacks. Sensors account for 27%, including LiDAR from Velodyne, radar from Continental, and cameras from Sony. AI hardware contributes 24%, with NVIDIA GPUs, Intel Mobileye chips, and Tesla Dojo processors driving real-time decision-making. Connectivity modules such as V2X, 5G, and edge devices hold 15%, enabling data exchange for cooperative driving. OEMs and startups integrate these components to achieve scalable automation. Demand for software-defined vehicles and sensor redundancy ensures reliability, while hardware accelerates training and inference efficiency in autonomous platforms.
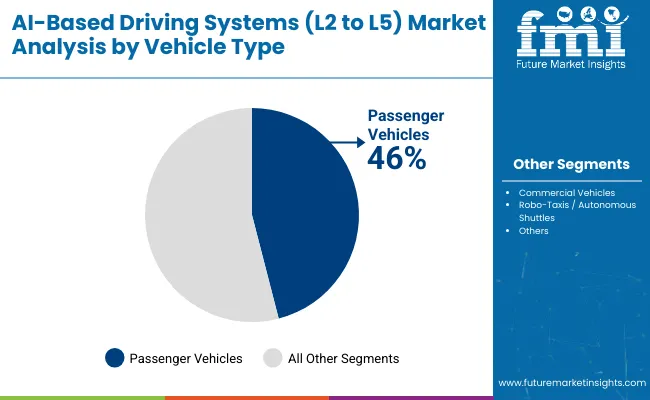
Passenger vehicles dominate vehicle type with 46% share, integrating Level 2 and Level 3 systems for safety and comfort. Commercial vehicles account for 32%, with OEMs such as Volvo, Daimler, and PACCAR testing AI-based systems for freight and logistics. Robo-taxis and autonomous shuttles contribute 22%, driven by Waymo, Cruise, and AutoX in urban deployment zones. Passenger adoption is boosted by consumer demand for driver assistance, while commercial fleets leverage autonomy for fuel savings and efficiency. Robo-taxis remain concentrated in pilot projects, gaining traction in Asia and North America. Vehicle type segmentation reflects diverse automation use cases, from everyday commuting to freight logistics and shared urban mobility.
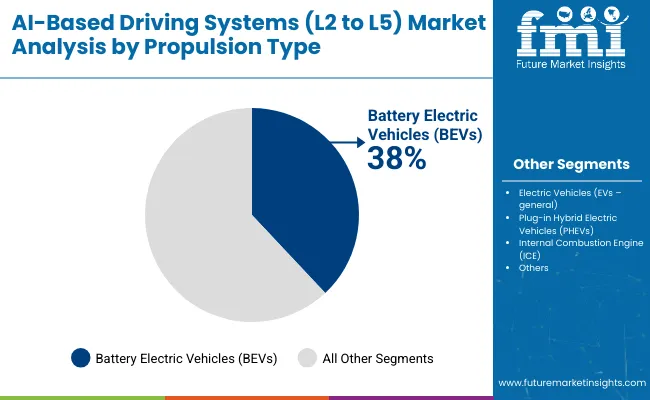
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) lead propulsion with 38% share, integrating AI-based driving systems due to higher computing compatibility and energy-efficient platforms. General Electric Vehicles (EVs) hold 25%, followed by Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) at 20%, combining fuel flexibility with automation. ICE-based vehicles still account for 17%, mainly in transitional markets. Tesla, BYD, and NIO dominate BEV-based autonomous trials, while Toyota and Hyundai deploy PHEV variants. OEMs prioritize BEV platforms for AI driving due to scalable battery systems, reduced vibrations, and digital integration. Propulsion alignment determines AI efficiency, energy consumption, and adaptability to different road networks and regulatory environments.
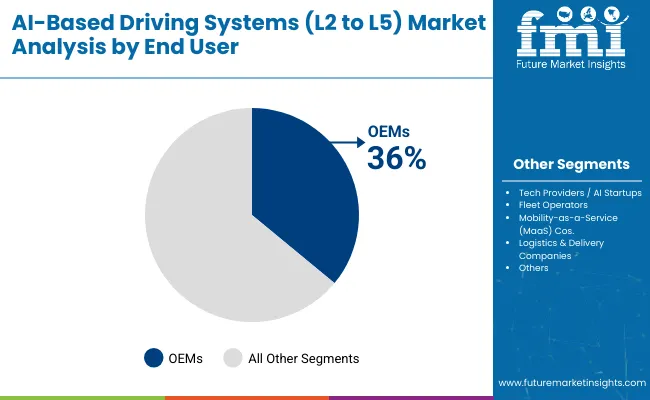
OEMs lead end-user adoption with 36% share, integrating AI systems directly into vehicle production, led by Tesla, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz. Tech providers and AI startups account for 26%, including NVIDIA, Mobileye, and Aurora, supplying software and hardware solutions. Fleet operators contribute 18%, with logistics companies adopting AI-driven trucks for freight optimization. Mobility-as-a-Service companies hold 12%, offering shared autonomous rides in urban zones, while logistics and delivery companies represent 8%, piloting AI vans for last-mile delivery. End-user segmentation highlights collaboration between traditional automakers and tech startups. Value creation is shaped by partnerships, fleet scaling, and AI-driven mobility services.
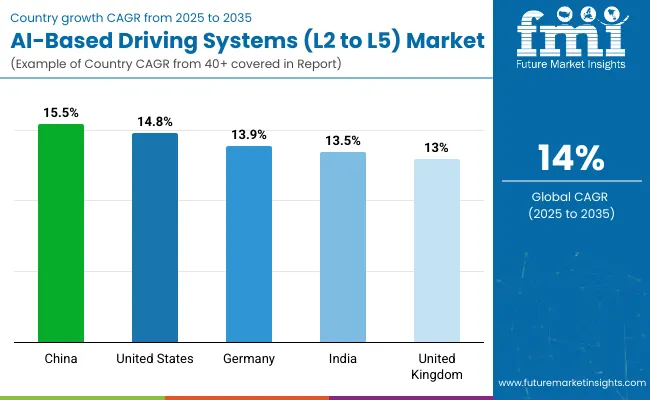
In 2025, the global AI-based driving systems (L2 to L5) market is growing at a CAGR of 14.0% through 2035. China leads at 15.5%, +11% above the global rate, supported by BRICS-driven adoption of autonomous technologies, large-scale testing programs, and government incentives for intelligent mobility. The United States follows at 14.8%, +6% higher than the global average, reflecting OECD-backed advancements in automotive software, sensor integration, and regulatory frameworks for autonomous vehicles. Germany records 13.9%, just below the global benchmark, influenced by strong engineering expertise and integration of AI in premium automotive manufacturing. India posts 13.5%, −4% under the global rate, with growth shaped by BRICS-linked demand and expanding pilot programs in urban mobility. The United Kingdom stands at 13.0%, −7% below the global level, reflecting steady but slower adoption in a mature OECD market. Together, BRICS economies fuel volume growth, while OECD nations emphasize precision, regulation, and safety-driven innovation.
China’s AI-based driving systems market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 15.5%, above the global average of 14.0%. Growth is being accelerated by aggressive adoption of Level 3 and Level 4 technologies in passenger and commercial fleets. Major players such as Baidu Apollo and Pony.ai are testing robo-taxis across urban hubs, while Huawei and BYD integrate AI-based autonomous functions into premium electric vehicles. Strong investments in AI training datasets and real-time vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication are strengthening China’s position in autonomous driving innovation.
The United States market for AI-based driving systems is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.8%, reflecting strong adoption in passenger cars and logistics fleets. Waymo, Cruise, and Tesla remain at the forefront of commercializing Level 3 and higher automation. Partnerships between tech companies and OEMs accelerate system integration, particularly in electric and hybrid platforms. Regulatory progress in California, Texas, and Arizona has created test environments for autonomous ride-hailing services, while demand for driver-assist technologies in freight fleets continues to expand.
Germany is anticipated to register a CAGR of 13.9% in the AI-based driving systems market, supported by strong OEM integration and regulatory frameworks. BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen are embedding Level 3 automation in high-end models, with Bosch and Continental supplying advanced sensor suites. The Autobahn Act already allows conditional autonomous driving on select highways, fostering faster rollouts of Level 3 capabilities. Investments in AI-driven decision-making systems for complex driving scenarios position Germany as a leading European test bed for higher automation.
India’s market for AI-based driving systems is expected to expand at a CAGR of 13.5%. While infrastructure readiness remains a barrier, OEMs such as Tata Motors and Mahindra are gradually introducing Level 2+ features in passenger vehicles. Collaborations with AI software providers support adaptive cruise control, blind spot detection, and emergency braking functions. Adoption is higher in premium vehicles, but cost-effective adaptations are emerging in mass-market models. The ecosystem is strengthened by Bengaluru and Hyderabad’s role as software development hubs.
The United Kingdom is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 13.0% in AI-based driving systems, with London and Oxfordshire acting as autonomous driving test corridors. Companies like Oxbotica and FiveAI are advancing Level 4 development, while Jaguar Land Rover integrates advanced driver-assist features in its portfolio. Government funding initiatives support AI testing in logistics and ride-hailing, while infrastructure investments promote sensor-rich road environments. The market is characterized by gradual consumer adoption in premium models and ongoing pilot projects for shared autonomous mobility.
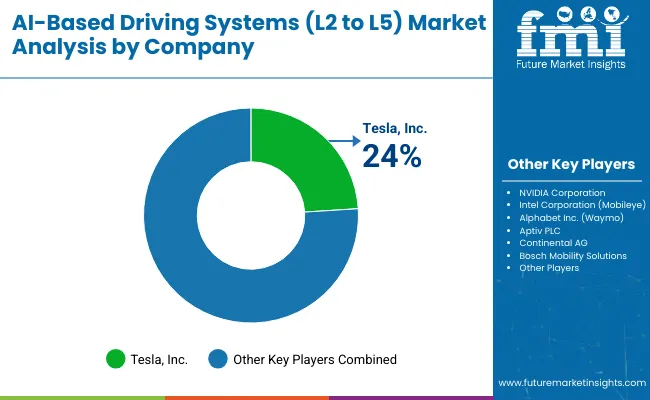
The AI-based driving systems market spanning Levels 2 to 5 is led by major technology firms and automotive manufacturers that are building advanced driver-assistance and autonomous driving solutions. Tesla, Inc. stands as the top player, benefiting from large-scale deployment of its Autopilot and Full Self-Driving systems. Its edge comes from continuous over-the-air updates, real-world fleet data, and powerful AI-driven software integration. NVIDIA Corporation and Intel Corporation (Mobileye) provide critical computing hardware and vision-based platforms, serving as the backbone for numerous OEM autonomous programs. Alphabet Inc. (Waymo) drives progress with robotaxi fleets and long-term testing, while Aptiv PLC partners with automakers to scale semi-autonomous driving features.
Complementing these leaders, system integrators and startups are accelerating innovation. Bosch Mobility Solutions, Continental AG, and ZF Friedrichshafen AG supply sensors, processors, and integration expertise. Autonomous-focused firms such as Aurora Innovation, Cruise, Pony.ai, AutoX, and Nuro Inc. test new deployment models, including autonomous logistics and ride-hailing. Regional players like XPeng Motors (XNGP System), Huawei Technologies, and Baidu Apollo extend adoption in Asian markets, while Qualcomm Technologies strengthens computing performance for next-generation vehicles. Together, these players shape a competitive and evolving market toward higher levels of autonomy.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025) | USD 2.35 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 8.7 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 14% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projection Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD billion for value |
| Automation Level Segments | Level 2 (Partial Automation), Level 3 (Conditional Automation), Level 4 (High Automation), Level 5 (Full Automation) |
| Component Segments | AI Hardware (Chips, GPUs, ASICs, FPGAs), Software (Perception, Planning, Control Algorithms), Sensors (LiDAR, Radar, Cameras, Ultrasonic Sensors), Connectivity Modules (V2X, 5G, Edge Devices) |
| Vehicle Type Segments | Passenger Vehicles, Commercial Vehicles, Robo -Taxis / Autonomous Shuttles |
| Propulsion Type Segments | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE), Electric Vehicles (EVs), Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) |
| End User Segments | OEMs, Tech Providers / AI Startups, Fleet Operators, Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Companies, Logistics & Delivery Companies |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Germany, France, Italy, United Kingdom, Spain, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, South Africa |
| Leading Players | Tesla Inc, NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation (Mobileye), Alphabet Inc (Waymo), Aptiv PLC, Continental AG, Bosch Mobility Solutions, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, Uber ATG (Aurora), Aurora Innovation, Cruise (GM), Pony.ai, Nuro Inc, AutoX, Valeo, Hyundai Mobis, XPeng Motors (XNGP System), Baidu Apollo, Huawei Technologies, Qualcomm Technologies |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by automation level and component type, demand dynamics across passenger vehicles, commercial fleets, and robo -taxis, regional adoption trends across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, innovation in AI chips, edge computing, and sensor fusion, environmental impact of electric propulsion, and emerging use cases in MaaS and logistics |
The market size is valued at USD 2.35 billion in 2025.
It is projected to reach USD 8.7 billion by 2035.
The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14% during 2025-2035.
Level 2 (partial automation) holds the largest share with 40% in 2025.
Tesla, Inc. is the leading player with 24% share.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
AI-based 3D reconstruction Tools Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Driving Protection Gear Market Analysis by Product, Material, Vehicle, Consumer Group, Distribution Channel and Region 2025 to 2035
Driving Helmet Market
Driving Armor Market
Driving Simulator Market
Pile Driving Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tool Holders Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tobacco Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Toilet Roll Converting Lines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
TOC Analyzer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tool Box Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tourism Independent Contractor Model Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tow Prepreg Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Topical Anti-infective Drugs Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Touch Controller IC Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Torrified Wheat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Total Dust Detector Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Total Aflatoxin Test Kit Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tocotrienol Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA