The Japan hydro-processing catalysts demand is valued at USD 112.7 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 135.7 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 1.9%. Demand is influenced by refinery maintenance cycles, requirements for cleaner fuel production, and ongoing adjustments to processing configurations in response to fuel-quality regulations. Steady utilization within hydrotreating, hydrocracking, and impurity-removal operations supports procurement, while replacement-driven purchasing remains central due to catalyst deactivation in continuous processing environments.
Hydrotreating catalysts lead the product landscape. These catalysts are widely used for Sulphur, nitrogen, and metal removal across diesel, kerosene, and naphtha streams. Their selection is shaped by predictable activity profiles, stable performance under variable feedstock conditions, and compatibility with refinery upgrading units. Incremental improvements in catalyst dispersion, pore structure, and metal loading continue to support operational efficiency.

Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilization levels. These regions host key refining assets, petrochemical complexes, and integrated processing facilities that depend on scheduled catalyst replacement and performance optimization. Access to established storage terminals, technical services, and logistics networks also supports reliable procurement.
Key suppliers include ExxonMobil Chemical Company, Shell Catalysts & Technologies, Chevron Phillips Chemical Company, Clariant International Ltd., and Johnson Matthey PLC. These companies provide hydrotreating and hydrocracking formulations used across refinery upgrading, hydrogen-treating units, and downstream petrochemical applications.
Breakpoint analysis shows two clear inflection periods shaped by refinery-operations stability and long catalyst-replacement intervals. The first breakpoint is expected between 2026 and 2028, when refiners adjust catalyst procurement in response to scheduled turnarounds, sulfur-reduction requirements, and incremental shifts in crude-slate composition. During this phase, demand shows a modest uplift driven by routine hydrotreating and hydrocracking maintenance cycles rather than structural expansion.
A second breakpoint appears between 2030 and 2032, when the segment transitions toward a flatter utilization pattern. By this period, Japanese refineries are expected to maintain steady throughput levels, with limited new capacity additions. Growth becomes tied to replacement demand, improved run-length formulations, and adoption of catalysts optimized for renewable-feed co-processing and lower-sulfur fuel compliance. Refinery upgrades remain incremental, leading to stable but subdued catalyst rotation rates. The breakpoint structure reflects an early phase influenced by operational maintenance schedules, followed by a mature phase defined by predictable catalyst lifecycles and a stable refining footprint across Japan.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Hydro-processing Catalysts Sales Value (2025) | USD 112.7 million |
| Japan Hydro-processing Catalysts Forecast Value (2035) | USD 135.7 million |
| Japan Hydro-processing Catalysts Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 1.9% |
The demand for hydro-processing catalysts in Japan is rising as refiners and petrochemical producers face stricter fuel quality regulations and a shift toward cleaner-fuel production. Processes such as hydrotreating and hydrocracking require advanced catalysts to remove sulfur, nitrogen and metal impurities from crude feedstocks while upgrading heavy or unconventional oils into lighter, higher-value products. Japan’s commitment to lower emissions and higher fuel standards increases the urgency for catalyst upgrades in refinery operations.
Growth in bio-refining and renewable feedstocks creates demand for catalysts that can handle diverse inputs and challenging process conditions. Challenges include high cost of premium catalyst materials (especially those with noble-metal components), long turnaround times and technical complexity in replacing or regenerating catalysts in live refining units. Supply-chain constraints for specialist catalyst formulations and materials may also delay procurement or deployment.
Demand for hydro-processing catalysts in Japan is shaped by refinery-upgrade cycles, fuel-quality standards, and the growth of renewable fuel production. Product-type selection reflects process conditions, sulfur-removal requirements, and hydrocarbon conversion intensity in refining operations. Ingredient patterns correspond to catalyst support structures and metal compositions that influence reactivity and regeneration performance. End-use distribution shows how refineries, chemical plants, and renewable-fuel facilities integrate catalysts to meet performance targets and regulatory expectations.
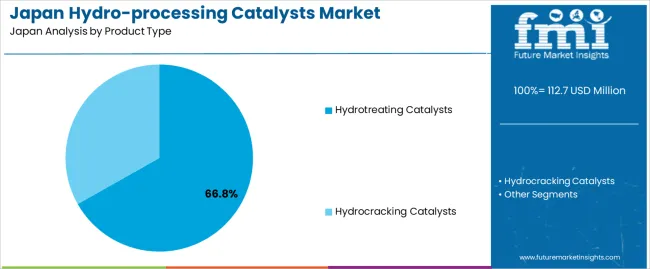
Hydrotreating catalysts hold 66.8% of national demand and represent the leading product category. These catalysts support sulfur, nitrogen, and contaminant removal across diesel, kerosene, and other petroleum fractions. Their application aligns with Japan’s regulations on fuel quality and emission control. Hydrocracking catalysts account for 33.2%, enabling deeper conversion of heavy feedstocks into lighter products such as jet fuel and naphtha. Product-type distribution reflects differences in refinery configurations, hydrotreating throughput, and conversion-unit utilization across Japanese facilities seeking improved fuel uniformity and stability under varying operating pressures and temperatures.
Key drivers and attributes:

Metal-based catalysts hold 54.9% of national demand and represent the dominant ingredient category. These catalysts rely on active metals such as nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum to support hydrotreating and hydrocracking reactions. Their reactivity enables controlled hydrogenation and impurity removal. Support materials account for 45.1%, including alumina and zeolite structures that stabilize metal dispersion, control pore distribution, and assist in maintaining catalyst durability during high-temperature operation. Ingredient distribution reflects the balance between active-site performance and structural stability required for efficient reaction pathways across Japanese refining and chemical-processing environments.
Key drivers and attributes:
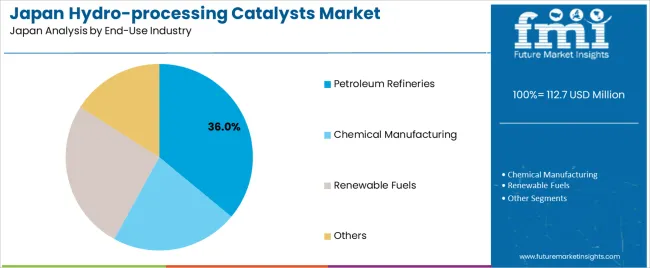
Petroleum refineries hold 36.0% of national demand and represent the leading end-use category. Catalysts support hydrotreating units, hydrocrackers, and other processing systems converting crude-oil fractions into transportation fuels. Renewable fuels account for 26.0%, reflecting the growing role of hydro-processing in producing bio-derived diesel and aviation fuels. Chemical manufacturing represents 22.0%, using catalysts for feedstock purification and intermediate processing. Other industries account for 16.0%, covering specialized operations requiring controlled hydrogenation. End-use distribution reflects Japan’s refining operations, renewable-fuel expansion, and chemical-processing requirements.
Key drivers and attributes:
Stricter fuel quality standards, rising processing of heavier crude feedstocks, and growth in bio-based fuels bolster demand.
Japan’s refining sector is under increasing pressure to upgrade catalysts that support hydro-processing for hydrotreating and hydrocracking in order to meet low-sulfur fuel regulations and higher product quality. Refiners processing heavier or high-contaminant crude blends require advanced catalysts capable of dealing with sulfur, nitrogen and metal impurities. Renewables integration, such as processing bio-oils and waste-derived feedstocks, further drives interest in high-performance hydro-processing catalysts suited for diverse feedstocks and upgraded fuel portfolios.
High catalyst cost, long replacement intervals and competition from alternate fuel pathways limit uptake.
Advanced hydro-processing catalysts involve precious metals and specialized supports which raise acquisition cost and lifecycle expenditure. Some refineries in Japan have extended asset lifetimes and may defer catalyst change-outs unless immediate benefit is evident. The growth of electric vehicles, alternative propulsion systems and non-fossil fuel options reduce long-term demand expectations for conventional petroleum fuels, leading some players to delay major catalyst investments.
Development of catalyst systems designed for bio- and waste-derived feedstocks, increased catalyst regeneration and shift toward tighter performance monitoring define the industry.
Suppliers are introducing catalysts optimized for challenging feedstocks such as used cooking oil, waste fats and lignocellulosic residues that are being co-processed in Japanese refineries. Catalyst life-extension services and regeneration technologies are gaining traction to improve sustainability and reduce total cost of ownership. Digital tools for real-time monitoring of catalyst performance and degradation are being adopted to optimize replacement timing and maximize uptime. These trends support evolving demand for hydro-processing catalysts in Japan’s refining and fuel-transition landscape.

Demand for hydro-processing catalysts in Japan is increasing through 2035 as refiners, petrochemical facilities, and hydrogen-oriented upgrading units adopt more efficient catalyst systems to improve fuel quality, reduce sulfur content, and comply with tightening emissions requirements. Hydro-processing catalysts support hydrotreating, hydrocracking, and renewable-feedstock upgrading, strengthening their role in transportation-fuel preparation, lubricant refining, and emerging biofuel pathways. Regional variation reflects industrial concentration, refinery distribution, hydrogen-supply planning, and modernization cycles across Japan’s refining and chemical-processing networks. Kyushu & Okinawa leads with 2.3%, followed by Kanto (2.2%), Kinki (1.9%), Chubu (1.7%), Tohoku (1.5%), and the Rest of Japan (1.4%).
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 2.3% |
| Kanto | 2.2% |
| Kinki | 1.9% |
| Chubu | 1.7% |
| Tohoku | 1.5% |
| Rest of Japan | 1.4% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 2.3% CAGR, supported by active refining, petrochemical operations, and industrial-fuel upgrading across Fukuoka, Oita, Kumamoto, and Okinawa. Regional refineries deploy hydro-processing catalysts for hydrotreating kerosene, diesel, and naphtha to meet sulfur-reduction standards. Facilities operating hydrocracking units adopt catalyst systems to enhance middle-distillate yields and maintain stable conversion rates. Chemical plants use hydrotreating catalysts to purify feedstocks used in polymer and solvent production. Interest in renewable and co-processed biofuels supports gradual integration of catalysts compatible with vegetable-oil hydrotreating and waste-feed upgrading.
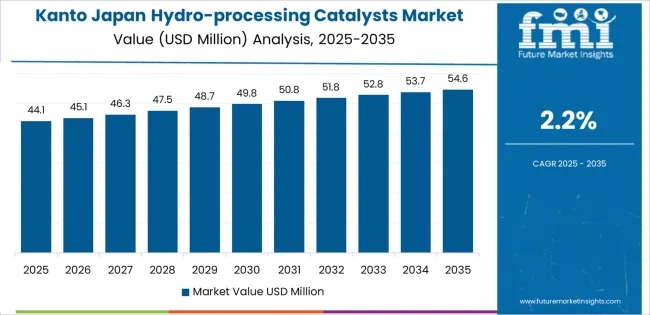
Kanto grows at 2.2% CAGR, influenced by significant energy consumption, industrial fuel demand, and upgrading requirements across Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, and Saitama. Refining units serving transportation and industrial sectors use hydro-processing catalysts to maintain low-sulfur fuel output. Petrochemical facilities integrate catalysts for feedstock purification supporting polymer, resin, and specialty-chemical production. Distributed hydrogen-supply development encourages improvements in hydrotreating performance for refinery upgrading. Storage-terminal operators upgrade fuel-quality systems, increasing use of catalyst-linked hydrotreating processes.
Kinki grows at 1.9% CAGR, supported by diversified industrial demand, petrochemical operations, and smaller-scale refining activity across Osaka, Hyogo, Kyoto, and Nara. Industrial plants rely on hydrotreating catalysts to supply purified feedstocks for lubricants, solvents, and chemical intermediates. Regional refineries maintain catalyst-dependent hydrotreating units for transportation-fuel production and compliance with sulfur-content standards. Chemical producers use hydro-processing catalysts for stabilizing naphtha and preparing clean feedstocks for polymer synthesis. Growth is steady as facilities prioritize catalyst cycles that maintain unit reliability.
Chubu grows at 1.7% CAGR, shaped by industrial clusters, transportation-fuel requirements, and petrochemical supply chains across Aichi, Shizuoka, and Gifu. Refining units linked to automotive and logistics sectors maintain hydro-processing catalysts to produce cleaner diesel and kerosene. Petrochemical manufacturers use catalysts to prepare refined aromatic and paraffinic feedstocks for resin, adhesive, and coating production. Industrial fuel distributors adopt hydrotreating systems to reduce impurities in heating fuels. Although refinery activity is moderate, ongoing modernization programs sustain catalyst demand.
Tohoku grows at 1.5% CAGR, supported by gradual refinery upgrades, industrial-fuel quality improvements, and growing interest in low-sulfur heating fuels across Miyagi, Iwate, Aomori, and Akita. Regional fuel distributors adopt hydrotreating catalysts to reduce sulfur in heating oils used in residential and commercial systems. Smaller petrochemical and materials producers integrate catalyst-based purification steps to improve feedstock consistency. Public-sector energy programs encourage cleaner fuel usage, indirectly supporting hydrotreating catalyst demand.
The Rest of Japan grows at 1.4% CAGR, shaped by small-scale industrial applications, localized refining activity, and gradual upgrades of fuel-quality systems. Industrial users adopt hydro-processing catalysts to stabilize feedstocks used in lubricants, solvents, and treated oils. Regional distributors incorporate hydrotreating solutions for cleaner heating and industrial fuels. Petrochemical units apply catalysts to improve consistency in specialty-chemical production. Adoption is steady but slower due to smaller-scale operations.

Demand for hydro-processing catalysts in Japan is shaped by a concentrated group of refining-technology suppliers supporting hydrotreating, hydrocracking, and renewable-feed conversion units across domestic refineries. ExxonMobil Chemical Company holds the leading position with an estimated 45.1% share, supported by controlled catalyst-formulation methods, consistent activity retention, and long-standing integration with Japanese refining operations. Its position is reinforced by predictable desulfurization, denitrification, and aromatics-saturation performance under varied process conditions.
Shell Catalysts & Technologies and Chevron Phillips Chemical Company follow as significant participants. Shell supplies hydrotreating and hydrocracking catalysts with controlled pore-structure design, stable metals dispersion, and reliable cycle length in units processing heavy or variable feeds. Chevron Phillips offers catalyst systems known for controlled hydrogen utilization, mechanical strength, and steady performance in units optimizing middle-distillate yields.
Clariant International Ltd. maintains a notable presence through alumina- and zeolite-based catalysts providing dependable acidity profiles and compatibility with both petroleum-derived and renewable feeds. Johnson Matthey PLC contributes additional capability with noble-metal and base-metal catalysts used in Japanese hydroprocessing units requiring high selectivity and extended run time.
Competition across this segment centers on activity stability, pore-structure optimization, impurity-management performance, mechanical robustness, regeneration efficiency, and compatibility with renewable-feed co-processing. Demand remains steady as Japanese refiners’ priorities clean-fuel compliance, efficient unit operation, and long-cycle catalyst performance across a maturing refining system.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Product Type | Hydrotreating Catalysts, Hydrocracking Catalysts |
| Ingredient | Metals, Support Materials |
| End-Use Industry | Petroleum Refineries, Chemical Manufacturing, Renewable Fuels, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | ExxonMobil Chemical Company, Shell Catalysts & Technologies, Chevron Phillips Chemical Company, Clariant International Ltd., Johnson Matthey PLC |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type, ingredient category, and end-use industry; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of hydro-processing catalyst suppliers; developments in desulfurization catalysts, high-activity hydrocracking catalysts, and renewable-feedstock processing systems; integration with refinery upgrading, petrochemical processing, and renewable fuels production across Japan. |
The demand for hydro-processing catalysts in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 112.7 million in 2025.
The market size for the hydro-processing catalysts in japan is projected to reach USD 135.7 million by 2035.
The demand for hydro-processing catalysts in japan is expected to grow at a 1.9% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in hydro-processing catalysts in japan are hydrotreating catalysts and hydrocracking catalysts.
In terms of ingredient, metals segment is expected to command 54.9% share in the hydro-processing catalysts in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
japan Tortilla Market - Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Japan Cosmetics ODM Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Yeast Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Green and Bio-based Polyol Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Natural Food Color Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025–2035
Japan Coated Fabrics Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan Barite Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan 1,4-Diisopropylbenzene Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035
Japan Compact Construction Equipment Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Social Employee Recognition System Market in Japan - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA