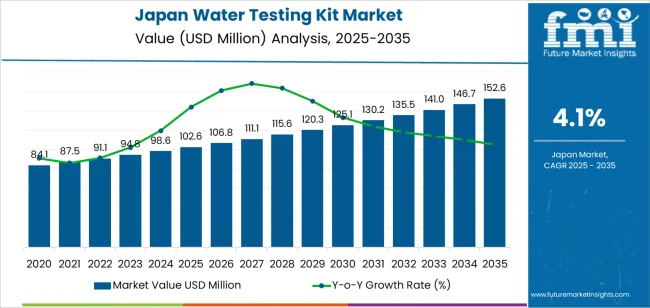
The Japan water testing kit demand is valued at USD 102.6 million in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 152.6 million by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 4.1%. Demand is influenced by stricter water-quality management requirements across municipal supplies, industrial facilities, and commercial establishments. Increased monitoring of contaminants, microbial loads, and chemical residues in drinking water and wastewater systems supports sustained adoption. The expansion of environmental testing programmes and quality-control protocols in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing sectors also contributes to continued use.
Portable water testing kits lead the product landscape. These kits are preferred for field-based assessment, rapid detection capabilities, and ease of deployment in distributed testing environments. Their use extends across on-site inspections, facility-level monitoring, and routine compliance checks. Improvements in sensor accuracy, reagent stability, and multi-parameter testing functions further support uptake among technical users and environmental compliance teams.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilization due to the dense concentration of industrial clusters, municipal water-treatment networks, and environmental testing laboratories. These regions also maintain strong infrastructure for equipment distribution, calibration, and technical support. Key suppliers include Kyoritsu Chemical-Check Lab Corp., HORIBA, Ltd., Hanna Instruments Japan, Kikkoman Biochemifa Company, and DKK-TOA Corporation. These companies provide portable kits, digital meters, and reagent-based testing systems used across environmental monitoring, industrial operations, and public water-safety programmes.
Peak-to-trough dynamics in Japan’s water-testing-kit segment reflect a controlled and steady pattern shaped by regulatory stability, institutional procurement cycles, and consistent environmental-monitoring requirements. The early period shows a mild peak driven by routine compliance testing across municipal facilities, industrial plants, and laboratories. Demand strengthens as monitoring standards tighten and water-quality audits expand within public utilities and regulated sectors. This creates a firm initial lift, though the segment does not experience abrupt spikes because purchasing remains methodical.
A shallow trough appears in the mid period as procurement intervals stabilize. Many institutions operate on multi-year replacement schedules, which spreads purchasing activity across longer cycles. Growth moderates as installed testing capacity reaches equilibrium, with incremental demand coming from calibration tools, consumables, and periodic kit upgrades. The trough remains limited due to ongoing regulatory obligations and continuous sampling needs in environmental, industrial, and residential settings.
In the later period, the segment moves into a renewed peak phase supported by advancements in portable test kits, digital readings, and faster detection formats. These improvements encourage gradual replacement of older manual systems. The overall peak-to-trough pattern remains restrained, reflecting predictable institutional usage and a stable compliance-driven operating environment in Japan.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Water Testing Kit Sales Value (2025) | USD 102.6 million |
| Japan Water Testing Kit Forecast Value (2035) | USD 152.6 million |
| Japan Water Testing Kit Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 4.1% |
Demand for water testing kits in Japan is rising because households, municipalities and industrial facilities need reliable tools to check water quality, safety and regulatory compliance. Ageing water infrastructure and periodic contamination concerns increase interest in simple test kits that measure pH, hardness, residual chlorine, heavy metals and microbial indicators. Housing complexes, small businesses and rural communities use these kits to verify tap water conditions and identify issues before requesting professional inspection.
Schools, laboratories and environmental groups also use portable kits for field sampling and educational activities. Growth in industries such as food processing, aquaculture and pharmaceuticals supports broader use of testing kits for routine monitoring within quality-control workflows. Constraints include limited accuracy of basic kits compared with laboratory methods, cost of specialized multi-parameter kits and variability in user interpretation. Some facilities prefer certified laboratory testing when regulatory documentation is required, which slows full adoption in industrial applications.
Demand for water testing kits in Japan reflects requirements across household use, facility management, environmental monitoring, and municipal oversight. Product selection varies by testing accuracy, portability, and suitability for rapid or detailed assessment. Test-type preferences show how Japanese users evaluate chemical, biological, and physical contaminants across drinking water, recreational facilities, and industrial systems. Water-type distribution highlights the diversity of environments requiring periodic analysis, including potable sources, sewage pathways, and marine settings.
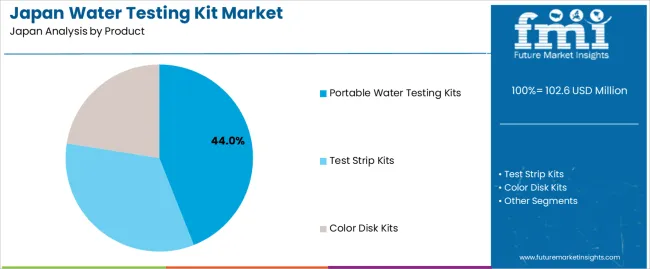
Portable water testing kits hold 44.0% of national demand and represent the leading product type in Japan. Their mobility, quick response time, and compatibility with multiple water sources support use by households, field inspectors, and small businesses. Test strip kits account for 33.5%, enabling rapid screening for basic parameters with minimal equipment. Color disk kits represent 22.5%, providing more structured measurement suitable for facility operators and environmental teams. Product distribution reflects Japanese users’ need for accessible testing methods that support routine safety checks, compliance monitoring, and quick verification of water quality in domestic and institutional settings.
Key drivers and attributes:
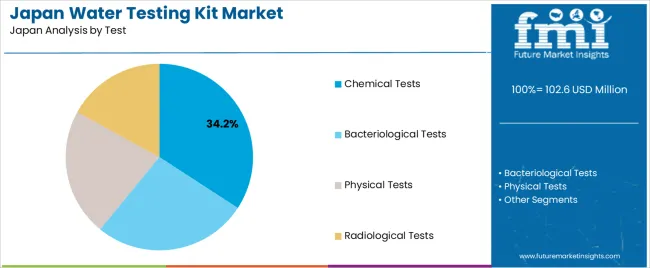
Chemical tests hold 34.2% of national demand and represent the leading test category in Japan. These tests measure pH, hardness, chlorine, heavy metals, and other chemical indicators essential for drinking water and facility compliance. Bacteriological tests account for 26.7%, supporting detection of microbial contamination in potable water and recreational facilities. Physical tests represent 22.1%, covering turbidity, colour, and odour assessments. Radiological tests hold 17.0%, used in specialized monitoring for areas where radiation exposure requires precautionary review. Test-type distribution reflects regulatory practices, household safety concerns, and environmental monitoring across Japanese water systems.
Key drivers and attributes:
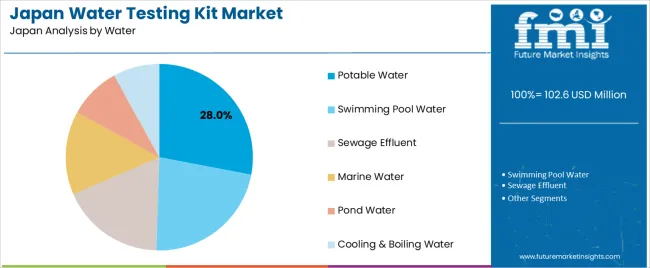
Potable water holds 28.0% of national demand and represents the leading water type tested in Japan. Testing supports routine household checks, municipal monitoring, and facility-based quality assurance. Swimming pool water accounts for 22.5%, reflecting regular safety checks in fitness centres, public pools, and hospitality facilities. Sewage effluent represents 18.0%, requiring regulated testing in wastewater management. Marine water holds 14.5%, used for coastal monitoring and environmental assessments. Pond water accounts for 9.0%, often linked to parks and agricultural settings. Cooling and boiling water represent 8.0%, supporting industrial system checks. Water-type distribution reflects diverse environmental conditions and regulatory needs across Japan.
Key drivers and attributes:
Municipal focus on drinking-water safety, rising household concern after ageing-pipe incidents and increased testing requirements in small food-service establishments are driving demand.
In Japan, demand for water testing kits grows as municipalities strengthen monitoring of tap-water quality in response to ageing pipeline networks, especially in regions with older infrastructure such as Hokkaido and parts of Tohoku. Households increasingly use simple test strips and microbial kits after localized discoloration or odor incidents, which receive strong media coverage and heighten awareness. Small restaurants, cafés and childcare facilities are required under local hygiene ordinances to verify water quality in kitchens and storage tanks, leading operators to use on-site testing kits for bacteria, chlorine levels and pH. These factors support steady demand across both public and private users.
Fragmented regulatory oversight, limited awareness of advanced testing methods and reliance on municipal testing services restrain growth.
Water-quality regulations in Japan differ across prefectures, and smaller facilities often rely on municipal water reports rather than performing their own tests. Many consumers are familiar only with basic chlorine or hardness strips, and awareness of heavy-metal or microbial-specific test kits remains low. Hotels, dormitories and public buildings frequently depend on contracted water-management firms that use professional laboratory testing, reducing direct demand for DIY kits. These elements limit broader penetration of higher-value or specialized water-testing products in Japan.
Shift toward multi-parameter digital meters, increased adoption in disaster-preparedness kits and rising use in agriculture and aquaculture define key trends.
Japanese households are purchasing compact digital testers that measure multiple parameters when assembling disaster-preparedness supplies, reflecting national emphasis on readiness for earthquakes and typhoons. Farmers and aquaculture operators in regions such as Shikoku, Kyushu and Hokkaido increasingly use water-testing kits to monitor pH, ammonia and dissolved oxygen to meet quality standards for produce and fish. Schools and community science programs are also incorporating simple testing kits into environmental education activities. These developments support diversified, year-round demand for water-testing kits throughout Japan.
Demand for water testing kits in Japan is increasing through 2035 as households, industrial facilities, laboratories, and municipal authorities expand monitoring of drinking water, groundwater, wastewater, and on-site facility systems. Japanese regions adopt test kits for routine safety checks, regulatory compliance, and environmental-quality tracking. Kits commonly measure pH, hardness, residual chlorine, heavy metals, and microbial contamination. Growth varies due to population density, industrial clusters, and municipal water-quality programs. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 5.1%, followed by Kanto (4.7%), Kinki (4.1%), Chubu (3.6%), Tohoku (3.2%), and Rest of Japan (3.0%).
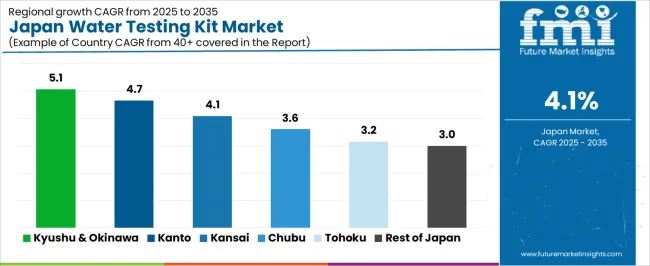
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 5.1% |
| Kanto | 4.7% |
| Kinki | 4.1% |
| Chubu | 3.6% |
| Tohoku | 3.2% |
| Rest of Japan | 3.0% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 5.1% CAGR, supported by widespread household use, agricultural water monitoring, and municipal quality-control programs across Fukuoka, Kumamoto, Nagasaki, Kagoshima, and Okinawa. Households use simple test strips and chemical-indicator kits to check residual chlorine and general drinking-water quality. Agricultural cooperatives rely on kits to monitor irrigation water and detect variations in pH and mineral levels that affect crop conditions. Municipal water departments conduct routine testing using comprehensive kits for distribution-network monitoring. Coastal communities depend on water-quality checks due to fluctuating groundwater conditions and seasonal contamination risks. Tourism-centered facilities in Okinawa adopt rapid test kits to meet internal hygiene requirements for guest-use water points.
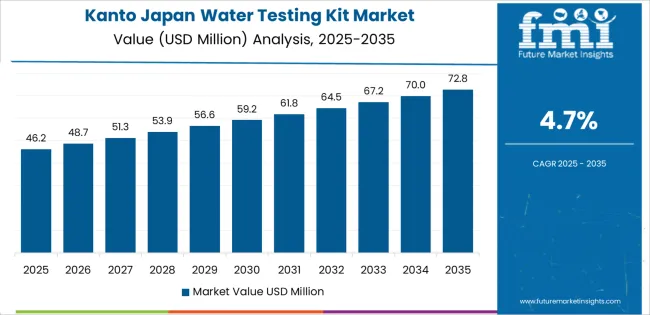
Kanto grows at 4.7% CAGR, driven by dense population centers, industrial facilities, and extensive municipal oversight across Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, Saitama, and Ibaraki. Urban households purchase test kits for chlorine, hardness, and general potability checks. Laboratories and industrial plants use multi-parameter testing tools for wastewater and process-water evaluation. Municipal utilities in Tokyo and Kanagawa conduct routine testing at multiple points throughout distribution lines. Food-processing facilities in Chiba and Saitama rely on rapid microbial- and chemical-testing kits for internal sanitation control. Condominium associations and commercial buildings use kits to verify water quality in storage tanks and distribution pipes.
Kinki grows at 4.1% CAGR, supported by industrial clusters, public water systems, and routine facility-level monitoring across Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo, Nara, Wakayama, and Shiga. Industrial plants in Osaka and Hyogo rely on chemical-parameter kits to evaluate cooling-water and process-water characteristics. Municipal water bureaus conduct periodic testing of reservoirs and treatment plants. Households and small businesses use simple kits for chlorine and pH checks. Food-service establishments in Osaka and Kyoto adopt test kits to maintain sanitation standards related to water used in cooking and cleaning. Research centers across Kyoto and Shiga employ advanced testing kits for environmental-quality studies.
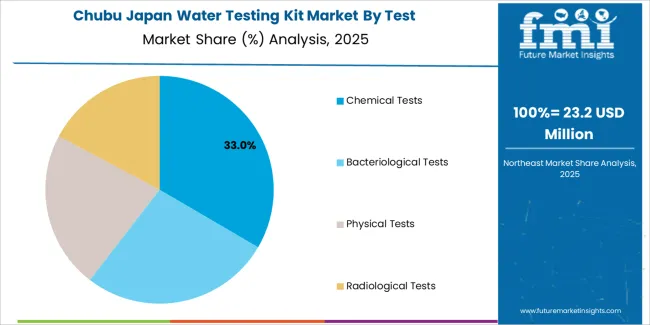
Chubu grows at 3.6% CAGR, shaped by manufacturing activity, agricultural use, and municipal testing needs across Aichi, Shizuoka, Gifu, Mie, and Nagano. Factories in Aichi employ multi-parameter kits for wastewater and cooling-water analysis. Agricultural communities in Nagano and Gifu use test kits to verify irrigation-water suitability. Municipal water authorities in Shizuoka conduct frequent testing of treatment outputs and distribution lines. Small hotels and ryokan in Gifu and Mie use testing kits for routine facility water checks. Retail availability of household kits supports modest demand across suburban and rural districts.
Tohoku grows at 3.2% CAGR, supported by rural water systems, agricultural dependence, and public-sector monitoring across Miyagi, Aomori, Fukushima, Akita, Iwate, and Yamagata. Rural households use test kits for well-water assessments. Agricultural cooperatives rely on pH, hardness, and mineral-content kits to evaluate water for crop and livestock use. Municipal agencies monitor small-scale treatment plants serving dispersed communities. Environmental centers conduct river- and groundwater-quality testing using advanced kits. Local schools and community programs use simple water-test sets for public-education initiatives.
Rest of Japan grows at 3.0% CAGR, supported by small municipal networks, household usage, and local facility monitoring across prefectures outside major regions. Households use chlorine and pH test kits for drinking-water checks. Municipalities rely on basic and intermediate kits for routine quality verification. Schools, community facilities, and small businesses use test kits for compliance and hygiene management. Local agricultural operations monitor irrigation water using simple test tools.
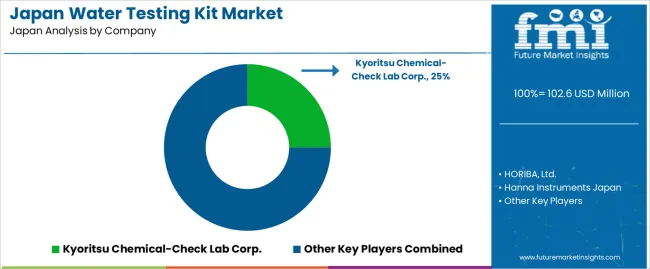
Demand for water-testing kits in Japan is shaped by domestic analytical-instrument manufacturers and reagent suppliers that support municipal waterworks, environmental laboratories, industrial facilities, and household testing. Kyoritsu Chemical-Check Lab Corp. holds an estimated 25.0% share, supported by controlled reagent-tablet production, consistent test-strip sensitivity, and long-standing use by Japanese water bureaus and schools. Its kits provide stable colour-development behaviour and reliable accuracy across drinking-water and wastewater checks.
HORIBA, Ltd. maintains strong participation through portable meters and field-test kits used by facilities managers and environmental monitoring teams. Its products offer consistent electrochemical stability and durable field performance. Hanna Instruments Japan contributes to demand with multiparameter kits designed for routine water-quality checks in food processing, aquaculture, and small industrial sites, emphasizing predictable reagent behaviour and straightforward operation.
Kikkoman Biochemifa Company supports additional use cases with ATP-based hygiene and microbial-monitoring kits, offering stable luminescence response and compatibility with Japanese sanitation requirements. DKK-TOA Corporation adds depth through compact test kits and portable analyzers used in environmental and industrial applications. Competition in Japan centers on measurement accuracy, reagent stability, kit durability, multilingual documentation, and dependable domestic distribution. Demand remains steady as utilities, manufacturers, and households rely on portable, reliable, and easy-to-use water-testing kits suited to Japan’s strict water-quality standards and routine monitoring practices.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD million |
| Product | Portable Water Testing Kits, Test Strip Kits, Color Disk Kits |
| Test | Chemical Tests, Bacteriological Tests, Physical Tests, Radiological Tests |
| Water | Potable Water, Swimming Pool Water, Sewage Effluent, Marine Water, Pond Water, Cooling & Boiling Water |
| End User | Laboratory and Diagnostic Centers, Hospital, Research and Academic Institutes, Clinic, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Kyoritsu Chemical-Check Lab Corp., HORIBA, Ltd., Hanna Instruments Japan, Kikkoman Biochemifa Company, DKK-TOA Corporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product type, test category, water sample type, and end-user segment; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape for water quality testing equipment providers; developments in rapid diagnostic kits, digital photometric systems, and multiparameter water analyzers; integration with public water monitoring, environmental compliance programs, industrial water treatment, laboratory workflows, and household water safety solutions in Japan. |
The demand for water testing kit in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 102.6 million in 2025.
The market size for the water testing kit in japan is projected to reach USD 152.6 million by 2035.
The demand for water testing kit in japan is expected to grow at a 4.1% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in water testing kit in japan are portable water testing kits, test strip kits and color disk kits.
In terms of test, chemical tests segment is expected to command 34.2% share in the water testing kit in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Water Testing Kit Market Analysis by Product, Test Type, Water Type, End User, and Region - Analysis for 2025 to 2035
Water Testing & Analysis Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sea Water Pumps Market Report – Trends & Innovations 2025-2035
Water Quality Testing Equipment Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2018-2027
Soil Testing Kit Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fungal Testing Kits Market Analysis – Size, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Cortisol Testing Kits Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Oxytocin Testing Kits Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapid RNA Testing Kits Market Trends- Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Irrigation testing kit Market
Microbiological Water Testing Services Market – Growth, Demand & Safety Trends
Demand for Water Ionizer in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Lab Confirmation Testing Kit Market
Demand for Water Treatment System in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Respiratory Pathogen Testing Kits Market Insights - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand for Water Soluble Fertilizers in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Paediatric & Neonatal Testing Kits Market – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Demand for Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) Testing Equipment in Japan Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Vapor Permeability Analyzers Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water and Waste Water Treatment Chemical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA