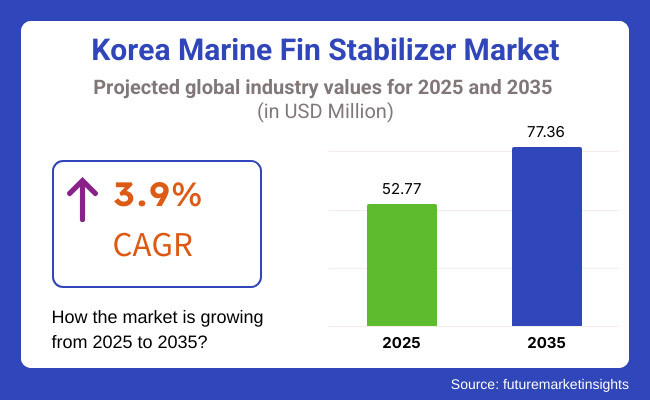
The need for marine fin stabilizers in Korea is growing continuously, especially in shipbuilding centers of South Jeolla and North Jeolla. The market is expected to hit a valuation of USD 52.77 million by the end of 2025, with a consistent growth path. The market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.9%, with an estimated valuation of USD 77.36 million by 2035.
The Korean marine fin stabilizer industry experienced accelerated growth between 2024 and 2025, fueled by high demand within the local shipbuilding industry. South Jeolla and North Jeolla became prominent manufacturing hubs, manufacturing stabilizers for commercial ships and naval vessels. Korean manufacturers continued to have an emphasis on advanced technologies, introducing upgraded stabilizer models with higher hydrodynamic efficiency and real-time monitoring capabilities.
Moreover, collaborations between domestic shipbuilders and international maritime companies spurred export expansion, enabling Korea to solidify its global presence. Through ongoing investment in R&D, Korean companies are seeking to launch AI-based stabilization technologies, lowering fuel consumption and enhancing ship maneuverability.
Being a world leader in shipbuilding, Korea focuses on stability-improving technology to enhance vessel performance, safety, and comfort for passengers. The export-based model of the industry enhances its presence in international maritime sectors.
| Factors | 2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Cruise Tourism Growth | From 2020 to 2024, the global cruise tourism expanded rapidly, driven by the surging demand for stabilizers in luxury and passenger ships. Moving forward to 2025 to 2035, the rapid shift of Gen Z’s interest towards offbeat travel experiences are further propelling the industry landscape, boosting the demand for sophisticated stabilizer systems. |
| Zero-Speed Stabilization | From 2020 to 2024, zero-speed marine fin stabilizers gained traction, allowing ships to offset rolling motions during unstable conditions. Looking forward to 2025 to 2035, these stabilizers will become a benchmark, redefining the ship stability while prioritizing the passenger comfort. |
| Market Valuation and Growth | The industry grew rapidly from 2020 to 2024 with minimal adoptions and improvements in commercial and naval ships. During 2025 to 2035, the industry will observes a robust growth with the increasing production and adopting of stabilizer technology. |
| Regional Market Dynamics | South Korea and other Asian-Pacific countries dominated the sector during 2020 to 2024 with over-the-top domestic production, toping international ship orders. From 2025 to 2035, these nations will further solidify their dominance, embracing automation and AI to streamline stabilizer production. |
| Product Innovations | From 2020 to 2024, companies launched retractable and non-retractable stabilizers appropriate for fishing, passenger, and naval ships. In 2025 to 2035, material and design improvements will improve efficiency, longevity, and versatility, increasing stabilizers' flexibility to support a wide variety of vessels. |
The marine fin stabilizer industry comes under the high-tech shipbuilding industrial equipment and naval defense industry, with macroeconomic drivers like world trade, national defense budgets, and developing technology in shipbuilding. During 2025 to 2035, the industry will witness consistent growth on the back of growing investment in maritime facilities, green regulatory norms, and growing demand for passenger ships, naval fleets, and luxury yachts.
Korea's dominance of shipbuilding will create demand for next-generation stabilizers with ship owners seeking fuel efficiency and passenger comfort. Economic forces such as volatile raw material prices and global supply chain interruptions are potential challenges but will be dampened by Korea's domestic production capabilities. The government's export-oriented policy will be helped by rising demand in European and North American sectors, which are replacing their fleets with next-generation stabilizers.
Besides, government subsidies for green shipping and digitalization will compel manufacturers to produce energy-efficient stabilizers with AI integration. This macroeconomic setting places Korea's marine fin stabilizer industry in a key position to drive the evolution of the maritime industry, ensuring innovation and economic balance.
The industry for marine fin stabilizers will keep on changing between 2025 and 2035, with retractable fin stabilizers leading the way. Close to 65% of the industry will depend on these stabilizers due to their adaptability and effectiveness across different sea conditions. Shipbuilders will favor retractable fin stabilizers for their capacity to increase vessel stability without permanently changing hydrodynamic performance. As ship technology becomes more advanced, the need for retractable systems will rise on passenger and naval ships.
Non-retractable fin stabilizers will continue to be relevant, especially for ships that need economical solutions where retractable elements are not required. Anchor or rest stabilizers will gradually gain popularity, serving luxury and moored ships that need greater stability when at anchor. Technological progress will enhance stabilizer design to be lighter, more energy-efficient, and sensitive to current sea conditions
Passenger ships remain the major consumer of marine fin stabilizer, holding approximately 80% of the industry demand between 2025 and 2035. With the growing frequency in travel segment and the continuous demand for luxury yachts and super-yachts, the industry landscape will further propel, driving the demand for innovative stabilizing solutions. Shipbuilders will put high emphasis towards the integration of next-generation stabilizers in new-build passenger ferries, cruise liners, and yachts to enhance the passenger comfort alongside reducing the prevalence of motion sickness.
The naval and coast guard will also grow steadily, with the ongoing investments by government in elevated vessel stability solution to improve patrol services and military use. Merchant ships and fishing ships will drive the demand at a negotiable rate. Moreover, Korean companies will continue to dominate the sector through advancing solutions and designs to cater to the evolving demand of passenger boats.
The industry for fin stabilizers in the ocean will witness balanced growth in first-fit and retrofit segments between 2025 and 2035. First-fit installations will lead a major part of the industry as new vessel builds increase to fulfill world maritime trade and passenger transport needs. Shipbuilders will integrate upgraded stabilizers in initial production for maximum performance and adherence to changing maritime safety regulations.
As automation and intelligent manufacturing methodologies become the cornerstone of shipbuilding, first-fit stabilizers will also see upgrades with technology, making them even more attractive to ship operators. Retrofit stabilizers will also see sizeable growth, particularly as old fleets look to upgrade stability to comply with tighter regulations as well as enhance passenger comfort.
Cruise ships, luxury yacht owners, and naval administrations will spend on retrofit options to upgrade their ships without major redesigns. Korean producers will utilize their technical skills to provide low-cost, high-performance retrofit stabilizers that are aligned with sustainability initiatives.
South Gyeongsang is the backbone of Korea's shipbuilding business, where large international shipyards are based. Its demand for marine fin stabilizers will rise as shipbuilders equip next-generation stabilizers on high-end commercial and passenger ships. Smart ship technology and automation initiatives sponsored by governments will expedite the implementation of AI-based stabilizers.
With concerns about sustainability on the rise, shipbuilders will look for energy-efficient stabilizers with lower fuel consumption and emissions. Having large R&D centers in South Gyeongsang will drive design innovation in hydrodynamic stabilizers to enhance operational efficiency. Moreover, partnership between local and foreign firms will bring in state-of-the-art stabilization technologies that suit the changing requirements of the sea transportation industry.
North Jeolla's shipping industry is fast growing, concentrating on mid-range ships, such as ferries and fishing vessels. The industry for stabilizers in the region will expand because of the expanding retrofitting of existing ships with sophisticated stabilizing technology. Shipbuilding will gain strength in North Jeolla as shipyards look to retractable stabilizers to maximize flexibility.
Maritime sustainability government policies will challenge manufacturers to innovate green stabilizer coatings and sound-reducing systems. The growth of commercial fishing fleets will also propel demand for affordable stabilizers that increase vessel performance during turbulent seas. Moreover, the strategic position of North Jeolla along key trade routes will accelerate investments in the production and servicing of stabilizers, leading to consistent industry growth.
South Jeolla's stabilizer industry will grow considerably, fueled by its robust position in coastal tourism and commercial fishing. The growth in the number of cruise ships and luxury yachts plying the waters in the region will drive demand for premium stabilizers that enhance ride comfort and minimize motion sickness. South Jeolla's fishing boats will gain from technologically advanced stabilizers that increase operational efficiency, even in unstable sea conditions.
Consistent investment by the province in enhancing their maritime research will push innovations in stabilizer designs, alongside focusing on light, corrosion-proof materials. Additionally, the efforts toward enhance cleaning solutions will motivate ship owners to employ stabilizers that utilize less energy consumption while adhering to the global sustainability approach.
Jeju, a well-established center for marine tourism will undergo robust growth in the marine fin stabilizers industry, especially in the yacht and passenger ferry segments. Stabilizers, incorporated with better stability and fuel efficiency will be best suited for high-speed ferries, eventually driving the industry demand.
The demand for luxury yacht in the region will also boost stabilizer sales, as high-net-worth individuals will prioritize comfort along with innovative features that will elevate their sailing experiences. Furthermore, Jeju’s high emphasis towards protecting environment will give rise in the utilization of low-emission stabilizers. Moreover, the recent advancements in digital stabilization technology will also allow ferry operators to maximize and elevate passenger comfort and fuel efficiency.
FMI conducted a recent survey that involved shipbuilders, naval engineers, and providers of maritime technology to evaluate the changing environment of marine fin stabilizers. The survey revealed increased demand for AI-based stabilizers that enhance vessel stability, fuel efficiency, and predictive maintenance. Ship operators noted the need for stabilizers that minimize downtime by providing real-time monitoring and automated adjustments in response to sea conditions.
Hybrid stabilizers, which incorporate both mechanical and electronic elements, were a prominent trend, as they offer higher performance in different maritime conditions. Shipbuilders emphasized that light materials, including carbon composites, are becoming a necessity for reducing fuel consumption while complying with stringent environmental regulations. The need for tailor-made stabilizers designed for individual vessel needs is increasing, especially in the cruise and luxury yacht sectors.
The poll also indicated that regulatory pressures are impacting innovation. Increased compliance expenses from tighter emissions and fuel efficiency regulations are prompting investments in green stabilizers. Naval architects noted retrofitting as a major issue, but modular designs are simplifying integration into older ships. Experts concurred that the future of stabilizers will be about smart automation, sustainability, and adaptive technology to address the changing demands of contemporary maritime operations.
| Regulation | Impact on Marine Fin Stabilizers in Korea |
|---|---|
| Ship Stability & Safety Standards (Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries) | Requires the implementation of advanced stabilizers to improve vessel stability, making it safer to operate at sea, particularly for passenger and business vessels. |
| Green Ship Initiative (Korea’s Green New Deal) | Promotes shipbuilders to implement environmentally friendly stabilizers from light-weight and energy-saving materials to meet emission reduction goals. |
| Emission Control Areas (ECA) Regulations | Imposes tighter restrictions on sulfur and nitrogen oxide emissions, stimulating demand for fuel-saving stabilizers that increase overall vessel efficiency. |
| Korean Shipbuilding Quality Standards (KSQS) | Needs stabilizers to achieve tough performance and life expectancy standards, prompting manufacturers to produce high-performing, durable solutions. |
| Subsidies for Maritime Innovation (Korean Government Support Programs) | Offers economic inducements for businesses creating advanced next-generation stabilizers with smart automation and hybrid technology. |
| Retrofitting Guidelines for Aging Fleets | Is stimulating shipowners to retrofit with advanced stabilizers, increasing demand for modular and retrofit-friendly equipment. |
The sector for marine fin stabilizers offers promising growth opportunities from 2025 to 2035, underpinned by technology advancements in stabilization, maritime trade growth, and growing need for energy-efficient ships. Organizations need to focus on AI-driven stabilizers, which will make automation and efficiency more effective. Penetration in high-growth sectors such as Southeast Asia and the Middle East will open new avenues. Development of stronger partnerships with international shipbuilders and defense organizations will expedite adoption rates.
Sustainability is a driving factor, with increasing regulatory focus on minimizing carbon footprints. Lighter stabilizers made from newer composite materials will enhance fuel economy while being environment-friendly. Hybrid stabilizers that combine mechanical and electronic elements are promising opportunities. Tailored solutions for various vessel types, ranging from luxury yachts to naval vessels, will help capture niche sectors. The integration of digitalization for predictive maintenance and remote monitoring will bring competitive benefits and long-term growth opportunities.
In 2024, the marine fin stabilizer industry saw large-scale mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances with a view to improving technological innovation and industry penetration.
Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. made a joint venture with a top AI-based maritime technology company to design next-generation stabilizers with real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. The alliance is likely to improve automation capabilities and fuel efficiency for commercial and naval ships.
Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. completed the acquisition of a European stabilizer producer to expand its global presence and incorporate state-of-the-art hybrid stabilizer technology in its product lineup. The purchase is intended to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient stabilizers in domestic as well as international segments.
New players have to concentrate on cost-efficient and technologically sophisticated stabilizer products to gain traction in the segment. R&D investment in future-generation stabilizers with intelligent sensors and real-time data analysis will appeal to shipbuilders looking for state-of-the-art solutions. Strategic partnerships with shipyards and defense agencies will build credibility and segment share. Modular stabilizer designs for easy retrofitting will expand the customer base.
Digital marketing and online platforms can facilitate effective global access for new entrants. Government incentives and grants for maritime innovation can counteract funding limitations. Gradual industry entry, starting with local sales followed by overseas expansion, will establish brand name and financial strength.
Retractable fin stabilizer, Non- retractable fin stabilizer, Anchor or rest stabilizer.
Passenger Vessels (Passenger & Vehicle Ferries, Cruise Ships, Yachts & Superyachts), Naval and Coast Guard Vessels, Fishing Vessels, Merchant Vessels.
First Fit, Retro Fit.
South Gyeongsang, North Jeolla, South Jeolla, Jeju.
Demand is spurred by the advancement of ship stabilization technology, expanding maritime trade, and the expanding demand for fuel-efficient and comfortable ships.
The major players are Hyundai Heavy Industries, Wärtsilä Corporation, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering, Quantum Marine Stabilizers, and Naiad Dynamics, among others.
Technological advances like AI integration, smart sensors, and hybrid stabilizer systems improve the stability of vessels, reduce fuel consumption, and are in line with sustainability laws, making them appealing to shipbuilders.
Tougher environmental regulations promote the use of light and efficient stabilizers, driving producers to create environmentally friendly solutions that cut emissions and fuel usage.
Passenger ships, naval craft, and luxury yachts demand high-performance stabilizers to ensure greater comfort and security, whereas fishing and merchant ships focus on toughness and efficiency in heavy seas.
Table 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Forecast by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 7: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 14: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 18: Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 30: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 33: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 34: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 35: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 37: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 38: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: South Gyeongsang Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 47: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 48: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 51: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 56: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: North Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 65: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 70: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 73: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 74: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: South Jeolla Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 83: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 84: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 86: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 87: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 88: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 91: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Jeju Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 101: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Product Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 102: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 105: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Vessel Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Volume (Units) Analysis by Fit Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Product Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Vessel Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: Rest of Industry Analysis and Outlook Attractiveness by Fit Type, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Korea Automotive Performance Tuning and Engine Remapping Service Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Smart Home Security Camera Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Bicycle Component Aftermarket Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Korea Isomalt Industry – Market Trends & Industry Growth 2025 to 2035
Korea Probiotic Supplement Industry – Industry Insights & Demand 2025 to 2035
Korea Calcium Supplement Market is segmented by form,end-use, application and province through 2025 to 2035.
The Korea Non-Dairy Creamer Market in Korea is segmented by form, nature, flavor, type, base, end-use, packaging, distribution channel, and province through 2025 to 2035.
Korea Women’s Intimate Care Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Korea Conference Room Solution Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Visitor Management System Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea fiber optic gyroscope market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Event Management Software Market Insights – Demand & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Last-mile Delivery Software Market in Korea – Trends & Forecast through 2035
Korea HVDC Transmission System Market Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea Base Station Antenna Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Smart Space Market Analysis in Korea-Demand & Growth 2025 to 2035
Korea Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Platform Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea I2C Bus Market Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Korea On-shelf Availability Solution Market – Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA