The global quinoa seed market is estimated at USD 384.2 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 487 million by 2035, advancing at a CAGR of 2.4% over the forecast period 2025 to 2035. In 2025, the quinoa seed market represents 0.06% of the broader grains market valued at USD 650 billion.
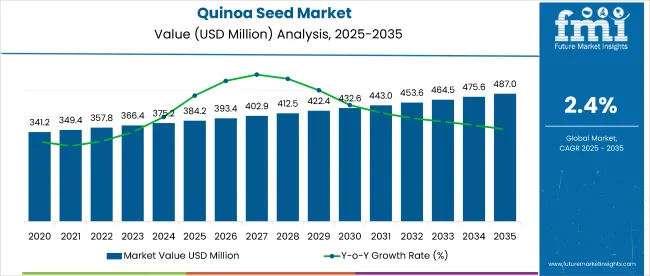
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Size 2025 | USD 384.2 million |
| Market Size 2035 | USD 487 million |
| CAGR 2025 to 2035 | 2.4% |
Quinoa exports remain heavily concentrated in the Andean region, with Peru accounting for roughly 48% of global export value and Bolivia contributing around 24% in 2025. The United States ranked third with about 5%, followed by the Netherlands at 3.5% and Germany at 3%.
On the import side, the United States led all markets with roughly USD 200 million of quinoa imports in 2024. Canada was also a key destination, sourcing about USD 11 million directly from Peru and USD 7 million from the United States. Within Europe, Germany, France, and the United Kingdom each featured among the top ten quinoa importers, reflecting growing demand for gluten-free and plant-based products.
It is observed that market expansion has been driven by rising health-conscious consumption-global quinoa seed volumes grew by 1.6% in 2024 as pricing firmed by 2.2% amid constrained supplies. Investment in non-traditional cultivation regions was spurred by processing technology advances, supporting a 2.4% CAGR outlook. However, high retail prices averaging USD 4,500 per ton in 2024 and limited consumer awareness in import-reliant regions (Europe’s import dependence exceeded 54% in 2024) have restrained broader adoption.
The market has been segmented by seed type into organic and inorganic; by colour into white, red, black, and others; by application into direct consumption and processed products; by distribution channel into online stores and offline stores; and by region into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, and Middle East & Africa.

In 2025, inorganic quinoa seeds hold a 60% share of the seed type segment, a 20.0-point edge over organic counterparts. Growth was driven by two key factors:
A hidden disruptor, rising consumer interest in heritage grain varieties, contributed an 8.5% incremental share growth, enabling specialty brands to secure niche positioning.
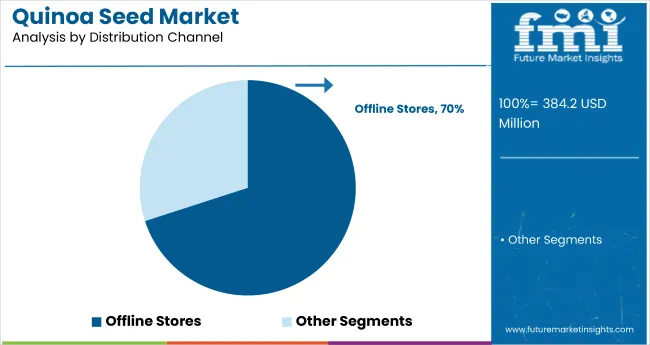
In 2025, offline stores held a 70.0% share of the distribution channel segment, a 40.0-point lead over online stores. Growth was driven by: 1. entrenched retail partnerships in major supermarkets; 2. limited digital infrastructure in emerging markets. A hidden disruptor-direct-to-consumer subscription platforms-added a 6.3% incremental share by offering curated quinoa-based meal kits.
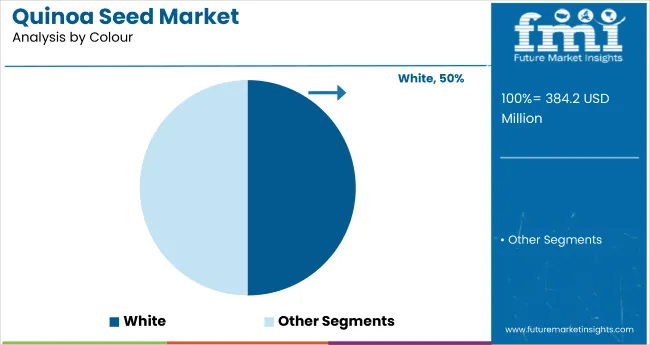
In 2025, white quinoa led the colour segment with a 50.0% share, outperforming red by 15.0 points. Growth is supported by broad retail adoption in Western supermarkets and premium pricing that reinforced its perceived value. A hidden disruptor, emergence of tri-colour blends, captured an incremental 4.2% share by appealing to niche premium-label consumers, prompting lineup expansions.
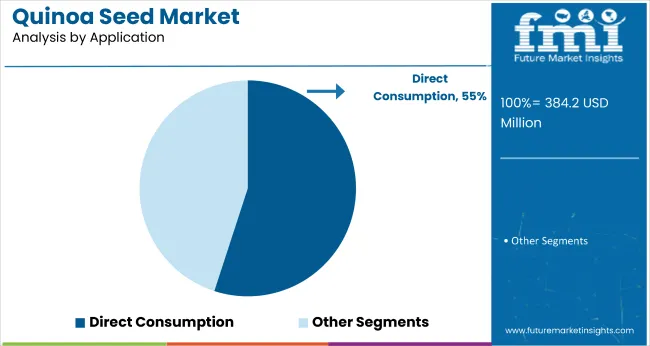
In 2025, direct consumption commanded 55% of the application segment, leading processed products by 10.0 points. Expansion was driven by 1. growing home-meal kit integrations; 2. logistical challenges in scaling ready-to-cook lines. A hidden disruptor subscription-based meal-kit services increased share by 5.2% through curated quinoa recipes, boosting retailer partnerships and recurring orders.
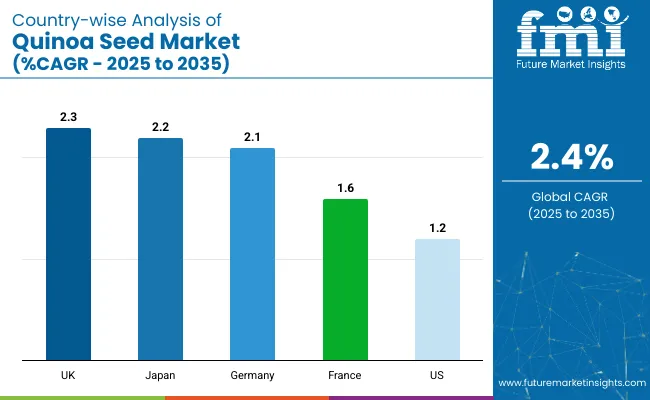
Across the global quinoa seed market, economic blocs show divergent trajectories shaped by dietary shifts, regulatory incentives, and cultivation feasibility.
USMCA: The United States remains the largest quinoa importer globally, while Canada is steadily increasing local production through domestic initiatives. Mexico’s consumption is rising in urban health-conscious segments, though production remains negligible.
EU-27: Imports dominate in France, Germany, and the Netherlands, but local cultivation is growing under CAP subsidies and sustainability mandates. Regulatory stringency-especially on pesticide residues-has led to increased traceability requirements and certification-led differentiation.
United Kingdom: Post-Brexit customs adjustments have slightly raised costs, but domestic players like The British Quinoa Company have expanded acreage. High organic premiums and growing farm shop distribution sustain margins despite modest consumer penetration outside metro areas.
BRICS+: Brazil shows potential as a cultivation hub, with small trials underway, while India’s quinoa uptake remains niche and confined to premium metros. China’s quinoa use is largely R&D-led, with minimal consumer traction so far.
RCEP Core: Japan leads demand in East Asia, leveraging quinoa’s fit in functional food formats. Elsewhere, consumption remains limited but rising, particularly in urban Australia and South Korea via plant-based diet trends.
GCC: High-income Gulf markets are import-dependent, with quinoa positioned as a premium health food. Distribution is concentrated in supermarkets and expat-targeted retail.
Mercosur 2.0: Bolivia and Argentina are key exporters. Bolivia, in particular, maintains robust global share through established organic supply chains, although pricing volatility and climate risk remain key concerns.
AfCFTA Rest of Africa: Uptake is nascent, limited to health-food imports in South Africa and small-scale trials in Kenya and Rwanda. Lack of awareness and agronomic barriers restrict wider market formation.
The quinoa seed market in the United States is projected at USD 114.0 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 128.4 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 1.2%. Despite moderate growth, the USA remains the world’s top quinoa importer, accounting for nearly 30% of global demand. However, domestic cultivation continues to face scale barriers, limiting substitution for imports.
Margins are supported by two factors: 1. premium pricing in the organic and specialty retail segment, contributing over 42% of market value; 2. direct-to-consumer channels, where cost markups exceed 18% over mass retail. Yet price sensitivity is a constraint-average unit prices rose 3.1% in 2025, slowing category penetration among middle-income households.
Policy frameworks such as the FDA’s gluten-free labeling rule (21 CFR 101.91) have improved consumer confidence, while USDA research funding supported quinoa trials in non-traditional states like Colorado and Washington. Survey data from 2025 showed that 67% of USA consumers associated quinoa with heart-health and protein density-an 11-point rise since 2020.
Sales of quinoa seeds in the United Kingdom is estimated at USD 18.6 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 23.5 million by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 2.3%. While the UK continues to depend on imports, primarily from Peru and the Netherlands, domestic cultivation has been gaining ground, with acreage expanding by 9.4% in 2025 driven by efforts from local producers like The British Quinoa Company.
Margins are shaped by two levers: price premiums in organic quinoa, which commands 26% higher retail prices than conventional and health-food retailers and farm shops, which accounted for 38% of quinoa sales in 2025. However, limited consumer familiarity remains a drag, especially outside London and major urban centres.
The UK Food Standards Agency maintains oversight of labeling and allergen compliance, while post-Brexit import policies have marginally tightened customs checks, increasing logistics costs by 6-7% year-on-year.
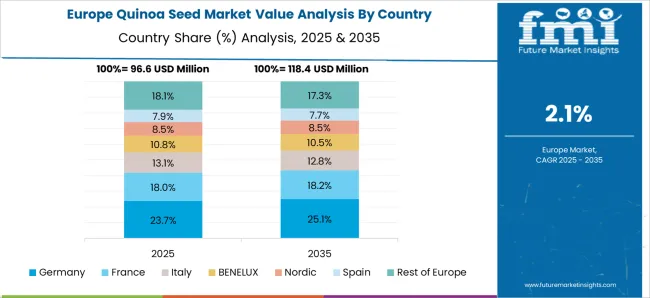
Germany’s quinoa seed demand is projected at USD 38.3 million in 2025 and forecast to reach USD 47.1 million by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 2.1%. While still import-reliant, local production expanded 6.2% in 2025, supported by subsidies for sustainable cropping under the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. Demand is rooted in plant-based diets, with quinoa featured in 19% of vegetarian and vegan SKUs launched in 2025.
Margins were driven by organic quinoa’s price premium in retail and demand from specialty bakeries and health-focused foodservice chains. A major friction persists, retail markups remain high due to limited domestic supply and fragmented small-batch imports.
Regulatory backing from the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) reinforced consumer trust through pesticide residue compliance.
France’s quinoa seed demand is estimated at USD 30.5 million in 2025 and projected to reach USD 35.7 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 1.6%. France remains Europe’s top importer of quinoa, although domestic production, largely in Pays de la Loire, met 15% of national demand in 2025.
Margins remain modest due to two challenges:
France applies EU organic certification (Regulation 2018/848), with stricter residue checks post-2023.
Japan’s quinoa seed market is valued at USD 21.4 million in 2025 and expected to reach USD 26.6 million by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 2.2%. Despite high price sensitivity, imports have risen steadily-driven by quinoa’s positioning in diabetic and heart-health diet regimens.
Margins are shaped by: 1. inclusion in high-value-added product categories such as bento meals and functional cereals; 2. limited but consistent sales through premium health retailers. However, domestic production remains negligible due to agro-climatic constraints and low farmer uptake.
Japan regulates quinoa under the Food Sanitation Act and Positive List System, ensuring zero tolerance for unapproved pesticides. A 2025 JHFA survey found quinoa recognition at 58% among health-conscious urban consumers, with highest recall among 30-45 age group.
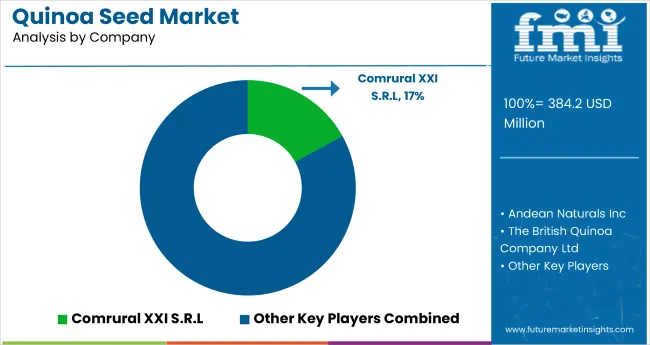
The players in the quinoa seed market are focusing on geographic diversification and vertical integration to stabilize supply chains and meet evolving consumer demand. South American exporters such as Quinoabol SRL and Irupana Andean Organic Food S.A. have invested in post-harvest processing units to reduce export-grade losses, while brands like The British Quinoa Company and Alter Eco are expanding traceable sourcing models across the UK and EU. USA-based Above Food Inc. has prioritized proprietary varietals and regenerative cultivation partnerships to ensure year-round supply alignment.
Short-term market dynamics are influenced by production volatility in Peru and Bolivia-regions that account for over 70% of global supply. Input cost inflation and climate-linked yield fluctuations prompted players to enter forward contracts with large retailers, hedging risk but tightening margins. M&A activity remains targeted, with buyers preferring players with established B2B distribution or certified-organic portfolios.
Over the next decade, players with direct control over cultivation and access to premium health-food retail networks are expected to outperform. Those dependent on fragmented sourcing or bulk wholesale channels may face growth stagnation under tightening import regulations and rising food traceability norms.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size Covered | 2025 to 2035 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Units | USD Million (Value), Tons (Volume) |
| Segments Covered | Seed Type, Colour, Application, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Seed Type | Organic, Inorganic |
| Colour | White, Red, Black, Others |
| Application | Direct Consumption, Processed Products |
| Distribution Channel | Online Stores, Offline Stores |
| Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, Middle East & Africa |
| Key Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, Netherlands, United Kingdom, Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Above Food Inc., Alter Eco, Irupana Andean Organic Food SA, Andean Naturals, Quinoabol SRL, The British Quinoa Company, Ancient Harvest, Arrowhead Mills Inc. |
The global quinoa seed market is estimated to be valued at USD 384.2 million in 2025.
The market size for the quinoa seed market is projected to reach USD 482.0 million by 2035.
The quinoa seed market is expected to grow at a 2.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in quinoa seed market are organic and conventional.
In terms of form, whole grain segment to command 52.7% share in the quinoa seed market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Quinoa Starch Market Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Paper Bag Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Processing Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Biostimulants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Health Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Additives Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Seed Coating Material Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Packaging Market Analysis – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Binders Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Market Share Breakdown of Seed Cracker Manufacturers
Seed Polymer Market
Seed Testing Services Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2018-2028
Teaseed Cake Market – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
The Linseed Oil Market is Analysis by Nature, Product Type, Application, and Region from 2025 to 2035
Rapeseed Protein Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Flaxseed Gum Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rapeseed Oil Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Analysis and Growth Projections for Hempseed Milk Business
Rapeseed Meal Market Analysis by Type, Application, Nature, and Region Through 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA