The Rail Logistics Market is estimated to be valued at USD 439.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 743.3 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% over the forecast period. Analysis of growth elasticity relative to macroeconomic indicators such as GDP expansion, industrial output, and trade volumes indicates a highly responsive correlation, where freight demand accelerates with economic recovery and infrastructure investments.
Historical data from 2020 to 2025 shows market growth from USD 337.7 billion to 439.3 billion, supported by increased bulk commodity movements and government-led rail modernization programs. The forecast period suggests that for every 1% rise in global GDP, rail logistics demand could increase by approximately 0.8%, driven by cost advantages over road transport and emphasis on energy-efficient freight movement.
Elasticity also reflects sensitivity to fuel price volatility and trade policy shifts, as rail offers resilience during oil price surges and cross-border trade normalization. With volumes expected to surge in agricultural exports, mining output, and containerized cargo, the market advances to USD 571.4 billion by 2031 and 743.3 billion by 2035, maintaining consistent alignment with industrial growth. Providers prioritizing digitized scheduling, intermodal integration, and capacity optimization will capture maximum value as economic cycles influence freight distribution efficiency.
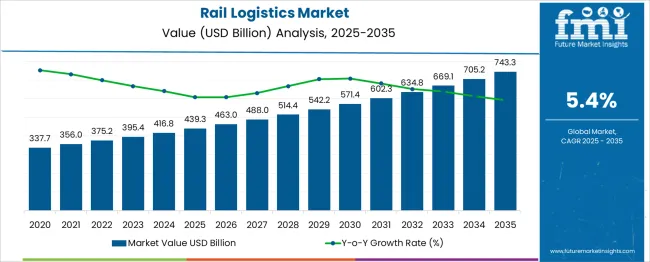
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Rail Logistics Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 439.3 billion |
| Rail Logistics Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 743.3 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.4% |
The rail logistics market contributes a substantial but variable share across its parent markets. Within the freight transportation and logistics market, rail logistics represents 20–22 %, as land-based freight is shared with road haulage, pipelines, and intramodal transfers. In the rail freight services market, rail logistics dominates with a 65–70 % share, since all rail-based cargo movements, inclusive of wagons and terminal services, fall under this segment. In the intermodal and multimodal logistics market, its share is 30–32 %, reflecting rail’s pivotal role in container transport and cross-border supply chains.
Within the broader supply chain and distribution management market, rail logistics captures 10–12 %, as it represents one module among transport planning, warehousing, and last-mile delivery. In the infrastructure and rail terminals equipment market, rail logistics contributes 8–10 %, given the diversity of assets including cranes, loaders, and yard management systems. While some shares may appear modest, rail logistics is growing due to increasing intermodal adoption, rising fuel costs detouring long-distance road haulage, and sustainability initiatives favoring lower-carbon transport. Rail investments in digital tracking, automation at terminals, and container-electric hybrid wagons are further enhancing its appeal in global supply chain networks.
The rail logistics market is undergoing sustained growth as industries prioritize cost-efficient and sustainable transportation solutions for large-volume goods. Rising congestion and emissions concerns in road transport have positioned rail as a reliable and environmentally favorable alternative for both domestic and cross-border logistics.
Advancements in intermodal infrastructure, digital tracking systems, and government investments in railway modernization are enhancing capacity and service quality. Increasing demand for bulk commodities and long-distance shipments, alongside evolving trade patterns, is expected to drive continued adoption of rail logistics.
Strategic collaborations between rail operators, port authorities, and logistics service providers are creating integrated supply chain solutions, paving the way for future growth. Market participants are focusing on optimizing operational efficiency, reducing transit times, and improving customer experience through digitization and asset utilization improvements, which are expected to unlock further opportunities across diverse industrial sectors.
The rail logistics market is segmented by service, cargo, distance, end use, and geographic regions. The rail logistics market is divided into Freight transport, Warehousing, Intermodal logistics, Supply chain management, and Digital solutions. The cargo of the rail logistics market is classified into Bulk, Liquid, Containers, Automotive, and Temperature-controlled goods. Based on the distance, the rail logistics market is segmented into Long-haul, Short-haul, and Medium-haul. The rail logistics market is segmented by end use into Mining, Agriculture, Energy, Manufacturing, Construction, Retail, Automotive, Chemical, Food & Beverages, and Others. Regionally, the rail logistics industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
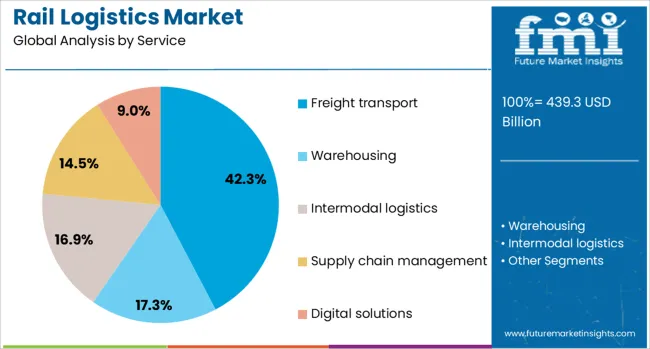
When segmented by service, freight transport is projected to account for 42.30% of the total market revenue in 2025, establishing itself as the dominant service segment. This leadership is attributed to its ability to handle high volumes of cargo efficiently while offering competitive pricing compared to other modes.
Rail freight has been preferred for its predictable schedules, greater energy efficiency, and resilience against fuel price volatility. Investments in double-stacking, electrification, and modern wagon designs have enhanced capacity and operational performance, enabling freight transport to meet diverse industry needs.
The segment’s prominence has also been supported by growing demand from industries such as mining, agriculture, and manufacturing, which rely heavily on rail for moving raw materials and finished goods over medium and long distances.
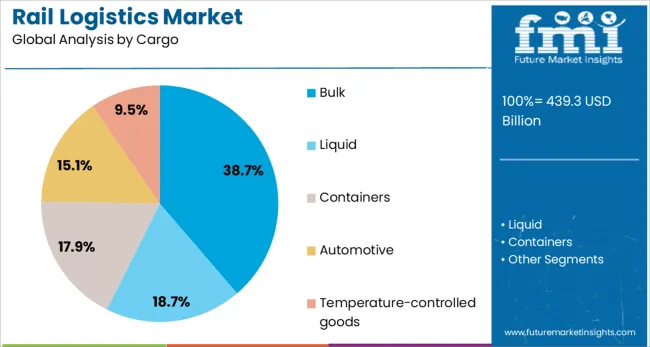
In terms of cargo, bulk shipments are expected to hold 38.7% of the market revenue in 2025, positioning this subsegment as the leading category. The segment’s strength has been reinforced by its suitability for transporting commodities like coal, grains, ores, and chemicals in large quantities.
Bulk cargo has benefited from rail’s inherent capability to move massive loads safely and cost-effectively while minimizing environmental impact per ton-kilometer. Upgrades in loading and unloading infrastructure, combined with improved scheduling and capacity planning, have reduced turnaround times and improved reliability for bulk transport.
Sustained demand from energy, construction, and agricultural sectors has maintained steady volumes, ensuring the bulk segment’s continued prominence within the market.
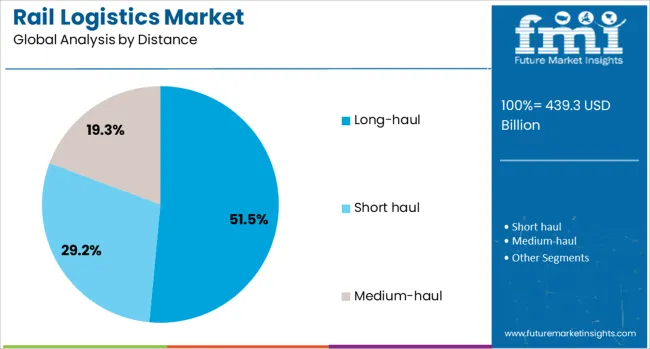
When analyzed by distance, long-haul shipments are forecast to capture 51.5% of the market revenue in 2025, securing their position as the leading segment. This leadership has been driven by rail’s competitive advantage over long distances, where it delivers lower per-unit costs and higher reliability compared to road transport.
The ability to connect major production centers with ports and consumption markets over extended routes has reinforced rail’s role in facilitating domestic and international trade flows. Enhancements in track infrastructure, signaling systems, and intermodal terminals have further improved transit times and service quality on long-haul corridors.
Industries prioritizing cost efficiency and sustainability have increasingly opted for rail for long-distance needs, sustaining this segment’s dominance as trade networks expand and supply chains become more integrated.
Rail logistics encompasses the movement of goods via freight trains, rail yards, intermodal terminals, and warehousing systems. These services are provided by rail operators, integrated logistics firms, and terminal operators across global corridors. Demand is driven by efficiency in long-distance cargo transport, land‑based network consistency, and capacity advantages over road haulage. Providers offering high‑capacity wagons, real‑time tracking platforms, and seamless terminal transfers have been positioned to support freight movement across regions. Equipment reliability during transit and cargo protection in loading and unloading continue to guide procurement and contract decisions within supply chains and logistics integrators.
Growth in rail logistics has been supported by the expansion of cross‑border trade corridors and increasing shipment volumes of bulk and containerised freight. Rail transport offers a lower cost per tonne-kilometer compared to road alternatives for long-haul routes. Governments have promoted rail freight corridors through infrastructure spending on rail tracks, terminals, and connectivity hubs. Bulk commodities such as coal, minerals, and grain have relied heavily on rail networks for volume movement. Supply chains requiring consistent delivery schedules over long distances have favoured rail services. Operators offering intermodal transfer options that reduce dock time and facilitate first‑mile and last‑mile connections have attracted large industrial and retail clients seeking reliable transport efficiency.
Expansion has been limited by uneven infrastructure development across regions, resulting in capacity bottlenecks and scheduling gaps on key corridors. Maintenance needs and outdated rail yard systems have reduced throughput efficiency and increased operating costs. Access to last‑mile connectivity in inland and remote terminals remains constrained by a lack of rail sidings or intermodal links. Variability in gauge standards and customs clearance procedures across borders has introduced delays and planning complexity. Funding constraints have slowed the modernization of terminal handling equipment and track upgrades. Competition from road transport over shorter distances remains significant in areas with fragmented rail networks. Performance reliability has been negatively impacted by disruptions as a result of weather, congestion, or industrial action affecting rail stake systems.
Opportunities are being identified in expansion of intermodal logistics services combining rail with trucking or inland water transport for end-to-end solutions. Development of logistics hubs adjacent to rail terminals enables consolidation, warehousing, and last‑mile distribution support. Partnerships with retail, manufacturing and e‑commerce firms allow tailored freight contracts and regular lane commitments. Use of technologies such as real‑time tracking, automated yard systems, and cargo condition monitoring enhances the value proposition. Rail-linked special economic zones and trade corridors continue to attract large-scale logistics investment. Dedicated freight lines for high-demand routes and express cargo services offer new service tiers. Supply of scheduled rail corridors with predictable transit times and cargo booking systems is gaining traction among shippers.
Adoption of cloud‑based digital platforms for shipment tracking, cargo booking and carrier allocation has accelerated across rail logistics. Integration of predictive maintenance tools in locomotive and wagon systems has reduced downtime and improved asset reliability. Flexible capacity provision through shared network access and dynamic train scheduling has enhanced responsiveness to seasonal demand. Focus on terminal automation, including robotic container handling and automated gate systems, is growing. Use of temperature‑controlled rail containers for perishable goods and pharmaceuticals is being expanded. Providers offering end‑to-end visibility from origin to delivery through unified dashboards have gained popularity. Coordination among cross‑border rail operators via shared scheduling and unified customs documentation systems continues to support seamless corridor transit.
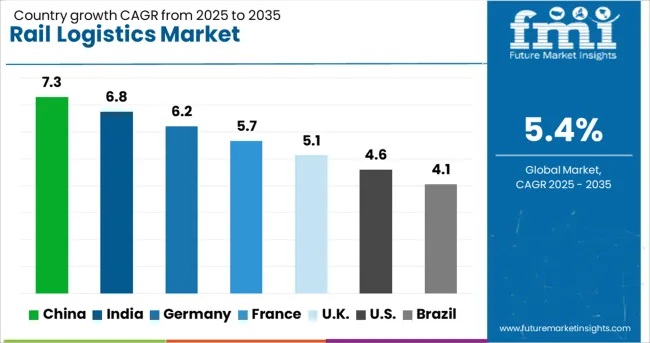
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.3% |
| India | 6.8% |
| Germany | 6.2% |
| France | 5.7% |
| UK | 5.1% |
| USA | 4.6% |
| Brazil | 4.1% |
The rail logistics market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% between 2025 and 2035, driven by rising freight demand, cost efficiency over road transport, and growing need for intermodal connectivity. China leads with 7.3% CAGR, supported by high-volume freight corridors and infrastructure expansion. India follows at 6.8%, fueled by bulk commodity transportation and capacity upgrades. Among OECD markets, Germany posts 6.2%, with growth supported by digital tracking systems and high-speed cargo trains. France records 5.7%, emphasizing multimodal hubs and enhanced network efficiency, while the United Kingdom grows at 5.1%, with strong adoption of rail-based distribution for containerized goods.The report covers over 40 countries, with detailed insights for five profiled below.
China is expected to register a 7.3% CAGR, the highest among major markets, supported by large-scale freight network development and cross-border rail trade expansion. The Belt and Road Initiative continues to strengthen China’s international rail connectivity, creating consistent demand for logistics services integrating inland ports and distribution hubs. Containerized freight movement remains dominant for intercontinental trade, especially with Europe and Central Asia. Advanced signaling systems and automation in freight scheduling are being deployed to improve network capacity. Cold chain rail solutions are also gaining traction for transporting perishable goods across long distances efficiently.
India is projected to achieve a 6.8% CAGR, driven by the movement of bulk commodities such as coal, steel, and agricultural goods. The development of dedicated freight corridors has increased operational speed and reduced congestion on passenger lines. Modernization of wagons and the adoption of GPS-based tracking systems have improved efficiency in supply chain management. Intermodal integration with road and port networks is strengthening the movement of containerized goods. Public-private partnerships in rail infrastructure and logistics parks are encouraging large-scale investments, creating opportunities for technology-driven rail operations and digital platforms for shipment visibility.
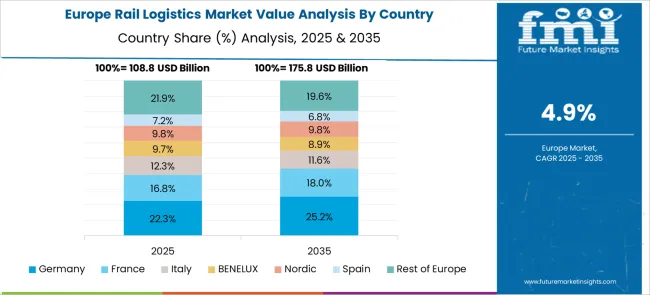
Germany is forecasted to grow at a 6.2% CAGR, supported by its strategic position as a European logistics hub. Rail freight plays a critical role in linking industrial regions with major seaports for automotive, chemicals, and machinery exports. Investments in digital freight solutions, predictive maintenance, and automated load-handling systems are improving operational efficiency. Integration of rail with inland waterway and road networks supports seamless multimodal connectivity. Growing demand for high-speed freight corridors for time-sensitive cargo, such as express parcels, is shaping future infrastructure developments in Germany.
France is projected to expand at a 5.7% CAGR, driven by demand for rail-based solutions in automotive, construction materials, and agricultural goods. Upgrades in signaling and terminal handling facilities have improved punctuality and operational performance across major freight corridors. Regional logistics operators are adopting real-time digital platforms for shipment visibility and inventory control. The development of rail-connected logistics parks is encouraging long-haul cargo movement within domestic and international routes. Increased cooperation between rail operators and port authorities enhances intermodal freight efficiency, reducing delays for containerized goods transport.
The United Kingdom is expected to grow at a 5.1% CAGR, supported by rising demand for rail-based container transport linked to maritime ports. Rail logistics has become essential for reducing congestion on road networks and improving cost efficiency for bulk cargo movements. Infrastructure development projects are focusing on enhancing capacity at freight terminals and improving double-stack container handling systems. Digital freight booking platforms and tracking solutions are increasingly being adopted by logistics operators to streamline operations. The expansion of dedicated freight routes to industrial hubs ensures faster delivery timelines for high-value goods.
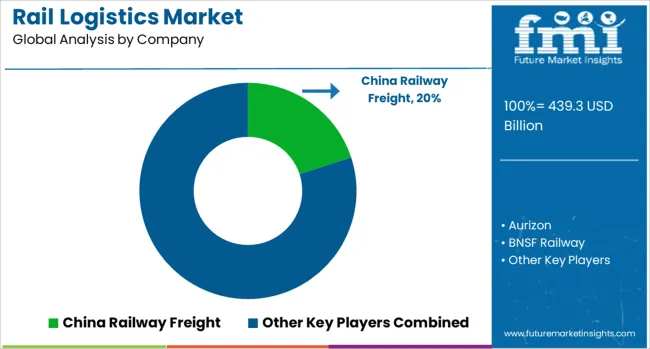
The rail logistics market is dominated by major freight operators such as China Railway Freight, Aurizon, BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway (CN), Canadian Pacific Kansas City (CPKC), CSX Transportation, Deutsche Bahn (DB Cargo), Euro Cargo Rail, Ferromex, Genesee & Wyoming, and Indian Railways. These companies provide critical bulk and containerized cargo transportation solutions across commodities like coal, minerals, automotive parts, chemicals, and agricultural products.
BNSF, CSX, and CPKC lead in North America with extensive networks and advanced intermodal services, supported by investments in real-time tracking and predictive maintenance systems. In Europe, Deutsche Bahn and Euro Cargo Rail dominate through integrated multimodal logistics solutions and cross-border freight operations. China Railway Freight maintains a stronghold in Asia with its expansive network and role in Belt and Road Initiative trade corridors, while Indian Railways leverages its government-backed infrastructure for bulk commodity transport. Aurizon leads in Australia, specializing in mining and resource-based rail logistics, and Ferromex plays a pivotal role in Mexico’s industrial freight movement.
The industry faces high entry barriers due to capital-intensive infrastructure, regulatory compliance, and the need for long-term asset investments. Competitive differentiation depends on network coverage, service reliability, intermodal connectivity, and integration of digital solutions like IoT-based asset monitoring and blockchain for secure documentation. Market rivalry is driven by rising demand for cost-efficient freight alternatives to road transport and the growing need for sustainable rail solutions in line with emission reduction goals. Future competitiveness will hinge on automation, energy-efficient locomotives, and real-time data analytics to optimize scheduling and improve operational resilience.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 439.3 Billion |
| Service | Freight transport, Warehousing, Intermodal logistics, Supply chain management, and Digital solutions |
| Cargo | Bulk, Liquid, Containers, Automotive, and Temperature-controlled goods |
| Distance | Long-haul, Short haul, and Medium-haul |
| End Use | Mining, Agriculture, Energy, Manufacturing, Construction, Retail, Automotive, Chemical, Food & beverages, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | China Railway Freight, Aurizon, BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway (CN), Canadian Pacific Kansas City (CPKC), CSX Transportation, Deutsche Bahn (DB Cargo), Euro Cargo Rail, Ferromex, Genesee & Wyoming, and Indian Railways |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by service type (bulk freight, intermodal services, containerized transport, automotive logistics) and industry application (mining, agriculture, chemicals, automotive, consumer goods), with demand driven by growing international trade and e-commerce supply chain optimization. Regional trends highlight strong growth in Asia-Pacific through industrial expansion and cross-border corridors, while North America and Europe focus on digitization, electrification, and infrastructure modernization. Innovation trends include AI-based network optimization, predictive maintenance, automated yard management, and low-emission locomotives to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. |
The global rail logistics market is estimated to be valued at USD 439.3 billion in 2025.
The market size for the rail logistics market is projected to reach USD 743.3 billion by 2035.
The rail logistics market is expected to grow at a 5.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in rail logistics market are freight transport, warehousing, intermodal logistics, supply chain management and digital solutions.
In terms of cargo, bulk segment to command 38.7% share in the rail logistics market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Railway Communication Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Rolling Stock Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Air Conditioning System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Braking System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Transit Vehicle Glass Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway CNC Wheel Lathe Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail System Dryer Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Flatcar Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Freight Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railroad Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Car Drying System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Gearbox Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Roof Switches Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Tank Cars Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Window Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Maintenance Machinery Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Rail Freight Digital Transformation Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Control Stands Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Horn Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA