The Railway Maintenance Machinery Market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.9 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 10.4 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% over the forecast period. This growth reflects both a stable demand in mature regions and rising traction in emerging economies. In 2025, Europe and North America collectively hold around 57% of the global market share due to strong rail infrastructure and scheduled maintenance programs. However, their combined share is expected to erode to 48% by 2035, as Asia-Pacific gains momentum, increasing from 31% in 2025 to 41% by 2035, driven by significant rail expansions in countries like India, China, and Southeast Asia. Notably, countries investing in high-speed rail and freight corridors are accelerating procurement of advanced machinery for track alignment, tamping, and diagnostics. Between 2027 and 2032, autonomous and semi-autonomous rail maintenance equipment is expected to capture 18% of total machinery sales, up from just 6% in 2025, contributing to share erosion of traditional OEMs. Additionally, local manufacturers in emerging markets are increasing their presence through cost-effective solutions, which could displace established global brands in price-sensitive tenders. Thus, incumbents must innovate and adapt regionally to retain market share against intensifying global and local competition.
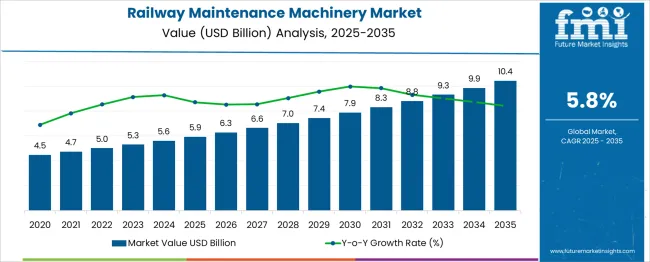
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Railway Maintenance Machinery Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 5.9 billion |
| Railway Maintenance Machinery Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 10.4 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.8% |
The railway maintenance machinery market is witnessing notable expansion, driven by increasing investments in rail infrastructure modernization, safety mandates, and network electrification. With governments prioritizing sustainable mass transit systems, there has been a surge in track renovation and maintenance activities across both developed and emerging economies.
Automation and digital monitoring integration have become critical, enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities and reducing track downtime. Lifecycle extension of aging rolling stock and a growing focus on high-speed rail corridors are pushing demand for advanced machinery solutions that ensure operational efficiency and safety.
Additionally, public-private partnerships and increased funding for urban and freight rail projects are supporting long-term growth. Innovations in hydraulics, machine vision, and GPS-based diagnostics are expected to redefine equipment performance standards, further consolidating the role of technologically advanced machinery in future railway upkeep strategies.
The railway maintenance machinery market is segmented by product, channel, application, technology, end user, and geographic regions. The product of the railway maintenance machinery market is divided into Tamping machines, stabilizing machinery, Ballast cleaning machinery, Rail handling machinery, surfacing machinery, and others. In terms of the channel, the railway maintenance machinery market is classified into OEM and Aftermarket. Based on the application, the railway maintenance machinery market is segmented into Ballast track and Non-ballast tracks. The technology of the railway maintenance machinery market is segmented into Fully-automatic, Manual, and Semi-automatic. The end users of the railway maintenance machinery market are segmented into Railway infrastructure companies, Contractors, Railway operators, and others. Regionally, the railway maintenance machinery industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
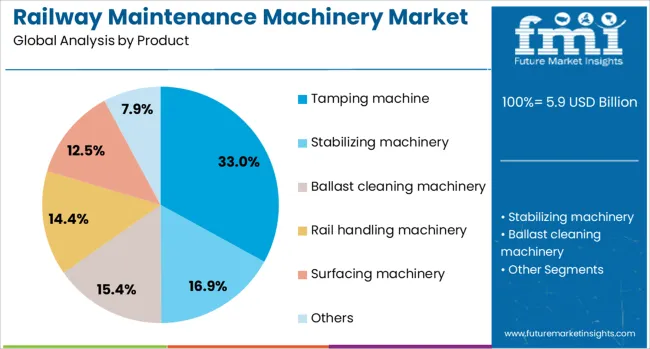
Tamping machines are projected to command a 33.00% revenue share in the railway maintenance machinery market by 2025, emerging as the leading product segment. Their widespread adoption is attributed to their ability to restore track geometry by compacting ballast under railway sleepers, ensuring alignment and stability.
As rail traffic intensifies, the need for efficient and automated track correction tools has increased, and tamping machines have become essential for maintaining smooth, safe rail operations. Their compatibility with mechanized maintenance programs and suitability for high-speed tracks make them indispensable in both freight and passenger corridors.
Increased focus on minimizing manual labor, reducing track possession times, and enhancing long-term track performance is reinforcing their role as a core component of modern railway maintenance fleets.
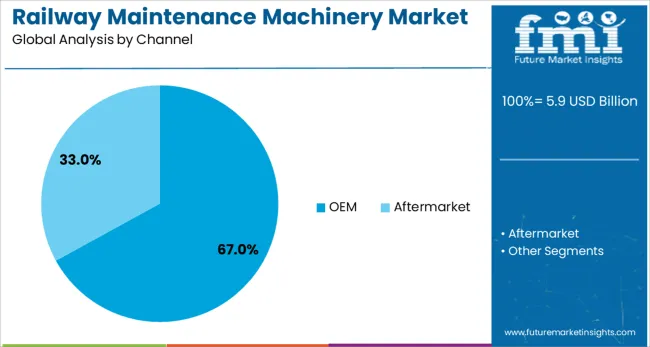
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are expected to account for 67.00% of the revenue share in 2025, solidifying their leadership in the distribution landscape. This dominance stems from the demand for technologically integrated, reliable, and warranty-backed equipment that meets regulatory and operational standards.
OEMs offer customization, faster service support, and post-delivery upgrades, which are highly valued by public transport authorities and private operators alike. Their ability to deliver machines embedded with telemetry, AI-based diagnostics, and modular maintenance capabilities further enhances lifecycle value.
With governments emphasizing safety and performance certifications, procurement from OEMs ensures compliance, boosting their share in both new deployment and replacement cycles.
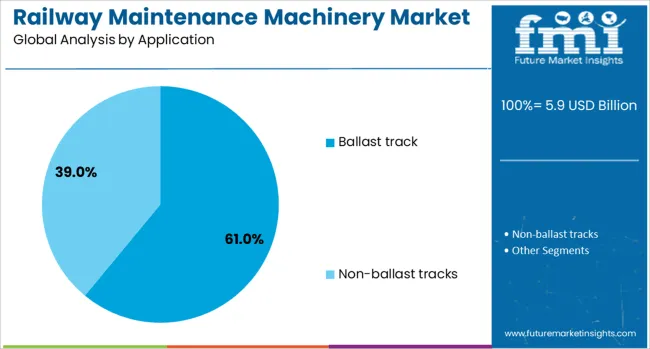
Ballast track applications are forecast to lead the market with a 61.00% share in 2025, underscoring their critical role in track infrastructure. The prevalence of ballast tracks in global railway networks, especially in long-distance and freight routes, has sustained the need for specialized maintenance machinery.
These tracks require regular realignment and compaction to prevent deformation and maintain ride quality, making them machinery-intensive. The focus on operational uptime, especially in heavy-haul and mixed-traffic corridors, necessitates periodic tamping, ballast cleaning, and stabilization tasks dependent on high-performance machinery.
Additionally, track upgrade projects and rural network expansions are primarily ballast-based, further elevating the demand for dedicated maintenance equipment in this segment.
The railway maintenance machinery market is advancing due to the rising focus on uninterrupted rail operations, asset lifespan extension, and safety compliance. Track inspection, tamping, ballast regulation, and grinding equipment are in high demand across freight and passenger networks. Regular upkeep ensures ride comfort and prevents track failures, making machinery essential for scheduled and emergency repairs. Demand is supported by network upgrades, expansion projects, and contractor outsourcing. Growth is also fueled by efforts to improve worksite efficiency, reduce downtime, and support non-disruptive rail maintenance.
As railway networks handle more frequent services, infrastructure wear and tear has become a critical concern. Track integrity must be preserved to support both high-speed and heavy-haul operations. Maintenance activities like rail welding, geometry correction, and tie replacement require specialized equipment capable of high throughput with minimal disruption. National and regional rail operators are investing in efficient maintenance machinery to reduce breakdowns, extend asset life, and comply with operating standards. The shift toward continuous monitoring and planned intervention has placed greater emphasis on mechanized track care over manual efforts. With more railroads shifting from reactive to preventive approaches, demand for reliable machinery capable of addressing a wide range of tasks from tamping to ultrasonic rail flaw detection is increasing. These machines help maintain safety margins, minimize downtime, and ensure operational continuity. The overall reliance on rail as a transportation backbone makes maintenance machinery an indispensable part of infrastructure management.
Railway maintenance machinery represents a significant capital investment, especially for small operators or regional contractors. These machines are highly specialized, often built for single-use functions such as rail grinding, ballast profiling, or overhead line maintenance. Their high cost of acquisition and maintenance can deter broad adoption unless offset by long-term contracts or large fleet requirements. Additionally, fleet utilization must be carefully managed to justify procurement, especially in systems with low daily mileage or infrequent repairs. Training operators and maintenance teams to work with advanced machinery adds complexity and cost. Logistics related to transporting large track-bound equipment to remote or underdeveloped areas may also be inefficient. Smaller rail operators often depend on leasing models or shared access, which can restrict availability during peak maintenance seasons. These factors collectively make the procurement process slower and more risk-averse, especially in markets with tight infrastructure budgets or fragmented operational models.
Outsourcing of railway maintenance to third-party contractors has become an effective strategy for rail operators seeking efficiency and flexibility. These service providers often maintain their own fleets of multi-functional machinery, making procurement decisions based on project-specific demands. As public-private partnerships expand in infrastructure management, contract-based maintenance is growing, generating equipment demand across different geographic and climatic environments. Maintenance tenders typically require modern, compliant machinery, which encourages investment in updated fleets. Contractors working on high-speed rail segments, cargo corridors, or metro networks require fast, accurate, and mobile equipment capable of meeting safety and availability standards. Demand also increases with the need for short window repairs, where rapid deployment and withdrawal of equipment are essential to avoid service disruption. The expanding role of service providers reduces the burden on public rail agencies while boosting demand for durable and versatile machinery designed for regular and emergency use across rail categories.
Railway maintenance machinery must meet region-specific standards related to axle load, clearance profiles, braking systems, and emission norms. This limits the ability to manufacture standardized products for global markets, increasing design and compliance costs. In some regions, regulatory approvals for new machinery models are lengthy, slowing down fleet upgrades and deployment. Operational constraints such as access to track during busy traffic schedules or limited night-time maintenance windows reduce machinery utilization and prolong project timelines. Weather conditions can further delay operations, especially in regions prone to heavy rainfall, snow, or extreme temperatures. Infrastructure limitations such as lack of siding space or loading platforms for heavy machinery complicate logistics. These operational barriers create inefficiencies that discourage rapid market expansion, especially in emerging economies with less mature rail systems. Until harmonized guidelines and supporting infrastructure improve, vendors and operators must navigate region-specific restrictions, reducing the scalability of maintenance machinery deployment.
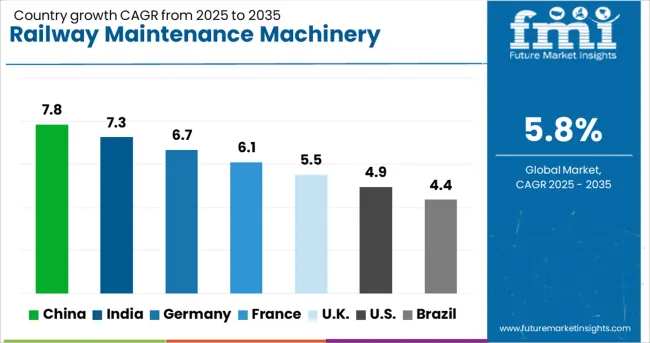
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 7.8% |
| India | 7.3% |
| Germany | 6.7% |
| France | 6.1% |
| UK | 5.5% |
| USA | 4.9% |
| Brazil | 4.4% |
The global multi-touch equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.0% through 2035, fueled by demand across consumer electronics, interactive displays, industrial control panels, and education technology. Among BRICS nations, China leads with a 13.5% growth rate, supported by high-volume manufacturing, OEM expansion, and rapid adoption in mobile and display devices. India follows at 12.5%, driven by digital learning initiatives, touchscreen POS systems, and domestic electronics assembly growth. Within the OECD region, Germany reports 11.5% growth, reflecting innovation in industrial and automotive touch interfaces, and precision component engineering. The United Kingdom grows at 9.5%, driven by adoption in retail, education, and design sectors. The United States, growing at 8.5%, focuses on interface innovation, durable commercial applications, and integration with gesture-based technologies. These countries lead in adapting multi-touch solutions to diverse digital environments. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
China is witnessing rapid growth in railway maintenance machinery market it is expanding steadily, recording a 7.8% CAGR. The country's extensive high-speed rail network and ongoing infrastructure upgrades drive sustained demand for advanced maintenance systems. Urban transit projects and freight corridor developments are also contributing to machinery adoption. Local manufacturers are investing in automation and AI-based inspection systems to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. The government supports large-scale procurement through public sector initiatives aimed at modernizing rail assets. Demand is especially high for track laying machines, ballast regulators, and ultrasonic flaw detectors. Domestic production capacity allows for cost-effective deployment across regional lines. Collaborations between rail operators and equipment manufacturers are fostering long-term service agreements. Innovations in predictive maintenance technologies are also gaining traction, supporting safer and more reliable rail operations.
India is seeing a 7.3% CAGR in its railway maintenance machinery market, driven by national-level infrastructure modernization and capacity expansion. With new freight corridors and semi-high-speed routes under construction, the need for precision maintenance tools has grown significantly. Indian Railways is prioritizing automated systems like ballast regulators, track tamping machines, and overhead inspection vehicles to improve efficiency and safety. Partnerships between public agencies and private firms are enabling access to advanced technology and international expertise. Local manufacturers are gradually scaling up production of essential machinery while collaborating with global companies for specialized systems. Digitization of maintenance logs and asset tracking is helping streamline operations. Government support for Make in India initiatives is accelerating the availability of homegrown solutions. Safety audits and compliance standards are contributing to sustained investment in smart monitoring equipment.
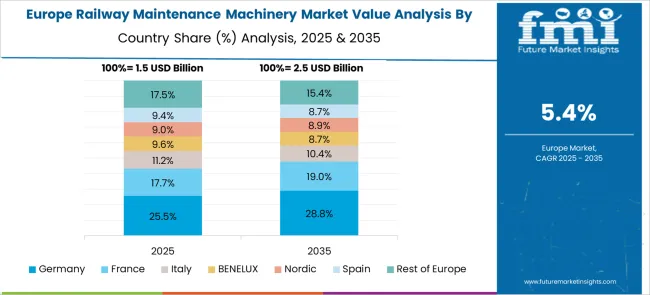
Germany is posting a 6.7% CAGR in the railway maintenance machinery sector, driven by stringent operational standards and continuous investment in infrastructure. As the country modernizes its rail networks to meet sustainability goals, operators are adopting advanced tools like laser-based inspection units and GPS-guided track alignment systems. The market benefits from a mature engineering base and well-established manufacturers known for high-precision machinery. Maintenance firms are offering end-to-end service models that cover diagnostics, repair, and real-time monitoring. Seasonal fluctuations and heavy commuter traffic require frequent track and signal maintenance, especially in regional and intercity networks. The government supports infrastructure renewal programs that include funding for state-of-the-art maintenance fleets. Real-time analytics and digital twins are being integrated into long-term maintenance planning. Export demand for German-built systems also contributes to the sector's innovation pipeline.
The United Kingdom is observing a 5.5 percent CAGR in the railway maintenance machinery market as the country focuses on renewing aging rail infrastructure. Upgrades to commuter lines and intercity services have led to increased investment in mobile track maintenance units and tunnel inspection systems. Operators are adopting compact and modular equipment suited to complex urban rail environments. Government-backed rail modernization initiatives are allocating budgets for automated inspection vehicles and smart diagnostics. British rail companies are working closely with engineering firms to develop machinery that meets both performance and environmental standards. Remote monitoring and condition-based maintenance are gaining traction, helping reduce disruptions and enhance scheduling accuracy. Partnerships with European and Asian manufacturers are introducing next-generation systems into the local market. Lightweight machinery and low-emission service units are also receiving attention in sustainability-focused projects.
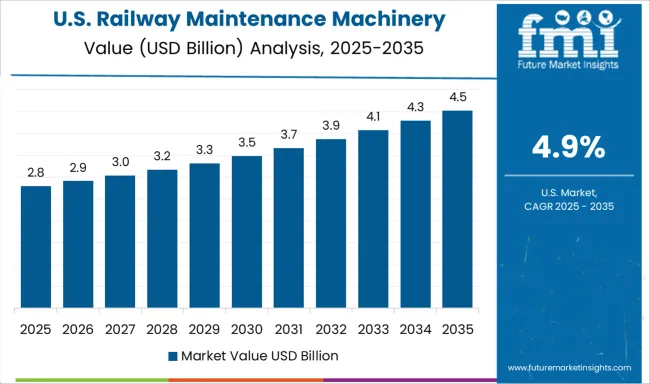
The United States is experiencing a 4.9 percent CAGR in the railway maintenance machinery market, supported by rising demand for rail freight and modernization of legacy systems. Federal and state agencies are investing in long-term infrastructure improvement plans, boosting procurement of rail grinders, ballast machines, and track geometry vehicles. The freight sector remains the primary driver, with Class I railroads deploying advanced equipment for extensive network coverage. North American manufacturers are upgrading machinery designs to include digital sensors and automated controls. There is also growing interest in hybrid-powered maintenance vehicles that align with emission reduction goals. Mobile maintenance teams are using GPS and remote data tools to monitor asset conditions in real time. Integration of maintenance software platforms is improving equipment utilization and workforce planning. Regional transit agencies are following suit, adopting scalable solutions for their expanding commuter rail systems.
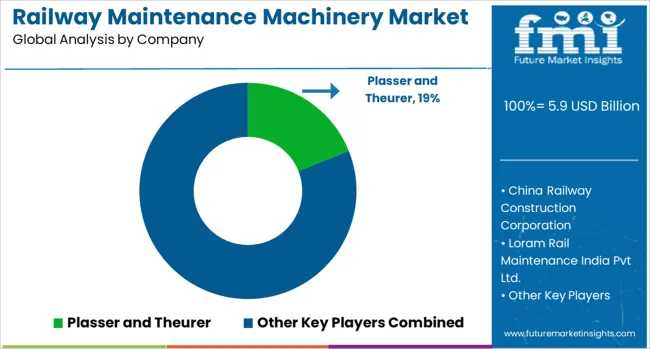
The Railway Maintenance Machinery Market continues to grow steadily as global rail networks prioritize track safety, minimize downtime, and enhance operational efficiency. As passenger and freight volumes increase, maintaining infrastructure through advanced mechanized systems has become a necessity rather than an option. Railway operators are investing in versatile machinery that can handle tasks such as tamping, ballast cleaning, rail grinding, and track inspection with greater precision and reduced human intervention. Leading manufacturers such as Plasser and Theurer, Loram Rail Maintenance India Pvt Ltd., and Harsco (Enviri Corporation) offer specialized equipment designed to meet varying maintenance needs across both high-speed and conventional railway systems.
Companies like China Railway Construction Corporation and Strukton Rail are also contributing significantly to the market by delivering integrated solutions for large-scale infrastructure upkeep, especially in countries undergoing extensive rail network expansions. These companies are increasingly focusing on modular, automated systems that allow for rapid deployment and minimal disruption to train schedules. Other players like Robel and Geatch Srl cater to more targeted needs, including small-scale machinery and customized maintenance units. The market is also witnessing growing demand for multi-functional and self-propelled equipment, which improves productivity on-site. As rail becomes a more critical mode of transport in both urban and cross-country transit, the need for consistent, cost-effective maintenance continues to support the demand for technologically capable machinery in this sector.
On March 19, 2025, L&T Technology Services launched TrackEi™, an AI-powered railway track inspection solution. Built on NVIDIA Jetson™, it uses edge AI and machine vision to detect defects in real time and enable predictive maintenance, enhancing railway safety, reliability, and operational efficiency globally.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 5.9 Billion |
| Product | Tamping machine, Stabilizing machinery, Ballast cleaning machinery, Rail handling machinery, Surfacing machinery, and Others |
| Channel | OEM and Aftermarket |
| Application | Ballast track and Non-ballast tracks |
| Technology | Fully-automatic, Manual, and Semi-automatic |
| End User | Railway infrastructure companies, Contractors, Railway operators, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Plasser and Theurer, China Railway Construction Corporation, Loram Rail Maintenance India Pvt Ltd., Harsco (Enviri Corporation), Strukton Rail, Robel, and Geatch Srl |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales vary by machinery type and application, with tamping and ballast-cleaning equipment dominating, while inspection and hybrid machinery grow fastest. Asia‑Pacific leads volume, while Europe and North America emphasize safety and automation. Pricing fluctuates with raw material and tech costs. Growth accelerates via IoT, predictive maintenance, digital twins, and green machinery under infrastructure and sustainability drives. |
The global railway maintenance machinery market is estimated to be valued at USD 5.9 billion in 2025.
The market size for the railway maintenance machinery market is projected to reach USD 10.4 billion by 2035.
The railway maintenance machinery market is expected to grow at a 5.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in railway maintenance machinery market are tamping machine, stabilizing machinery, ballast cleaning machinery, rail handling machinery, surfacing machinery and others.
In terms of channel, oem segment to command 67.0% share in the railway maintenance machinery market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Railway Communication Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Rolling Stock Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Air Conditioning System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Braking System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway CNC Wheel Lathe Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Flatcar Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Roof Switches Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Window Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Control Stands Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Horn Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway Axlebox Housing Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Railway After-Cooler Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Railway Emergency Valves Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Railway Generators Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Railway Coupler Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Railway Fishplate Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Railway Draft Gears Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Railway Air Filter Market – Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Railway Traction Motor Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA