The Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Treatment Market is anticipated to be valued at USD 434.1 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 788.2 million by 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.1%.
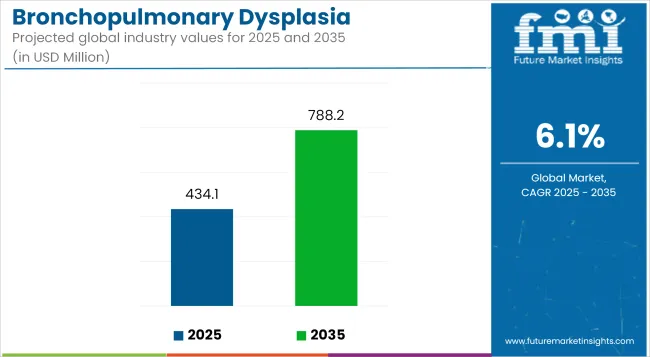
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 434.1 million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 788.2 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.1% |
The Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) Treatment Market is undergoing a structural evolution fueled by advancements in neonatal intensive care and a rising incidence of premature births globally. With the increasing survival rate of neonates born before 28 weeks gestation, demand for targeted therapies to manage chronic lung complications has significantly surged.
Recent annual reports from leading neonatal healthcare companies emphasize strategic investment in R&D for surfactant therapies, stem cell research, and oxygen delivery systems, all of which are enhancing patient care protocols. Industry analysts highlight the shift toward less invasive ventilation techniques and biologics as promising long-term growth avenues.
Furthermore, a multi-stakeholder approach including government policy support, specialized neonatal centers, and public-private partnerships is accelerating therapeutic innovation in this space. Over the coming years, market dynamics are expected to be driven by personalized medicine initiatives and increased clinical trials focusing on combination therapies for moderate to severe BPD cases.
Key manufacturers actively shaping the BPD treatment landscape include Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A., Medipost, Airway Therapeutics, Therabron Therapeutics, and AbbVie. These firms are consistently developing neonatal-focused biologics and respiratory support solutions to improve lung function in extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants. A major driver behind market acceleration is the integration of stem cell-based therapies, with Medipost and Airway Therapeutics investing in clinical-stage development programs showing promising safety profiles.
In Oct 2024, Airway Therapeutics, Inc. announced it will launch a multinational Phase 3 clinical trial of zelpultide alfa (rhSP-D) for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) and minimization of resulting lung damage in preterm infants.
“The approval of this Phase 3 trial is based on the successful completion of our randomized blinded Phase 1b study in the USA and Europe, in which no dose limiting toxicities were found and indications of efficacy were observed, Zelpultide alfa would be the first preventive therapy to protect babies from BPD, which is a debilitating lung disease.” said Airway Chairman, CEO and Chief Medical Officer Marc Salzberg, M.D.
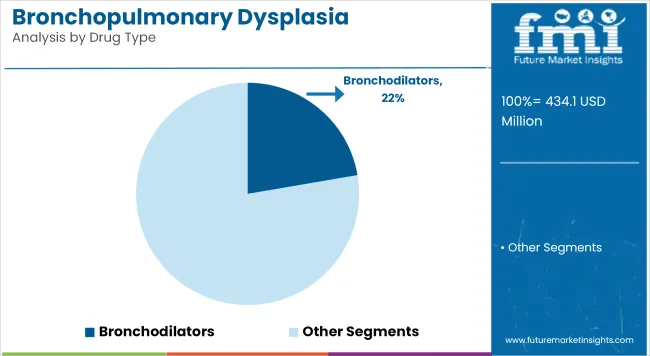
Bronchodilators are estimated to account for approximately 22.3% of total revenue in 2025, emerging as the dominant drug type in the BPD treatment landscape. Their adoption has been strongly supported by clinical protocols recommending bronchodilators for alleviating airway resistance in neonates with chronic lung disease.
The segment’s leadership has been reinforced by evidence-based inclusion in neonatal care guidelines, particularly in managing airflow limitation caused by pulmonary inflammation and smooth muscle constriction. A rising prevalence of premature births especially in low birth weight infants who are prone to lung underdevelopment has created consistent therapeutic demand.
Inhalation-based bronchodilator formulations have also been optimized for neonatal delivery, further enhancing clinical compliance. Healthcare providers have continued to favor bronchodilators for their rapid onset of action and ability to improve oxygenation, often serving as the first line of pharmacologic intervention. These factors, combined with strong physician familiarity and availability in hospital settings, have positioned bronchodilators as the most trusted and widely utilized drug category in BPD care protocols.
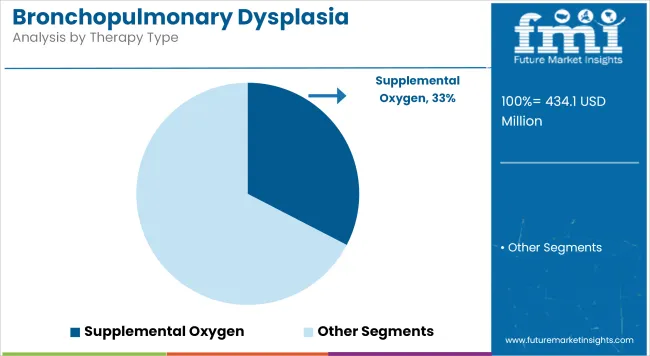
Holding an estimated 32.6% share of the BPD treatment market in 2025, supplemental oxygen therapy is considered the most widely applied therapeutic modality for managing respiratory insufficiency in neonates.
This dominance has been attributed to its critical role in stabilizing oxygen saturation levels during the acute and chronic phases of BPD. In neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), supplemental oxygen continues to be a foundational therapy used in both mechanical and non-invasive ventilation strategies.
The preference for this modality has been reinforced by its ability to immediately support gas exchange in underdeveloped lungs, thus preventing hypoxemia-related complications. Additionally, advancements in oxygen delivery systems such as high-flow nasal cannulas and pulse oximetry monitoring have improved therapy precision and minimized oxygen toxicity risk. The therapy’s broad applicability across all severity grades of BPD and its integration into both early intervention and post-discharge management protocols have further contributed to segment growth.
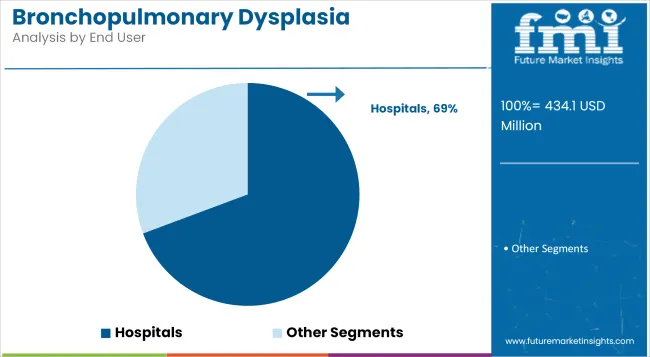
Hospitals are projected to capture nearly 69.3% of the market share in 2025, making them the leading end-user segment in the BPD treatment landscape. This dominance has been supported by the widespread presence of Level III and IV Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), which offer specialized respiratory support, surfactant administration, and ventilator-assisted therapies.
BPD treatment requires high-frequency monitoring, continuous oxygen titration, and access to pediatric pulmonologists facilities that are predominantly concentrated in hospital environments. The adoption of bundled neonatal care protocols and integrated clinical pathways in tertiary care hospitals has further strengthened the reliance on institutional settings for effective BPD management.
Additionally, hospitals are often the first point of care for premature births, which enables early initiation of evidence-based treatment plans. Technological capabilities, including access to advanced diagnostic tools and real-time respiratory monitoring, have positioned hospitals as the central hub for comprehensive BPD intervention and follow-up care.
Scalability limits of stem cell and nitric oxide therapies hinder broader adoption in developing markets
While stem cell and nitric oxide therapies are providing clinically favorable outcomes for severe cases of BPD, their application is limited by infrastructure and cost constraints. These modern interventions are largely available in tertiary care hospitals that have the capacity of specialized neonatal units but many low- and middle-income countries are not adequately catered for in this respect.
In areas where there is a high prevalence of preterm births, the lack of trained staff, storage systems, and continuous monitoring ability limits the real-world employment of such therapies. Moreover, operational restrictions in decentralized care environments impede the integration of these advanced options into routine neonatal practice.
This creates a dichotomy in the global market, with access in developing countries strongly focused on low-cost drug classes such as bronchodilators and diuretics. This gap is hampering the innovation-led expansion of the market, and is restricting treatment outcomes in high-need geographies.
Combinational therapy models drive long-term clinical and commercial value in BPD care
Newly emerging science on sequential and combinational treatment pathways are reshaping the BPD treatment landscape such that interventions become incremental and outcome-driven. Such regimens typically consist of a structured sequence of bronchodilators, surfactants and protein replacements, tailored to the fibrotic disease trajectory of the individual.
Such protocols have had positive impacts in terms of reducing mechanical ventilation dependency, promoting alveolar development and inflammation in both preventative and established BPD. Institutions with advanced neonatal research capabilities are pursuing testing of these strategies, with the advancement of fixed-dose combination formulations in clinical evaluation.
Growing interest from pharmaceutical players in these types of multi-action therapies are also setting the stage for commercial-scale solutions. With its unique focus on personalized, outcome-based treatment architecture, not only does this increase the chances of recovery but it also slashes hospitalization time and costs, realising long term clinical and economic value at both high-resource and tier two/three healthcare settings.
Market Outlook
The United States leads the geographical split of the global market for bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) treatment due to the high rate of preterm births and an established neonatal intensive care system as well as a robust pipeline of new innovative therapies for chronic lung disease in neonates.
Clinical management entails the application of oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, surfactants, corticosteroids, and, more recently, investigational biologics, with growing emphasis on personalized and preventive approaches.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
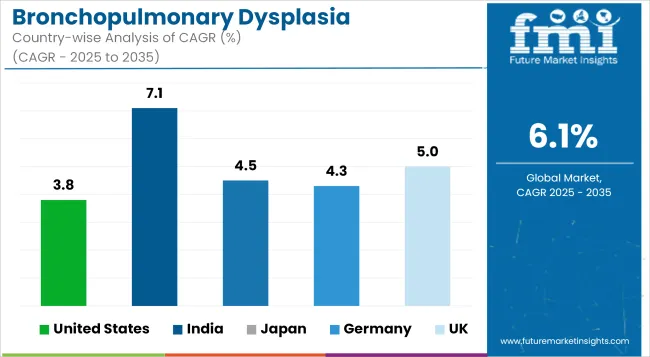
| United States | 3.8% |
Market Outlook
India’s BPD treatment market is growingat an increased pace owing to rising burden of preterm births, better NICU infrastructure, and rising utilization of standardized neonatal care protocols in both private and public hospitals. Rural areas have limited resources, but urban tertiary centers are up-taking non-invasive ventilation, surfactant therapy, and postnatal corticosteroids as part of the government and NGO initiatives.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| India | 7.1% |
Market Outlook
The Japan BPD treatment market features advanced technology, particularly in reducing ventilator use, enhancing maturation of the lung, and incorporating biomarker-based monitoring. Despite a low and decreasing birth rate and an increasingly aging population, Japan continues to pursue high-quality perinatal care, leading to improved survival of such infants born prematurely with BPD.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 4.5% |
Market Outlook
The BPD treatment market in Germany is more advanced and systematized owing to infrastructure with well-equipped perinatal centers, strong emphasis on standardized protocols in NICU, and improved clinical research on lung-protective ventilation and pharmacological approaches. Antenatal steroids, surfactant therapy, and caffeine citrate are used widely and hospitals are working to reduce ventilator-induced lung injury.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Germany | 4.3% |
Market Outlook
The UK BPD treatment market is growing at a vigorous pace due to allied NHS neonatal programs, a robust focus on premature infant outcome, and the in-clinic integration of non-invasive respiratory support, pharmacotherapy, and long-term pulmonary monitoring. This adds to therapeutic diversification and also falls in line with advances in neonatal care and ongoing trials of anti-inflammatory and growth factor-based therapies.
Market Growth Factors
Market Forecast
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 5.0% |
The bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) treatment market is being propelled by the growing frequency of preterm births and advancements made in neonatal intensive care. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia, or BPD, is a chronic lung disease that occurs in premature infants and often necessitates prolonged respiratory support and anti-inflammatory therapies.
Cell therapies for respiratory diseases and surfactant replacement innovations further bolster the market, along with a robust biologics pipeline. This is the most important aspect along with the types of stakeholders involved, such as pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, healthcare organization focusing on NICU facilities.
The market is segmented into Bronchodilators, Diuretics, Antibiotics, Steroids, Immunomodulators, and Surfactant Homeostasis.
The market is segmented into Nitric Oxide Therapy, Protein Replacement Therapy, Stem Cell Therapy, and Supplemental Oxygen.
The market is segmented into Hospitals, Nursing Homes, and Critical Care Centers.
The Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Treatment Market is analyzed across North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
The overall market size for bronchopulmonary dysplasia treatment market was USD 434.1 million in 2025.
The bronchopulmonary dysplasia treatment market is expected to reach USD 788.2 million in 2035.
Revolutionizing neonatal care with cutting-edge therapies for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia recovery.
The top key players that drives the development of bronchopulmonary Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A., AbbVie Inc., Medtronic plc, Merck & Co., Inc. and Philips Healthcare
Bronchodilators is expected to command significant share over the assessment period.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Cervical Dysplasia Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Barrett’s Esophagus with Dysplasia Treatment Industry Analysis by Type, Treatment, Distribution Channel, and Region through 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment Pumps Market Insights Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Pretreatment Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Air Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
CNS Treatment and Therapy Market Insights - Trends & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Acne Treatment Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Scar Treatment Market Overview - Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Soil Treatment Chemicals Market
Water Treatment Chemical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Algae Treatment Chemical Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
CRBSI Treatment Market Insights - Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Polymers Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA