The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market is estimated to be valued at USD 238.8 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2019.6 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.8% over the forecast period. A rolling CAGR view, applied in five-year windows, highlights both acceleration and momentum consolidation. Between 2025 and 2030, the compounded annualized rate stood at 24.5%, driven by a transition from USD 238.8 million to USD 694.5 million. The segment spanning 2026 to 2031 delivered a similar 24.1% annualized rise, confirming sustained investor alignment with hydrogen mobility alternatives. The 2027–2032 block maintained a 23.8% rolling CAGR, illustrating consistent capital infusion and early-stage scaling. From 2028 to 2033, the CAGR stabilized at 23.4%, with absolute gains growing from USD 453.1 million to USD 1,317.7 million.
The final five-year span (2030–2035) delivered a rolling CAGR of 23.3%, as values surged from USD 694.5 million to USD 2,019.6 million. These figures demonstrate that while CAGR values showed minor tapering, the market's core drivers remained intact. Large fleet conversions, hydrogen refueling buildouts, and regional policy mandates have collectively supported this high-consistency growth profile. No major rolling block experienced disruption, suggesting that long-term trajectory assumptions remain intact across OECD and selected ASEAN economies.
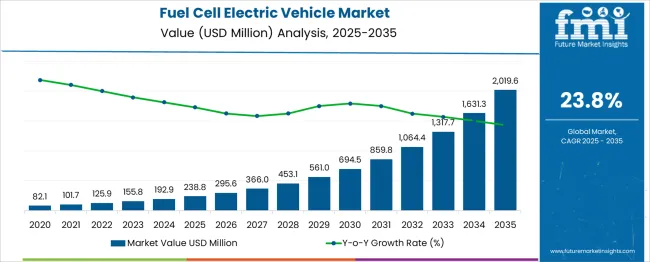
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 238.8 million |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 2019.6 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 23.8% |
The fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) market is witnessing strong momentum, driven by stricter emission norms, global hydrogen infrastructure development, and rising investment from automotive OEMs in clean propulsion systems. Government-led initiatives promoting zero-emission transport, coupled with declining hydrogen production costs and improved fuel cell durability, have positioned FCEVs as a long-range complement to battery-electric vehicles.
In urban and intercity mobility scenarios, range, refueling time, and fleet electrification goals are further accelerating adoption. With the convergence of policy backing and private-sector innovation, the sector is expected to transition from pilot deployments to mainstream scalability across both passenger and commercial vehicle categories.
The fuel cell electric vehicle market is segmented by fuel cell type, vehicle typerange category, and geographic regions. By fuel cell type of the fuel cell electric vehicle market is divided into Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), Phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFC)Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). In terms of vehicle type of the fuel cell electric vehicle market is classified into Passenger vehiclesCommercial vehicles. Based on range category of the fuel cell electric vehicle market is segmented into Medium Range (250 - 500 Miles), Short Range (below 250 Miles)Long Range (above 500 Miles). Regionally, the fuel cell electric vehicle industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
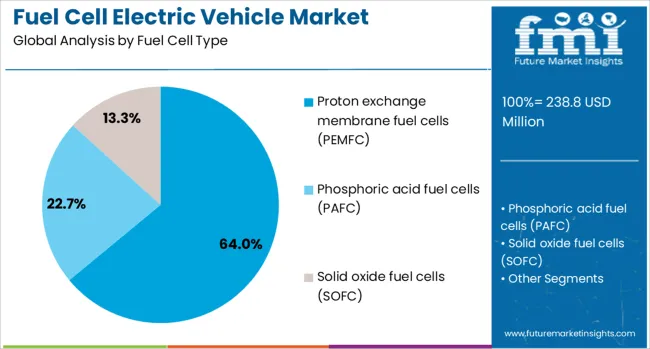
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) are projected to account for 64.0% of the revenue share in the fuel cell type segment by 2025, making them the market leader. The growth of this segment is being underpinned by its high-power density, compact size, and operational efficiency at low temperatures, which are critical for automotive integration.
The scalability of PEMFCs for both light-duty and heavy-duty applications, along with faster cold-start capabilities, has strengthened their commercial viability.
Increased funding into PEM stack R&D, coupled with higher adoption by global OEMs, is reinforcing the segment’s dominant position.
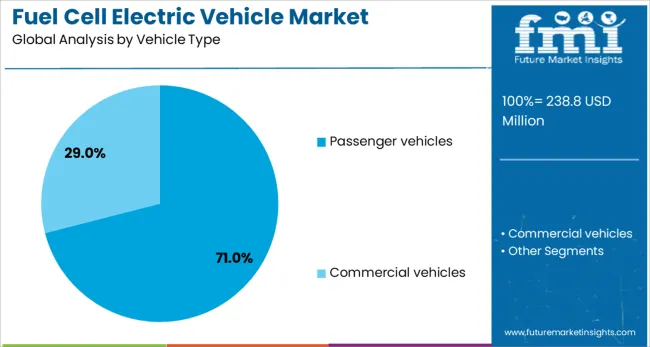
Passenger vehicles are estimated to contribute 71.0% of total revenue in the fuel cell electric vehicle market by 2025, making it the leading vehicle type. This segment’s dominance is being shaped by rising consumer demand for clean mobility, supported by national incentives, purchase subsidies, and toll exemptions across key automotive markets.
Automakers are aligning fuel cell development roadmaps with urban sustainability goals and long-distance travel requirements, encouraging fleet-scale rollouts.
Enhanced hydrogen fueling infrastructure and advancements in onboard hydrogen storage have also improved passenger vehicle performance metrics, making them a strategic entry point for mass FCEV adoption.
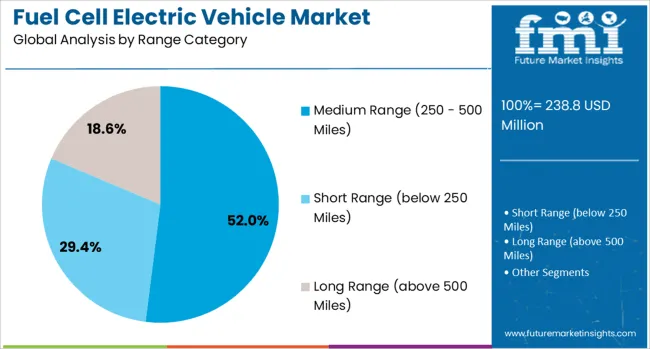
The medium-range category, covering 250 to 500 miles, is expected to account for 52.0% of market revenue in 2025, emerging as the leading range category. This segment’s leadership is being driven by the optimal balance it provides between operational efficiency, vehicle cost, and real-world usability for both urban commuters and regional travel.
Hydrogen refueling network expansion along major corridors is supporting broader use of medium-range FCEVs, addressing range anxiety without imposing excessive fuel tank weight.
Manufacturers are prioritizing this range bracket for initial commercialization, aligning it with infrastructure rollout phases and practical travel expectations of end users.
The global fuel cell electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23.8% between 2025 and 2035. China, India, and Germany are progressing well above this global pace, while the United Kingdom and United States remain slightly below. Within OECD countries, FCEV deployments have remained concentrated around commercial vehicle pilots and hydrogen corridor projects. ASEAN nations such as Singapore and Thailand have initiated fuel cell bus adoption through public-private trials. Fuel cell system integration, hydrogen fueling infrastructure, and commercial fleet conversions have dictated competitive momentum across regional markets. Export strategies have been aligned with hydrogen diplomacy initiatives. Automotive OEMs have collaborated with hydrogen producers, enabling upstream-to-downstream localization. Fleet-centric policies in Asia, compared to infrastructure-led efforts in Europe and North America, have created segmented growth paths for this vehicle segment.
China’s fuel cell electric vehicle market is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 32.1%, outpacing the global average by over 34%. State-sponsored hydrogen ecosystem development has sustained deployment across freight and transit fleets. Provincial subsidies and performance-linked incentives have boosted the commercialization of hydrogen trucks. Integration of domestic fuel cell stacks has improved supply-side economics for major OEMs.
India is projected to grow its fuel cell electric vehicle market at a CAGR of 29.8%, surpassing the global average by 25%. National hydrogen mission policies and city bus pilots have accelerated early-stage commercialization. Domestic R&D programs in polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) stacks have secured funding under clean mobility grants. Public sector logistics entities have initiated field trials in New Delhi, Bengaluru, and Ahmedabad.
Germany’s FCEV market is set to grow at a CAGR of 27.4% through 2035, 15% above the global average. Hydrogen mobility programs under Germany’s National Hydrogen Strategy have been applied to regional bus networks and light commercial vehicles. Urban refueling station expansion and localized hydrogen hubs have improved network coverage. Fuel cell truck demonstrations are being scaled across cross-border freight corridors in cooperation with Austria and France.
The United Kingdom is expected to grow its fuel cell electric vehicle market at a CAGR of 22.6%, slightly below the global average. Focused procurement by metropolitan transit authorities and hydrogen roadmap alignment have encouraged small-scale deployments. Scottish and Welsh bus routes have adopted hydrogen-electric propulsion under local clean air targets. Industry partnerships have supported stack manufacturing within the UK’s Midlands region.
The United States fuel cell electric vehicle market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 20.2%, remaining 15% under the global average. Adoption has remained focused in California, supported by state-level ZEV credits and dense refueling infrastructure. The Department of Energy’s H2@Scale initiative has catalyzed research in long-haul fuel cell truck applications. Fleet deployments by federal agencies have supplemented market stability.
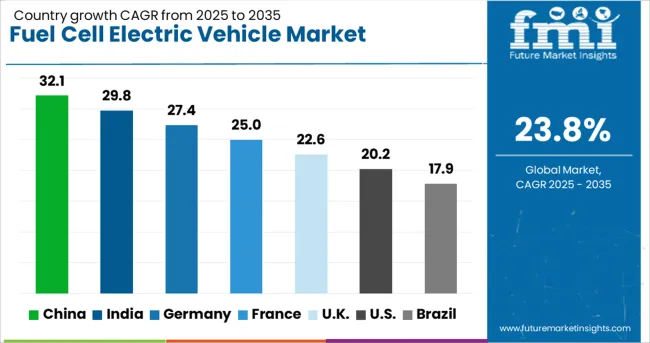
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 32.1% |
| India | 29.8% |
| Germany | 27.4% |
| France | 25.0% |
| UK | 22.6% |
| USA | 20.2% |
| Brazil | 17.9% |
The global fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) market is growing at a CAGR of 23.8% between 2025 and 2035. China leads at 32.1%, +35% above the global level, supported by BRICS-backed hydrogen mobility programs and strong policy incentives. Germany follows at 27.4%, +15% higher than the global average, driven by OECD investment in hydrogen transport networks and automotive innovation. France records 25.0%, +5% above the global rate, reflecting OECD efforts to strengthen zero-emission transport adoption. The United Kingdom stands at 22.6%, −5% under the global CAGR, influenced by a gradual build-out of hydrogen fueling capacity. The United States posts 20.2%, −15% below the global benchmark, where adoption is limited by infrastructure gaps despite OECD-linked clean transport initiatives. The trend shows BRICS economies, particularly China, moving faster than OECD peers, positioning hydrogen-powered vehicles as a key segment in future mobility.
China leads the fuel cell electric vehicle market with a CAGR of 32.1%, much higher than the global rate of 23.8%. This momentum is driven by state-supported hydrogen infrastructure, with over 300 hydrogen refueling stations operational by 2024. Government subsidies for commercial fleets have increased adoption in logistics and public transportation. Heavy trucks and buses are the dominant categories, as China targets mass deployment of hydrogen vehicles to complement battery-powered EV adoption. By 2030, production is expected to cross 1 million units, representing nearly half of global FCEV output.
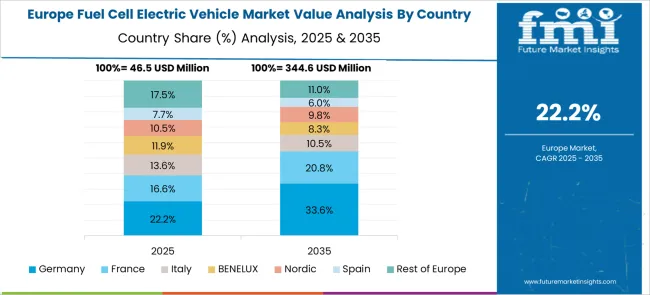
Germany shows a CAGR of 27.4%, surpassing the global 23.8% growth. Strong investment in green hydrogen and Europe’s largest pilot projects are positioning Germany as a core hub for FCEVs. German automakers are expanding production of passenger cars and light-duty FCEVs, complementing ongoing investments in battery-electric technology. More than 100 hydrogen refueling stations are active, covering key corridors across the country. Federal and EU-level funding for clean mobility has accelerated technology readiness, ensuring domestic adoption as well as export opportunities. By 2030, Germany could account for more than 20% of Europe’s hydrogen vehicle fleet.
France is expanding at a CAGR of 25%, higher than the global 23.8%. Growth is supported by national hydrogen strategies emphasizing rail and heavy-duty road transport. The government is targeting 100,000 hydrogen-powered vehicles by 2030, backed by subsidies and fleet adoption programs. Industrial partnerships between domestic automakers and energy companies are shaping infrastructure expansion. France’s unique focus on integrating hydrogen into trains, along with buses in major cities, provides a differentiated growth trajectory compared with other European peers.
The United Kingdom, with a CAGR of 22.6%, is slightly below the global rate of 23.8%. Adoption is growing in fleet operations, particularly in public transport and taxis. The UK government has outlined plans for over 300 refueling stations by 2035, which would create one of Europe’s most extensive hydrogen networks. Bus deployment in London and other cities is expanding rapidly, with demand shifting towards regional freight fleets. Domestic R&D in fuel cell stacks is also supporting long-term market competitiveness.
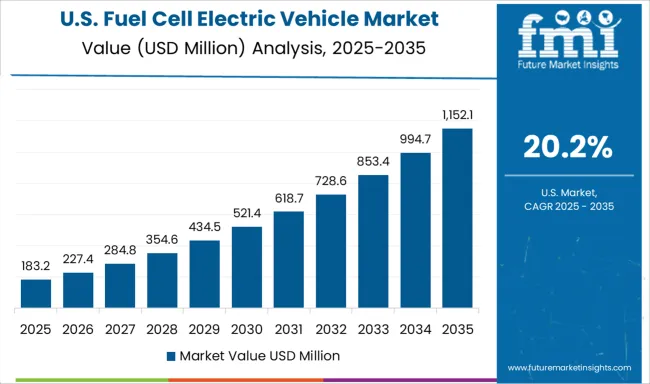
The United States records a CAGR of 20.2%, trailing the global 23.8%. Adoption has been concentrated in California, which hosts nearly 60 refueling stations, but nationwide expansion remains slow due to limited infrastructure. Light-duty passenger cars dominate deployments, while commercial fleet adoption is lagging compared to China and Europe. Federal funding programs are increasing, with over 8 billion USD allocated to hydrogen hubs across multiple states. By 2030, accelerated infrastructure rollouts could close the gap with global averages.
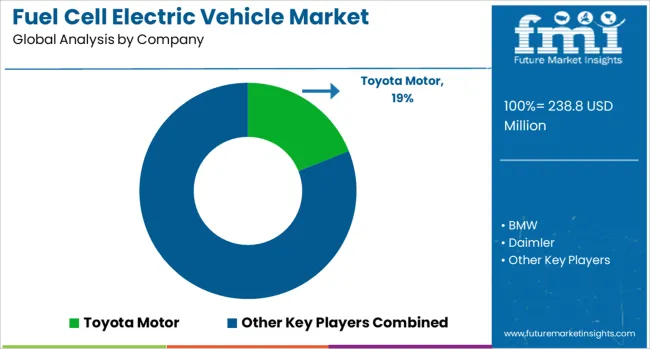
Toyota Motor has continued expanding its Mirai fuel cell vehicle line, with second-generation models offering improved range and cost efficiency. Hyundai Motor remains active in both passenger and commercial segments through its NEXO and XCIENT lines, supported by deployment in Europe and Asia. Honda Motor’s Clarity Fuel Cell, though limited in markets, has influenced drivetrain research and infrastructure partnerships.
BMW and Daimler have integrated hydrogen technology through collaborative ventures such as H2 Mobility and joint prototype development for heavy-duty vehicles. Iveco Group is advancing hydrogen-powered buses and trucks in the EU market, supported by regional clean energy mandates. Renault is piloting light commercial hydrogen-electric vans, combining range extension with payload flexibility. Hopium and Riversimple are targeting niche luxury and urban mobility markets respectively, with fuel cell platforms adapted for low-carbon vehicle trials in France and the UK.
The fuel cell electric vehicle market is shaped by expanding green hydrogen infrastructure, fleet decarbonization targets, and policy incentives across OECD and Asian regions. Manufacturers are concentrating on stack efficiency, hydrogen tank safety, and public-private refueling collaborations to address adoption barriers in commercial and high-utilization transport sectors.
Volvo tested hydrogen combustion trucks in the EU, and BMW renewed its collaboration with Toyota for future hydrogen models. These developments confirmed a clear push toward hydrogen mobility beyond passenger segments.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 238.8 Million |
| Fuel Cell Type | Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), Phosphoric acid fuel cells (PAFC), and Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) |
| Vehicle Type | Passenger vehicles and Commercial vehicles |
| Range Category | Medium Range (250 - 500 Miles), Short Range (below 250 Miles), and Long Range (above 500 Miles) |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Toyota Motor, BMW, Daimler, Honda Motor, Hopium, Hyundai Motor, Iveco Group, Renault, and Riversimple |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by vehicle type (passenger, commercial), demand surges in buses/trucks, regional dominance in Asia Pacific, innovation in PEM fuel cells and hydrogen infrastructure, environmental gain via zero-tailpipe emissions, emerging use in long-haul and public transport. |
The global fuel cell electric vehicle market is estimated to be valued at USD 238.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the fuel cell electric vehicle market is projected to reach USD 2,019.6 million by 2035.
The fuel cell electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a 23.8% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in fuel cell electric vehicle market are proton exchange membrane fuel cells (pemfc), phosphoric acid fuel cells (pafc) and solid oxide fuel cells (sofc).
In terms of vehicle type, passenger vehicles segment to command 71.0% share in the fuel cell electric vehicle market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Fuel rail for CNG Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Storage Tank Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Capacitance Test Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Gas Heater Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Management Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Injection System Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fuel Additives Market Segmentation based on Type, Application, and Region: Forecast for 2025 and 2035
Fuel Analyzer Market
Fuel Vending Machines Market
Fuel Operated Heaters Market
Fuel Resistant Sealant Market
Fuel Feed Pumps Market
Fuel Measuring Devices Market
Fuel Cell Powertrain Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell UAV Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell Stack Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell for Data Center Market - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell for Stationary Power Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fuel Cell Commercial Vehicle Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA