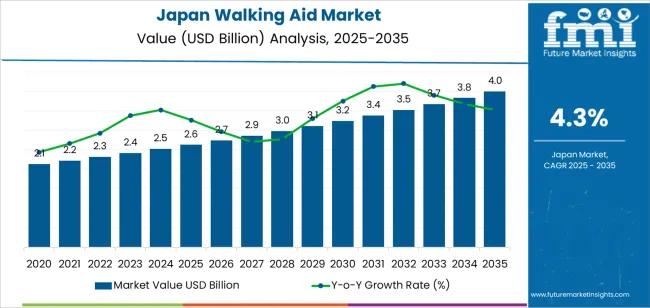
The Japan walking aid demand is valued at USD 2.6 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 4.3%. Demand increases due to the expanding older adult population, higher prevalence of mobility-related disorders, and growing use of assistive devices within rehabilitation and long-term care settings. Hospitals, outpatient clinics, home-care environments, and community support programmes continue to integrate mobility aids to improve stability, independence, and fall prevention among users.
Rollators lead the product landscape. These devices are selected for their enhanced maneuverability, integrated braking systems, adjustable frames, and suitability for both indoor and outdoor use. Their adoption is supported by improvements in lightweight materials, ergonomic handle designs, and foldable structures that simplify storage and transportation for users and caregivers.
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, and Kinki record the highest utilization levels. These regions host concentrated networks of rehabilitation centers, geriatric hospitals, and home-care service providers. They also maintain strong distribution and equipment-maintenance infrastructure, supporting continuous access to mobility devices. Key suppliers include Matsunaga Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Kawamura Cycle Co., Ltd., Nissin Medical Industries Co., Ltd., Invacare Corporation Japan, and Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare Japan. These companies provide rollators, walkers, canes, and related mobility aids used across clinical rehabilitation, elderly-care facilities, and home-based mobility support programmes.
Growth contribution in Japan’s walking-aid segment is distributed across several steady drivers that collectively shape a consistent upward trajectory. The strongest contribution comes from demographic factors, as an ageing population increases long-term demand for mobility-support products across home-care settings, community facilities, and rehabilitation centres. This demographic base provides a stable structural driver, ensuring that annual growth remains anchored in predictable clinical and daily-living requirements.
Product innovation contributes an additional layer of incremental growth. Improvements in lightweight materials, ergonomics, and stability features support gradual shifts toward upgraded models, prompting periodic replacement and encouraging adoption of more specialized devices. Rehabilitation programmes and assistive-care services also add to the contribution index by supplying a continual stream of users who require walking aids during recovery or long-term mobility management.
Distribution expansion across retail pharmacies, medical-device channels, and home-care networks further strengthens growth contributions by improving accessibility and reducing procurement barriers. While no single factor creates sharp acceleration, the combined effect of demographic need, steady innovation, and service-driven usage forms a balanced contribution structure. Overall, the segment’s growth index reflects a stable mix of essential-use demand and incremental product advancement within Japan’s mobility-support ecosystem.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Japan Walking Aid Sales Value (2025) | USD 2.6 billion |
| Japan Walking Aid Forecast Value (2035) | USD 4.0 billion |
| Japan Walking Aid Forecast CAGR (2025-2035) | 4.3% |
Demand for walking aids in Japan is increasing because the country has one of the world’s largest ageing populations, with rising prevalence of mobility limitations linked to osteoporosis, arthritis and balance disorders. Older adults rely on canes, walkers and rollators to maintain independence, prevent falls and support daily movement in homes and community spaces. Healthcare providers and rehabilitation centers recommend walking aids as part of recovery after joint replacement, stroke or lower-limb surgery, which strengthens institutional demand.
Urban planning improvements, barrier-free housing and accessible public transport further encourage regular use of mobility devices. Retail channels and home-care service networks also make a wide range of walking aids readily available, supporting consistent adoption across age groups. Constraints include cost sensitivity among users who prefer basic models, limited storage space in compact homes and cautious adoption among older adults who may delay mobility-aid use. Some regions face shortages of rehabilitation staff who guide patients in selecting and adjusting appropriate devices.
Demand for walking aids in Japan reflects the mobility needs of an ageing population, rehabilitation requirements, and support provided across hospitals, home care environments, and clinical facilities. Product selection varies based on user stability, gait support, upper-body strength, and rehabilitation goals. Technology preferences illustrate reliance on manual devices for routine use and automated units for specialized mobility assistance. End-user distribution shows how different Japanese healthcare settings integrate walking aids into treatment, recovery, and long-term mobility support.
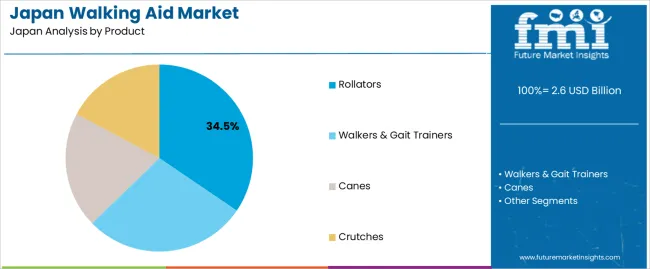
Rollators hold 34.5% of national demand and represent the leading product category in Japan. Their wheeled design, braking systems, and seating options support mobility for older adults requiring stability during daily activities. Walkers and gait trainers account for 28.2%, serving patients in early rehabilitation or those needing structured gait assistance. Canes represent 20.1%, supporting individuals with mild balance issues or unilateral weakness. Crutches hold 17.2%, used for short-term injury recovery or postoperative mobility. Product distribution reflects Japan’s emphasis on safe ambulation, adaptable support devices, and clinical use across rehabilitation pathways.
Key drivers and attributes:
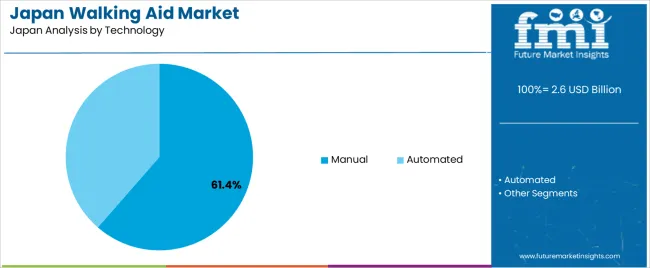
Manual walking aids hold 61.4% of national demand and represent the dominant technology category in Japan. These devices support straightforward mobility assistance without reliance on automated control, making them suitable for home care, hospitals, and routine rehabilitation. Automated aids account for 38.6%, including powered gait trainers and support units used in advanced therapy programs. Technology distribution reflects cost considerations, patient adaptability, and training requirements within Japanese care environments. Manual devices remain widely preferred for durability, simplicity, and ease of use, while automated systems support targeted rehabilitation and controlled movement patterns in specialized facilities.
Key drivers and attributes:

Hospitals hold 32.6% of national demand and represent the leading end-use category in Japan. Walking aids support postoperative recovery, injury rehabilitation, and early mobilization programs within inpatient units. Home care settings account for 25.4%, reflecting Japan’s ageing population and emphasis on maintaining independence in residential environments. Rehabilitation centers represent 22.8%, using structured devices for gait training, strength restoration, and long-term mobility improvement. Ambulatory surgical centers account for 19.2%, supporting short-term recovery after same-day procedures. End-user distribution reflects Japan’s coordinated approach to mobility management across acute care, home-based support, and specialized rehabilitation.
Key drivers and attributes:
Rapid population ageing, expansion of community-based rehabilitation programs and strong household preference for assistive mobility devices are driving demand.
In Japan, demand for walking aids rises as the proportion of adults aged 65 and above continues to increase, especially in prefectures such as Akita, Kochi and Shimane where ageing rates exceed national averages. Municipal long-term care programs encourage early mobility support to reduce fall risk, leading to higher use of canes, walkers and rollators. The Long-Term Care Insurance system allows partial reimbursement for assistive devices, which increases adoption among seniors living independently. Rehabilitation departments in hospitals and day-care centres use walking aids routinely for gait training and post-surgery recovery, reinforcing sustained purchasing across care settings.
Limited workforce in home-care services, uneven reimbursement coverage for premium devices and narrow living spaces in urban housing restrain demand.
Japan faces a shortage of home-care workers who typically provide guidance on proper device selection and usage. Without adequate support, some older adults hesitate to adopt new mobility aids. Reimbursement under the Long-Term Care Insurance system favours standard devices, making advanced rollators or ergonomically enhanced models less accessible for price-sensitive households. Many apartments in Tokyo and other dense urban regions have narrow corridors and compact layouts, which can limit the usability of wide rollators or multi-function walkers. These challenges slow broader adoption of higher-end mobility equipment.
Shift toward lightweight foldable designs, increased adoption of stability-enhancing rollators and rising integration of safety and monitoring features define key trends.
Manufacturers in Japan are introducing lightweight aluminium and carbon-fibre walking aids that suit seniors navigating public transportation and narrow residential spaces. Rollators with improved stability, braking assistance and height adjustment are becoming common in physiotherapy settings. Smart walking aids with fall-detection sensors, alert functions and location tracking are gaining interest among families caring for elders who live alone. Retailers and community rehabilitation providers are also offering more customized fitting services, reflecting Japan’s growing emphasis on personalized mobility support.
Demand for walking aids in Japan is increasing through 2035 as aging demographics, rehabilitation needs, mobility-support programs, and community care systems expand across the country. Products such as canes, walkers, rollators, and supportive mobility frames are used widely by older adults, post-surgery patients, and individuals undergoing physical rehabilitation. Regional demand reflects differences in population aging, healthcare-institution density, rehabilitation infrastructure, and community-level care practices. Kyushu & Okinawa leads at 5.3%, followed by Kanto (4.9%), Kinki (4.3%), Chubu (3.8%), Tohoku (3.3%), and Rest of Japan (3.2%).
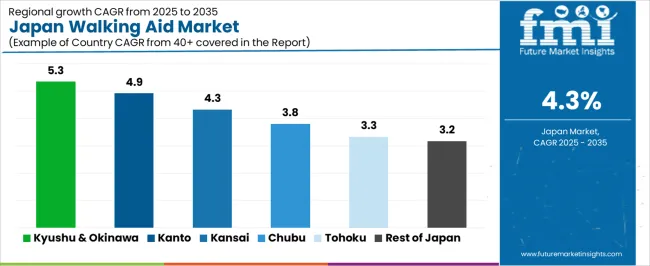
| Region | CAGR (2025-2035) |
|---|---|
| Kyushu & Okinawa | 5.3% |
| Kanto | 4.9% |
| Kinki | 4.3% |
| Chubu | 3.8% |
| Tohoku | 3.3% |
| Rest of Japan | 3.2% |
Kyushu & Okinawa grows at 5.3% CAGR, supported by high aging rates, community care programs, and strong rehabilitation infrastructure across Fukuoka, Kumamoto, Nagasaki, Kagoshima, and Okinawa. Public health centers and hospitals manage frequent mobility-related cases linked to age-associated conditions, joint issues, and balance limitations. Rehabilitation clinics in Fukuoka and Kumamoto integrate walkers, rollators, and canes into long-term mobility-recovery programs. Municipal care services supply walking aids to older adults enrolled in home-support initiatives. Okinawa’s rural and semi-rural areas rely on durable and lightweight aids suited to frequent outdoor use. Retail medical stores maintain high turnover of adjustable canes, foldable walkers, and wheeled mobility frames used by seniors for daily stability and movement.
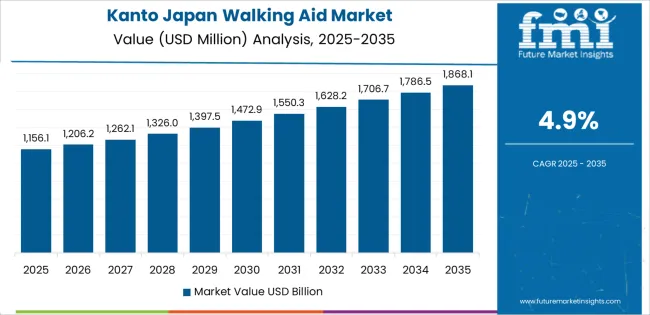
Kanto grows at 4.9% CAGR, driven by dense urban populations, large hospital networks, and extensive rehabilitation services across Tokyo, Kanagawa, Chiba, Saitama, and Ibaraki. Hospitals in Tokyo and Kanagawa manage orthopedic and neurological cases requiring structured mobility support. Rehabilitation clinics rely on walking aids for post-surgical recovery, stroke rehabilitation, and age-related gait assistance. Municipal home-care services distribute adjustable walking aids to registered elderly residents. Urban living increases demand for compact, foldable, and lightweight mobility devices suited to public transit use. Retailers in metropolitan districts supply a wide range of canes, rollators, and specialty supports aligned with diverse mobility needs.
Kinki grows at 4.3% CAGR, supported by regional hospital systems, aging demographics, and rehabilitation demand across Osaka, Kyoto, Hyogo, Nara, Wakayama, and Shiga. Hospitals in Osaka and Kyoto use walking aids for recovery from joint replacements, spinal conditions, and chronic mobility limitations. Rehabilitation centers integrate rollators and support frames into patient therapy plans. Residents in Nara and Wakayama show rising mobility-aid usage linked to aging and chronic conditions. Retail outlets in Osaka supply adjustable canes, compact walkers, and wheeled frames. Local care programs assist older adults who require mobility support for daily activities.
Chubu grows at 3.8% CAGR, shaped by rehabilitation utilization, regional aging, and community health programs across Aichi, Shizuoka, Gifu, Mie, and Nagano. Hospitals in Aichi provide walking aids for patients recovering from orthopedic procedures or chronic mobility issues. Rehabilitation centers in Nagano and Gifu integrate rollators and canes into structured therapy sessions. Community health-support programs distribute walking aids to older adults living independently. Retail outlets in regional cities sell lightweight, height-adjustable walkers suited for routine use.
Tohoku grows at 3.3% CAGR, supported by aging rural populations, hospital-based mobility programs, and local government care initiatives across Miyagi, Aomori, Fukushima, Akita, Iwate, and Yamagata. Public hospitals use walking aids for rehabilitation following fractures, joint deterioration, and stroke cases. Rural communities rely on durable walking aids suited to outdoor terrain and seasonal conditions. Municipal home-care services provide canes and walkers to elderly residents requiring mobility support. Retail access expands as local stores supply basic and mid-range walking aids for daily use.
Rest of Japan grows at 3.2% CAGR, supported by smaller hospital networks, community rehabilitation centers, and steady elderly-care needs across prefectures outside major clusters. Clinics and hospitals supply walking aids for post-injury recovery and chronic gait instability. Local care programs provide canes and simple walkers to older adults living independently. Retail availability supports moderate demand for everyday mobility aids. Rural and semi-urban environments require stable and durable walking supports.
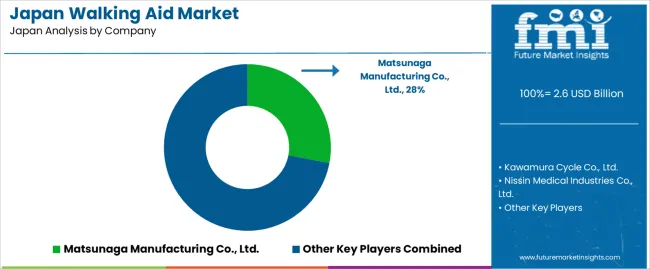
Matsunaga Manufacturing Co., Ltd. holds an estimated 28.0% share, supported by controlled production of walkers and rollators designed for Japan’s senior population. Its devices provide stable frame geometry, reliable braking, and compatibility with LTCI reimbursement standards. Kawamura Cycle Co., Ltd. maintains strong nationwide adoption with lightweight aluminium rollators and four-wheel walkers selected by rehabilitation centres and home-care providers. Its consistent build quality and broad distribution reinforce its position.
Nissin Medical Industries Co., Ltd. contributes major volume through foldable walkers and rehabilitation supports offering stable weight distribution and reliable indoor manoeuvrability, aligning with Japan’s compact-living environments. Invacare Corporation Japan holds a meaningful imported-equipment share, supplying rollators and mobility aids with verified durability and established service access within metropolitan regions.
Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare Japan adds presence with cost-efficient walking aids utilized in outpatient rehabilitation and community-care programmes. Competition across Japan centres on frame stability, ease of folding, manoeuvrability in narrow indoor spaces, LTCI eligibility, and domestic service availability. Demand remains strong as Japan’s ageing population prioritizes lightweight, reliable, and indoor-friendly mobility aids that support daily movement, fall prevention, and rehabilitation needs.
| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD billion |
| Product | Rollators, Walkers & Gait Trainers, Canes, Crutches |
| Technology | Manual, Automated |
| End User | Hospitals, Home Care Settings, Rehabilitation Centers, Ambulatory Surgical Centers |
| Regions Covered | Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan |
| Key Companies Profiled | Matsunaga Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Kawamura Cycle Co., Ltd., Nissin Medical Industries Co., Ltd., Invacare Corporation Japan, Drive DeVilbiss Healthcare Japan |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by product category, technology type, and end-user segment; regional adoption trends across Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu, Tohoku, and Rest of Japan; competitive landscape of mobility-aid providers and rehabilitation equipment manufacturers; developments in lightweight materials, ergonomic designs, automated and sensor-enabled walking aids; integration with eldercare programs, hospital rehabilitation units, home-care support, and ambulatory surgical facility needs in Japan. |
The demand for walking aid in japan is estimated to be valued at USD 2.6 billion in 2025.
The market size for the walking aid in japan is projected to reach USD 4.0 billion by 2035.
The demand for walking aid in japan is expected to grow at a 4.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in walking aid in japan are rollators, walkers & gait trainers, canes and crutches.
In terms of technology, manual segment is expected to command 61.4% share in the walking aid in japan in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Walking Aid Market Analysis by Product, Technology, End-user, and Region 2025 to 2035
Bariatric Walking Aids Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Walking Type Sprinkler Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Faith-based Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Sports Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Respiratory Inhaler Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Halal Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automated People Mover Industry Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Load Floor Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Food Cling Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Japan Polypropylene Packaging Films Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
AIDS Related Primary CNS Lymphoma Market Report – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Japan Probiotic Yogurt Market is segmented by product type, source type, nature type, flavor type, fat content, sales channel and key city/province through 2025 to 2035.
japan Tortilla Market - Growth, Trends and Forecast from 2025 to 2035
Japan Cosmetics ODM Market Analysis - Size, Share & Trends 2025 to 2035
Japan Automotive Turbocharger Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Yeast Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Green and Bio-based Polyol Market Insights – Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025–2035
Japan Natural Food Color Market Trends – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025–2035
Japan Coated Fabrics Market Growth – Trends, Demand & Innovations 2025–2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA