The Low Voltage Composite Insulators Market is estimated to be valued at USD 676.8 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1369.1 million by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% over the forecast period.
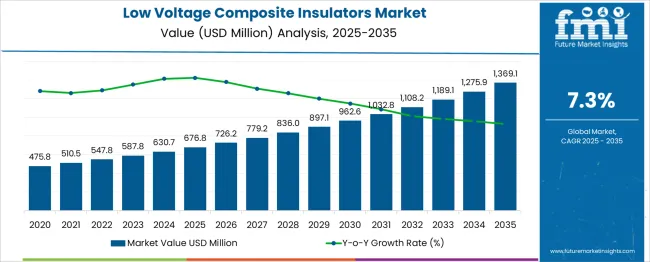
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Low Voltage Composite Insulators Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 676.8 million |
| Low Voltage Composite Insulators Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 1369.1 million |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 7.3% |
The demand for composite insulators has been influenced by their superior mechanical strength, resistance to moisture and pollution, and lighter weight compared to traditional ceramic or glass alternatives.
These benefits are becoming critical in urban and rural electrical distribution networks where space constraints, installation speed, and maintenance are key considerations. Future growth is expected to be shaped by the expansion of residential electrification, grid modernization projects, and increasing integration of renewable energy sources.
Additionally, aging grid infrastructure in developed regions and the electrification of off-grid areas in developing countries are accelerating the deployment of low-voltage composite insulators. As government policies and private investments align to promote energy access and reduce power losses, composite insulators are anticipated to play a crucial role in strengthening the reliability and sustainability of global power distribution networks..
The low-voltage composite insulators market is segmented by end-user and geographic regions. The end-use of the low-voltage composite insulators market is divided into residential, commercial, and industrial. In terms of rating of the low voltage composite insulators market is classified into ≤ 11 kV, > 11 kV to ≤ 22 kV, > 22 kV to ≤ 33 kV, > 33 kV to ≤ 72.5 kV> 72.5 kV. Regionally, the low voltage composite insulators industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
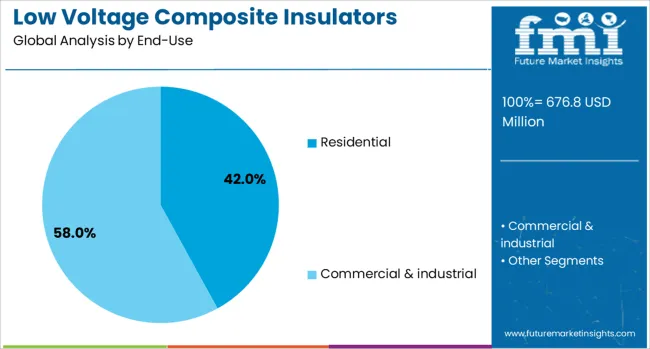
The residential end-use segment is expected to account for 42% of the Low Voltage Composite Insulators market revenue share in 2025, making it the leading consumer in the industry. The widespread need for efficient and compact insulating solutions in home electrical systems has driven this segment’s dominance. The increase in new housing developments, combined with the growing electrification of rural and peri-urban regions, has amplified the demand for reliable low voltage insulation.
Composite insulators have been increasingly adopted in residential grids due to their light weight, easier handling during installation, and lower risk of breakage, all of which reduce maintenance costs and enhance operational reliability. In densely populated and environmentally diverse regions, their strong resistance to pollution and moisture further supports their preference over traditional alternatives.
The rise in rooftop solar installations and smart home electrical infrastructure is also creating new opportunities for residential deployment of advanced insulators. As governments prioritize energy access and safety in residential areas, the use of composite insulators is projected to remain prominent within this segment..
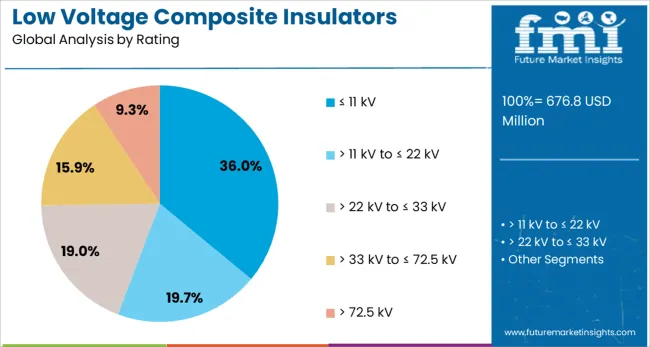
The ≤ 11 kV rating segment is projected to hold 36% of the Low Voltage Composite Insulators market revenue share in 2025, positioning it as the leading voltage category. This segment’s growth has been attributed to the widespread utilization of low voltage distribution networks in both urban and rural electrification projects. Systems operating at or below 11 kV are critical in delivering electricity directly to homes, small businesses, and public infrastructure.
Composite insulators within this voltage class have been preferred for their durability, hydrophobic properties, and reduced risk of flashover in contaminated or high-humidity environments. These performance characteristics have been particularly valuable in regions where weather fluctuations or environmental pollutants challenge conventional insulation systems.
Their adaptability to compact and constrained installation environments has also contributed to their expanding use in densely built urban zones. Additionally, the segment’s dominance is being reinforced by the increasing adoption of distributed energy resources and localized energy storage, which rely heavily on efficient and safe low voltage power delivery systems supported by reliable insulator performance..
Low voltage composite insulators are gaining traction due to their durability, low maintenance needs, and compatibility with modern power distribution and renewable energy systems. Innovations in materials and design continue to expand their application scope globally.
Increasing investment in power infrastructure upgrades has significantly boosted the adoption of low voltage composite insulators. Their lightweight structure, mechanical durability, and resistance to pollution make them a preferred choice for both new installations and replacements in distribution grids. Growing electrification projects in rural and semi-urban regions, alongside grid reliability improvement programs, are driving procurement volumes. Utilities are replacing conventional porcelain and glass insulators with composite variants to reduce breakage rates, minimize downtime, and enhance performance in harsh climates. The ability of composite insulators to withstand electrical stress and mechanical loads without excessive maintenance positions them as a critical component in ensuring stable and cost-efficient electricity distribution worldwide.
End-users are increasingly prioritizing equipment with lower lifecycle costs, and low voltage composite insulators are benefitting from this shift. These insulators require minimal cleaning, resist vandalism, and maintain hydrophobic properties over extended periods. Their polymeric materials prevent moisture penetration and reduce surface contamination, making them ideal for areas with high pollution or salt exposure. Industrial applications, railway electrification, and compact substations are particularly reliant on such features to maintain operational efficiency. The reduction in maintenance interventions not only lowers operational expenditure but also improves uptime for power delivery systems, ensuring consistent service levels. This reliability factor is accelerating replacement demand from utilities seeking long-term cost benefits.
The expansion of renewable energy projects, including solar farms and wind power plants, has created new application areas for low voltage composite insulators. Their adaptability to various mounting configurations and resistance to weathering ensures compatibility with distributed energy systems. Composite designs reduce structural load on poles and towers, making them suitable for remote and off-grid setups where maintenance access is limited. The growing need for resilient grid components that can operate under fluctuating loads and environmental stress is strengthening their role in renewable integration. Manufacturers are customizing designs for hybrid grids, enabling efficient interconnection between renewable sources and conventional distribution networks.
Ongoing developments in polymer chemistry and structural engineering are enhancing the performance parameters of low voltage composite insulators. Improved housing materials offer better ultraviolet resistance, increased tensile strength, and extended hydrophobicity retention. Core rod innovations improve electrical and mechanical endurance, reducing the likelihood of failure under high stress. Compact and modular designs allow easier transportation, faster installation, and adaptability across different voltage classes. Utility companies are favoring suppliers with strong R&D pipelines that address specific regional requirements such as high humidity, coastal salinity, or industrial pollution. Such advancements are helping manufacturers differentiate products in a competitive market and secure long-term supply contracts.
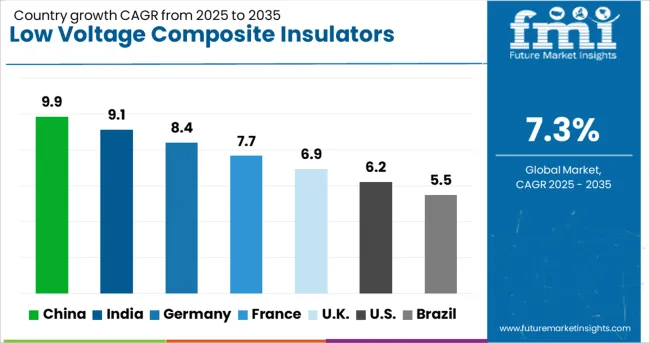
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 9.9% |
| India | 9.1% |
| Germany | 8.4% |
| France | 7.7% |
| UK | 6.9% |
| USA | 6.2% |
| Brazil | 5.5% |
The low voltage composite insulators sector is projected to register a global CAGR of 8.1% from 2025 to 2035, supported by infrastructure modernization, renewable energy integration, and grid reliability enhancement programs. China leads with a CAGR of 9.9%, driven by extensive rural electrification, high replacement demand for aging porcelain units, and large-scale renewable grid tie-ins. India follows at 9.1%, supported by distribution network expansions, railway electrification, and industrial power projects. France achieves 7.7% growth, benefiting from grid reinforcement projects, renewable power connectivity, and replacement of outdated grid components. The United Kingdom posts 6.9% growth, influenced by offshore wind integration, smart grid deployment, and compact power infrastructure upgrades. The United States records 6.2% growth, underpinned by grid resilience programs, storm-hardening initiatives, and increased investment in distribution automation. The analysis covers more than 40 countries, with these markets serving as strategic indicators for technology adaptation, material optimization, and procurement frameworks within the global low voltage composite insulators industry.
China is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.9% during 2025–2035, ahead of the global 8.1% pace. The earlier period, 2020–2024, is inferred at about 8.3%, supported by steady buildout of distribution feeders, accelerated replacement of brittle porcelain units, and wider use of hydrophobic polymer housings in coastal and industrial belts. The next phase improves as utilities enlarge rural electrification, expand compact substations for dense load pockets, and connect new wind and solar clusters that require robust insulator performance under variable weather. Procurement is shifting to longer creepage designs and anti-fog sheds that cut wash cycles. Local producers have scaled automated crimping and silicone compounding, raising consistency and shortening lead times. Field data show fewer flashovers per circuit-km after composite swaps, which encourages multi-year framework buys across provinces.
India is projected to post a 9.1% CAGR during 2025–2035. For 2020–2024, growth is estimated near 7.7%, when state utilities prioritized feeder segregation, agricultural connections, and loss-reduction programs that included limited composite rollouts. The lift into 2025–2035 reflects larger allocations to distribution modernization, railway electrification yards using compact gantries, and industrial parks that seek low maintenance components. Vendor-managed inventory near OEM yards has trimmed delivery time for crossarms, pins, and polymer sheds. Utilities report lower breakage during transport versus ceramic, which reduces spares holding. Smart meter projects also trigger pole refurbishment, creating bundled orders for insulators and hardware. Rural schemes expand single-phase lines where lightweight units cut erection time and improve crew safety, supporting higher annual placements across southern and western corridors.
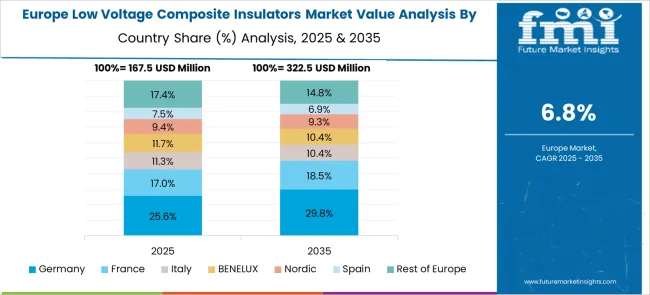
France is set to grow at 7.7% CAGR for 2025–2035. Earlier momentum in 2020–2024 is assessed at 6.4%, driven by targeted replacements in salt-spray zones and industrial belts where contamination drove outages. The forward step is tied to feeder hardening for storm resilience, interconnections for distributed generation, and standardization on silicone housings with arc-tracking resistance. Distribution operators are updating design books to longer creepage distances and interchangeable metal fittings that simplify spares. Retrofit programs pair insulator swaps with surge protection on critical laterals, which reduces momentary interruptions. Procurement adopts multi-year frameworks that lock pricing and guarantee response time for emergency call-offs, making deployment predictable. Training centers now certify field crews on crimp quality and torque checks, cutting installation defects and improving first-time pass rates.
The United Kingdom is projected at 6.9% CAGR during 2025–2035. Using proportional scaling versus the global 8.1% benchmark and adjusting for delayed capex in 2021–2022, the 2020–2024 UK CAGR is estimated at about 5.7%. One sentence quantifies the past: growth averaged roughly 5.7% as utilities focused on selective porcelain replacements and storm repair backlogs. A different sentence characterizes the outlook: the climb to 6.9% reflects larger programs linked to offshore wind landing points, compact substations in urban cores, and pole-top standardization on silicone units that reduce wash cycles. DNOs are bundling insulators with crossarm and surge upgrades, improving cost per circuit-km. Local stocking by hardware distributors has shortened outage windows. Reliability incentives in the price control period encourage lower fault minutes, which favors composite adoption on exposed feeders.
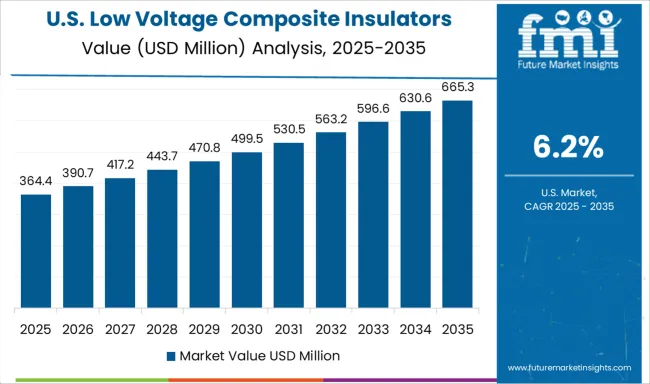
The United States is expected to post a 6.2% CAGR in 2025–2035. For 2020–2024, growth is gauged near 5.1%, when utilities focused on wildfire mitigation, selective recloser upgrades, and immediate storm repairs that limited broad insulator programs. The improvement ahead is associated with storm-hardening grants, grid resilience funds, and vegetation-management tie-ins that include pole replacements with polymer insulators as standard. Co-ops and IOUs report lower truck rolls after swapping to hydrophobic housings in coastal humidity and desert dust, improving lifecycle economics. Suppliers are expanding US molding capacity for silicone sheds and fiberglass cores, reducing import risks and improving response to hurricane seasons. Multi-state utilities are aligning specifications to common hardware, which supports scale buys and simplifies training across regions.
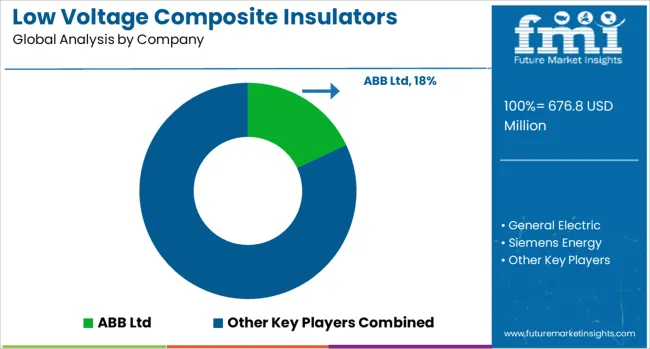
The low voltage composite insulators sector demonstrates a competitive environment shaped by the involvement of leading global electrical equipment companies and specialized insulator producers. ABB Ltd has been actively strengthening its portfolio of polymer insulators, particularly for power distribution and railway electrification, where its advanced silicone formulations are engineered to deliver superior hydrophobicity and resistance to environmental stress. General Electric integrates its composite insulator solutions into broader transmission and distribution modernization projects, leveraging its expertise in grid reliability and resilience. Siemens Energy focuses on enhancing lifecycle performance, with designs that provide optimal operation in high-pollution industrial regions and coastal areas subject to salt and moisture ingress.
TE Connectivity brings its electrical connectivity expertise into the insulator space, delivering compact and lightweight systems that address space constraints in urban substations and complex grid layouts. NGK Insulators strategically targets the transition from ceramic to composite technologies, prioritizing reliability, mechanical strength, and ease of installation. Seves Group is expanding its polymer insulator capabilities while retaining its leadership in glass and hybrid insulator formats, providing utilities with diverse product options. Lapp Insulators continues to cater to global utilities with customizable, high-strength composite solutions supported by both large-scale manufacturing and localized technical service, ensuring consistent quality and tailored performance for varied grid environments.
In February 2025, TE Connectivity announced the acquisition of Richards Manufacturing, enhancing its position in energy utilities and underground grid connectivity solutions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 676.8 Million |
| End-Use | Residential and Commercial & industrial |
| Rating | ≤ 11 kV, > 11 kV to ≤ 22 kV, > 22 kV to ≤ 33 kV, > 33 kV to ≤ 72.5 kV, and > 72.5 kV |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | ABB Ltd, General Electric, Siemens Energy, TE Connectivity, NGK Insulators, Seves Group, and Lapp Insulators |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales, share, competitive landscape, regional demand trends, key growth drivers, pricing analysis, regulatory impacts, material innovations, and major utility procurement patterns. |
The global low voltage composite insulators market is estimated to be valued at USD 676.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the low voltage composite insulators market is projected to reach USD 1,369.1 million by 2035.
The low voltage composite insulators market is expected to grow at a 7.3% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in low voltage composite insulators market are residential and commercial & industrial.
In terms of rating, ≤ 11 kv segment to command 36.0% share in the low voltage composite insulators market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Low Alloy Steels Powder Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Alkali Cement Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Vibration Thermostat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low-Level Order Picker Pallet Truck Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Temperature Flexible Tester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Light Imaging Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Density Polyethylene Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low-Temperature Cable Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Molecular Weight Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Temperature Radiators Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Rolling Resistance Tire Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Temperature Commercial Boiler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Emissivity Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Migration Inks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Density Polyethylene Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Temperature Insulation Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Clearance Loaders Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Calorie Desserts Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low-Grade Glioma Therapeutics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA