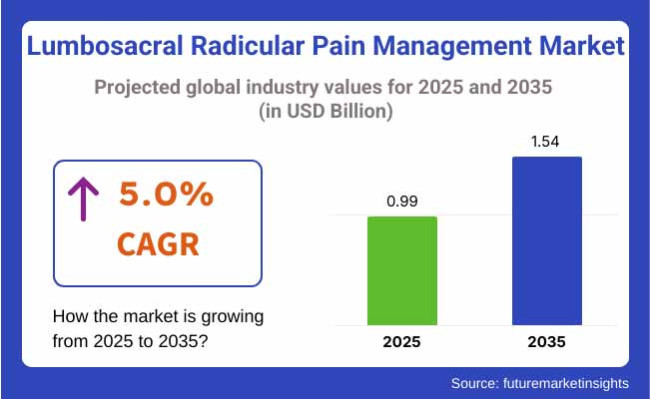
The lumbosacral radicular pain management industry will be valued at USD 0.99 billion in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, lumbosacral radicular pain management will grow at a CAGR of 5.0% and reach USD 1.54 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the lumbosacral radicular pain treatment industry grew steadily on the back of an aging population worldwide and a rise in chronic lower back pain cases. There was significant movement toward non-opioid treatment with NSAIDs, gabapentinoids, and epidural steroid injections due to regulatory pressure and safety issues curbing opioid dependence.
Minimally invasive procedures like nerve root blocks and radiofrequency ablation became popular with their lower-risk profile compared to conventional surgery. Tele-rehabilitation also came into the forefront as a top trend, as digital platforms helped increase access to physical therapy among chronic pain sufferers.
Emerging industries in the Asia-Pacific region witnessed increased demand with improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing awareness of advanced pain management options.
Looking to the future as far as 2025 and beyond, the industry will continue to transform with the development of biologics and regenerative medicine, such as stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma injections, which offer sustained pain relief solutions.
Artificially intelligent diagnostics and tailored pain management will further enhance treatment accuracy, minimizing trial-and-error methods. Surgical technologies such as endoscopic discectomy will become more widespread as outpatient procedures, reducing recovery periods.
However, cost pressures in mature industries might impede the uptake of expensive therapies, while emerging markets will power volume-driven growth. With a 5% CAGR, the industry is expected to grow to USD 1.54 billion by 2035, backed by advances in technology and chronic unmet needs in pain management.
FMI Survey Findings: Forces Based on Stakeholder Insights
(Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholders evenly distributed across physicians, hospital administrators, pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers, and payers in the USA, Western Europe, Japan, and South Korea)
Clinical Effectiveness & Safety:
87% of all stakeholders worldwide indicated "demonstrated clinical outcomes" as their number-one priority, followed by reducing side effects (79%).
Cost-Effectiveness:
72% highlighted reimbursement policies as a key driver of treatment adoption.
Regional Variance:
High Variance in Technology Use
ROI Perspectives
Consensus:
Epidural Steroid Injections (ESIs): 58% viewed ESIs as the "first-line interventional option."
Regional Variance:
Shared Concerns:
89% mentioned increasing expenses of biologics and higher-end implants as a significant impediment.
Regional Differences:
Manufacturers:
Providers (Hospitals/Clinics):
Patients:
Alignment:
78% of pharma/device companies engineered R&D in non-opioid analgesics and neuromodulator technology.
Divergence:
High Consensus: Clinical effectiveness, cost containment, and opioid reduction are concerns everywhere.
Main Differences:
Strategic Insight:
Regional tailoring (e.g., biologics in EU, telemedicine in USA, hybrid therapies in Asia) is essential for penetration.
| Country/Region | Key Regulations & Policies |
|---|---|
| USA |
|
| European Union |
|
| Japan |
|
| South Korea |
|
The lumbosacral radicular pain treatment industry is trending toward non-opioid, minimally invasive treatments (e.g., biologics, neuromodulation, and AI-assisted diagnostics) under pressure from tightened opioid laws and cost burdens for payers.
Tele-rehabilitation players and medical device entrepreneurs will be the winners, whereas legacy opioid makers and unwilling clinics will become obsolete. Fragmentation by region (US adoption of technology versus Asia's budget constraints) necessitates region-specific strategies to reach growth.
Speed Non-Opioid & Minimally Invasive Solutions
Action: Invest in biologics (e.g., stem cell therapy), neuromodulator devices (spinal cord stimulators), and AI-driven diagnostics to catch up with tightening opioid regulations and payer preference for cost-effective, low-risk interventions.
Regionalize Commercialization Strategies
Action: Tailor industry entry push high-tech products (robotics, tele-rehab) in the US/EU and cost-optimized hybrid treatments (nerve blocks, generics) in Asia to meet budget limitations and reimbursement deficits.
Establish Regulatory & Reimbursement Channels Early
Action: Make FDA Breakthrough Designation (US) and CE Marking (EU) a priority for expedited approvals, and establish agreements with insurers and public health systems to cover next-gene therapies (e.g., bioabsorbable implants, wearables).
| Risk | Probability/Impact |
|---|---|
| Stricter Opioid Regulations (e.g., CDC/EU bans high-dose prescriptions) | High |
| Reimbursement Rejections for Advanced Therapies (e.g., AI diagnostics, stem cells) | Medium |
| Supply Chain Disruptions (e.g., semiconductor shortages for IoT pain devices) | Medium |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Fast-Track Non-Opioid Product Launches | Run feasibility on biologics (e.g., stem cell production scaling) and secure FDA Breakthrough Designation for 1-2 pipeline candidates by Q2. |
| Preempt Reimbursement Barriers | Initiate payer feedback loops with Medicare/private insurers (e.g., pilot coverage for 1 neuromodulation device in 3 states by Q3). |
| Strengthen Supply Chain for Critical Components | Dual-source semiconductors for IoT pain devices and lock in contracts with Tier-2 suppliers to avoid 2025 shortages. |
| Regional Entry Plays | Launch tele-rehab partnerships in the EU (Germany first) and cost-optimized nerve block kits in Japan/South Korea by Q4. |
| Regulatory Pathway Acceleration | Assign a dedicated team to expedite CE Marking (EU) and PMDA (Japan) submissions for flagship spinal implant. |
To stay ahead, companies should take advantage of the USD1.4B lumbosacral radicular pain industry and shift investment steadily to non-opioid, high-margin solutions-namely biologics (e.g., stem cell therapies) and AI-powered diagnostic tools-while rapidly seeking FDA Breakthrough and CE Mark approvals to catch up with rivals.
At the same time, initiate regional pilots: aim for the USA with insurer-supported neuromodulation programs, Europe with tele-rehab partnerships, and Asia with low-cost hybrid nerve blocks to beat reimbursement and adoption hurdles.
This changes your playbook from compliance in reaction (opioid limitation) to controlling the next cycle of pain management-where clinical differentiation and alignment with payers will determine champions.
Among the medications listed-cyclobenzaprine, oxycodone, tramadol, and gabapentin-gabapentin is the most commonly used to treat lumbosacral radicular pain (nerve pain like sciatica) because of its good safety profile, reduced risk of abuse, and efficacy for neuropathic pain.
Gabapentin, unlike oxycodone (high-risk opioid addiction) and tramadol (partial opioid with serotonin risks), is a non-opioid, anticonvulsant drug that is specifically designed to treat nerve pain by modulating calcium channels. While cyclobenzaprine is a muscle relaxant, it's not as effective for radicular pain (which is due to nerve compression, not purely spasms).
Gabapentin's supremacy is also bolstered by clinical guidelines, which recommend it over opioids, owing to the CDC's limitations on prescribing opioids and its established use as an adjunct with physical therapy/injections.
Yet, its side effects (drowsiness, dizziness) and unpredictable efficacy continue to create demand for substitutes such as SNRIs (e.g., duloxetine) or spinal injections in refractory patients.
Oral medications are now the mainstream treatment modalities for lumbosacral radicular pain, with medications such as gabapentin, NSAIDs, and low-dose opioids being prescribed in large numbers because of their systemic action on neuropathic pain pathways and better insurance coverage.
The oral formulation preference is due to their established effectiveness in addressing nerve pain at its origin, as attested by clinical practice guidelines from bodies such as the American Academy of Neurology, which support oral anticonvulsants and SNRIs as initial treatments.
Whereas local agents like lidocaine patches and capsaicin creams provide regional relief, their failure to penetrate sufficiently to influence compressed nerve roots makes them less than ideal in genuine radicular pain. Topicals are best reserved for adjunctive therapy in selected instances, such as patients with opioid intolerance or those who have superficial allodynia.
Retail pharmacies are the most common channel used for dispensing medication for lumbosacral radicular pain, mostly because of their convenience, general accessibility, and patient and prescriber-established relationships.
Hospital pharmacies, which mostly serve inpatients or acute-care patients, are different from retail pharmacies that serve the outpatient population at large, providing more convenient access to both immediate- and maintenance-phase medications.
Online pharmacies, although becoming increasingly popular, remain restricted in the dispensing of controlled substances such as opioids and do not have the face-to-face consultation that retail pharmacies offer for complex pain management programs.
The USA industry is expected to grow at 5.5% CAGR during the forecast period. USA accounts for a considerable share of the Lumbosacral Radicular Pain Management industry. The prevalence of back pain is high, and an aging population fuels the demand for successful treatments.
Sophisticated healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare spending enable the uptake of new therapies, including pharmacological treatments such as NSAIDs and opioids and non-pharmacological treatments like physical therapy and chiropractic treatment.
The market is also seeing growing interest in minimally invasive surgical techniques and implantable neurostimulation devices. Challenges like the opioid crisis and regulatory pressures could, however, impact dynamics.
The UK industry is expected to register at 4.8% CAGR during the study period. In the UK, the Lumbosacral Radicular Pain Management market is fueled by increasing awareness of back pain conditions and the presence of sophisticated treatment facilities in the National Health Service (NHS).
The focus on non-pharmacological treatments, including physiotherapy and acupuncture, is significant. The UK also has a strong market for over-the-counter painkillers.
The convergence of digital health technologies and telemedicine offerings is improving the access of patients to care. Nevertheless, cost pressures in the NHS and the effects of healthcare policy might hinder growth in the industry.
French industry is expected to grow at 4.9% CAGR during forecast period. The industry of France is underpinned by a well-established healthcare system coupled with a very high level of medical care. The emphasis of the country on patient education and preventive care is a factor in the early diagnosis and treatment of lumbosacral radicular pain.
Pharmacological interventions are prevalent, with increasing acceptance of complementary therapies such as osteopathy. Government support for research and development in pain management by the French government further supports the industry. However, regulatory issues and cost containment within the healthcare system could affect growth.
Germany is expected to grow at 5.2% from 2025 to 2035. The healthcare infrastructure of Germany is robust, with a strong focus on medical research. The population in the country is aging, and there is a high prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders, which fuels the need for lumbosacral radicular pain management products.
Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments, including physiotherapy and massage, are part of patient treatment. Germany's approach towards incorporating traditional and alternative medicine methods gives the treatment landscape a holistic look.
However, the dynamics may be affected by stringent regulatory policies and health insurance fund pricing pressures.
Italy's industry is expected to register at 4.7% CAGR during forecast period. In Italy, the industry is fueled by a growing awareness of back pain problems and the presence of various treatment opportunities. The nation's high reputation for manual therapies, such as physiotherapy and chiropractic, adds to the application of pharmacological treatments.
The healthcare system in Italy offers access to various pain management opportunities, although regional variations might influence service provision. Financial constraints and budget limitations in the public healthcare system could be barriers to expansion.
South Korea is expected to grow at 5.3% from 2025 to 2035. A sophisticated healthcare infrastructure and rapid uptake of medical technology in South Korea drive a vibrant industry for the management of lumbosacral radicular pain. The aging population in the country, along with the high rate of sedentary lifestyles, contributes to a high rate of back pain.
Western-based pain treatments, as well as traditional Korean medicine, including acupuncture, are used to manage pain. Government programs that support healthcare innovation and the use of digital health solutions increase patients' access to care. Reimbursement strategies and cultural values, though, can affect treatment options and directions.
Japan's industry is expected to grow at 5.0% CAGR during forecast period. The industry in Japan is influenced by the country's super-aged society and the resultant growth in age-related musculoskeletal disorders. The healthcare system there focuses on both traditional medical care and traditional therapy, including Kampo medicine.
Japan's dedication to technological advancement is illustrated in the creation of high-tech medical devices for the treatment of pain. The government's emphasis on preventive medicine and patient education enhances early intervention approaches. However, issues with healthcare funding and cost-saving measures may affect expansion.
China's industry is expected to grow 6.0% during the forecast period. China's fast-growing healthcare industry and rising incidence of back pain disorders fuel strong growth in the lumbosacral radicular pain management industry. Urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and population aging are among the factors that fuel the growing number of such disorders.
The market is dominated by a mix of Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine, such as acupuncture and herbal treatments. Government spending on medical infrastructure and initiatives to enhance healthcare access to health services further promote market development. Disparities in healthcare between rural and urban regions and administrative issues can act as challenges to development in the industry.
Pfizer (22%)
Ruling with Lyrica (pregabalin) and gabapentin generics, using brand power and first-line guideline ranking for neuropathic pain.
Novartis (18%)
Maintaining with gabapentin generics and Voltaren (NSAIDs), targeting cost-sensitive markets and mild-to-moderate pain situations.
Johnson & Johnson (12%)
Emphasizing Nucynta (tapentadol, opioid alternative) and Topamax (topiramate), treating refractory pain with decreased abuse potential.
Teva (10%)
Teva dominates generic opioids and muscle relaxants, supplying cost-conscious healthcare systems, but it is exposed to opioid regulatory headwinds.
Eli Lilly (9%)
Shares gain with Cymbalta (duloxetine, SNRI) as a non-opioid alternative for comorbid depression/anxiety pain patients.
Other Generics (29%)
Local fragmented players compete on price, particularly in emerging markets where price beats brand loyalty.
With respect to the route of administration, it is classified into oral and topical.
In terms of drug class, it is divided into cyclobenzaprine, oxycodone, tramadol, and gabapentin.
In terms of end-users, it is divided into hospital pharmacy, retail pharmacy, and online pharmacy.
In terms of region, it is segmented into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, and MEA.
Gabapentin is the most commonly prescribed because it is effective for nerve pain and has less abuse potential than opioids.
Minimally invasive interventions such as epidural steroid injections and spinal cord stimulation are seeing the fastest adoption.
Tele-rehab and AI-based pain management platforms are being used more often for distant monitoring and therapy guidance.
The USA prefers sophisticated interventions, Europe emphasizes non-opioid treatments, and Asia uses more budget-friendly generics.
Stem cell therapy and bioelectronic implants have the potential for durable pain relief without drug risk.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Tax Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Key Management as a Service Market
Cash Management Supplies Packaging Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Fuel Management Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Risk Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
SBOM Management and Software Supply Chain Compliance Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Case Management Software (CMS) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Farm Management Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Lead Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Data Management Platforms Market Analysis and Forecast 2025 to 2035, By Type, End User, and Region
Cash Management Services Market – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
CAPA Management (Corrective Action / Preventive Action) Market
Exam Management Software Market
Light Management System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Labor Management System In Retail Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Waste Management Carbon Credit Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Waste Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Stool Management System Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Power Management System Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Quote Management Software Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA