The Middle Mile Delivery Market is estimated to be valued at USD 110.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 217.8 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0% over the forecast period.
Within this ecosystem, middle-mile delivery accounts for approximately 1.1% of the total logistics spend in 2025. By 2035, its share is anticipated to increase modestly to 1.55%, driven by optimization technologies, growing e-commerce volumes, and the strategic need for faster fulfillment between distribution centers and retail hubs. While last-mile delivery garners attention for consumer-facing services, the middle mile remains the backbone of bulk movement, enabling time-sensitive redistribution between warehouses, ports, and regional hubs. Innovations in route planning, autonomous trucking, and intermodal transport integration are helping reduce costs and increase efficiency in this segment. Companies are increasingly investing in dedicated middle mile fleets and automated sorting hubs, reflecting the segment’s growing strategic importance. Additionally, emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are witnessing rising investments in regional logistics infrastructure, thereby boosting the middle mile’s contribution to the overall logistics framework.
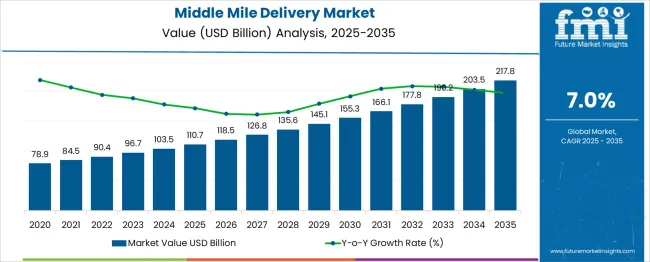
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Middle Mile Delivery Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 110.7 billion |
| Middle Mile Delivery Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 217.8 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 7.0% |
The middle mile delivery market is currently positioned in the early growth-to-expansion stage on the market maturity curve. In 2025, the sector is experiencing accelerated adoption of digitized routing systems, fleet telematics, and hub automation, primarily in developed economies such as the USA, Germany, Japan, and the UK These regions account for over 65% of early adopters, with North America leading technological integration. However, most emerging economies remain in the early adoption phase, where infrastructural limitations and regulatory hurdles slow the pace of modernization. By 2030, the market is expected to enter a mature growth phase, marked by widespread deployment of AI-driven supply chain orchestration, EV-based freight fleets, and dedicated middle mile drones and autonomous vehicles. These advancements will significantly reshape cost structures and delivery timelines.
The adoption curve shows a sharp upward trend between 2025 and 2030, with adoption levels expected to surpass 70% globally by 2035, especially as retailers and logistics players seek more resilient, scalable networks. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and investments in regional fulfillment ecosystems will further push the market toward late-stage maturity. However, complete saturation is unlikely before 2040 due to global infrastructure disparity.
The middle mile delivery market is gaining momentum due to the rapid growth of e-commerce, demand for same-day fulfillment, and increased supply chain decentralization. Middle mile logistics, defined by the transportation of goods from warehouses to distribution centers, has become a focal point for efficiency optimization.
Companies are adopting digital route planning, real-time tracking, and predictive analytics to reduce costs and improve on-time delivery performance. Innovations in vehicle telematics, automated scheduling, and collaborative logistics platforms are further streamlining mid-point delivery operations.
As urban distribution zones expand and consumer expectations for speed rise, businesses are rethinking middle mile strategies by incorporating regional fulfillment centers and micro-warehousing solutions.
The middle mile delivery market is segmented by service type, transportation mode, end user industry and geographic regions. The middle mile delivery market is divided by service type into Transportation management, Warehousing and distribution, and Freight forwarding. In terms of transportation modes, the middle mile delivery market is classified into Roadways, Railways, Airways, and Maritime. Based on the end user industry, the middle mile delivery market is segmented into Retail and e-commerce, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Automotive, Food and beverage, Energy and utilities, Aerospace and defense, and Others. Regionally, the middle mile delivery industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
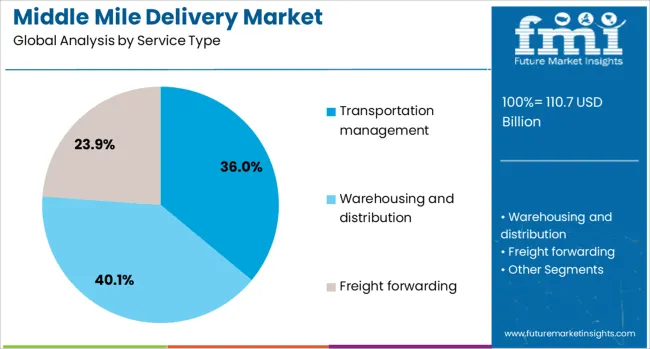
Transportation management is projected to account for 36.0% of the total revenue in the middle mile delivery market by 2025, making it the leading service type. This segment is growing due to the increasing use of centralized platforms that coordinate routes, carrier selection, and load optimization.
Real-time visibility and integration with warehouse management systems are enhancing operational agility, while AI-driven decision-making is helping reduce idle time and fuel consumption.
Transportation management services also allow shippers to monitor delivery metrics and optimize cost-efficiency, especially in high-volume regional movements.
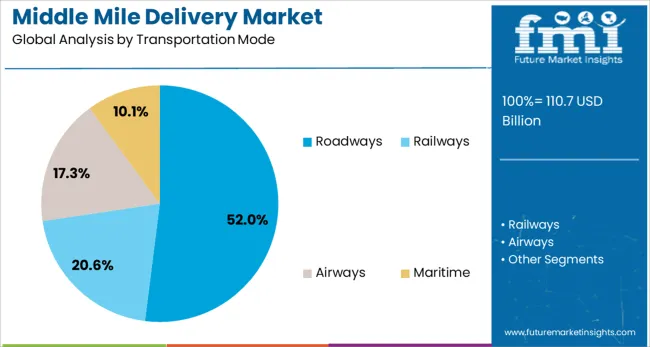
Roadways are expected to dominate the middle mile delivery market with a 52.0% share in 2025, reflecting their flexibility, wide geographic reach, and cost-effectiveness. Trucks and vans offer scalability across varying load sizes and are increasingly supported by telematics, GPS routing, and driver management tools.
Road transport’s ability to link regional fulfillment hubs with urban centers is critical for mid-mile efficiency.
Additionally, advancements in electric vehicle adoption and route optimization software are helping reduce the carbon footprint of road-based deliveries, aligning with sustainability goals of logistics operators.
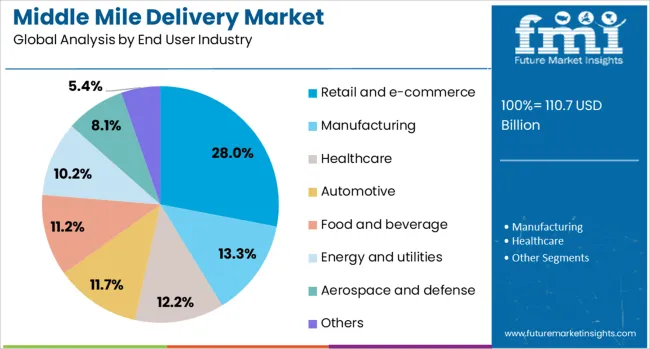
Retail and e-commerce are forecast to hold a 28.0% share of the middle mile delivery market by 2025, leading all other industries in adoption. This segment is driven by the need for fast, reliable transit between inventory hubs and local dispatch points.
The rise of omnichannel retail, click-and-collect services, and flash sales has increased pressure on retailers to maintain accurate, high-speed inventory transfers. Middle mile solutions offer e-commerce players improved order consolidation and delivery predictability, making them indispensable in competitive last-mile ecosystems.
As online retail continues to expand globally, investment in resilient and adaptive middle mile infrastructure remains a top priority.
The middle mile delivery market is evolving rapidly as logistics providers and retailers seek to improve efficiency between warehouses, fulfillment centers, and distribution hubs. This segment plays a vital role in ensuring goods reach the final delivery stage quickly and cost-effectively. As e-commerce expands and retailers optimize supply chains, middle mile logistics gains strategic importance. Increasing interest in route planning software, centralized tracking, and cross-docking infrastructure supports market development across regional distribution corridors and urban-rural supply routes.
Retailers and logistics providers are increasingly prioritizing the middle mile to reduce delays between storage facilities and local distribution centers. This phase of delivery is essential to meeting shorter delivery windows and maintaining inventory accuracy. Businesses are deploying hub-and-spoke models and integrating regional warehouses to streamline movement and minimize stockouts. Automation within fulfillment centers, such as high-speed sorting and bulk transfer vehicles, is reducing transit times. Retail networks with centralized inventory strategies rely heavily on well-scheduled middle mile operations to support frequent restocking. Improved visibility between hubs allows better coordination of shipments and reduces inefficiencies. Demand from sectors like grocery, electronics, and fashion further underscores the need for a responsive middle mile framework. Companies investing in fleet management systems, real-time routing tools, and facility upgrades can ensure faster and more reliable middle mile performance, making it a critical differentiator in a competitive logistics environment.
One of the significant challenges facing the middle mile delivery market is the fragmented nature of transportation networks, particularly across regions with uneven infrastructure. Inconsistent road conditions, lack of standardized hubs, and variable traffic patterns disrupt timely movement between distribution centers. Without harmonized systems, planning optimal routes becomes complex and labor-intensive. Smaller logistics providers often operate independently without shared data or route visibility, leading to duplicated efforts or inefficient asset utilization. Coordination between regional and national carriers can also be inconsistent, especially when operating on different platforms or service models. These inefficiencies impact delivery predictability and increase operational costs. Seasonal demand fluctuations further complicate planning, causing underutilized or overloaded transit links. Addressing these structural issues requires greater cooperation across carriers and broader investment in route planning tools, interoperability protocols, and regional logistics infrastructure. Until such integration is realized, scalability will remain a challenge for providers serving diverse distribution territories.
As retailers restructure supply chains to support faster delivery, the formation of regional distribution hubs is creating opportunities for middle mile service providers. These hubs act as centralized sorting and transfer points, requiring frequent and reliable inbound and outbound transit. Retail consolidation is also giving rise to fewer, but larger, fulfillment centers that depend on robust middle mile connections to feed last mile operations. This shift allows logistics providers to offer dedicated middle mile services between known nodes, improving load planning and turnaround time. Retailers collaborating with third-party logistics firms can further optimize fleet deployment, reduce empty miles, and enhance delivery precision. Urban infill warehouses and dark stores are also contributing to increased middle mile traffic as goods are moved frequently to meet variable local demand. Businesses offering tailored middle mile solutions, including multi-stop routing, co-loading, and temperature-controlled transfers, are well-positioned to capitalize on this supply chain realignment.
Despite growing demand for efficient transport between distribution points, rising operating costs present a major restraint in the middle mile delivery segment. Fuel expenses, fleet maintenance, insurance, and equipment leasing significantly increase overhead. In addition, driver availability continues to be a bottleneck, particularly for long-haul and irregular shift patterns that middle mile routes often require. The scarcity of trained drivers places pressure on existing staff and limits scalability. Regulatory compliance with vehicle standards and labor requirements adds another layer of complexity and cost. In densely populated regions, congestion and limited delivery windows further constrain route planning. For smaller providers, absorbing these operational pressures while remaining competitive on price can be challenging. Without scalable labor solutions or cost-effective fleet management strategies, businesses may struggle to meet service expectations. These limitations hinder expansion efforts, particularly in regions where labor markets are tight or where logistics infrastructure is underdeveloped.
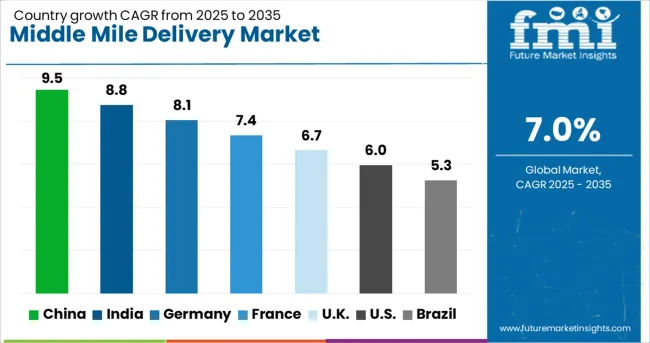
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 9.5% |
| India | 8.8% |
| Germany | 8.1% |
| France | 7.4% |
| UK | 6.7% |
| USA | 6.0% |
| Brazil | 5.3% |
The global middle mile delivery market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% through 2035, driven by e-commerce expansion, warehouse network optimization, and demand for faster, more cost-efficient transportation links. Among BRICS nations, China leads with 9.5% growth, fueled by investments in autonomous trucking, AI-based route planning, and integrated distribution hubs. India follows at 8.8%, supported by infrastructure upgrades, digital logistics platforms, and rising demand from regional e-commerce firms. Within the OECD region, Germany reports 8.1% growth, driven by logistics automation, intermodal freight strategies, and sustainability goals in transport. The United Kingdom, at 6.7%, focuses on urban consolidation centers and electric fleet integration. The United States, growing at 6.0%, emphasizes optimization of regional distribution routes, warehouse proximity modeling, and smart logistics partnerships. These countries are leading the transformation of the middle mile as a critical link in the global supply chain. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
In China, the middle mile delivery market is growing at a CAGR of 9.5%, driven by expanded warehousing networks and increased e-commerce volume. Regional distribution hubs have been optimized to reduce intercity transit times and streamline inventory transfer between central and last-mile depots. Large logistics operators are investing in dedicated trunk route services connecting inland industrial zones with coastal consumption centers. Automated sorting systems are being installed at relay centers to manage growing parcel loads without delaying dispatches. Retailers are signing agreements with third-party fleet providers to reduce dependency on fragmented carrier networks. Heavy-duty electric vehicles and mini freight trains are being used in provincial corridors to maintain shipment regularity. Traffic coordination platforms are also improving fleet efficiency by rerouting in real time.
India’s middle mile delivery market is rising at a CAGR of 8.8% as retailers focus on reducing warehouse-to-outlet transit delays. Logistics companies are expanding mid-route distribution centers across Haryana, Maharashtra, and Telangana to serve retail zones more effectively. Improved national highway access and 24-hour freight permissions have enabled faster parcel movement between state hubs. Retail chains are relying on leased truck fleets to manage seasonal volumes during festivals and product launches. Smaller players are adopting consolidated container loads to reduce fuel costs and improve turnaround times. Cloud-based delivery management software is gaining popularity among regional operators to optimize dispatch timing and vehicle utilization. Packaging firms are also coordinating with logistics providers to ensure stackable cargo for space-efficient transit.
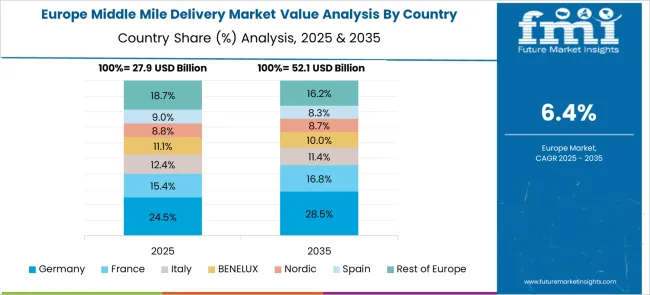
Germany’s middle mile delivery market is expanding at a CAGR of 8.1%, largely due to rising retail warehouse upgrades and cold chain deliveries. Retailers are moving to multi-node distribution models, where inventory is shipped from regional stock points to urban hubs before final delivery. Time-definite transit requirements have increased the need for reliable trunk routes and cross-docking facilities. Major logistics firms are upgrading their vehicle fleets with real-time tracking tools and temperature-regulated compartments for perishable cargo. Coordination between rail and road networks has improved parcel transfer efficiency during peak hours. Specialized carriers are partnering with food and pharma firms to ensure scheduled movement between depots. Courier aggregators are integrating AI-based load balancing for consistent fleet performance.
The middle mile delivery market in United Kingdom is growing at a CAGR of 6.7%, as supply chain operators focus on improving speed and consistency across regional routes. Retailers and logistics providers are collaborating to improve order bundling between storage centers and retail sites. Mid-mile facilities are increasingly equipped with automated conveyor systems and smart scanners to reduce sorting delays. Supermarket chains are leasing transport corridors from national networks to ensure uninterrupted cargo movement across counties. Real estate developers are offering space for mid-sized cross-docking facilities along major roadways. Fleet operators are incorporating driver scheduling tools to reduce idle times and increase truck turnaround. Equipment rentals for lift-gate trucks and container vehicles are also gaining traction among smaller delivery contractors.
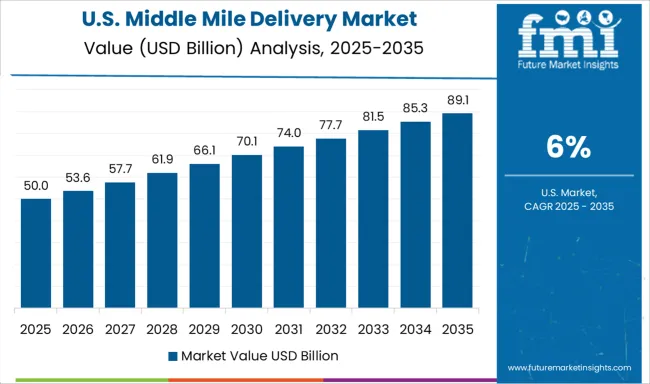
The middle mile delivery market in United States is expanding at a CAGR of 6.0%, led by adjustments in how goods move between primary warehouses and regional distribution centers. Retailers are reconfiguring delivery lanes to bypass congested urban zones and reduce delays between suburban hubs. Logistics providers are adopting night-shift trucking to avoid peak-hour traffic and improve vehicle utilization. Hub infrastructure is being retrofitted with faster loading bays and RFID-based inventory scanning to reduce dwell time. Containerized shipments are becoming common for electronics, apparel, and high-value items, minimizing loss and damage during transfer. Collaborative freight programs are on the rise, where non-competing retailers share trunk line capacity to reduce delivery costs. Temperature-sensitive cargo such as produce and medicine is being routed through pre-cooled facilities to maintain standards.
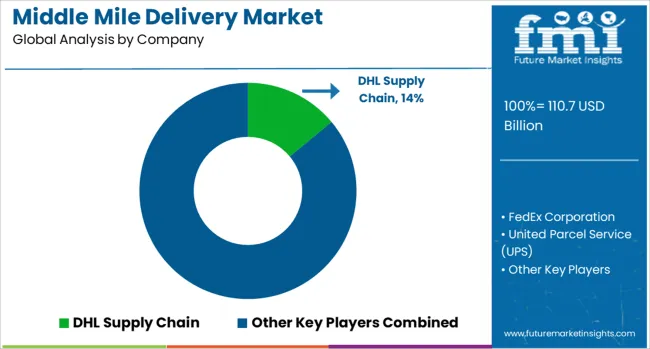
The middle mile delivery market plays a crucial role in connecting distribution centers to retail outlets, parcel hubs, or last-mile service providers. Dominating this space are global logistics leaders such as DHL Supply Chain, FedEx Corporation, and United Parcel Service (UPS). These companies manage massive transport networks and optimized warehousing systems, allowing them to handle large volumes of freight with consistent transit times. Their scale enables rapid point-to-point movement, helping clients maintain inventory turnover and shelf availability without disruption. Established freight forwarders and contract logistics providers like DB Schenker, Kuehne + Nagel, and C.H. Robinson are also instrumental in the middle mile segment. They bring flexibility to the supply chain through multi-modal transportation, combining road, rail, air, and sea routes depending on the delivery window and cargo sensitivity.
Their integrated systems and transport visibility solutions are essential for retailers and manufacturers managing tight delivery schedules across regions. Regional specialists and asset-light operators such as XPO Logistics, Expeditors International, J.B. Hunt Transport Services, and Nippon Express are well-positioned for customized services. They support e-commerce players, temperature-controlled goods, and large-item shipping by offering consolidated freight runs, route optimization, and strategically located transit points. These firms also emphasize reliable handoffs between fulfillment centers and last-mile carriers, ensuring that goods reach consumers or outlets without delays or inconsistencies, especially in peak demand seasons.
As announced on February 5, 2025, CEVA Logistics expanded its European operations with 23 new electric trucks (ranging from 7.5 t to tractor units) in France, Belgium, and the Netherlands. This brings its low-carbon fleet to over 1,100 EVs, cutting annual CO₂ emissions by ~39,000 tons. On June 12, 2025, ShipBob launched zone skipping across its USA middle-mile network. By consolidating package flows into regional hubs and reducing handoffs, zone-skipped shipments offer faster transit, lower cost, and full tracking visibility via its proprietary logistics platform.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 110.7 Billion |
| Service Type | Transportation management, Warehousing and distribution, and Freight forwarding |
| Transportation Mode | Roadways, Railways, Airways, and Maritime |
| End User Industry | Retail and e-commerce, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Automotive, Food and beverage, Energy and utilities, Aerospace and defense, and Others |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | DHL Supply Chain, FedEx Corporation, United Parcel Service (UPS), DB Schenker, Kuehne + Nagel, C.H. Robinson, XPO Logistics, Expeditors International, J.B. Hunt Transport Services, and Nippon Express |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales vary by transport mode and service type, with road freight and warehousing/distribution dominating. North America leads in revenue, while Asia‑Pacific posts fastest growth. Pricing fluctuates with fuel, labor and infrastructure costs. Growth accelerates via AI/IoT route optimization, electric/autonomous vehicles, automation and blockchain transparency, under sustainability pressures. |
The global middle mile delivery market is estimated to be valued at USD 110.7 billion in 2025.
The market size for the middle mile delivery market is projected to reach USD 217.8 billion by 2035.
The middle mile delivery market is expected to grow at a 7.0% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in middle mile delivery market are transportation management, warehousing and distribution and freight forwarding.
In terms of transportation mode, roadways segment to command 52.0% share in the middle mile delivery market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Middle East & Africa Sachet Packaging Machines Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East & Africa Hydrolyzed Bovine Collagen Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East Flooring and Carpet Industry Analysis Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East and North Africa Frozen Food Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East and Africa Bio-Stimulants Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East and Africa Latex Foil Balloons Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Middle East & Africa Data Storage Market Report – Trends & Industry Forecast 2025–2035
Middle East Veterinary Vaccine Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Middle East and Africa Rough Terrain Cranes Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Middle East/North Africa (MENA) Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Middle East Conveyor Belts Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Analysis and Growth Projections for Middle East and Mediterranean Tahini Business
Middle East and Africa (MEA) Tourism Security Market Analysis 2025 to 2035
Middle East Paints & Coatings Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Middle East Wood Flooring Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2024-2034
MEA Stick Packaging Machines Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2023-2033
Middle East 3D Printing Materials Market Trends 2022 to 2032
MENA Nutraceuticals Market Trends – Dietary Supplements & Functional Foods
B2B Middleware Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Low and Middle Income Countries Opioid Substitution Therapy Market Analysis by Drug Class, Indication, Distribution Channel, and Region through 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA