The Smart Building Market is estimated to be valued at USD 128.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1137.3 billion by 2035, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.4% over the forecast period. This expansion is being driven by increasing implementation of connected systems for building operations, energy monitoring, and centralized control in commercial, residential, and institutional buildings. From 2025 to 2026, the market is set to grow from USD 128.1 billion to 159.4 billion, marking a YoY increase of 24.5%.
The upward trend continues, with the market reaching USD 306.9 billion by 2030, adding more than USD 178 billion in just five years. Year-on-year growth during this phase ranges between 23% and 25%, reflecting strong momentum from increased deployment across both new construction and retrofit projects. Between 2030 and 2035, the market sees even faster expansion, growing by over USD 830 billion in five years. During this time, annual gains accelerate consistently, with YoY growth holding steady above 24%, supported by widespread adoption in mid-sized and large-scale developments. This strong and persistent YoY growth pattern suggests that smart building systems are transitioning into a core element of modern infrastructure development, with demand showing no signs of slowdown through 2035.
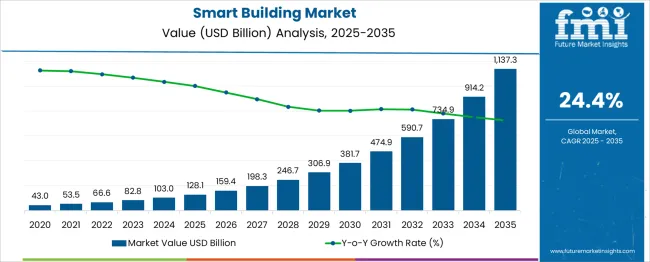
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Smart Building Market Estimated Value in (2025 E) | USD 128.1 billion |
| Smart Building Market Forecast Value in (2035 F) | USD 1137.3 billion |
| Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 24.4% |
The Smart Building market operates as a rapidly expanding segment within the broader Smart Infrastructure market, which includes interconnected systems that enhance operational efficiency across buildings, transportation, utilities, and cities. Within this larger ecosystem, smart buildings account for a significant and growing share, largely due to the need for centralized management of lighting, HVAC, security, and occupancy systems in real estate assets. As of 2025, smart buildings are estimated to comprise approximately 32% to 35% of the total smart infrastructure market, reflecting their prominence in driving demand for intelligent and responsive environments. The parent market itself is shaped by increasing digital integration across public and private infrastructure. However, smart buildings are outpacing other segments in growth due to their direct impact on cost savings, comfort, and building performance. By 2035, the share of smart buildings within the parent market is expected to rise further, potentially exceeding 40%, driven by mass adoption across commercial, educational, healthcare, and high-density residential spaces. While smart cities and utilities remain important, smart buildings serve as the foundational layer where most immediate and measurable gains occur making them a key driver of the overall smart infrastructure market’s value creation.
The smart building market is undergoing sustained growth, driven by a rising demand for energy-efficient infrastructure, digital transformation initiatives, and strict regulatory frameworks for carbon emission reduction. Organizations are accelerating the integration of IoT-enabled building management systems, automation controls, and AI-driven analytics to optimize energy use, occupant comfort, and operational efficiency.
Technological convergence across HVAC, lighting, access, and surveillance systems has resulted in unified smart platforms, enhancing cost savings and real-time responsiveness. Additionally, urbanization and smart city initiatives are catalyzing adoption, especially in commercial hubs.
Increasing investments in retrofitting legacy infrastructure with intelligent systems are expected to drive significant market traction in developed regions, while emerging economies are witnessing uptake due to green building incentives and sustainability mandates. The continued advancement in edge computing, 5G integration, and cybersecurity readiness is set to shape the next phase of innovation in the sector
The smart building market is segmented by component type, end use segment, and geographic regions. By component type of the smart building market is divided into Solution and Service. In terms of the end-use segment of the smart building market, it is classified into Commercial, Residential, and Industrial. Regionally, the smart building industry is classified into North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Balkan & Baltic Countries, Russia & Belarus, Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa.
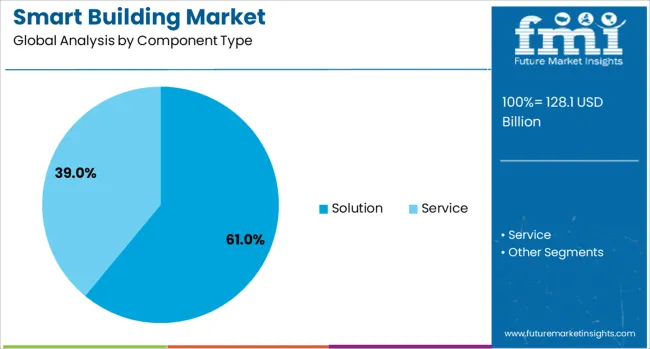
The solution segment is expected to account for 61.0% of the total market revenue in 2025, making it the leading component type in the smart building ecosystem. This leadership is being supported by widespread deployment of integrated building management systems (BMS), energy analytics, and smart HVAC, lighting, and access control solutions.
These systems offer real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automation capabilities that significantly reduce operational costs. Enterprises and facility managers are increasingly prioritizing interoperable and scalable software platforms that align with digital transformation goals.
Cloud connectivity, AI integration, and remote control functionality have further reinforced the adoption of comprehensive solution suites. Additionally, increased awareness of ESG metrics and building efficiency certifications is driving demand for solutions that enable precise energy and sustainability tracking, making them essential components in both new and retrofit projects
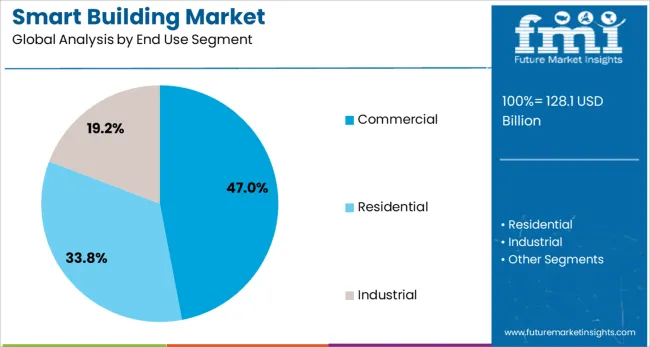
The commercial sector is projected to hold 47.0% of the overall smart building market revenue in 2025, emerging as the dominant end-use segment. This segment’s growth is being propelled by the increasing need for centralized building automation in offices, retail spaces, hospitality, and mixed-use developments.
Organizations are investing in smart infrastructure to improve tenant experience, comply with green building codes, and reduce facility management overhead. As hybrid work models evolve, commercial real estate operators are leveraging smart technologies to optimize space utilization, energy consumption, and indoor air quality.
Government mandates for energy reporting and building sustainability have further accelerated digital upgrades across commercial properties. Moreover, the scalability and modularity of smart building platforms have made them particularly attractive for multi-site operations and high-density urban environments, where operational efficiency and occupant satisfaction are top priorities
The smart building market is expanding as property managers and developers focus on connected infrastructure that improves occupant comfort, resource management, and operational oversight. These buildings integrate automated systems such as lighting, HVAC, and security into centralized platforms. Demand is driven by goals of reducing maintenance, improving asset efficiency, and ensuring indoor safety. Adoption varies across commercial, residential, and institutional segments. Market dynamics are shaped by installation complexity, evolving software ecosystems, vendor partnerships, and the need for long-term cost predictability.
One of the main barriers to smart building adoption is integration with existing structures. Many buildings rely on legacy systems not designed for connectivity, which creates difficulties when incorporating new automation platforms. For example, outdated HVAC or lighting systems may lack communication modules required for remote control. In older properties, rewiring and retrofitting increase the cost and time of smart system deployment. Inconsistent data protocols, wiring standards, and system compatibility between vendors also make integration complex. Facility managers must often work with multiple providers to bridge older infrastructure with modern digital interfaces. This slows project implementation and introduces risk of partial system functionality. Companies addressing these challenges with modular, backward-compatible hardware and adaptable middleware reduce implementation friction. Integrators offering consulting, mapping tools, and site-specific planning are increasingly valuable. Seamless integration is a critical success factor as many building owners prefer upgrades over full reconstruction when modernizing their properties.
Smart building technologies are gaining popularity due to the increasing desire for centralized control and real-time monitoring of building systems. Property managers want accurate data on temperature, occupancy, energy use, air quality, and security incidents to inform operational decisions. Platforms that provide user-friendly dashboards and system alerts help streamline daily building management. For large facilities, smart automation reduces the need for manual checks, minimizes oversight errors, and improves response times to maintenance needs. In multi-unit residential and commercial spaces, system control from a single interface enhances service consistency and tenant satisfaction. Applications include smart lighting that adjusts based on motion detection, HVAC systems that respond to occupancy patterns, and access control integrated with surveillance. As building users expect greater comfort, convenience, and responsiveness, these features are no longer viewed as add-ons but as core requirements. Providers that emphasize user interface clarity, customizable controls, and remote access are seeing increased adoption.
With the growing presence of connected devices in buildings, concerns about data security and user privacy continue to influence buying decisions. Smart buildings generate and transmit large volumes of data, including occupancy patterns, access records, and equipment performance metrics. Without proper safeguards, these systems are vulnerable to unauthorized access or data leaks. Building operators must ensure encrypted communication, secure authentication, and regular software updates. In some cases, data may be shared with third parties for maintenance or analytics, which introduces additional risks if privacy policies are unclear. Compliance with local and international privacy regulations requires system audits and ongoing monitoring. Building owners are increasingly seeking vendors who can demonstrate strong security architectures and transparency around data handling. Failure to address these risks can result in service disruption or reputational harm. Therefore, investment in security protocols, employee training, and vendor due diligence is now considered essential in smart building planning.
The smart building ecosystem includes numerous vendors offering hardware, software, and services that may not easily interconnect. This fragmented market landscape complicates the procurement process, especially for buyers unfamiliar with system interoperability requirements. Some vendors offer proprietary platforms that limit third-party integration, which restricts flexibility in choosing future components. Others may specialize in isolated functions such as lighting or access control, requiring facility managers to coordinate across multiple contracts. The lack of consistent performance benchmarks, certification standards, or open platforms can increase installation time and long-term support costs. Buyers must navigate technical jargon, unclear specifications, and uncertain future compatibility. As a result, procurement teams often delay investments or default to limited-scope pilots. Market participants who offer integrated solutions, transparent documentation, and post-sale support gain trust. Industry collaboration around standardization and certification is also becoming a priority as decision-makers seek more straightforward paths to full-building connectivity.
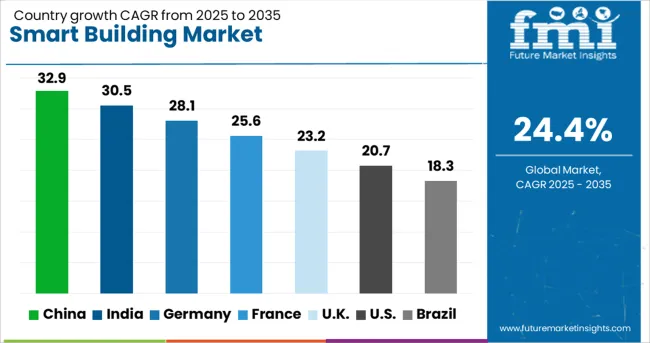
| Country | CAGR |
|---|---|
| China | 32.9% |
| India | 30.5% |
| Germany | 28.1% |
| France | 25.6% |
| UK | 23.2% |
| USA | 20.7% |
| Brazil | 18.3% |
The global smart building market is projected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 24.4% through 2035, driven by urbanization, energy efficiency mandates, and the integration of intelligent automation systems. Among BRICS nations, China leads with an exceptional 32.9% growth rate, driven by large-scale urban infrastructure, government-backed digitalization, and AI-driven building management systems. India follows at 30.5%, supported by smart city missions, rising energy demands, and rapid commercial real estate expansion. In the OECD region, Germany posts a strong 28.1% growth, reflecting leadership in sustainable building technologies, integrated IoT platforms, and regulatory innovation. The United Kingdom grows steadily at 23.2%, with momentum from retrofit projects and digital twin adoption. The United States, a mature but fast-evolving market growing at 20.7%, emphasizes cybersecurity, automation, and occupant-centered building systems. These countries are shaping the future of intelligent infrastructure worldwide. This report includes insights on 40+ countries; the top five markets are shown here for reference.
China is setting the global pace in the smart building market, with a leading CAGR of 32.9%, driven by urban development, digital policy mandates, and green building certifications. Major cities like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen are embracing intelligent building systems for energy optimization, real-time monitoring, and safety compliance. Government programs such as "New Infrastructure" and carbon neutrality goals are prompting large-scale retrofits and new constructions equipped with AI, IoT, and cloud-based controls. Chinese tech giants and construction firms are partnering to create self-learning buildings that adjust lighting, HVAC, and access systems based on occupancy and usage data. Demand is also strong from industrial parks, airports, and commercial complexes aiming to reduce energy costs and environmental impact. Integration with 5G and edge computing platforms is expected to further transform building automation capabilities nationwide.
India is witnessing a smart building boom with a CAGR of 30.5%, fueled by rapid urbanization, smart city projects, and rising demand for energy-efficient infrastructure. Metros like Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune are leading the charge with intelligent office parks, green-certified housing, and digital government buildings. The Smart Cities Mission and real estate digitization policies are spurring installations of integrated systems for lighting, air conditioning, fire safety, and surveillance. Developers are also embracing IoT-based building management systems to reduce operational costs and meet ESG requirements. Affordable housing projects are being outfitted with basic automation features to improve security and utility efficiency. Indian startups and IT firms are co-developing scalable, cloud-ready platforms that cater to local needs, including multilingual interfaces and off-grid energy integration.
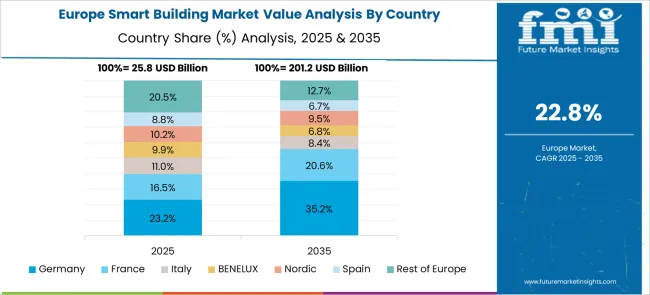
Germany is making impressive strides in the smart building market, growing at a CAGR of 28.1%, supported by sustainability mandates, digital twins, and advanced energy regulations. Urban regions such as Munich, Frankfurt, and Hamburg are focusing on carbon-neutral buildings with embedded IoT systems for HVAC, lighting, and energy management. Industrial and institutional facilities are increasingly deploying predictive maintenance and AI-powered fault detection to minimize downtime and emissions. Germany’s federal initiatives, such as the Climate Protection Program 2030, are pushing for intelligent retrofitting of legacy infrastructure with smart sensors and centralized control systems. Smart façades, occupancy-aware HVAC, and renewable energy integration are becoming standard in new construction. Universities and research institutes are piloting advanced automation frameworks that combine efficiency with long-term cost reduction.
The United Kingdom is experiencing significant momentum in the smart building sector, registering a CAGR of 23.2%, backed by decarbonization targets, energy legislation, and post-Brexit infrastructure investment. London and Manchester are leading smart building adoption, particularly in commercial real estate, education campuses, and transport terminals. Integration of building automation systems with net-zero goals is creating demand for sensors, occupancy analytics, and energy dashboards. Smart buildings are now central to the UK’s digital infrastructure strategy, with landlords upgrading older facilities to maintain rental value and meet sustainability benchmarks. Modular systems with plug-and-play compatibility are enabling faster upgrades across retail, office, and hospitality spaces. Public-sector partnerships are supporting smart retrofits in NHS buildings, schools, and housing associations.
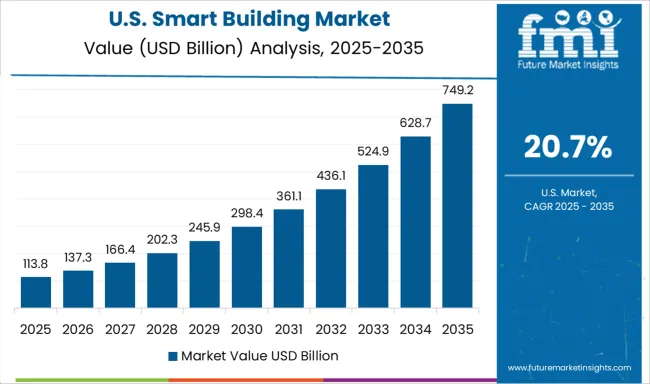
In the United States, the smart building market is advancing at a CAGR of 20.7%, supported by ESG commitments, grid resilience needs, and smart real estate investments. Urban centers like New York, Chicago, and San Francisco are deploying intelligent systems to optimize lighting, HVAC, and security across both old and new buildings. Federal energy efficiency programs and smart grid initiatives are promoting adoption of connected sensors and building analytics platforms. Large corporate campuses, tech parks, and healthcare facilities are deploying AI-driven systems for energy savings, predictive maintenance, and occupant comfort. Property tech firms are developing custom dashboards to give building managers real-time insights into usage patterns and emissions. There’s also growing demand from educational institutions and public infrastructure projects incorporating solar panels, EV charging, and demand response systems.
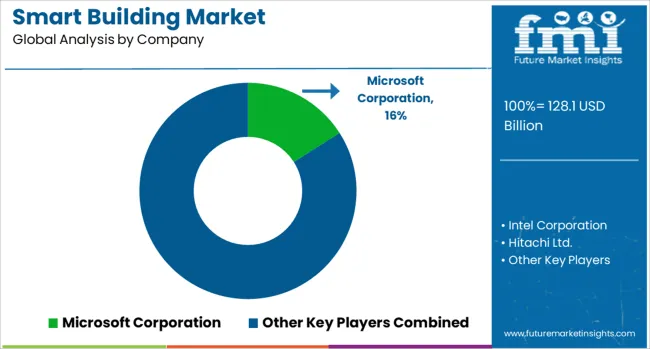
The smart building market is driven by the need for greater operational efficiency, resource management, and occupant comfort across commercial, institutional, and residential infrastructure. Central to this market are integrated platforms that manage building systems such as lighting, HVAC, access control, and energy distribution. Key suppliers compete based on the ability to offer scalable, interoperable, and data-driven solutions that optimize facility performance and enable remote control and monitoring. Microsoft Corporation and Intel Corporation play foundational roles by providing cloud computing, AI, and edge processing capabilities essential to building management platforms.
Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins and Intel’s IoT-enabled processors allow real-time data capture and control across building subsystems, offering system integrators flexible infrastructure for developing smart environments. Their influence extends through partnerships with building technology providers and real estate developers. ABB and Hitachi Ltd. offer end-to-end automation and control systems, integrating energy management, predictive maintenance, and environmental monitoring into a unified framework.
These companies serve large-scale commercial buildings and industrial campuses with platforms tailored for centralized control and diagnostics. Huawei contributes with smart connectivity, IoT networking gear, and energy solutions, making it a key supplier for connected building ecosystems, especially in high-density urban regions. As demand grows, suppliers emphasizing system interoperability, real-time insights, and lifecycle cost reduction remain competitive in shaping the future of smart infrastructure.
As stated in Siemens Smart Infrastructure’s press release dated March 17, 2025, the company launched Building X Portfolio Manager, a SaaS platform consolidating real estate, energy, sustainability, and operational data across multiple sites. It delivers AI-driven insights, emissions reporting, and real-time asset visibility.
The platform will be available from May 2025. As released by Honeywell on February 27, 2025, its study revealed 84% of commercial building decision makers intend to increase AI usage over the next year to optimize security, predictive maintenance, energy, water, and temperature management signaling strong demand for AI-powered building automation solutions.
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Quantitative Units | USD 128.1 Billion |
| Component Type | Solution and Service |
| End Use Segment | Commercial, Residential, and Industrial |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
| Country Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, China, Japan, India, Brazil, South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled | Microsoft Corporation, Intel Corporation, Hitachi Ltd., Huawei, and ABB |
The global smart building market is estimated to be valued at USD 128.1 billion in 2025.
The market size for the smart building market is projected to reach USD 1,137.3 billion by 2035.
The smart building market is expected to grow at a 24.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in smart building market are solution, _safety & security management, _energy management, _building infrastructure management, _integrated workplace management system (iwms), _network management and service.
In terms of end use segment, commercial segment to command 47.0% share in the smart building market in 2025.






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Smart Building Delivery Robot Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Building Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart School Bus Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Home Wireless Smoke Detector Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Bus Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Vision Processing Chips Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Touch Screen Scale Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Magnetic Drive Conveyor System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Wheelchair market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Mining Technologies Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Parking Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Digital Valve Positioner Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Card IC Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart-Tag Inlay Inserters Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart TV Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart/AI Toy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Locks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Sprinkler Controller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Indoor Gardening System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Watch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA