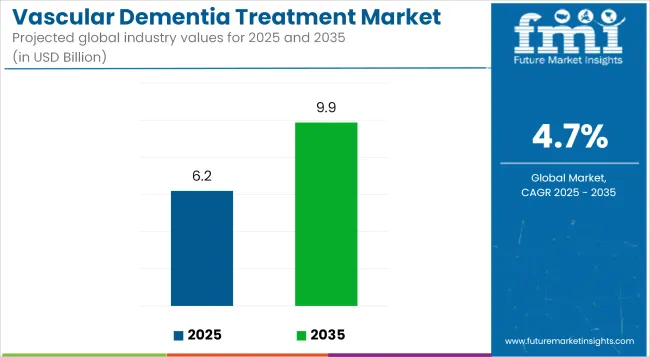
The vascular dementia treatment industry will be valued at USD 6.19 billion by 2025 end. As per FMI's analysis, vascular dementia treatment will grow at a CAGR of 4.7% and reach USD 9.87 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the industry was marked by significant progress. Developments in diagnostic imaging technology increased early detection rates to facilitate on-time intervention and control of the disease. Drug firms increased research efforts, driving the development of new drugs focused on retarding disease progression.
Healthcare providers also partnered with technology firms to create innovative care solutions, such as AI-powered cognitive training programs specifically designed for patients suffering from vascular dementia. These innovations helped enhance patient outcomes and expand demand.
Looking forward to 2025 and beyond, the industry will likely sustain its growth curve. Continued research in the pathophysiology of vascular dementia will likely provide more specific and effective therapies. Consolidation of digital health technologies is likely to improve patient monitoring and individualized care approaches even further.
Additionally, as vascular dementia awareness continues to grow around the world, early diagnosis rates are expected to increase, boosting demand for pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical treatments. Overall, these factors are expected to continue fueling growth in the following years.
Key Metrics
| Metrics | Values |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 6.19 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 9.87 billion |
| Value-based CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.7% |
FMI Survey Findings: Trends Based on Stakeholder Insights
Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholders: USA, Western Europe, Japan, and South Korea neurologists, geriatric care providers, pharmaceutical companies, and USA, Western European, Japanese, and South Korean caregivers
Consensus
Regional Variance
High Variance
ROI Perspectives
68% of USA/EU stakeholders viewed novel drugs as worth the investment vs. 32% in Asia, where generics dominated.
Consensus
Pharmacotherapy: 70% used cholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil) as first line.
Variance
Shared Challenges
90% identified high drug prices (e.g., USD 2,500/month for newer biologics) as a hindrance.
Regional Differences
Pharmaceutical Companies
Healthcare Providers
Patients/Caregivers
Global: 60% mentioned a shortage of available clinical trials for advanced treatment.
Alignment
76% of biotech companies invested in R&D in biomarker-based therapies.
Divergence
High Consensus: Demand for early diagnosis, cost management, and support for caregivers.
Key Variances
Strategic Insight: Regionalization is essential-e.g., biologics in the USA, preventive care in the EU, and home tech in Asia.
| Countries | Policies and Regulations |
|---|---|
| India |
|
| USA |
|
| UK |
|
| Australia |
|
| Japan |
|
The industry is in a steady growth pattern, fueled by the increasing global prevalence of dementia, improved early diagnostics, and growing investment in cognitive therapies. Pharmaceutical firms, healthcare providers, and digital health companies are likely to gain from widening treatment choices and supportive government policies, while areas with restricted healthcare access may find it difficult to keep up. As understanding and regulatory systems mature, investors in innovative, patient-focused solutions will benefit the most in this growing industry.
Speed up Investment in Early Diagnosis & Intervention
Leaders need to allocate funding for next-generation diagnostic technologies, such as AI-based imaging and biomarker testing, to allow for early detection and precise treatment of vascular dementia. This will not only enhance patient care but also put firms at the leading edge of precision medicine.
Align with Digital Health & Personalized Treatment Trends
To remain competitive, companies need to incorporate digital health solutions like remote patient monitoring, cognitive training applications, and AI-based therapy suggestions. Tech companies and healthcare organizations will be important partners in tap these innovations.
Increase Global Market Penetration Through Strategic Alliances
Pharmaceutical and healthcare firms must partner with local healthcare systems, insurers, and telemedicine providers to expand penetration. Mergers, acquisitions, and licensing deals in high-growth can propel scalability and long-term profitability.
| Risk | Probability/Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Uncertainty & Compliance Challenges-Evolving government policies and varying regional regulations may delay drug approvals and entry. | Medium-High |
| High R&D Costs & Long Development Cycles-Developing new vascular dementia treatments is expensive and time-consuming, with uncertain clinical success rates. | High |
| Limited Reimbursement & Access Barriers-Insurance coverage gaps and high treatment costs may restrict patient access, especially in emerging industries. | Medium |
Executive Watchlist
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Expand Early Diagnosis Capabilities | Invest in AI-driven diagnostic tools and partner with imaging tech firms to enhance early detection accuracy. |
| Enhance Access & Reimbursement Strategies | Engage with policymakers and insurers to secure better coverage for vascular dementia treatments. |
| Strengthen Digital Health Integration | Develop or acquire cognitive health apps and remote monitoring solutions to complement pharmaceutical treatments. |
To stay ahead and remain competitive in the industry, the company will need to speed up investments in early diagnosis technology, increase collaborations with digital health innovators, and actively influence regulatory debates to secure wider reimbursement coverage. This insight highlights the need to implement AI-based diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies to compete with others.
The strategy must focus on international growth in high-growth through strategic partnerships while matching R&D spending with near-term commercialization plans. Delivering on these fronts will make the company a leader in the next generation of cognitive healthcare innovation.
Donepezil is the most prescribed drug for the treatment of vascular dementia, followed mainly because of its established efficacy, tolerability, and worldwide approval from various regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA.
Donepezil, being a cholinesterase inhibitor, enhances the cognitive ability by boosting the level of acetylcholine within the brain, which facilitates learning and memory. It tends to be taken over Rivastigmine and Galantamine due to the convenience of once a day dosing, less incidence of gastrointestinal side effects, and robust clinical evidence for mild and moderate dementia.
Although Memantine, an antagonist of the NMDA receptor, is well used, it is usually advised for moderate-severe or donepezil + Memantine therapy. The extensive use of Donepezil is also aided by its availability in generic form, rendering it more affordable and accessible over newer options.
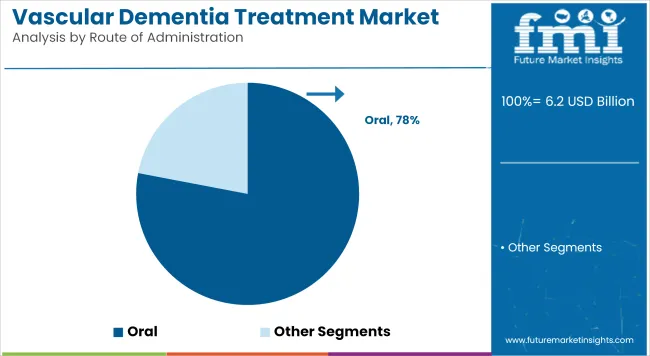
The most common route for the treatment of vascular dementia is oral administration, owing to its cost-effectiveness, ease of compliance by patients, and convenience. The majority of first-line medications such as Donepezil, Rivastigmine,
Galantamine, and Memantine are in tablet or capsule formulations, which can be easily given without medical oversight. Oral drug formulations are specifically preferred for diseases such as dementia, where long-term maintenance of medication has to be adhered to.
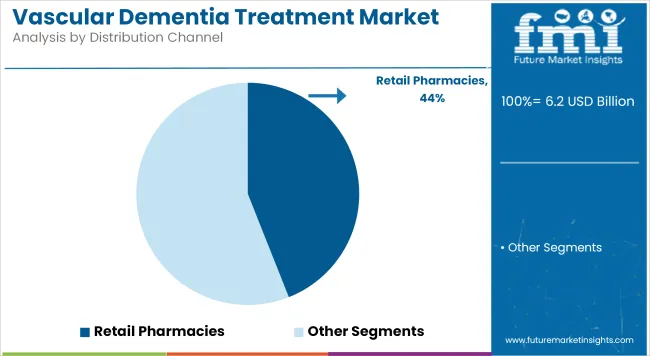
Retail pharmacies are the most common method of vascular dementia treatment distribution because they are convenient, easily accessible, and abundant in number. The majority of dementia drugs, such as Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine, and Memantine, are prescribed to be taken on a long-term basis; hence, retail pharmacies are the best option for continuous refills and medication maintenance. Retail pharmacies are mostly depended on by patients and caregivers for easy access, drug consultations with pharmacists, and insurance coverage.
| Countries | CAGR |
|---|---|
| USA | 5.5% |
| UK | 4.8% |
| France | 4.5% |
| Germany | 5.0% |
| Italy | 4.2% |
| Japan | 4.0% |
| China | 6.0% |
The USA industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.5% from 2025 to 2035, which is higher than the global average due to wide healthcare spending, strong R&D investments, and the growing occurrence of dementia. Government subsidies by Medicare and Medicaid ensure broad coverage of therapies, and private insurance companies pay for a wide range of dementia medicines.
USA pharmaceutical companies are backed by a robust regulatory framework of the FDA, which has recently accelerated the approval of new cognitive therapies. Greater use of AI in diagnostics and expansion of telemedicine-based dementia care are transforming trends.
Retail pharmacies dominate distribution, but web-based pharmacies are increasing because caregivers need convenient-to-obtain prescription fill options. Growing focus on combination therapies (e.g., Memantine-Donepezil) and biologics is likely to fuel the growth further. Priced and reimbursed products continue to be a sore in the sides of stakeholders.
The UK industry is projected to record a CAGR of around 4.8% over 2025 to 2035, lower than that in the USA but an important one in Europe nevertheless. The National Health Service (NHS) plays the leading role in treating dementia, dispensing subsidized or free medicines through government-funded programs.
The UK industry has strong research activity, with organizations such as Alzheimer's Research UK and Dementia Research Institute spearheading the push to accelerate drug development. However, strict regulatory review by NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) can slow new treatments from reaching the industry, posing difficulties for pharmaceutical firms.
Distribution is managed by retail pharmacies and hospital pharmacies, but take-up of digital health is on the rise, with solutions delivering remote cognitive testing and AI-driven symptom monitoring.
The industry of France is forecast to increase at a CAGR of around 4.5% between 2025 and 2035, driven by growing disease awareness and supportive government policies. The Assurance Maladie (national health insurance system) ensures that most treatments for dementia are reimbursed, thus making drugs relatively accessible.
However, in 2018, the French government revoked reimbursement of drugs like Donepezil and Rivastigmine on the basis of insufficient clinical efficacy. It led to increased out-of-pocket expenses for patients and diversion toward non-pharmaceutical interventions like cognitive therapies. While pharmaceutical manufacturers are pushing for reinstatement, the action slowed down pharmaceutical development compared to other European nations.
Germany's industry is likely to achieve a CAGR of around 5.0% from 2025 to 2035, led by Europe's biggest aging population and strong government healthcare policies. With over 1.6 million people afflicted with dementia, the German industry is highly lucrative for pharma players. The country's universal healthcare system, along with statutory health insurer coverage, ensures that most vascular dementia treatments are reimbursed.
Germany is a hub for pharma innovation, with leading players investing in precision medicine, digital health, and AI-based cognitive technologies. Retail pharmacies dominate drug distribution, and hospital-based neurology clinics are at the heart of patient management. There are stringent pricing controls by the German Federal Joint Committee (G-BA), which can restrict pharma company price power, but this is compensated by strong government-funded dementia care systems.
Italy's industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 4.2% during 2025 to 2035, with growth hindered by an aging population and a constrained healthcare workforce capacity. Italy has one of the highest ratios of old populations in Europe, but there are healthcare access disparities in the northern and southern regions of the nation.
The Italian National Health Service (SSN) only covers partially medication for treatment of vascular dementia, and budget constraints typically render approval of new drugs sluggish. Retail pharmacies are preponderant in the industry, and hospital pharmacies cover the specialist requirements of dementia patients. Italy has lower acceptance rates of digital health products compared to Germany or the UK, which retards penetration by new therapies.
Japan's vascular dementia industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 4.0% from 2025 to 2035. Being the world's oldest population, dementia cases are growing fast, but healthcare policy is aimed at cost containment and generic drugs. The National Health Insurance (NHI) system offers extensive medication coverage, but tight reimbursement policies limit expensive treatments.
Japan's drug industry is investing in emerging neurotherapeutics, particularly in gene therapy and regenerative medicine. Hospital pharmacies predominate in the distribution of medication, whereas retail pharmacies are transforming to offer dementia care service. Low digital uptake levels and overdependence on traditional caregiving methods pose industry challenges.
China's industry is likely to expand at a CAGR of approximately 6.0%, the highest among large economies, as spurred by an aging populace, accelerated healthcare growth, and increasing urbanization. Government healthcare reforms such as the Healthy China 2030 plan are likely to enhance the availability of dementia care.
Eisai Co., Ltd. (18 to 20%)-The World Leader
Eisai is the unchallenged industry leader in vascular dementia therapy, thanks in large part to Aricept (Donepezil), which is the dominant player in the cholinesterase inhibitor industry. The firm enjoys a strategic alliance with Pfizer in North America while having a direct presence in Japan, Europe, and the emerging Asian industry.
AbbVie Inc. (14-16%)-NMDA Leader
With the acquisition of Allergan, AbbVie consolidated its position with Namenda (Memantine), the most prescribed NMDA receptor antagonist for moderate-to-severe to severe. AbbVie enjoys a vast global supply chain, excellent penetration in Europe and North America, and high hospital adoption.
Novartis AG (12-14%)-Rivastigmine Dominance
Novartis has a firm grip on Exelon (Rivastigmine), enjoying a wide base of patients thanks to its patches and capsules. The company registers increased demand for the product in Europe and Asia, where existing regulatory systems accommodate established cholinesterase inhibitors.
Johnson & Johnson (Janssen) (9-11%)-Galantamine Expert
Johnson & Johnson subsidiary Janssen Pharmaceuticals holds a prominent share in North America and Europe with Galantamine-derived products (Reminyl, Razadyne). The organization is investing in emerging therapies but is subject to price pressures following generic competition.
Pfizer Inc. (7-9%)-Co-Leader in Donepezil
Although Pfizer and Eisai co-promote Aricept in North America, Eisai maintains worldwide control, constraining Pfizer's growth. The firm still maintains a dominant position in the USA, but patent losses and generic erosion have slowed growth.
Merz Pharmaceuticals (5-7%)-Generic Growth
Merz specializes in affordable Memantine-based generics, a solid player in Eastern Europe, Latin America, and some areas of Asia. The firm uses cutthroat pricing to fight against branded medication. Merz adopts aggressive pricing maneuvers and streamlined supply chains to offer generic competition for branded NMDA receptor antagonists such as AbbVie's Namenda (Memantine), positioning the firm as an important player within the generic pharmaceutical segment of the industry.
Lundbeck A/S (4-6%)-Focusing on New Therapies
Lundbeck is banking on combination therapies and biologic-based cognition therapy, offering it distinctively over competitors who are more dependent on conventional cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA antagonists.
Generic Drug Companies (10-12%)-Increasing Reach
Major generic drug companies like Sun Pharma, Dr. Reddy's, Cipla, and Teva are quickly increasing their share in price-sensitive areas such as India, China, Africa, and Latin America. Their cost-focused strategies and enhanced production capacities enable them to be tough competitors for branded drugs.
With respect to the drug class, it is classified into donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine, and memantine.
In terms of route of administration, it is divided into oral and parenteral.
In terms of distribution channels, it is divided into retail pharmacies, hospital pharmacies, and online pharmacies.
In terms of region, it is segmented into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, and MEA.
The market is anticipated to reach USD 6.19 billion in 2025.
The market is predicted to reach a size of USD 9.87 billion by 2035.
Prominent players include Charsire Biotechnology Corp, ProNeurogen Therapeutics, Resverlogix Corp., Eisai Co., Ltd., Novartis AG, Cipla Inc., Aurobindo Pharma, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd, and Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
Donepezil drug class is being widely used.
China, expected to grow at 6.0% CAGR during the study period, is poised for the fastest growth.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Route of Administration, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Route of Administration, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by Distribution Channel, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Our Research Products

The "Full Research Suite" delivers actionable market intel, deep dives on markets or technologies, so clients act faster, cut risk, and unlock growth.

The Leaderboard benchmarks and ranks top vendors, classifying them as Established Leaders, Leading Challengers, or Disruptors & Challengers.

Locates where complements amplify value and substitutes erode it, forecasting net impact by horizon

We deliver granular, decision-grade intel: market sizing, 5-year forecasts, pricing, adoption, usage, revenue, and operational KPIs—plus competitor tracking, regulation, and value chains—across 60 countries broadly.

Spot the shifts before they hit your P&L. We track inflection points, adoption curves, pricing moves, and ecosystem plays to show where demand is heading, why it is changing, and what to do next across high-growth markets and disruptive tech

Real-time reads of user behavior. We track shifting priorities, perceptions of today’s and next-gen services, and provider experience, then pace how fast tech moves from trial to adoption, blending buyer, consumer, and channel inputs with social signals (#WhySwitch, #UX).

Partner with our analyst team to build a custom report designed around your business priorities. From analysing market trends to assessing competitors or crafting bespoke datasets, we tailor insights to your needs.
Supplier Intelligence
Discovery & Profiling
Capacity & Footprint
Performance & Risk
Compliance & Governance
Commercial Readiness
Who Supplies Whom
Scorecards & Shortlists
Playbooks & Docs
Category Intelligence
Definition & Scope
Demand & Use Cases
Cost Drivers
Market Structure
Supply Chain Map
Trade & Policy
Operating Norms
Deliverables
Buyer Intelligence
Account Basics
Spend & Scope
Procurement Model
Vendor Requirements
Terms & Policies
Entry Strategy
Pain Points & Triggers
Outputs
Pricing Analysis
Benchmarks
Trends
Should-Cost
Indexation
Landed Cost
Commercial Terms
Deliverables
Brand Analysis
Positioning & Value Prop
Share & Presence
Customer Evidence
Go-to-Market
Digital & Reputation
Compliance & Trust
KPIs & Gaps
Outputs
Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
The Vascular Ulcer Treatment Market Is Segmented by Ulcer Type, Treatment and Distribution Channel from 2025 To 2035
Neovascular AMD Treatment Market Growth, Analysis & Forecast by Drug Type, Disease Type, Age Group, Gender, Stage of Disease, Distribution Channel and Region through 2035
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) Treatment Market Analysis – Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vascular Sheath Group Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vascular Patches Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vascular Access System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Dementia Management Market Trends - Size, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vascular Parkinsonism Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Vascular Boot Market Trends and Forecast 2025 to 2035
The Dementia Care Products Market is segmented by Memory Exercise & Activity Products, Daily Reminder Products and Dining Aids from 2025 to 2035
Treatment Pumps Market Insights Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vascular Imaging Systems Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vascular Closure Devices Analysis by Product Type by Product, By Age Group and by Distribution Channel through 2035
Vascular Access Catheters Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Market
Vascular Dressings Market
Vascular prostheses market
Vascular Screening Market

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA